Alistair Plum
Do LLMs Judge Distantly Supervised Named Entity Labels Well? Constructing the JudgeWEL Dataset
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:We present judgeWEL, a dataset for named entity recognition (NER) in Luxembourgish, automatically labelled and subsequently verified using large language models (LLM) in a novel pipeline. Building datasets for under-represented languages remains one of the major bottlenecks in natural language processing, where the scarcity of resources and linguistic particularities make large-scale annotation costly and potentially inconsistent. To address these challenges, we propose and evaluate a novel approach that leverages Wikipedia and Wikidata as structured sources of weak supervision. By exploiting internal links within Wikipedia articles, we infer entity types based on their corresponding Wikidata entries, thereby generating initial annotations with minimal human intervention. Because such links are not uniformly reliable, we mitigate noise by employing and comparing several LLMs to identify and retain only high-quality labelled sentences. The resulting corpus is approximately five times larger than the currently available Luxembourgish NER dataset and offers broader and more balanced coverage across entity categories, providing a substantial new resource for multilingual and low-resource NER research.
Neural Text Normalization for Luxembourgish using Real-Life Variation Data
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Orthographic variation is very common in Luxembourgish texts due to the absence of a fully-fledged standard variety. Additionally, developing NLP tools for Luxembourgish is a difficult task given the lack of annotated and parallel data, which is exacerbated by ongoing standardization. In this paper, we propose the first sequence-to-sequence normalization models using the ByT5 and mT5 architectures with training data obtained from word-level real-life variation data. We perform a fine-grained, linguistically-motivated evaluation to test byte-based, word-based and pipeline-based models for their strengths and weaknesses in text normalization. We show that our sequence model using real-life variation data is an effective approach for tailor-made normalization in Luxembourgish.
Text Generation Models for Luxembourgish with Limited Data: A Balanced Multilingual Strategy
Dec 12, 2024



Abstract:This paper addresses the challenges in developing language models for less-represented languages, with a focus on Luxembourgish. Despite its active development, Luxembourgish faces a digital data scarcity, exacerbated by Luxembourg's multilingual context. We propose a novel text generation model based on the T5 architecture, combining limited Luxembourgish data with equal amounts, in terms of size and type, of German and French data. We hypothesise that a model trained on Luxembourgish, German, and French will improve the model's cross-lingual transfer learning capabilities and outperform monolingual and large multilingual models. To verify this, the study at hand explores whether multilingual or monolingual training is more beneficial for Luxembourgish language generation. For the evaluation, we introduce LuxGen, a text generation benchmark that is the first of its kind for Luxembourgish.
LuxBank: The First Universal Dependency Treebank for Luxembourgish
Nov 07, 2024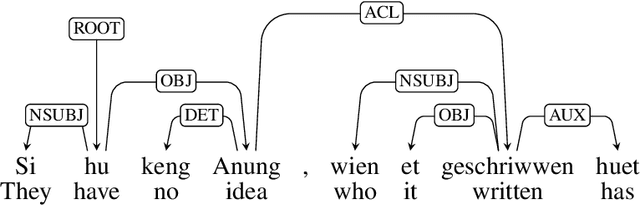
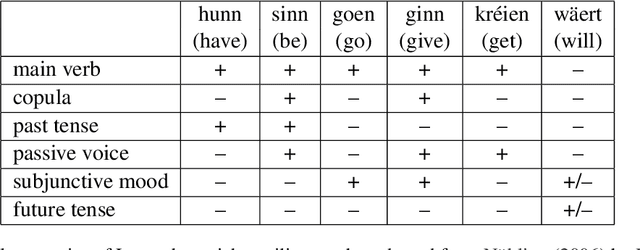
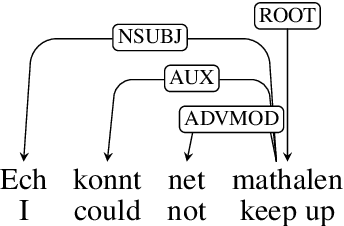

Abstract:The Universal Dependencies (UD) project has significantly expanded linguistic coverage across 161 languages, yet Luxembourgish, a West Germanic language spoken by approximately 400,000 people, has remained absent until now. In this paper, we introduce LuxBank, the first UD Treebank for Luxembourgish, addressing the gap in syntactic annotation and analysis for this `low-research' language. We establish formal guidelines for Luxembourgish language annotation, providing the foundation for the first large-scale quantitative analysis of its syntax. LuxBank serves not only as a resource for linguists and language learners but also as a tool for developing spell checkers and grammar checkers, organising existing text archives and even training large language models. By incorporating Luxembourgish into the UD framework, we aim to enhance the understanding of syntactic variation within West Germanic languages and offer a model for documenting smaller, semi-standardised languages. This work positions Luxembourgish as a valuable resource in the broader linguistic and NLP communities, contributing to the study of languages with limited research and resources.
Guided Distant Supervision for Multilingual Relation Extraction Data: Adapting to a New Language
Mar 27, 2024



Abstract:Relation extraction is essential for extracting and understanding biographical information in the context of digital humanities and related subjects. There is a growing interest in the community to build datasets capable of training machine learning models to extract relationships. However, annotating such datasets can be expensive and time-consuming, in addition to being limited to English. This paper applies guided distant supervision to create a large biographical relationship extraction dataset for German. Our dataset, composed of more than 80,000 instances for nine relationship types, is the largest biographical German relationship extraction dataset. We also create a manually annotated dataset with 2000 instances to evaluate the models and release it together with the dataset compiled using guided distant supervision. We train several state-of-the-art machine learning models on the automatically created dataset and release them as well. Furthermore, we experiment with multilingual and cross-lingual experiments that could benefit many low-resource languages.
Biographical: A Semi-Supervised Relation Extraction Dataset
May 02, 2022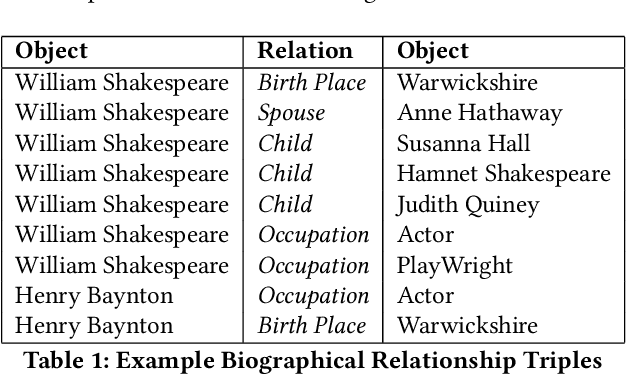
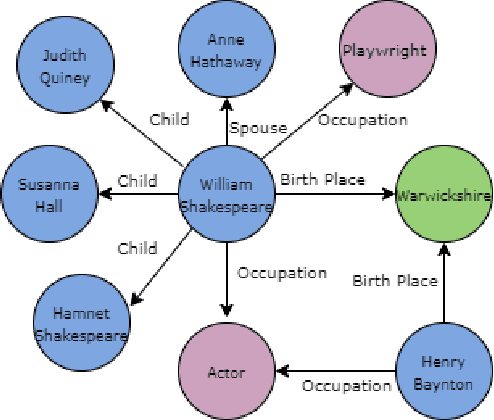
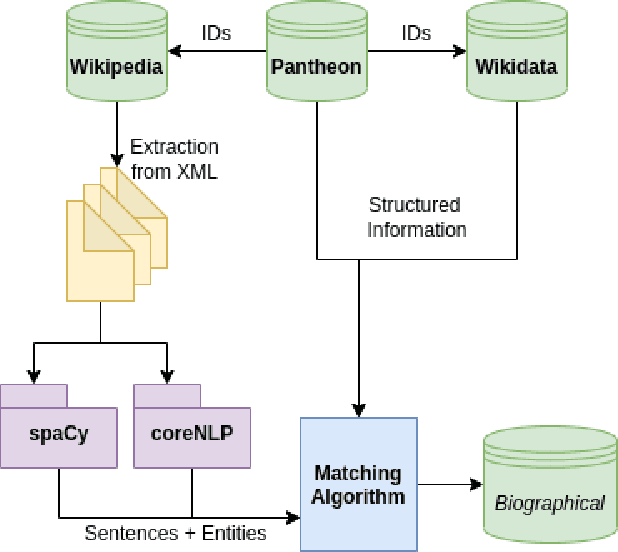
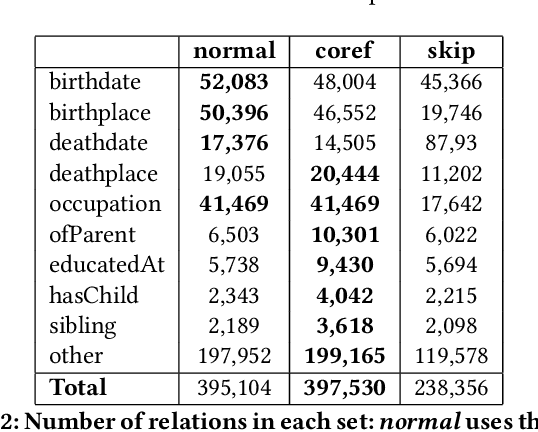
Abstract:Extracting biographical information from online documents is a popular research topic among the information extraction (IE) community. Various natural language processing (NLP) techniques such as text classification, text summarisation and relation extraction are commonly used to achieve this. Among these techniques, RE is the most common since it can be directly used to build biographical knowledge graphs. RE is usually framed as a supervised machine learning (ML) problem, where ML models are trained on annotated datasets. However, there are few annotated datasets for RE since the annotation process can be costly and time-consuming. To address this, we developed Biographical, the first semi-supervised dataset for RE. The dataset, which is aimed towards digital humanities (DH) and historical research, is automatically compiled by aligning sentences from Wikipedia articles with matching structured data from sources including Pantheon and Wikidata. By exploiting the structure of Wikipedia articles and robust named entity recognition (NER), we match information with relatively high precision in order to compile annotated relation pairs for ten different relations that are important in the DH domain. Furthermore, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the dataset by training a state-of-the-art neural model to classify relation pairs, and evaluate it on a manually annotated gold standard set. Biographical is primarily aimed at training neural models for RE within the domain of digital humanities and history, but as we discuss at the end of this paper, it can be useful for other purposes as well.
RGCL at SemEval-2020 Task 6: Neural Approaches to Definition Extraction
Oct 13, 2020

Abstract:This paper presents the RGCL team submission to SemEval 2020 Task 6: DeftEval, subtasks 1 and 2. The system classifies definitions at the sentence and token levels. It utilises state-of-the-art neural network architectures, which have some task-specific adaptations, including an automatically extended training set. Overall, the approach achieves acceptable evaluation scores, while maintaining flexibility in architecture selection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge