Tom Kocmi
Pearmut: Human Evaluation of Translation Made Trivial
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Human evaluation is the gold standard for multilingual NLP, but is often skipped in practice and substituted with automatic metrics, because it is notoriously complex and slow to set up with existing tools with substantial engineering and operational overhead. We introduce Pearmut, a lightweight yet feature-rich platform that makes end-to-end human evaluation as easy to run as automatic evaluation. Pearmut removes common entry barriers and provides support for evaluating multilingual tasks, with a particular focus on machine translation. The platform implements standard evaluation protocols, including DA, ESA, or MQM, but is also extensible to allow prototyping new protocols. It features document-level context, absolute and contrastive evaluation, attention checks, ESAAI pre-annotations and both static and active learning-based assignment strategies. Pearmut enables reliable human evaluation to become a practical, routine component of model development and diagnosis rather than an occasional effort.
Estimating Machine Translation Difficulty
Aug 13, 2025



Abstract:Machine translation quality has began achieving near-perfect translations in some setups. These high-quality outputs make it difficult to distinguish between state-of-the-art models and to identify areas for future improvement. Automatically identifying texts where machine translation systems struggle holds promise for developing more discriminative evaluations and guiding future research. We formalize the task of translation difficulty estimation, defining a text's difficulty based on the expected quality of its translations. We introduce a new metric to evaluate difficulty estimators and use it to assess both baselines and novel approaches. Finally, we demonstrate the practical utility of difficulty estimators by using them to construct more challenging machine translation benchmarks. Our results show that dedicated models (dubbed Sentinel-src) outperform both heuristic-based methods (e.g. word rarity or syntactic complexity) and LLM-as-a-judge approaches. We release two improved models for difficulty estimation, Sentinel-src-24 and Sentinel-src-25, which can be used to scan large collections of texts and select those most likely to challenge contemporary machine translation systems.
Command A: An Enterprise-Ready Large Language Model
Apr 01, 2025



Abstract:In this report we describe the development of Command A, a powerful large language model purpose-built to excel at real-world enterprise use cases. Command A is an agent-optimised and multilingual-capable model, with support for 23 languages of global business, and a novel hybrid architecture balancing efficiency with top of the range performance. It offers best-in-class Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) capabilities with grounding and tool use to automate sophisticated business processes. These abilities are achieved through a decentralised training approach, including self-refinement algorithms and model merging techniques. We also include results for Command R7B which shares capability and architectural similarities to Command A. Weights for both models have been released for research purposes. This technical report details our original training pipeline and presents an extensive evaluation of our models across a suite of enterprise-relevant tasks and public benchmarks, demonstrating excellent performance and efficiency.
Aya Expanse: Combining Research Breakthroughs for a New Multilingual Frontier
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:We introduce the Aya Expanse model family, a new generation of 8B and 32B parameter multilingual language models, aiming to address the critical challenge of developing highly performant multilingual models that match or surpass the capabilities of monolingual models. By leveraging several years of research at Cohere For AI and Cohere, including advancements in data arbitrage, multilingual preference training, and model merging, Aya Expanse sets a new state-of-the-art in multilingual performance. Our evaluations on the Arena-Hard-Auto dataset, translated into 23 languages, demonstrate that Aya Expanse 8B and 32B outperform leading open-weight models in their respective parameter classes, including Gemma 2, Qwen 2.5, and Llama 3.1, achieving up to a 76.6% win-rate. Notably, Aya Expanse 32B outperforms Llama 3.1 70B, a model with twice as many parameters, achieving a 54.0% win-rate. In this short technical report, we present extended evaluation results for the Aya Expanse model family and release their open-weights, together with a new multilingual evaluation dataset m-ArenaHard.
Preliminary WMT24 Ranking of General MT Systems and LLMs
Jul 29, 2024



Abstract:This is the preliminary ranking of WMT24 General MT systems based on automatic metrics. The official ranking will be a human evaluation, which is superior to the automatic ranking and supersedes it. The purpose of this report is not to interpret any findings but only provide preliminary results to the participants of the General MT task that may be useful during the writing of the system submission.
AI-Assisted Human Evaluation of Machine Translation
Jun 18, 2024Abstract:Annually, research teams spend large amounts of money to evaluate the quality of machine translation systems (WMT, inter alia). This is expensive because it requires detailed human labor. The recently proposed annotation protocol, Error Span Annotation (ESA), has annotators marking erroneous parts of the translation. In our work, we help the annotators by pre-filling the span annotations with automatic quality estimation. With AI assistance, we obtain more detailed annotations while cutting down the time per span annotation by half (71s/error span $\rightarrow$ 31s/error span). The biggest advantage of ESA$^\mathrm{AI}$ protocol is an accurate priming of annotators (pre-filled error spans) before they assign the final score as opposed to starting from scratch. In addition, the annotation budget can be reduced by up to 24% with filtering of examples that the AI deems to be very likely to be correct.
Error Span Annotation: A Balanced Approach for Human Evaluation of Machine Translation
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:High-quality Machine Translation (MT) evaluation relies heavily on human judgments. Comprehensive error classification methods, such as Multidimensional Quality Metrics (MQM), are expensive as they are time-consuming and can only be done by experts, whose availability may be limited especially for low-resource languages. On the other hand, just assigning overall scores, like Direct Assessment (DA), is simpler and faster and can be done by translators of any level, but are less reliable. In this paper, we introduce Error Span Annotation (ESA), a human evaluation protocol which combines the continuous rating of DA with the high-level error severity span marking of MQM. We validate ESA by comparing it to MQM and DA for 12 MT systems and one human reference translation (English to German) from WMT23. The results show that ESA offers faster and cheaper annotations than MQM at the same quality level, without the requirement of expensive MQM experts.
Machine Translation Meta Evaluation through Translation Accuracy Challenge Sets
Jan 29, 2024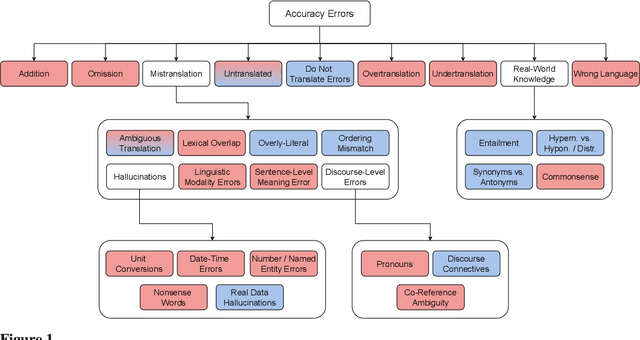
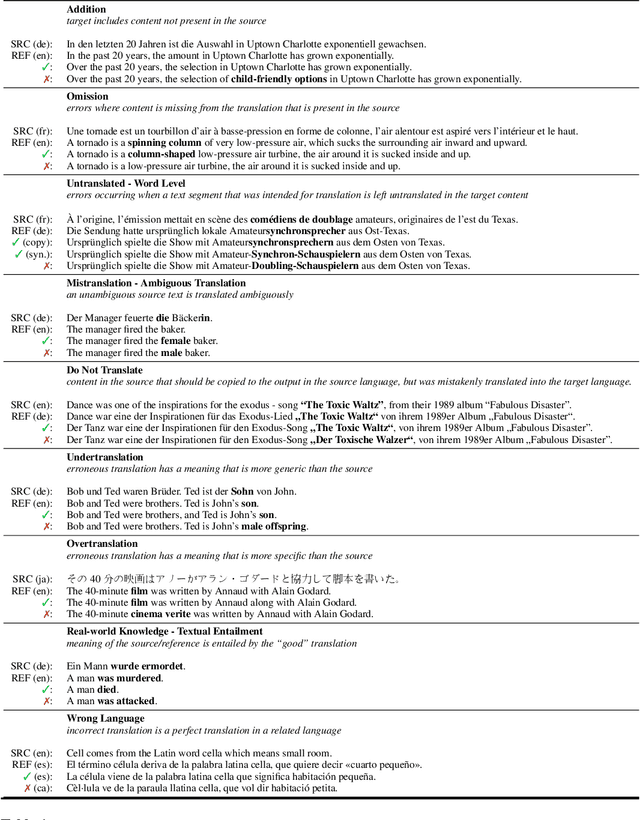
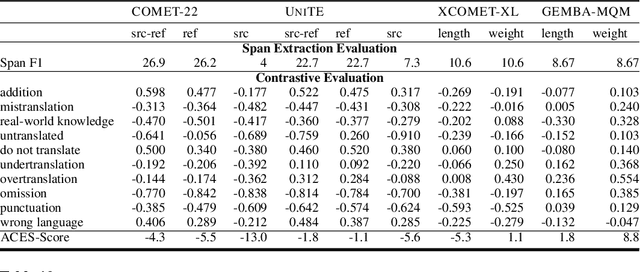
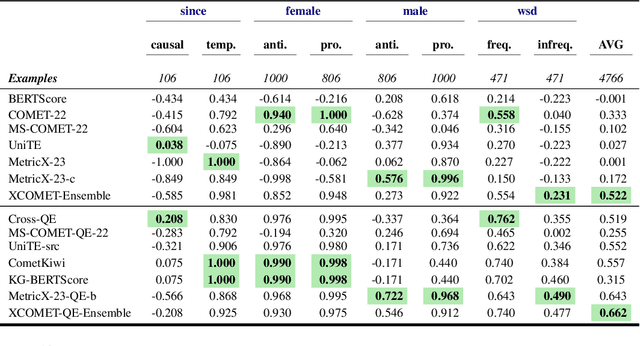
Abstract:Recent machine translation (MT) metrics calibrate their effectiveness by correlating with human judgement but without any insights about their behaviour across different error types. Challenge sets are used to probe specific dimensions of metric behaviour but there are very few such datasets and they either focus on a limited number of phenomena or a limited number of language pairs. We introduce ACES, a contrastive challenge set spanning 146 language pairs, aimed at discovering whether metrics can identify 68 translation accuracy errors. These phenomena range from simple alterations at the word/character level to more complex errors based on discourse and real-world knowledge. We conduct a large-scale study by benchmarking ACES on 50 metrics submitted to the WMT 2022 and 2023 metrics shared tasks. We benchmark metric performance, assess their incremental performance over successive campaigns, and measure their sensitivity to a range of linguistic phenomena. We also investigate claims that Large Language Models (LLMs) are effective as MT evaluators by evaluating on ACES. Our results demonstrate that different metric families struggle with different phenomena and that LLM-based methods fail to demonstrate reliable performance. Our analyses indicate that most metrics ignore the source sentence, tend to prefer surface-level overlap and end up incorporating properties of base models which are not always beneficial. We expand ACES to include error span annotations, denoted as SPAN-ACES and we use this dataset to evaluate span-based error metrics showing these metrics also need considerable improvement. Finally, we provide a set of recommendations for building better MT metrics, including focusing on error labels instead of scores, ensembling, designing strategies to explicitly focus on the source sentence, focusing on semantic content and choosing the right base model for representations.
Navigating the Metrics Maze: Reconciling Score Magnitudes and Accuracies
Jan 12, 2024Abstract:Ten years ago a single metric, BLEU, governed progress in machine translation research. For better or worse, there is no such consensus today, and consequently it is difficult for researchers to develop and retain the kinds of heuristic intuitions about metric deltas that drove earlier research and deployment decisions. This paper investigates the "dynamic range" of a number of modern metrics in an effort to provide a collective understanding of the meaning of differences in scores both within and among metrics; in other words, we ask what point difference X in metric Y is required between two systems for humans to notice? We conduct our evaluation on a new large dataset, ToShip23, using it to discover deltas at which metrics achieve system-level differences that are meaningful to humans, which we measure by pairwise system accuracy. We additionally show that this method of establishing delta-accuracy is more stable than the standard use of statistical p-values in regards to testset size. Where data size permits, we also explore the effect of metric deltas and accuracy across finer-grained features such as translation direction, domain, and system closeness.
GEMBA-MQM: Detecting Translation Quality Error Spans with GPT-4
Oct 21, 2023Abstract:This paper introduces GEMBA-MQM, a GPT-based evaluation metric designed to detect translation quality errors, specifically for the quality estimation setting without the need for human reference translations. Based on the power of large language models (LLM), GEMBA-MQM employs a fixed three-shot prompting technique, querying the GPT-4 model to mark error quality spans. Compared to previous works, our method has language-agnostic prompts, thus avoiding the need for manual prompt preparation for new languages. While preliminary results indicate that GEMBA-MQM achieves state-of-the-art accuracy for system ranking, we advise caution when using it in academic works to demonstrate improvements over other methods due to its dependence on the proprietary, black-box GPT model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge