Marcely Zanon Boito
SpeechMapper: Speech-to-text Embedding Projector for LLMs
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Current speech LLMs bridge speech foundation models to LLMs using projection layers, training all of these components on speech instruction data. This strategy is computationally intensive and susceptible to task and prompt overfitting. We present SpeechMapper, a cost-efficient speech-to-LLM-embedding training approach that mitigates overfitting, enabling more robust and generalizable models. Our model is first pretrained without the LLM on inexpensive hardware, and then efficiently attached to the target LLM via a brief 1K-step instruction tuning (IT) stage. Through experiments on speech translation and spoken question answering, we demonstrate the versatility of SpeechMapper's pretrained block, presenting results for both task-agnostic IT, an ASR-based adaptation strategy that does not train in the target task, and task-specific IT. In task-agnostic settings, Speechmapper rivals the best instruction-following speech LLM from IWSLT25, despite never being trained on these tasks, while in task-specific settings, it outperforms this model across many datasets, despite requiring less data and compute. Overall, SpeechMapper offers a practical and scalable approach for efficient, generalizable speech-LLM integration without large-scale IT.
From TOWER to SPIRE: Adding the Speech Modality to a Text-Only LLM
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown remarkable performance and generalization capabilities across multiple languages and tasks, making them very attractive targets for multi-modality integration (e.g., images or speech). In this work, we extend an existing LLM to the speech modality via speech discretization and continued pre-training. In particular, we are interested in multilingual LLMs, such as TOWER, as their pre-training setting allows us to treat discretized speech input as an additional translation language. The resulting open-source model, SPIRE, is able to transcribe and translate English speech input while maintaining TOWER's original performance on translation-related tasks, showcasing that discretized speech input integration as an additional language is feasible during LLM adaptation. We make our code and models available to the community.
mHuBERT-147: A Compact Multilingual HuBERT Model
Jun 11, 2024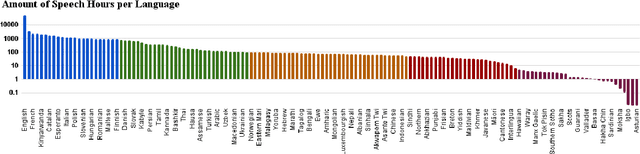
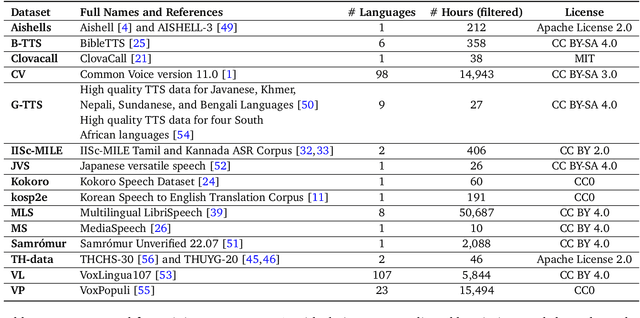
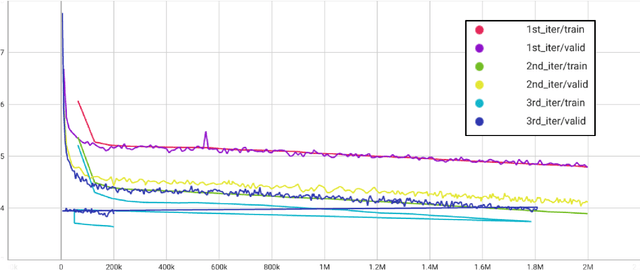
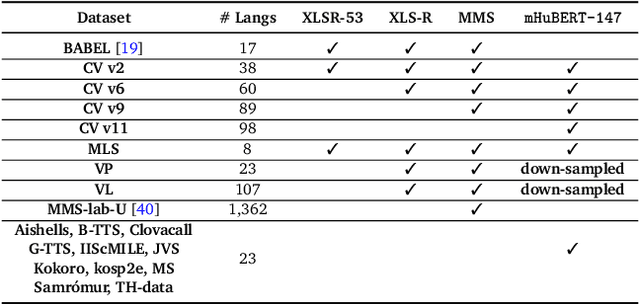
Abstract:We present mHuBERT-147, the first general-purpose massively multilingual HuBERT speech representation model trained on 90K hours of clean, open-license data. To scale up the multi-iteration HuBERT approach, we use faiss-based clustering, achieving 5.2x faster label assignment than the original method. We also apply a new multilingual batching up-sampling strategy, leveraging both language and dataset diversity. After 3 training iterations, our compact 95M parameter mHuBERT-147 outperforms larger models trained on substantially more data. We rank second and first on the ML-SUPERB 10min and 1h leaderboards, with SOTA scores for 3 tasks. Across ASR/LID tasks, our model consistently surpasses XLS-R (300M params; 436K hours) and demonstrates strong competitiveness against the much larger MMS (1B params; 491K hours). Our findings indicate that mHuBERT-147 is a promising model for multilingual speech tasks, offering an unprecedented balance between high performance and parameter efficiency.
DistilWhisper: Efficient Distillation of Multi-task Speech Models via Language-Specific Experts
Nov 02, 2023



Abstract:Whisper is a multitask and multilingual speech model covering 99 languages. It yields commendable automatic speech recognition (ASR) results in a subset of its covered languages, but the model still under-performs on a non-negligible number of under-represented languages, a problem exacerbated in smaller model versions. In this work, we propose DistilWhisper, an approach able to bridge the performance gap in ASR for these languages while retaining the advantages of multitask and multilingual capabilities. Our approach involves two key strategies: lightweight modular ASR fine-tuning of whisper-small using language-specific experts, and knowledge distillation from whisper-large-v2. This dual approach allows us to effectively boost ASR performance while keeping the robustness inherited from the multitask and multilingual pre-training. Results demonstrate that our approach is more effective than standard fine-tuning or LoRA adapters, boosting performance in the targeted languages for both in- and out-of-domain test sets, while introducing only a negligible parameter overhead at inference.
LeBenchmark 2.0: a Standardized, Replicable and Enhanced Framework for Self-supervised Representations of French Speech
Sep 11, 2023Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) is at the origin of unprecedented improvements in many different domains including computer vision and natural language processing. Speech processing drastically benefitted from SSL as most of the current domain-related tasks are now being approached with pre-trained models. This work introduces LeBenchmark 2.0 an open-source framework for assessing and building SSL-equipped French speech technologies. It includes documented, large-scale and heterogeneous corpora with up to 14,000 hours of heterogeneous speech, ten pre-trained SSL wav2vec 2.0 models containing from 26 million to one billion learnable parameters shared with the community, and an evaluation protocol made of six downstream tasks to complement existing benchmarks. LeBenchmark 2.0 also presents unique perspectives on pre-trained SSL models for speech with the investigation of frozen versus fine-tuned downstream models, task-agnostic versus task-specific pre-trained models as well as a discussion on the carbon footprint of large-scale model training.
NAVER LABS Europe's Multilingual Speech Translation Systems for the IWSLT 2023 Low-Resource Track
Jun 13, 2023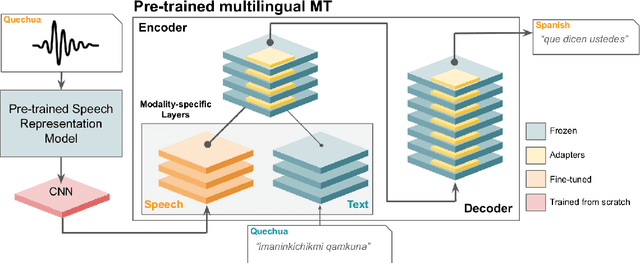
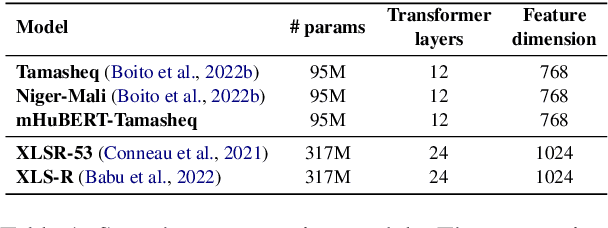
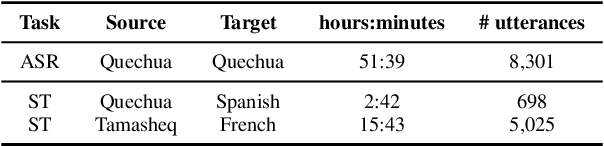
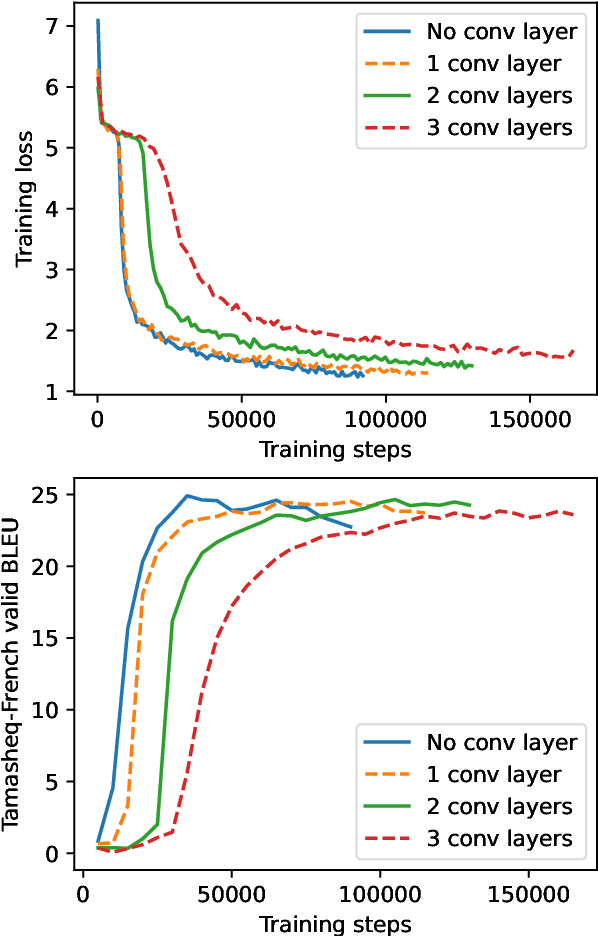
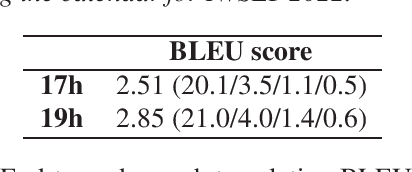
Abstract:This paper presents NAVER LABS Europe's systems for Tamasheq-French and Quechua-Spanish speech translation in the IWSLT 2023 Low-Resource track. Our work attempts to maximize translation quality in low-resource settings using multilingual parameter-efficient solutions that leverage strong pre-trained models. Our primary submission for Tamasheq outperforms the previous state of the art by 7.5 BLEU points on the IWSLT 2022 test set, and achieves 23.6 BLEU on this year's test set, outperforming the second best participant by 7.7 points. For Quechua, we also rank first and achieve 17.7 BLEU, despite having only two hours of translation data. Finally, we show that our proposed multilingual architecture is also competitive for high-resource languages, outperforming the best unconstrained submission to the IWSLT 2021 Multilingual track, despite using much less training data and compute.
ON-TRAC Consortium Systems for the IWSLT 2022 Dialect and Low-resource Speech Translation Tasks
May 04, 2022
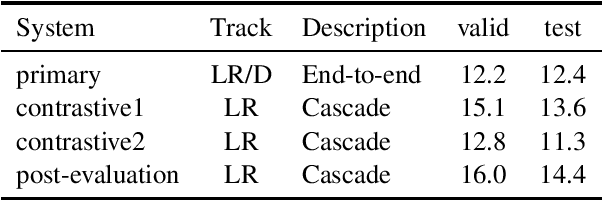
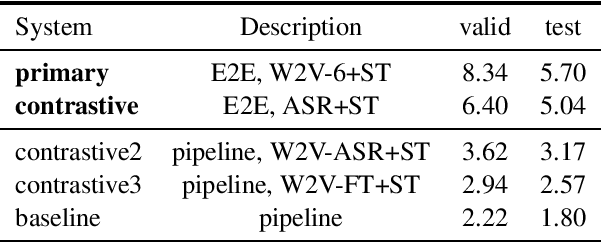
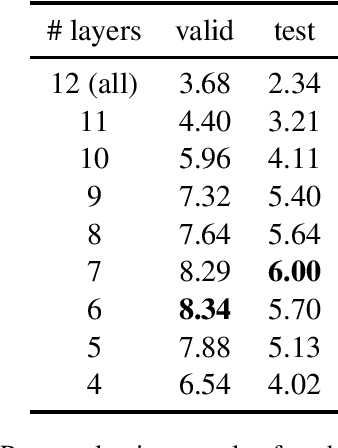
Abstract:This paper describes the ON-TRAC Consortium translation systems developed for two challenge tracks featured in the Evaluation Campaign of IWSLT 2022: low-resource and dialect speech translation. For the Tunisian Arabic-English dataset (low-resource and dialect tracks), we build an end-to-end model as our joint primary submission, and compare it against cascaded models that leverage a large fine-tuned wav2vec 2.0 model for ASR. Our results show that in our settings pipeline approaches are still very competitive, and that with the use of transfer learning, they can outperform end-to-end models for speech translation (ST). For the Tamasheq-French dataset (low-resource track) our primary submission leverages intermediate representations from a wav2vec 2.0 model trained on 234 hours of Tamasheq audio, while our contrastive model uses a French phonetic transcription of the Tamasheq audio as input in a Conformer speech translation architecture jointly trained on automatic speech recognition, ST and machine translation losses. Our results highlight that self-supervised models trained on smaller sets of target data are more effective to low-resource end-to-end ST fine-tuning, compared to large off-the-shelf models. Results also illustrate that even approximate phonetic transcriptions can improve ST scores.
A Study of Gender Impact in Self-supervised Models for Speech-to-Text Systems
Apr 04, 2022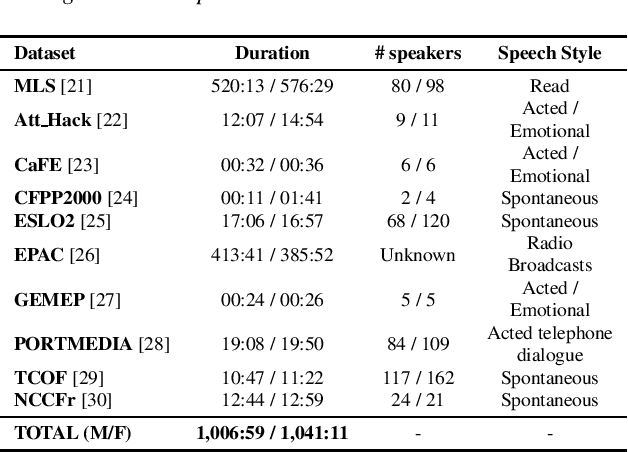
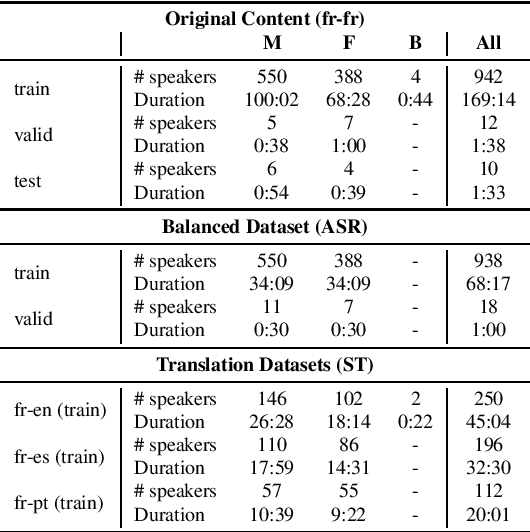
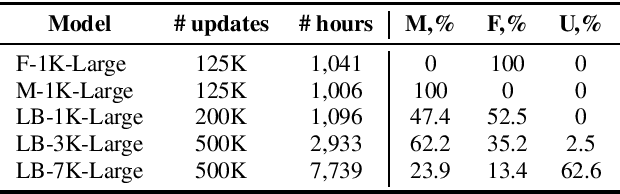
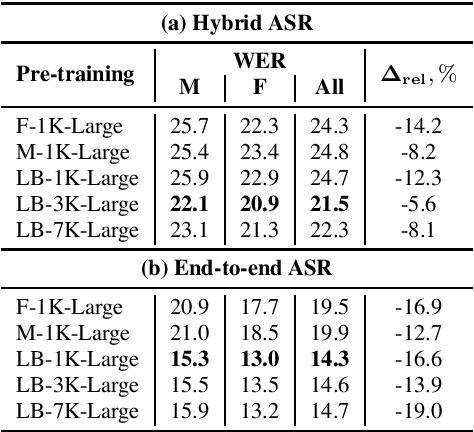
Abstract:Self-supervised models for speech processing emerged recently as popular foundation blocks in speech processing pipelines. These models are pre-trained on unlabeled audio data and then used in speech processing downstream tasks such as automatic speech recognition (ASR) or speech translation (ST). Since these models are now used in research and industrial systems alike, it becomes necessary to understand the impact caused by some features such as gender distribution within pre-training data. Using French as our investigation language, we train and compare gender-specific wav2vec 2.0 models against models containing different degrees of gender balance in their pre-training data. The comparison is performed by applying these models to two speech-to-text downstream tasks: ASR and ST. Our results show that the type of downstream integration matters. We observe lower overall performance using gender-specific pre-training before fine-tuning an end-to-end ASR system. However, when self-supervised models are used as feature extractors, the overall ASR and ST results follow more complex patterns, in which the balanced pre-trained model is not necessarily the best option. Lastly, our crude 'fairness' metric, the relative performance difference measured between female and male test sets, does not display a strong variation from balanced to gender-specific pre-trained wav2vec 2.0 models.
Speech Resources in the Tamasheq Language
Jan 14, 2022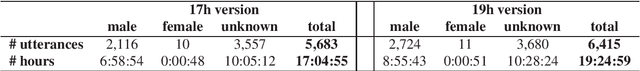
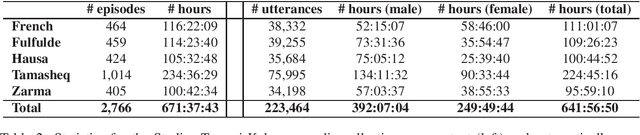
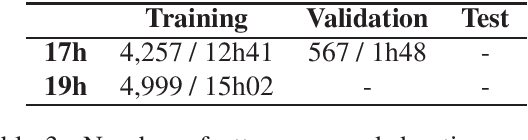
Abstract:In this paper we present two datasets for Tamasheq, a developing language mainly spoken in Mali and Niger. These two datasets were made available for the IWSLT 2022 low-resource speech translation track, and they consist of collections of radio recordings from the Studio Kalangou (Niger) and Studio Tamani (Mali) daily broadcast news. We share (i) a massive amount of unlabeled audio data (671 hours) in five languages: French from Niger, Fulfulde, Hausa, Tamasheq and Zarma, and (ii) a smaller parallel corpus of audio recordings (17 hours) in Tamasheq, with utterance-level translations in the French language. All this data is shared under the Creative Commons BY-NC-ND 3.0 license. We hope these resources will inspire the speech community to develop and benchmark models using the Tamasheq language.
Unsupervised Word Segmentation from Discrete Speech Units in Low-Resource Settings
Jun 08, 2021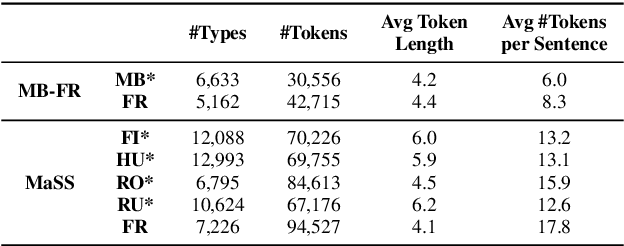
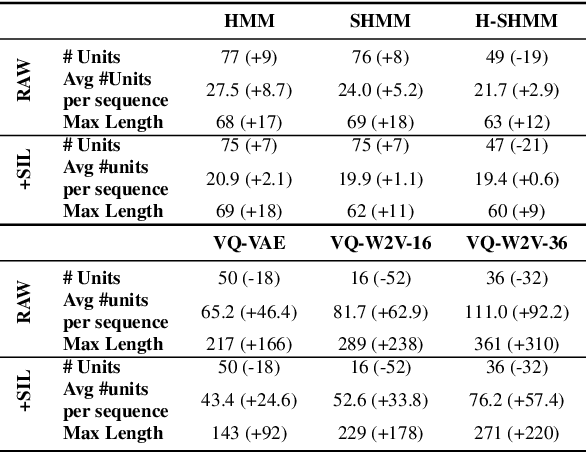
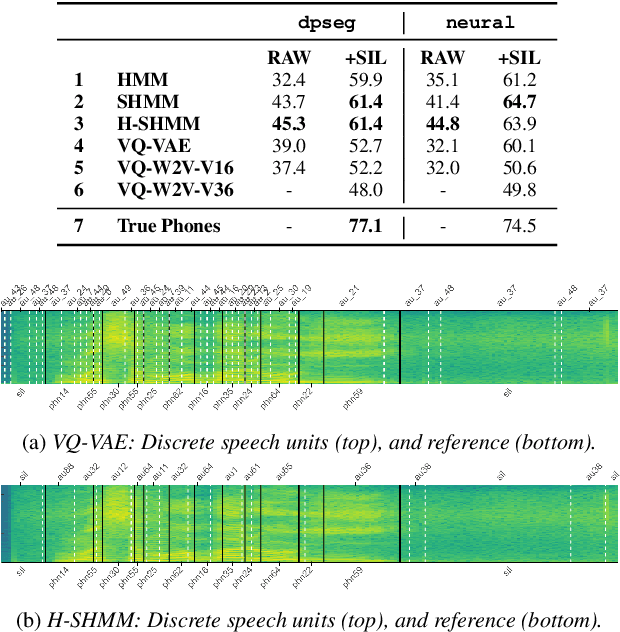
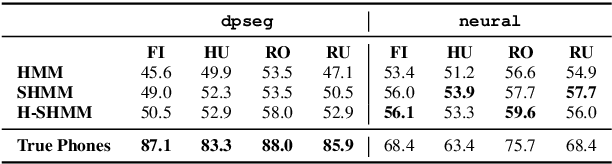
Abstract:When documenting oral-languages, Unsupervised Word Segmentation (UWS) from speech is a useful, yet challenging, task. It can be performed from phonetic transcriptions, or in the absence of these, from the output of unsupervised speech discretization models. These discretization models are trained using raw speech only, producing discrete speech units which can be applied for downstream (text-based) tasks. In this paper we compare five of these models: three Bayesian and two neural approaches, with regards to the exploitability of the produced units for UWS. Two UWS models are experimented with and we report results for Finnish, Hungarian, Mboshi, Romanian and Russian in a low-resource setting (using only 5k sentences). Our results suggest that neural models for speech discretization are difficult to exploit in our setting, and that it might be necessary to adapt them to limit sequence length. We obtain our best UWS results by using the SHMM and H-SHMM Bayesian models, which produce high quality, yet compressed, discrete representations of the input speech signal.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge