Lily H. Zhang
Learning from others' mistakes: Finetuning machine translation models with span-level error annotations
Oct 21, 2024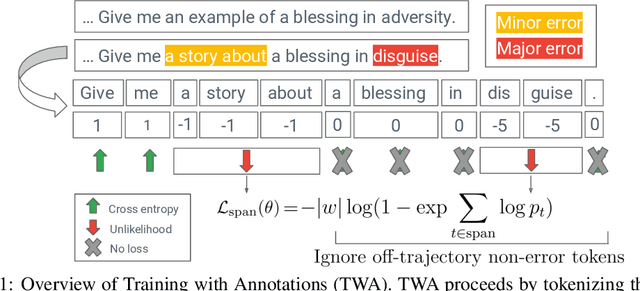


Abstract:Despite growing interest in incorporating feedback to improve language models, most efforts focus only on sequence-level annotations. In this work, we explore the potential of utilizing fine-grained span-level annotations from offline datasets to improve model quality. We develop a simple finetuning algorithm, called Training with Annotations (TWA), to directly train machine translation models on such annotated data. TWA utilizes targeted span-level error information while also flexibly learning what to penalize within a span. Moreover, TWA considers the overall trajectory of a sequence when deciding which non-error spans to utilize as positive signals. Experiments on English-German and Chinese-English machine translation show that TWA outperforms baselines such as Supervised FineTuning on sequences filtered for quality and Direct Preference Optimization on pairs constructed from the same data.
Towards Minimal Targeted Updates of Language Models with Targeted Negative Training
Jun 19, 2024
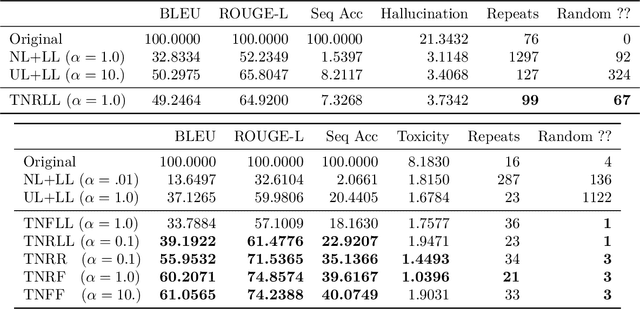
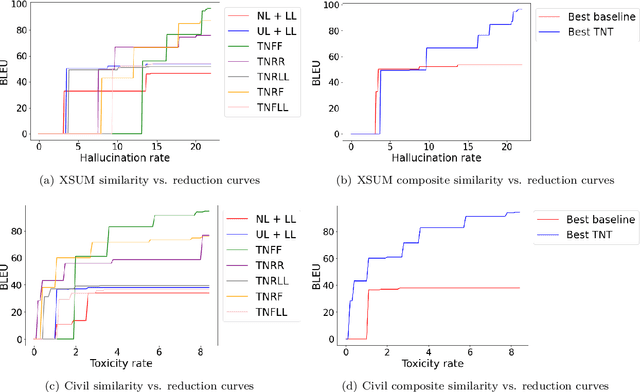
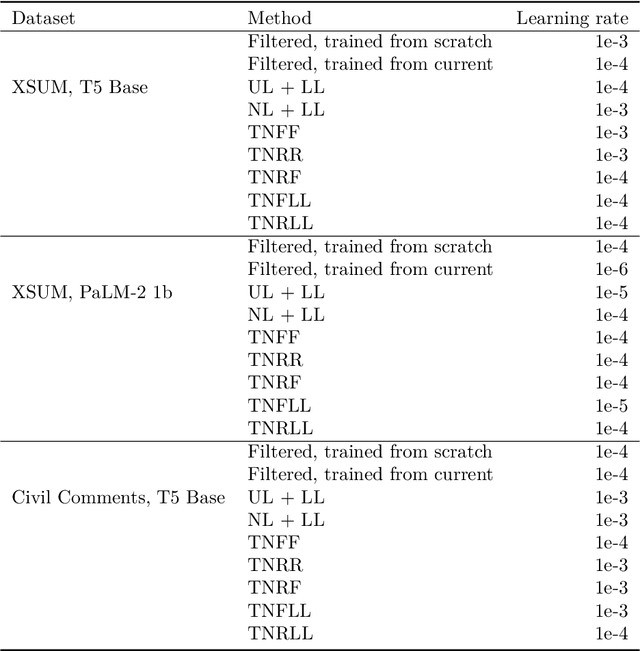
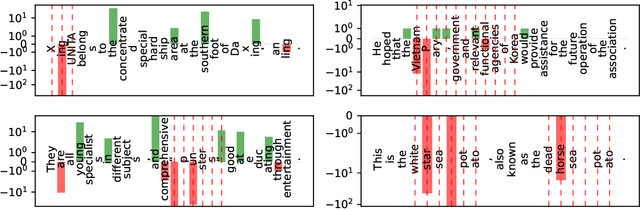
Abstract:Generative models of language exhibit impressive capabilities but still place non-negligible probability mass over undesirable outputs. In this work, we address the task of updating a model to avoid unwanted outputs while minimally changing model behavior otherwise, a challenge we refer to as a minimal targeted update. We first formalize the notion of a minimal targeted update and propose a method to achieve such updates using negative examples from a model's generations. Our proposed Targeted Negative Training (TNT) results in updates that keep the new distribution close to the original, unlike existing losses for negative signal which push down probability but do not control what the updated distribution will be. In experiments, we demonstrate that TNT yields a better trade-off between reducing unwanted behavior and maintaining model generation behavior than baselines, paving the way towards a modeling paradigm based on iterative training updates that constrain models from generating undesirable outputs while preserving their impressive capabilities.
Preference Learning Algorithms Do Not Learn Preference Rankings
May 29, 2024Abstract:Preference learning algorithms (e.g., RLHF and DPO) are frequently used to steer LLMs to produce generations that are more preferred by humans, but our understanding of their inner workings is still limited. In this work, we study the conventional wisdom that preference learning trains models to assign higher likelihoods to more preferred outputs than less preferred outputs, measured via $\textit{ranking accuracy}$. Surprisingly, we find that most state-of-the-art preference-tuned models achieve a ranking accuracy of less than 60% on common preference datasets. We furthermore derive the $\textit{idealized ranking accuracy}$ that a preference-tuned LLM would achieve if it optimized the DPO or RLHF objective perfectly. We demonstrate that existing models exhibit a significant $\textit{alignment gap}$ -- $\textit{i.e.}$, a gap between the observed and idealized ranking accuracies. We attribute this discrepancy to the DPO objective, which is empirically and theoretically ill-suited to fix even mild ranking errors in the reference model, and derive a simple and efficient formula for quantifying the difficulty of learning a given preference datapoint. Finally, we demonstrate that ranking accuracy strongly correlates with the empirically popular win rate metric when the model is close to the reference model used in the objective, shedding further light on the differences between on-policy (e.g., RLHF) and off-policy (e.g., DPO) preference learning algorithms.
Robustness to Spurious Correlations Improves Semantic Out-of-Distribution Detection
Feb 08, 2023Abstract:Methods which utilize the outputs or feature representations of predictive models have emerged as promising approaches for out-of-distribution (OOD) detection of image inputs. However, these methods struggle to detect OOD inputs that share nuisance values (e.g. background) with in-distribution inputs. The detection of shared-nuisance out-of-distribution (SN-OOD) inputs is particularly relevant in real-world applications, as anomalies and in-distribution inputs tend to be captured in the same settings during deployment. In this work, we provide a possible explanation for SN-OOD detection failures and propose nuisance-aware OOD detection to address them. Nuisance-aware OOD detection substitutes a classifier trained via empirical risk minimization and cross-entropy loss with one that 1. is trained under a distribution where the nuisance-label relationship is broken and 2. yields representations that are independent of the nuisance under this distribution, both marginally and conditioned on the label. We can train a classifier to achieve these objectives using Nuisance-Randomized Distillation (NuRD), an algorithm developed for OOD generalization under spurious correlations. Output- and feature-based nuisance-aware OOD detection perform substantially better than their original counterparts, succeeding even when detection based on domain generalization algorithms fails to improve performance.
Set Norm and Equivariant Skip Connections: Putting the Deep in Deep Sets
Jun 23, 2022



Abstract:Permutation invariant neural networks are a promising tool for making predictions from sets. However, we show that existing permutation invariant architectures, Deep Sets and Set Transformer, can suffer from vanishing or exploding gradients when they are deep. Additionally, layer norm, the normalization of choice in Set Transformer, can hurt performance by removing information useful for prediction. To address these issues, we introduce the clean path principle for equivariant residual connections and develop set norm, a normalization tailored for sets. With these, we build Deep Sets++ and Set Transformer++, models that reach high depths with comparable or better performance than their original counterparts on a diverse suite of tasks. We additionally introduce Flow-RBC, a new single-cell dataset and real-world application of permutation invariant prediction. We open-source our data and code here: https://github.com/rajesh-lab/deep_permutation_invariant.
Understanding Failures in Out-of-Distribution Detection with Deep Generative Models
Jul 16, 2021


Abstract:Deep generative models (DGMs) seem a natural fit for detecting out-of-distribution (OOD) inputs, but such models have been shown to assign higher probabilities or densities to OOD images than images from the training distribution. In this work, we explain why this behavior should be attributed to model misestimation. We first prove that no method can guarantee performance beyond random chance without assumptions on which out-distributions are relevant. We then interrogate the typical set hypothesis, the claim that relevant out-distributions can lie in high likelihood regions of the data distribution, and that OOD detection should be defined based on the data distribution's typical set. We highlight the consequences implied by assuming support overlap between in- and out-distributions, as well as the arbitrariness of the typical set for OOD detection. Our results suggest that estimation error is a more plausible explanation than the misalignment between likelihood-based OOD detection and out-distributions of interest, and we illustrate how even minimal estimation error can lead to OOD detection failures, yielding implications for future work in deep generative modeling and OOD detection.
Predictive Modeling in the Presence of Nuisance-Induced Spurious Correlations
Jul 06, 2021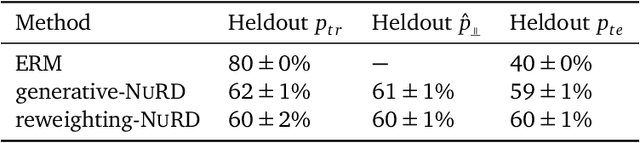
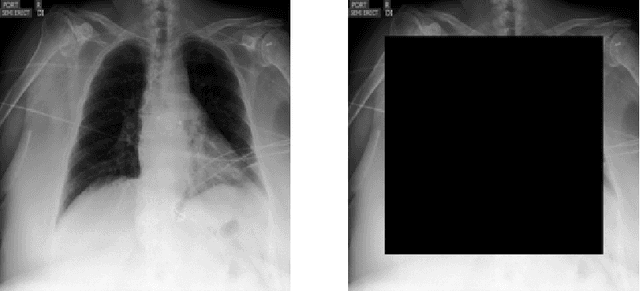
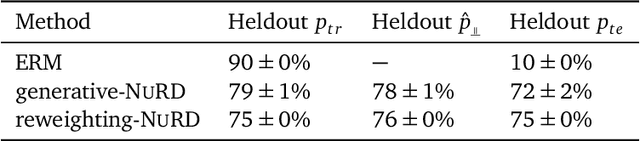
Abstract:Deep predictive models often make use of spurious correlations between the label and the covariates that differ between training and test distributions. In many classification tasks, spurious correlations are induced by a changing relationship between the label and some nuisance variables correlated with the covariates. For example, in classifying animals in natural images, the background, which is the nuisance, can predict the type of animal. This nuisance-label relationship does not always hold. We formalize a family of distributions that only differ in the nuisance-label relationship and introduce a distribution where this relationship is broken called the nuisance-randomized distribution. We introduce a set of predictive models built from the nuisance-randomized distribution with representations, that when conditioned on, do not correlate the label and the nuisance. For models in this set, we lower bound the performance for any member of the family with the mutual information between the representation and the label under the nuisance-randomized distribution. To build predictive models that maximize the performance lower bound, we develop Nuisance-Randomized Distillation (NURD). We evaluate NURD on a synthetic example, colored-MNIST, and classifying chest X-rays. When using non-lung patches as the nuisance in classifying chest X-rays, NURD produces models that predict pneumonia under strong spurious correlations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge