Mark Fishel
LLMs for Extremely Low-Resource Finno-Ugric Languages
Oct 24, 2024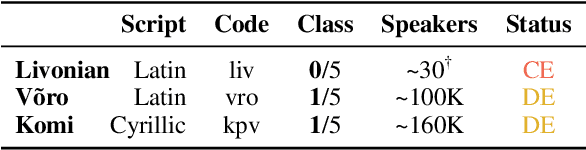
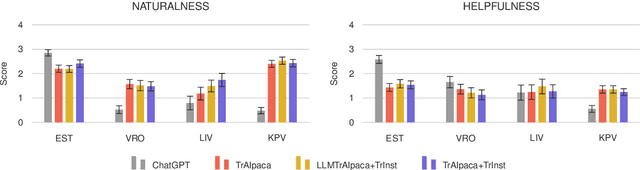
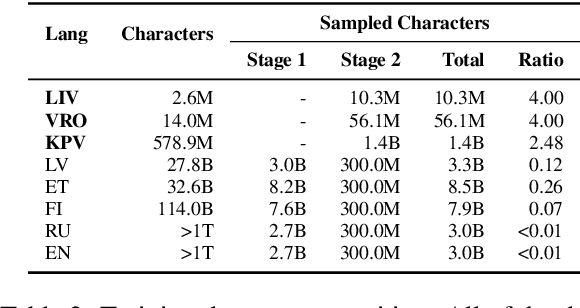
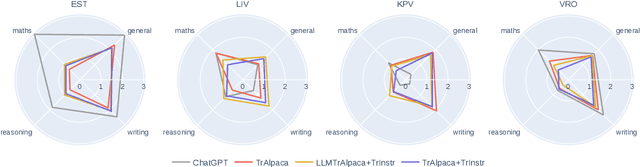
Abstract:The advancement of large language models (LLMs) has predominantly focused on high-resource languages, leaving low-resource languages, such as those in the Finno-Ugric family, significantly underrepresented. This paper addresses this gap by focusing on V\~oro, Livonian, and Komi. We cover almost the entire cycle of LLM creation, from data collection to instruction tuning and evaluation. Our contributions include developing multilingual base and instruction-tuned models; creating evaluation benchmarks, including the smugri-MT-bench multi-turn conversational benchmark; and conducting human evaluation. We intend for this work to promote linguistic diversity, ensuring that lesser-resourced languages can benefit from advancements in NLP.
Preliminary WMT24 Ranking of General MT Systems and LLMs
Jul 29, 2024



Abstract:This is the preliminary ranking of WMT24 General MT systems based on automatic metrics. The official ranking will be a human evaluation, which is superior to the automatic ranking and supersedes it. The purpose of this report is not to interpret any findings but only provide preliminary results to the participants of the General MT task that may be useful during the writing of the system submission.
Teaching Llama a New Language Through Cross-Lingual Knowledge Transfer
Apr 05, 2024Abstract:This paper explores cost-efficient methods to adapt pretrained Large Language Models (LLMs) to new lower-resource languages, with a specific focus on Estonian. Leveraging the Llama 2 model, we investigate the impact of combining cross-lingual instruction-tuning with additional monolingual pretraining. Our results demonstrate that even a relatively small amount of additional monolingual pretraining followed by cross-lingual instruction-tuning significantly enhances results on Estonian. Furthermore, we showcase cross-lingual knowledge transfer from high-quality English instructions to Estonian, resulting in improvements in commonsense reasoning and multi-turn conversation capabilities. Our best model, named \textsc{Llammas}, represents the first open-source instruction-following LLM for Estonian. Additionally, we publish Alpaca-est, the first general task instruction dataset for Estonia. These contributions mark the initial progress in the direction of developing open-source LLMs for Estonian.
To Err Is Human, but Llamas Can Learn It Too
Mar 08, 2024



Abstract:This study explores enhancing grammatical error correction (GEC) through artificial error generation (AEG) using language models (LMs). Specifically, we fine-tune Llama 2-based LMs for error generation and find that this approach yields synthetic errors akin to human errors. Next, we train GEC Llama models with the help of these artificial errors and outperform previous state-of-the-art error correction models, with gains ranging between 0.8 and 6 F0.5 points across all tested languages (German, Ukrainian, and Estonian). Moreover, we demonstrate that generating errors by fine-tuning smaller sequence-to-sequence models and prompting large commercial LMs (GPT-3.5 and GPT-4) also results in synthetic errors beneficially affecting error generation models.
Autocorrect for Estonian texts: final report from project EKTB25
Feb 18, 2024Abstract:The project was funded in 2021-2023 by the National Programme of Estonian Language Technology. Its main aim was to develop spelling and grammar correction tools for the Estonian language. The main challenge was the very small amount of available error correction data needed for such development. To mitigate this, (1) we annotated more correction data for model training and testing, (2) we tested transfer-learning, i.e. retraining machine learning models created for other tasks, so as not to depend solely on correction data, (3) we compared the developed method and model with alternatives, including large language models. We also developed automatic evaluation, which can calculate the accuracy and yield of corrections by error category, so that the effectiveness of different methods can be compared in detail. There has been a breakthrough in large language models during the project: GPT4, a commercial language model with Estonian-language support, has been created. We took into account the existence of the model when adjusting plans and in the report we present a comparison with the ability of GPT4 to improve the Estonian language text. The final results show that the approach we have developed provides better scores than GPT4 and the result is usable but not entirely reliable yet. The report also contains ideas on how GPT4 and other major language models can be implemented in the future, focusing on open-source solutions. All results of this project are open-data/open-source, with licenses that allow them to be used for purposes including commercial ones.
True Detective: A Challenging Benchmark for Deep Abductive Reasoning \\in Foundation Models
Dec 20, 2022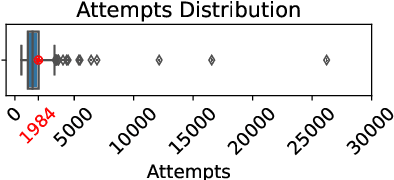
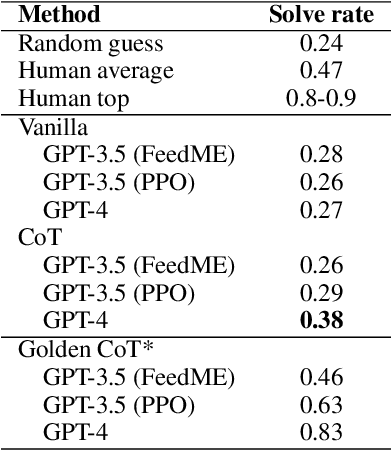
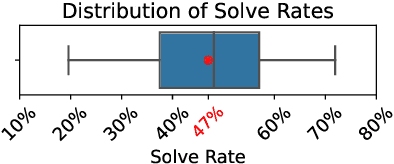
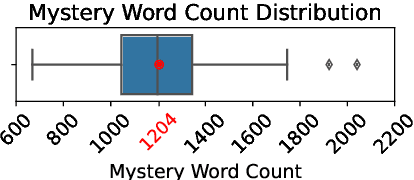
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong performance in zero-shot reasoning tasks, including abductive reasoning. This is reflected in their ability to perform well on current benchmarks in this area. However, to truly test the limits of LLMs in abductive reasoning, a more challenging benchmark is needed. In this paper, we present such a benchmark, consisting of 191 long-form mystery stories, each approximately 1200 words in length and presented in the form of detective puzzles. Each puzzle includes a multiple-choice question for evaluation sourced from the "5 Minute Mystery" platform. Our results show that state-of-the-art GPT models perform significantly worse than human solvers on this benchmark, with an accuracy of 28\% compared to 47\% for humans. This indicates that there is still a significant gap in the abductive reasoning abilities of LLMs and highlights the need for further research in this area. Our work provides a challenging benchmark for future studies on reasoning in language models and contributes to a better understanding of the limits of LLMs' abilities.
Cross-lingual Similarity of Multilingual Representations Revisited
Dec 04, 2022Abstract:Related works used indexes like CKA and variants of CCA to measure the similarity of cross-lingual representations in multilingual language models. In this paper, we argue that assumptions of CKA/CCA align poorly with one of the motivating goals of cross-lingual learning analysis, i.e., explaining zero-shot cross-lingual transfer. We highlight what valuable aspects of cross-lingual similarity these indexes fail to capture and provide a motivating case study \textit{demonstrating the problem empirically}. Then, we introduce \textit{Average Neuron-Wise Correlation (ANC)} as a straightforward alternative that is exempt from the difficulties of CKA/CCA and is good specifically in a cross-lingual context. Finally, we use ANC to construct evidence that the previously introduced ``first align, then predict'' pattern takes place not only in masked language models (MLMs) but also in multilingual models with \textit{causal language modeling} objectives (CLMs). Moreover, we show that the pattern extends to the \textit{scaled versions} of the MLMs and CLMs (up to 85x original mBERT).\footnote{Our code is publicly available at \url{https://github.com/TartuNLP/xsim}}
* Accepted at AACL 2022
Establishing Interlingua in Multilingual Language Models
Sep 16, 2021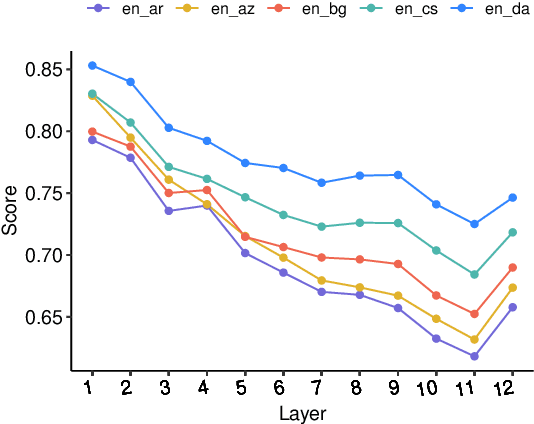


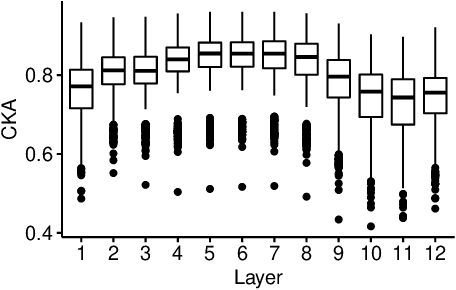
Abstract:Large multilingual language models show remarkable zero-shot cross-lingual transfer performance on a range of tasks. Follow-up works hypothesized that these models internally project representations of different languages into a shared interlingual space. However, they produced contradictory results. In this paper, we correct the famous prior work claiming that "BERT is not an Interlingua" and show that with the proper choice of sentence representation different languages actually do converge to a shared space in such language models. Furthermore, we demonstrate that this convergence pattern is robust across four measures of correlation similarity and six mBERT-like models. We then extend our analysis to 28 diverse languages and find that the interlingual space exhibits a particular structure similar to the linguistic relatedness of languages. We also highlight a few outlier languages that seem to fail to converge to the shared space. The code for replicating our results is available at the following URL: https://github.com/maksym-del/interlingua.
Translation Transformers Rediscover Inherent Data Domains
Sep 16, 2021


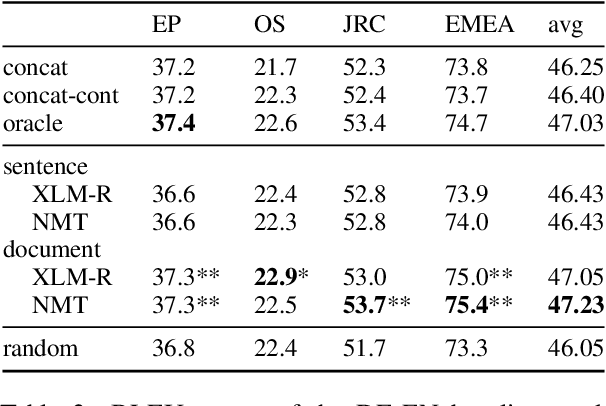
Abstract:Many works proposed methods to improve the performance of Neural Machine Translation (NMT) models in a domain/multi-domain adaptation scenario. However, an understanding of how NMT baselines represent text domain information internally is still lacking. Here we analyze the sentence representations learned by NMT Transformers and show that these explicitly include the information on text domains, even after only seeing the input sentences without domains labels. Furthermore, we show that this internal information is enough to cluster sentences by their underlying domains without supervision. We show that NMT models produce clusters better aligned to the actual domains compared to pre-trained language models (LMs). Notably, when computed on document-level, NMT cluster-to-domain correspondence nears 100%. We use these findings together with an approach to NMT domain adaptation using automatically extracted domains. Whereas previous work relied on external LMs for text clustering, we propose re-using the NMT model as a source of unsupervised clusters. We perform an extensive experimental study comparing two approaches across two data scenarios, three language pairs, and both sentence-level and document-level clustering, showing equal or significantly superior performance compared to LMs.
Unsupervised Quality Estimation for Neural Machine Translation
May 21, 2020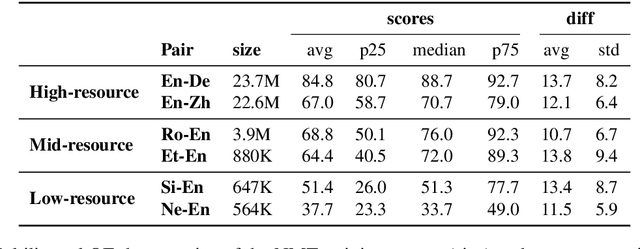



Abstract:Quality Estimation (QE) is an important component in making Machine Translation (MT) useful in real-world applications, as it is aimed to inform the user on the quality of the MT output at test time. Existing approaches require large amounts of expert annotated data, computation and time for training. As an alternative, we devise an unsupervised approach to QE where no training or access to additional resources besides the MT system itself is required. Different from most of the current work that treats the MT system as a black box, we explore useful information that can be extracted from the MT system as a by-product of translation. By employing methods for uncertainty quantification, we achieve very good correlation with human judgments of quality, rivalling state-of-the-art supervised QE models. To evaluate our approach we collect the first dataset that enables work on both black-box and glass-box approaches to QE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge