Aline Villavicencio
StealthMark: Harmless and Stealthy Ownership Verification for Medical Segmentation via Uncertainty-Guided Backdoors
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Annotating medical data for training AI models is often costly and limited due to the shortage of specialists with relevant clinical expertise. This challenge is further compounded by privacy and ethical concerns associated with sensitive patient information. As a result, well-trained medical segmentation models on private datasets constitute valuable intellectual property requiring robust protection mechanisms. Existing model protection techniques primarily focus on classification and generative tasks, while segmentation models-crucial to medical image analysis-remain largely underexplored. In this paper, we propose a novel, stealthy, and harmless method, StealthMark, for verifying the ownership of medical segmentation models under black-box conditions. Our approach subtly modulates model uncertainty without altering the final segmentation outputs, thereby preserving the model's performance. To enable ownership verification, we incorporate model-agnostic explanation methods, e.g. LIME, to extract feature attributions from the model outputs. Under specific triggering conditions, these explanations reveal a distinct and verifiable watermark. We further design the watermark as a QR code to facilitate robust and recognizable ownership claims. We conducted extensive experiments across four medical imaging datasets and five mainstream segmentation models. The results demonstrate the effectiveness, stealthiness, and harmlessness of our method on the original model's segmentation performance. For example, when applied to the SAM model, StealthMark consistently achieved ASR above 95% across various datasets while maintaining less than a 1% drop in Dice and AUC scores, significantly outperforming backdoor-based watermarking methods and highlighting its strong potential for practical deployment. Our implementation code is made available at: https://github.com/Qinkaiyu/StealthMark.
A Parallel Cross-Lingual Benchmark for Multimodal Idiomaticity Understanding
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Potentially idiomatic expressions (PIEs) construe meanings inherently tied to the everyday experience of a given language community. As such, they constitute an interesting challenge for assessing the linguistic (and to some extent cultural) capabilities of NLP systems. In this paper, we present XMPIE, a parallel multilingual and multimodal dataset of potentially idiomatic expressions. The dataset, containing 34 languages and over ten thousand items, allows comparative analyses of idiomatic patterns among language-specific realisations and preferences in order to gather insights about shared cultural aspects. This parallel dataset allows to evaluate model performance for a given PIE in different languages and whether idiomatic understanding in one language can be transferred to another. Moreover, the dataset supports the study of PIEs across textual and visual modalities, to measure to what extent PIE understanding in one modality transfers or implies in understanding in another modality (text vs. image). The data was created by language experts, with both textual and visual components crafted under multilingual guidelines, and each PIE is accompanied by five images representing a spectrum from idiomatic to literal meanings, including semantically related and random distractors. The result is a high-quality benchmark for evaluating multilingual and multimodal idiomatic language understanding.
Beyond surface form: A pipeline for semantic analysis in Alzheimer's Disease detection from spontaneous speech
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Alzheimer's Disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative condition that adversely affects cognitive abilities. Language-related changes can be automatically identified through the analysis of outputs from linguistic assessment tasks, such as picture description. Language models show promise as a basis for screening tools for AD, but their limited interpretability poses a challenge in distinguishing true linguistic markers of cognitive decline from surface-level textual patterns. To address this issue, we examine how surface form variation affects classification performance, with the goal of assessing the ability of language models to represent underlying semantic indicators. We introduce a novel approach where texts surface forms are transformed by altering syntax and vocabulary while preserving semantic content. The transformations significantly modify the structure and lexical content, as indicated by low BLEU and chrF scores, yet retain the underlying semantics, as reflected in high semantic similarity scores, isolating the effect of semantic information, and finding models perform similarly to if they were using the original text, with only small deviations in macro-F1. We also investigate whether language from picture descriptions retains enough detail to reconstruct the original image using generative models. We found that image-based transformations add substantial noise reducing classification accuracy. Our methodology provides a novel way of looking at what features influence model predictions, and allows the removal of possible spurious correlations. We find that just using semantic information, language model based classifiers can still detect AD. This work shows that difficult to detect semantic impairment can be identified, addressing an overlooked feature of linguistic deterioration, and opening new pathways for early detection systems.
SemEval-2025 Task 1: AdMIRe -- Advancing Multimodal Idiomaticity Representation
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Idiomatic expressions present a unique challenge in NLP, as their meanings are often not directly inferable from their constituent words. Despite recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs), idiomaticity remains a significant obstacle to robust semantic representation. We present datasets and tasks for SemEval-2025 Task 1: AdMiRe (Advancing Multimodal Idiomaticity Representation), which challenges the community to assess and improve models' ability to interpret idiomatic expressions in multimodal contexts and in multiple languages. Participants competed in two subtasks: ranking images based on their alignment with idiomatic or literal meanings, and predicting the next image in a sequence. The most effective methods achieved human-level performance by leveraging pretrained LLMs and vision-language models in mixture-of-experts settings, with multiple queries used to smooth over the weaknesses in these models' representations of idiomaticity.
Vocabulary Expansion of Chat Models with Unlabeled Target Language Data
Dec 16, 2024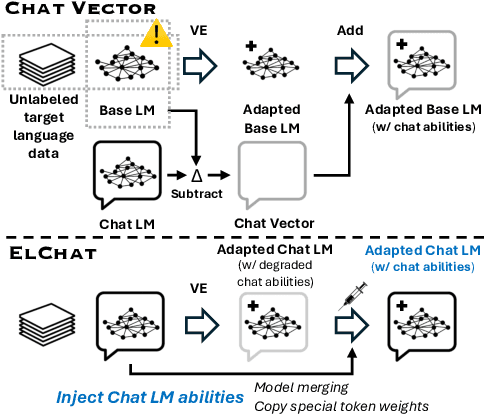
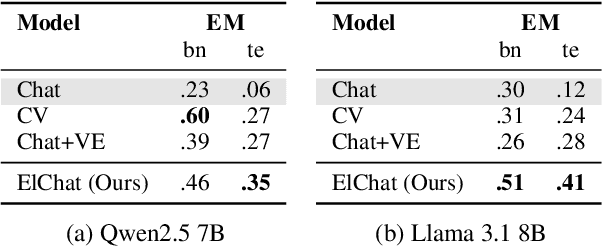
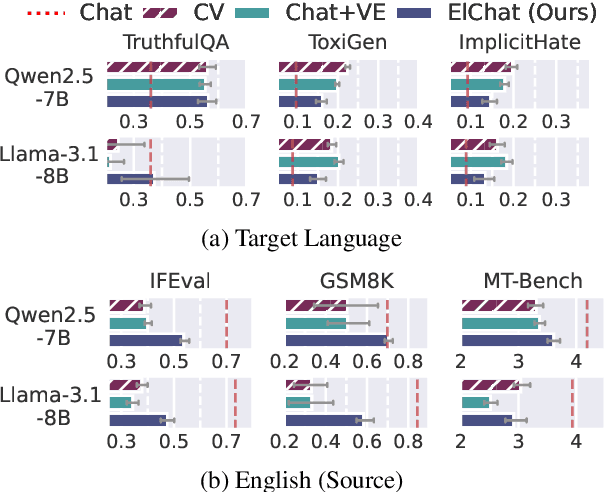
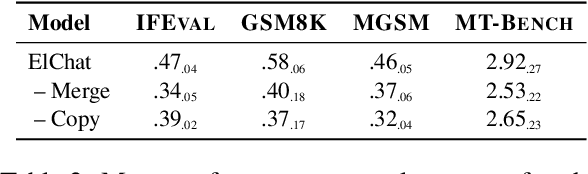
Abstract:Chat models (i.e. language models trained to follow instructions through conversation with humans) outperform base models (i.e. trained solely on unlabeled data) in both conversation and general task-solving abilities. These models are generally English-centric and require further adaptation for languages that are underrepresented in or absent from their training data. A common technique for adapting base models is to extend the model's vocabulary with target language tokens, i.e. vocabulary expansion (VE), and then continually pre-train it on language-specific data. Using chat data is ideal for chat model adaptation, but often, either this does not exist or is costly to construct. Alternatively, adapting chat models with unlabeled data is a possible solution, but it could result in catastrophic forgetting. In this paper, we investigate the impact of using unlabeled target language data for VE on chat models for the first time. We first show that off-the-shelf VE generally performs well across target language tasks and models in 71% of cases, though it underperforms in scenarios where source chat models are already strong. To further improve adapted models, we propose post-hoc techniques that inject information from the source model without requiring any further training. Experiments reveal the effectiveness of our methods, helping the adapted models to achieve performance improvements in 87% of cases.
A Deep Learning Approach to Language-independent Gender Prediction on Twitter
Nov 29, 2024

Abstract:This work presents a set of experiments conducted to predict the gender of Twitter users based on language-independent features extracted from the text of the users' tweets. The experiments were performed on a version of TwiSty dataset including tweets written by the users of six different languages: Portuguese, French, Dutch, English, German, and Italian. Logistic regression (LR), and feed-forward neural networks (FFNN) with back-propagation were used to build models in two different settings: Inter-Lingual (IL) and Cross-Lingual (CL). In the IL setting, the training and testing were performed on the same language whereas in the CL, Italian and German datasets were set aside and only used as test sets and the rest were combined to compose training and development sets. In the IL, the highest accuracy score belongs to LR whereas in the CL, FFNN with three hidden layers yields the highest score. The results show that neural network based models underperform traditional models when the size of the training set is small; however, they beat traditional models by a non-trivial margin, when they are fed with large enough data. Finally, the feature analysis confirms that men and women have different writing styles independent of their language.
Investigating Idiomaticity in Word Representations
Nov 04, 2024



Abstract:Idiomatic expressions are an integral part of human languages, often used to express complex ideas in compressed or conventional ways (e.g. eager beaver as a keen and enthusiastic person). However, their interpretations may not be straightforwardly linked to the meanings of their individual components in isolation and this may have an impact for compositional approaches. In this paper, we investigate to what extent word representation models are able to go beyond compositional word combinations and capture multiword expression idiomaticity and some of the expected properties related to idiomatic meanings. We focus on noun compounds of varying levels of idiomaticity in two languages (English and Portuguese), presenting a dataset of minimal pairs containing human idiomaticity judgments for each noun compound at both type and token levels, their paraphrases and their occurrences in naturalistic and sense-neutral contexts, totalling 32,200 sentences. We propose this set of minimal pairs for evaluating how well a model captures idiomatic meanings, and define a set of fine-grained metrics of Affinity and Scaled Similarity, to determine how sensitive the models are to perturbations that may lead to changes in idiomaticity. The results obtained with a variety of representative and widely used models indicate that, despite superficial indications to the contrary in the form of high similarities, idiomaticity is not yet accurately represented in current models. Moreover, the performance of models with different levels of contextualisation suggests that their ability to capture context is not yet able to go beyond more superficial lexical clues provided by the words and to actually incorporate the relevant semantic clues needed for idiomaticity.
Rolling the DICE on Idiomaticity: How LLMs Fail to Grasp Context
Oct 21, 2024



Abstract:Human processing of idioms relies on understanding the contextual sentences in which idioms occur, as well as language-intrinsic features such as frequency and speaker-intrinsic factors like familiarity. While LLMs have shown high performance on idiomaticity detection tasks, this success may be attributed to reasoning shortcuts in existing datasets. To this end, we construct a novel, controlled contrastive dataset designed to test whether LLMs can effectively use context to disambiguate idiomatic meaning. Additionally, we explore how collocational frequency and sentence probability influence model performance. Our findings reveal that LLMs often fail to resolve idiomaticity when it is required to attend to the surrounding context, and that models perform better on sentences that have higher likelihood. The collocational frequency of expressions also impacts performance. We make our code and dataset publicly available.
Enhancing Idiomatic Representation in Multiple Languages via an Adaptive Contrastive Triplet Loss
Jun 21, 2024Abstract:Accurately modeling idiomatic or non-compositional language has been a longstanding challenge in Natural Language Processing (NLP). This is partly because these expressions do not derive their meanings solely from their constituent words, but also due to the scarcity of relevant data resources, and their impact on the performance of downstream tasks such as machine translation and simplification. In this paper we propose an approach to model idiomaticity effectively using a triplet loss that incorporates the asymmetric contribution of components words to an idiomatic meaning for training language models by using adaptive contrastive learning and resampling miners to build an idiomatic-aware learning objective. Our proposed method is evaluated on a SemEval challenge and outperforms previous alternatives significantly in many metrics.
Vocabulary Expansion for Low-resource Cross-lingual Transfer
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown remarkable capabilities in many languages beyond English. Yet, LLMs require more inference steps when generating non-English text due to their reliance on English-centric tokenizers, vocabulary, and pre-training data, resulting in higher usage costs to non-English speakers. Vocabulary expansion with target language tokens is a widely used cross-lingual vocabulary adaptation approach to remedy this issue. Despite its effectiveness in inference speedup, the majority of previous work has focused on high-resource settings assuming access to a substantial amount of target language data to effectively initialize the embeddings of the new tokens and adapt the LLM to the target language. However, vocabulary expansion for LLMs in low-resource settings (i.e. languages and compute) has yet to be explored. In this paper, we investigate sample-efficient adaptation strategies from different angles, including target vocabulary size and initialization methods, and the amount of target data available for adaptation. Extensive experiments across typologically diverse languages, tasks and models show that simpler heuristic-based embedding initialization is more efficient and robust to changes in target vocabulary size and adaptation data in low-resource settings, outperforming a popular random initialization and a more sophisticated state-of-the-art approach that relies on external data and model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge