Ruslan Mitkov
AHaSIS: Shared Task on Sentiment Analysis for Arabic Dialects
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:The hospitality industry in the Arab world increasingly relies on customer feedback to shape services, driving the need for advanced Arabic sentiment analysis tools. To address this challenge, the Sentiment Analysis on Arabic Dialects in the Hospitality Domain shared task focuses on Sentiment Detection in Arabic Dialects. This task leverages a multi-dialect, manually curated dataset derived from hotel reviews originally written in Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) and translated into Saudi and Moroccan (Darija) dialects. The dataset consists of 538 sentiment-balanced reviews spanning positive, neutral, and negative categories. Translations were validated by native speakers to ensure dialectal accuracy and sentiment preservation. This resource supports the development of dialect-aware NLP systems for real-world applications in customer experience analysis. More than 40 teams have registered for the shared task, with 12 submitting systems during the evaluation phase. The top-performing system achieved an F1 score of 0.81, demonstrating the feasibility and ongoing challenges of sentiment analysis across Arabic dialects.
From Text to Graph: Leveraging Graph Neural Networks for Enhanced Explainability in NLP
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:Researchers have relegated natural language processing tasks to Transformer-type models, particularly generative models, because these models exhibit high versatility when performing generation and classification tasks. As the size of these models increases, they achieve outstanding results. Given their widespread use, many explainability techniques are developed based on these models. However, this process becomes computationally expensive due to the large size of the models. Additionally, transformers interpret input information through tokens that fragment input words into sequences lacking inherent semantic meaning, complicating the explanation of the model from the very beginning. This study proposes a novel methodology to achieve explainability in natural language processing tasks by automatically converting sentences into graphs and maintaining semantics through nodes and relations that express fundamental linguistic concepts. It also allows the subsequent exploitation of this knowledge in subsequent tasks, making it possible to obtain trends and understand how the model associates the different elements inside the text with the explained task. The experiments delivered promising results in determining the most critical components within the text structure for a given classification.
Overview of the First Workshop on Language Models for Low-Resource Languages (LoResLM 2025)
Dec 20, 2024


Abstract:The first Workshop on Language Models for Low-Resource Languages (LoResLM 2025) was held in conjunction with the 31st International Conference on Computational Linguistics (COLING 2025) in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. This workshop mainly aimed to provide a forum for researchers to share and discuss their ongoing work on language models (LMs) focusing on low-resource languages, following the recent advancements in neural language models and their linguistic biases towards high-resource languages. LoResLM 2025 attracted notable interest from the natural language processing (NLP) community, resulting in 35 accepted papers from 52 submissions. These contributions cover a broad range of low-resource languages from eight language families and 13 diverse research areas, paving the way for future possibilities and promoting linguistic inclusivity in NLP.
DORE: A Dataset For Portuguese Definition Generation
Mar 28, 2024



Abstract:Definition modelling (DM) is the task of automatically generating a dictionary definition for a specific word. Computational systems that are capable of DM can have numerous applications benefiting a wide range of audiences. As DM is considered a supervised natural language generation problem, these systems require large annotated datasets to train the machine learning (ML) models. Several DM datasets have been released for English and other high-resource languages. While Portuguese is considered a mid/high-resource language in most natural language processing tasks and is spoken by more than 200 million native speakers, there is no DM dataset available for Portuguese. In this research, we fill this gap by introducing DORE; the first dataset for Definition MOdelling for PoRtuguEse containing more than 100,000 definitions. We also evaluate several deep learning based DM models on DORE and report the results. The dataset and the findings of this paper will facilitate research and study of Portuguese in wider contexts.
Can Model Fusing Help Transformers in Long Document Classification? An Empirical Study
Jul 18, 2023



Abstract:Text classification is an area of research which has been studied over the years in Natural Language Processing (NLP). Adapting NLP to multiple domains has introduced many new challenges for text classification and one of them is long document classification. While state-of-the-art transformer models provide excellent results in text classification, most of them have limitations in the maximum sequence length of the input sequence. The majority of the transformer models are limited to 512 tokens, and therefore, they struggle with long document classification problems. In this research, we explore on employing Model Fusing for long document classification while comparing the results with well-known BERT and Longformer architectures.
Deep Learning Methods for Extracting Metaphorical Names of Flowers and Plants
May 21, 2023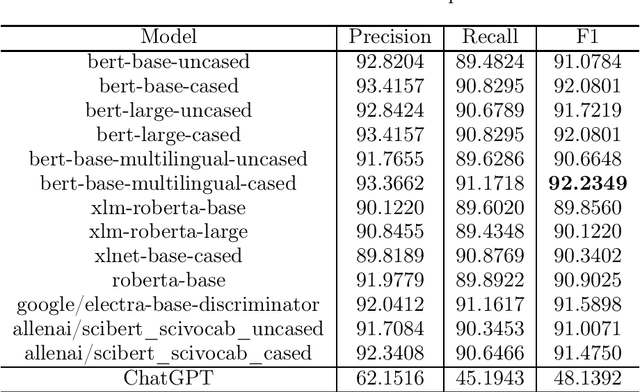
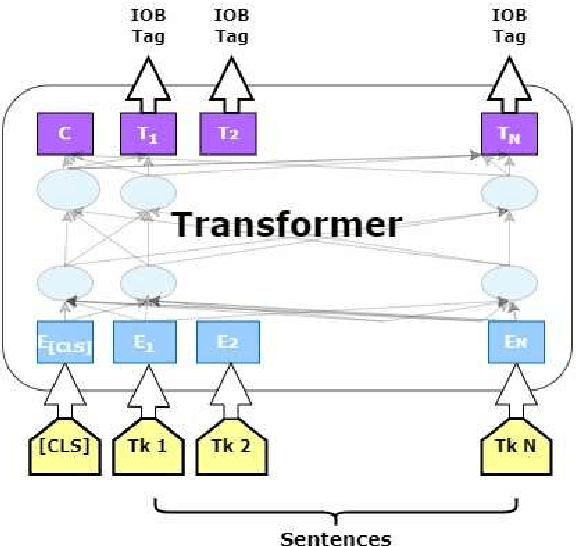
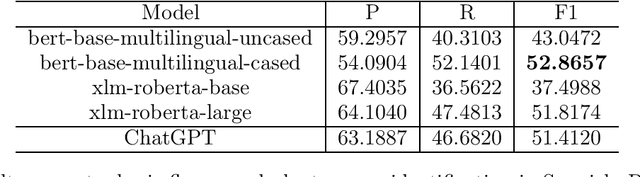
Abstract:The domain of Botany is rich with metaphorical terms. Those terms play an important role in the description and identification of flowers and plants. However, the identification of such terms in discourse is an arduous task. This leads in some cases to committing errors during translation processes and lexicographic tasks. The process is even more challenging when it comes to machine translation, both in the cases of single-word terms and multi-word terms. One of the recent concerns of Natural Language Processing (NLP) applications and Machine Translation (MT) technologies is the automatic identification of metaphor-based words in discourse through Deep Learning (DL). In this study, we seek to fill this gap through the use of thirteen popular transformer based models, as well as ChatGPT, and we show that discriminative models perform better than GPT-3.5 model with our best performer reporting 92.2349% F1 score in metaphoric flower and plant names identification task.
Transformer-based Detection of Multiword Expressions in Flower and Plant Names
Sep 20, 2022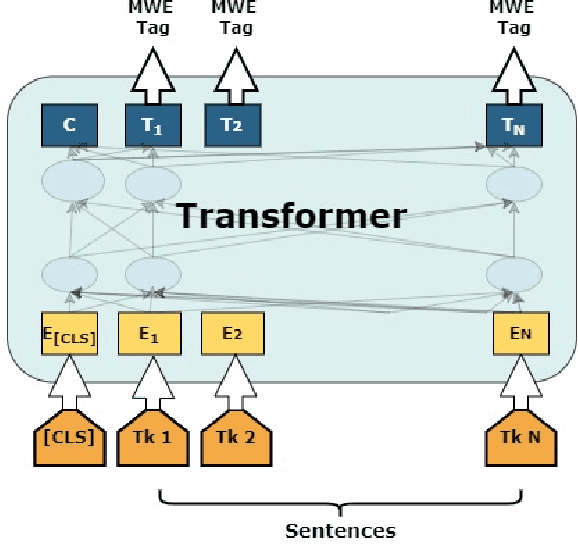
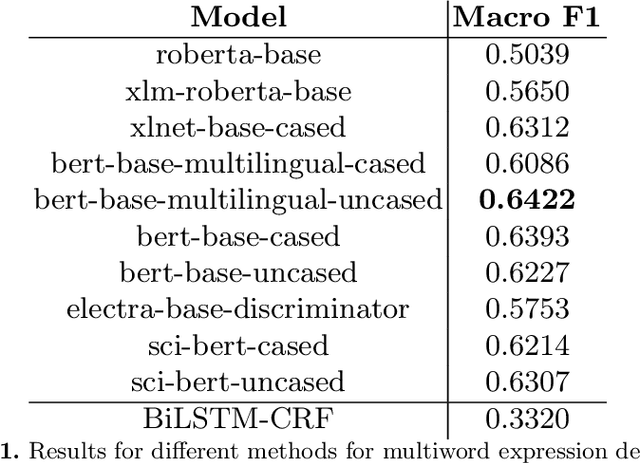
Abstract:Multiword expression (MWE) is a sequence of words which collectively present a meaning which is not derived from its individual words. The task of processing MWEs is crucial in many natural language processing (NLP) applications, including machine translation and terminology extraction. Therefore, detecting MWEs in different domains is an important research topic. In this paper, we explore state-of-the-art neural transformers in the task of detecting MWEs in flower and plant names. We evaluate different transformer models on a dataset created from Encyclopedia of Plants and Flower. We empirically show that transformer models outperform the previous neural models based on long short-term memory (LSTM).
DTW at Qur'an QA 2022: Utilising Transfer Learning with Transformers for Question Answering in a Low-resource Domain
May 12, 2022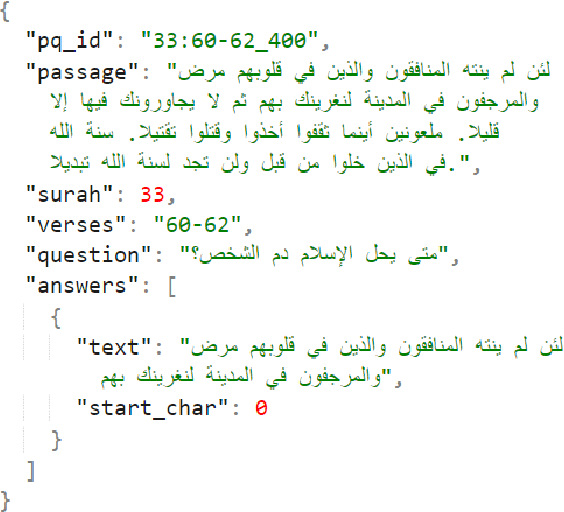
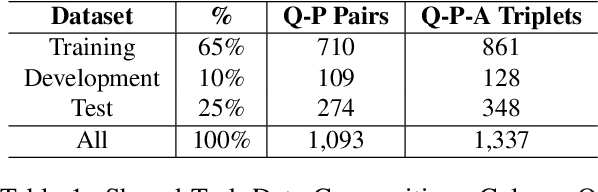
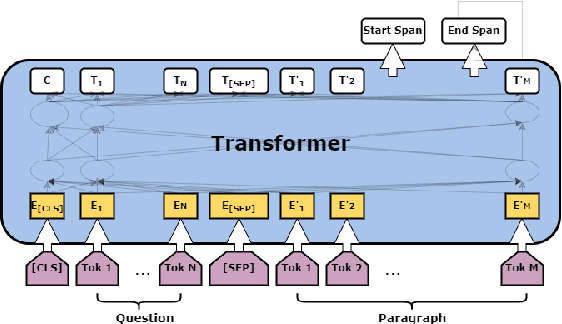
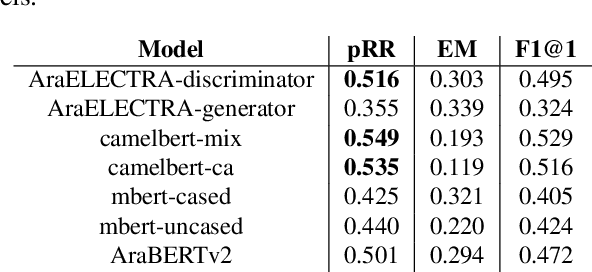
Abstract:The task of machine reading comprehension (MRC) is a useful benchmark to evaluate the natural language understanding of machines. It has gained popularity in the natural language processing (NLP) field mainly due to the large number of datasets released for many languages. However, the research in MRC has been understudied in several domains, including religious texts. The goal of the Qur'an QA 2022 shared task is to fill this gap by producing state-of-the-art question answering and reading comprehension research on Qur'an. This paper describes the DTW entry to the Quran QA 2022 shared task. Our methodology uses transfer learning to take advantage of available Arabic MRC data. We further improve the results using various ensemble learning strategies. Our approach provided a partial Reciprocal Rank (pRR) score of 0.49 on the test set, proving its strong performance on the task.
Biographical: A Semi-Supervised Relation Extraction Dataset
May 02, 2022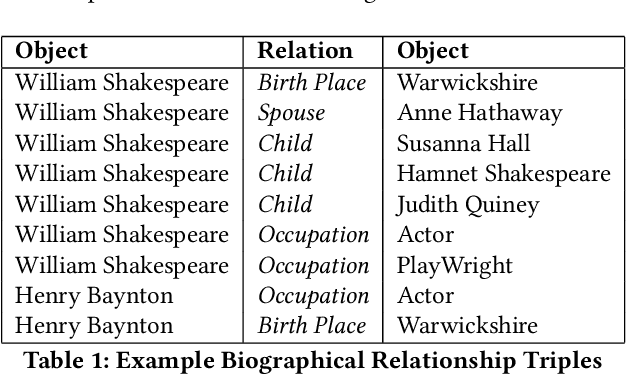
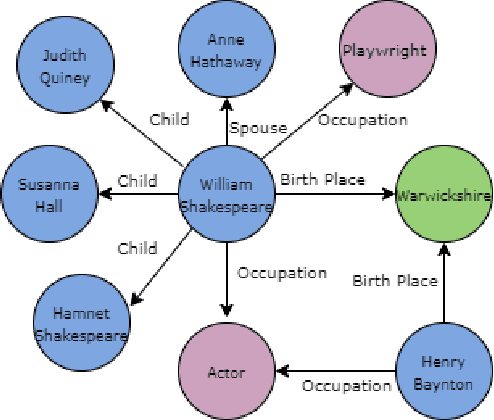
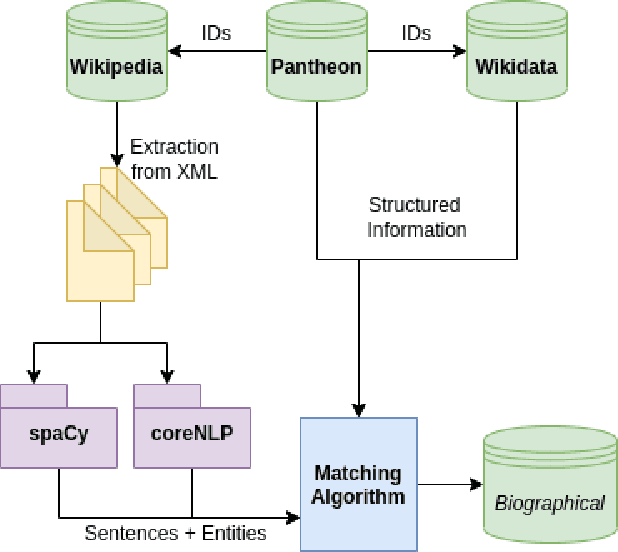
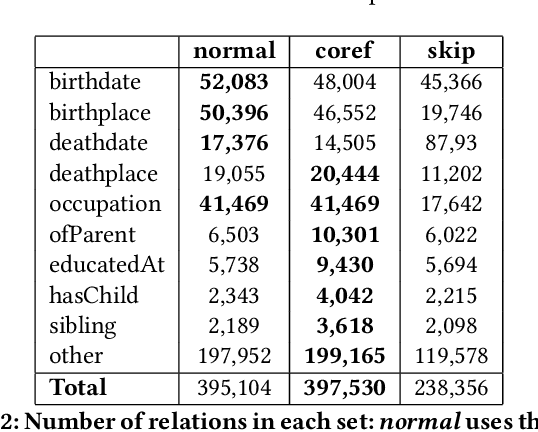
Abstract:Extracting biographical information from online documents is a popular research topic among the information extraction (IE) community. Various natural language processing (NLP) techniques such as text classification, text summarisation and relation extraction are commonly used to achieve this. Among these techniques, RE is the most common since it can be directly used to build biographical knowledge graphs. RE is usually framed as a supervised machine learning (ML) problem, where ML models are trained on annotated datasets. However, there are few annotated datasets for RE since the annotation process can be costly and time-consuming. To address this, we developed Biographical, the first semi-supervised dataset for RE. The dataset, which is aimed towards digital humanities (DH) and historical research, is automatically compiled by aligning sentences from Wikipedia articles with matching structured data from sources including Pantheon and Wikidata. By exploiting the structure of Wikipedia articles and robust named entity recognition (NER), we match information with relatively high precision in order to compile annotated relation pairs for ten different relations that are important in the DH domain. Furthermore, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the dataset by training a state-of-the-art neural model to classify relation pairs, and evaluate it on a manually annotated gold standard set. Biographical is primarily aimed at training neural models for RE within the domain of digital humanities and history, but as we discuss at the end of this paper, it can be useful for other purposes as well.
An Exploratory Analysis of Multilingual Word-Level Quality Estimation with Cross-Lingual Transformers
May 31, 2021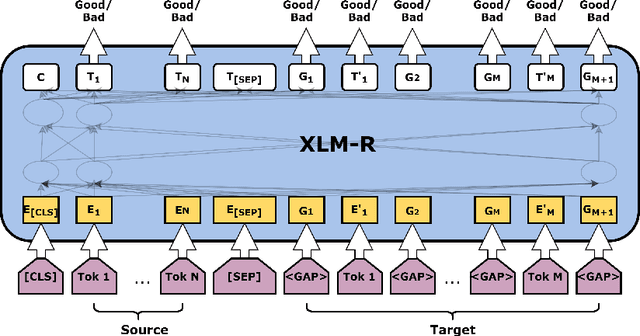
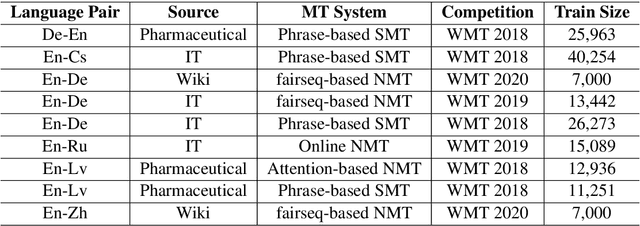
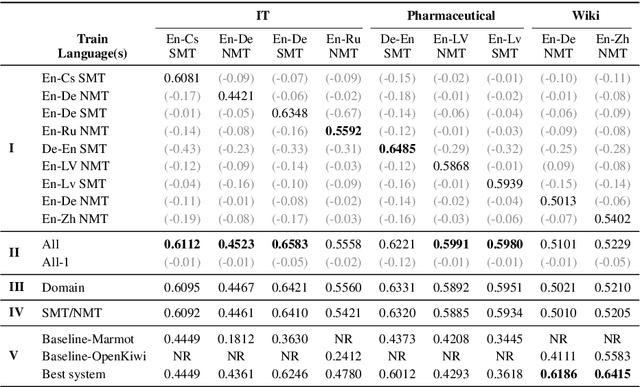
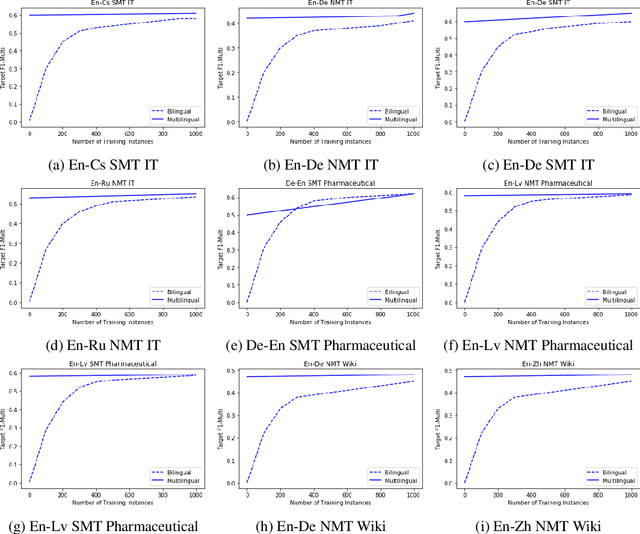
Abstract:Most studies on word-level Quality Estimation (QE) of machine translation focus on language-specific models. The obvious disadvantages of these approaches are the need for labelled data for each language pair and the high cost required to maintain several language-specific models. To overcome these problems, we explore different approaches to multilingual, word-level QE. We show that these QE models perform on par with the current language-specific models. In the cases of zero-shot and few-shot QE, we demonstrate that it is possible to accurately predict word-level quality for any given new language pair from models trained on other language pairs. Our findings suggest that the word-level QE models based on powerful pre-trained transformers that we propose in this paper generalise well across languages, making them more useful in real-world scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge