Kyunghyun Cho
Characterizing the Predictive Impact of Modalities with Supervised Latent-Variable Modeling
Feb 19, 2026Abstract:Despite the recent success of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), existing approaches predominantly assume the availability of multiple modalities during training and inference. In practice, multimodal data is often incomplete because modalities may be missing, collected asynchronously, or available only for a subset of examples. In this work, we propose PRIMO, a supervised latent-variable imputation model that quantifies the predictive impact of any missing modality within the multimodal learning setting. PRIMO enables the use of all available training examples, whether modalities are complete or partial. Specifically, it models the missing modality through a latent variable that captures its relationship with the observed modality in the context of prediction. During inference, we draw many samples from the learned distribution over the missing modality to both obtain the marginal predictive distribution (for the purpose of prediction) and analyze the impact of the missing modalities on the prediction for each instance. We evaluate PRIMO on a synthetic XOR dataset, Audio-Vision MNIST, and MIMIC-III for mortality and ICD-9 prediction. Across all datasets, PRIMO obtains performance comparable to unimodal baselines when a modality is fully missing and to multimodal baselines when all modalities are available. PRIMO quantifies the predictive impact of a modality at the instance level using a variance-based metric computed from predictions across latent completions. We visually demonstrate how varying completions of the missing modality result in a set of plausible labels.
Paradox of De-identification: A Critique of HIPAA Safe Harbour in the Age of LLMs
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Privacy is a human right that sustains patient-provider trust. Clinical notes capture a patient's private vulnerability and individuality, which are used for care coordination and research. Under HIPAA Safe Harbor, these notes are de-identified to protect patient privacy. However, Safe Harbor was designed for an era of categorical tabular data, focusing on the removal of explicit identifiers while ignoring the latent information found in correlations between identity and quasi-identifiers, which can be captured by modern LLMs. We first formalize these correlations using a causal graph, then validate it empirically through individual re-identification of patients from scrubbed notes. The paradox of de-identification is further shown through a diagnosis ablation: even when all other information is removed, the model can predict the patient's neighborhood based on diagnosis alone. This position paper raises the question of how we can act as a community to uphold patient-provider trust when de-identification is inherently imperfect. We aim to raise awareness and discuss actionable recommendations.
Group Contrastive Learning for Weakly Paired Multimodal Data
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:We present GROOVE, a semi-supervised multi-modal representation learning approach for high-content perturbation data where samples across modalities are weakly paired through shared perturbation labels but lack direct correspondence. Our primary contribution is GroupCLIP, a novel group-level contrastive loss that bridges the gap between CLIP for paired cross-modal data and SupCon for uni-modal supervised contrastive learning, addressing a fundamental gap in contrastive learning for weakly-paired settings. We integrate GroupCLIP with an on-the-fly backtranslating autoencoder framework to encourage cross-modally entangled representations while maintaining group-level coherence within a shared latent space. Critically, we introduce a comprehensive combinatorial evaluation framework that systematically assesses representation learners across multiple optimal transport aligners, addressing key limitations in existing evaluation strategies. This framework includes novel simulations that systematically vary shared versus modality-specific perturbation effects enabling principled assessment of method robustness. Our combinatorial benchmarking reveals that there is not yet an aligner that uniformly dominates across settings or modality pairs. Across simulations and two real single-cell genetic perturbation datasets, GROOVE performs on par with or outperforms existing approaches for downstream cross-modal matching and imputation tasks. Our ablation studies demonstrate that GroupCLIP is the key component driving performance gains. These results highlight the importance of leveraging group-level constraints for effective multi-modal representation learning in scenarios where only weak pairing is available.
TwinWeaver: An LLM-Based Foundation Model Framework for Pan-Cancer Digital Twins
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Precision oncology requires forecasting clinical events and trajectories, yet modeling sparse, multi-modal clinical time series remains a critical challenge. We introduce TwinWeaver, an open-source framework that serializes longitudinal patient histories into text, enabling unified event prediction as well as forecasting with large language models, and use it to build Genie Digital Twin (GDT) on 93,054 patients across 20 cancer types. In benchmarks, GDT significantly reduces forecasting error, achieving a median Mean Absolute Scaled Error (MASE) of 0.87 compared to 0.97 for the strongest time-series baseline (p<0.001). Furthermore, GDT improves risk stratification, achieving an average concordance index (C-index) of 0.703 across survival, progression, and therapy switching tasks, surpassing the best baseline of 0.662. GDT also generalizes to out-of-distribution clinical trials, matching trained baselines at zero-shot and surpassing them with fine-tuning, achieving a median MASE of 0.75-0.88 and outperforming the strongest baseline in event prediction with an average C-index of 0.672 versus 0.648. Finally, TwinWeaver enables an interpretable clinical reasoning extension, providing a scalable and transparent foundation for longitudinal clinical modeling.
Neural Neural Scaling Laws
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Neural scaling laws predict how language model performance improves with increased compute. While aggregate metrics like validation loss can follow smooth power-law curves, individual downstream tasks exhibit diverse scaling behaviors: some improve monotonically, others plateau, and some even degrade with scale. We argue that predicting downstream performance from validation perplexity suffers from two limitations: averaging token-level losses obscures signal, and no simple parametric family can capture the full spectrum of scaling behaviors. To address this, we propose Neural Neural Scaling Laws (NeuNeu), a neural network that frames scaling law prediction as time-series extrapolation. NeuNeu combines temporal context from observed accuracy trajectories with token-level validation losses, learning to predict future performance without assuming any bottleneck or functional form. Trained entirely on open-source model checkpoints from HuggingFace, NeuNeu achieves 2.04% mean absolute error in predicting model accuracy on 66 downstream tasks -- a 38% reduction compared to logistic scaling laws (3.29% MAE). Furthermore, NeuNeu generalizes zero-shot to unseen model families, parameter counts, and downstream tasks. Our work suggests that predicting downstream scaling laws directly from data outperforms parametric alternatives.
Solar Open Technical Report
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:We introduce Solar Open, a 102B-parameter bilingual Mixture-of-Experts language model for underserved languages. Solar Open demonstrates a systematic methodology for building competitive LLMs by addressing three interconnected challenges. First, to train effectively despite data scarcity for underserved languages, we synthesize 4.5T tokens of high-quality, domain-specific, and RL-oriented data. Second, we coordinate this data through a progressive curriculum jointly optimizing composition, quality thresholds, and domain coverage across 20 trillion tokens. Third, to enable reasoning capabilities through scalable RL, we apply our proposed framework SnapPO for efficient optimization. Across benchmarks in English and Korean, Solar Open achieves competitive performance, demonstrating the effectiveness of this methodology for underserved language AI development.
Walrus: A Cross-Domain Foundation Model for Continuum Dynamics
Nov 19, 2025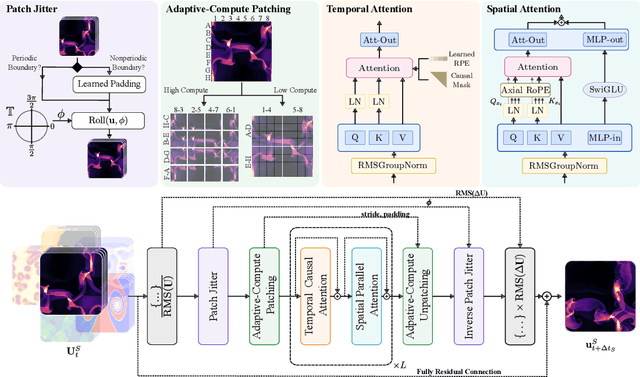


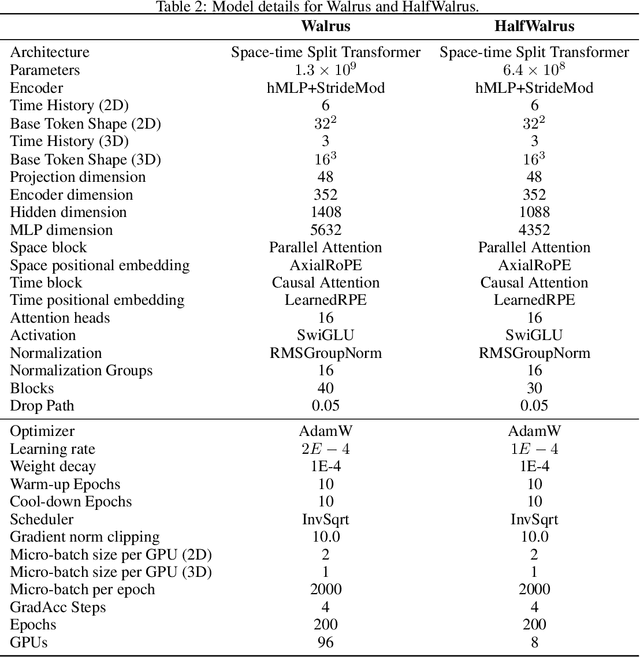
Abstract:Foundation models have transformed machine learning for language and vision, but achieving comparable impact in physical simulation remains a challenge. Data heterogeneity and unstable long-term dynamics inhibit learning from sufficiently diverse dynamics, while varying resolutions and dimensionalities challenge efficient training on modern hardware. Through empirical and theoretical analysis, we incorporate new approaches to mitigate these obstacles, including a harmonic-analysis-based stabilization method, load-balanced distributed 2D and 3D training strategies, and compute-adaptive tokenization. Using these tools, we develop Walrus, a transformer-based foundation model developed primarily for fluid-like continuum dynamics. Walrus is pretrained on nineteen diverse scenarios spanning astrophysics, geoscience, rheology, plasma physics, acoustics, and classical fluids. Experiments show that Walrus outperforms prior foundation models on both short and long term prediction horizons on downstream tasks and across the breadth of pretraining data, while ablation studies confirm the value of our contributions to forecast stability, training throughput, and transfer performance over conventional approaches. Code and weights are released for community use.
Generalist Foundation Models Are Not Clinical Enough for Hospital Operations
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Hospitals and healthcare systems rely on operational decisions that determine patient flow, cost, and quality of care. Despite strong performance on medical knowledge and conversational benchmarks, foundation models trained on general text may lack the specialized knowledge required for these operational decisions. We introduce Lang1, a family of models (100M-7B parameters) pretrained on a specialized corpus blending 80B clinical tokens from NYU Langone Health's EHRs and 627B tokens from the internet. To rigorously evaluate Lang1 in real-world settings, we developed the REalistic Medical Evaluation (ReMedE), a benchmark derived from 668,331 EHR notes that evaluates five critical tasks: 30-day readmission prediction, 30-day mortality prediction, length of stay, comorbidity coding, and predicting insurance claims denial. In zero-shot settings, both general-purpose and specialized models underperform on four of five tasks (36.6%-71.7% AUROC), with mortality prediction being an exception. After finetuning, Lang1-1B outperforms finetuned generalist models up to 70x larger and zero-shot models up to 671x larger, improving AUROC by 3.64%-6.75% and 1.66%-23.66% respectively. We also observed cross-task scaling with joint finetuning on multiple tasks leading to improvement on other tasks. Lang1-1B effectively transfers to out-of-distribution settings, including other clinical tasks and an external health system. Our findings suggest that predictive capabilities for hospital operations require explicit supervised finetuning, and that this finetuning process is made more efficient by in-domain pretraining on EHR. Our findings support the emerging view that specialized LLMs can compete with generalist models in specialized tasks, and show that effective healthcare systems AI requires the combination of in-domain pretraining, supervised finetuning, and real-world evaluation beyond proxy benchmarks.
How to Find Fantastic Papers: Self-Rankings as a Powerful Predictor of Scientific Impact Beyond Peer Review
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Peer review in academic research aims not only to ensure factual correctness but also to identify work of high scientific potential that can shape future research directions. This task is especially critical in fast-moving fields such as artificial intelligence (AI), yet it has become increasingly difficult given the rapid growth of submissions. In this paper, we investigate an underexplored measure for identifying high-impact research: authors' own rankings of their multiple submissions to the same AI conference. Grounded in game-theoretic reasoning, we hypothesize that self-rankings are informative because authors possess unique understanding of their work's conceptual depth and long-term promise. To test this hypothesis, we conducted a large-scale experiment at a leading AI conference, where 1,342 researchers self-ranked their 2,592 submissions by perceived quality. Tracking outcomes over more than a year, we found that papers ranked highest by their authors received twice as many citations as their lowest-ranked counterparts; self-rankings were especially effective at identifying highly cited papers (those with over 150 citations). Moreover, we showed that self-rankings outperformed peer review scores in predicting future citation counts. Our results remained robust after accounting for confounders such as preprint posting time and self-citations. Together, these findings demonstrate that authors' self-rankings provide a reliable and valuable complement to peer review for identifying and elevating high-impact research in AI.
Scaling Laws Are Unreliable for Downstream Tasks: A Reality Check
Jul 01, 2025Abstract:Downstream scaling laws aim to predict task performance at larger scales from pretraining losses at smaller scales. Whether this prediction should be possible is unclear: some works demonstrate that task performance follows clear linear scaling trends under transformation, whereas others point out fundamental challenges to downstream scaling laws, such as emergence and inverse scaling. In this work, we conduct a meta-analysis of existing data on downstream scaling laws, finding that close fit to linear scaling laws only occurs in a minority of cases: 39% of the time. Furthermore, seemingly benign changes to the experimental setting can completely change the scaling trend. Our analysis underscores the need to understand the conditions under which scaling laws succeed. To fully model the relationship between pretraining loss and downstream task performance, we must embrace the cases in which scaling behavior deviates from linear trends.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge