Amal Haddad Haddad
Deep Learning Methods for Extracting Metaphorical Names of Flowers and Plants
May 21, 2023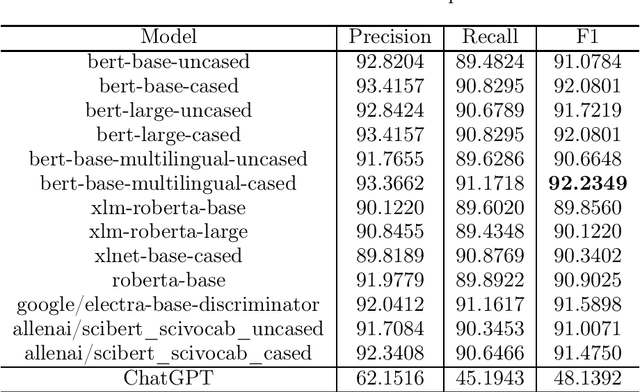
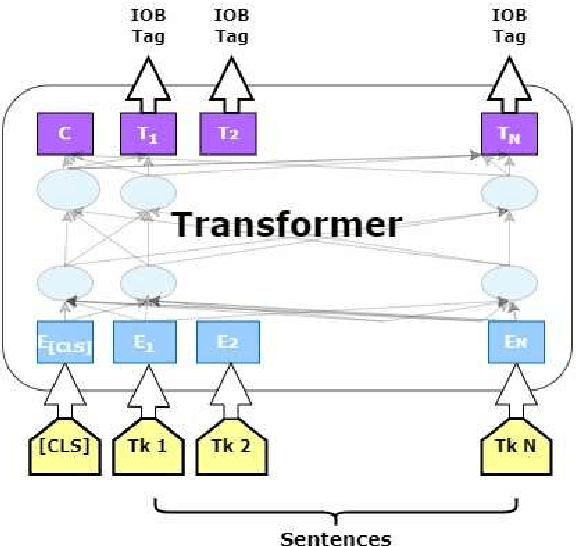
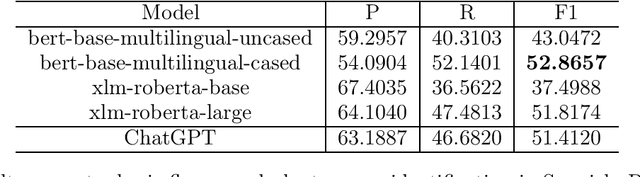
Abstract:The domain of Botany is rich with metaphorical terms. Those terms play an important role in the description and identification of flowers and plants. However, the identification of such terms in discourse is an arduous task. This leads in some cases to committing errors during translation processes and lexicographic tasks. The process is even more challenging when it comes to machine translation, both in the cases of single-word terms and multi-word terms. One of the recent concerns of Natural Language Processing (NLP) applications and Machine Translation (MT) technologies is the automatic identification of metaphor-based words in discourse through Deep Learning (DL). In this study, we seek to fill this gap through the use of thirteen popular transformer based models, as well as ChatGPT, and we show that discriminative models perform better than GPT-3.5 model with our best performer reporting 92.2349% F1 score in metaphoric flower and plant names identification task.
Transformer-based Detection of Multiword Expressions in Flower and Plant Names
Sep 20, 2022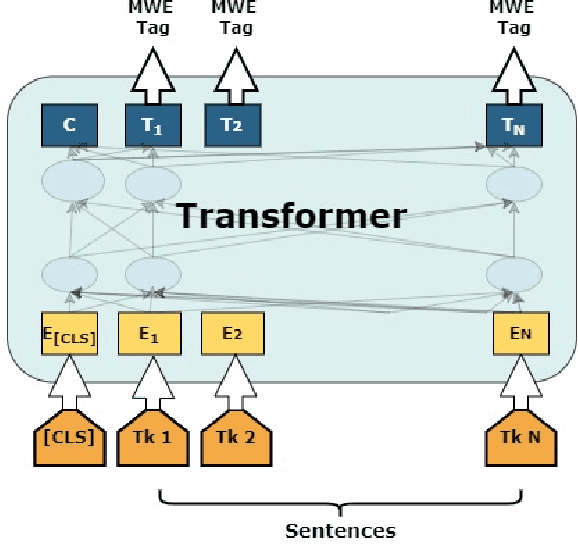
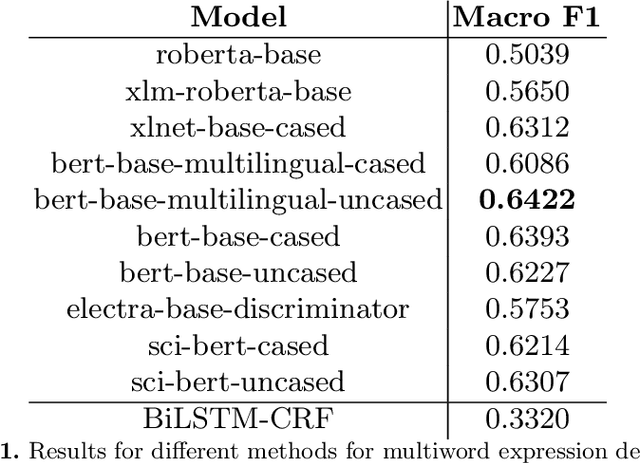
Abstract:Multiword expression (MWE) is a sequence of words which collectively present a meaning which is not derived from its individual words. The task of processing MWEs is crucial in many natural language processing (NLP) applications, including machine translation and terminology extraction. Therefore, detecting MWEs in different domains is an important research topic. In this paper, we explore state-of-the-art neural transformers in the task of detecting MWEs in flower and plant names. We evaluate different transformer models on a dataset created from Encyclopedia of Plants and Flower. We empirically show that transformer models outperform the previous neural models based on long short-term memory (LSTM).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge