Heather Lent
Limited-Resource Adapters Are Regularizers, Not Linguists
May 30, 2025Abstract:Cross-lingual transfer from related high-resource languages is a well-established strategy to enhance low-resource language technologies. Prior work has shown that adapters show promise for, e.g., improving low-resource machine translation (MT). In this work, we investigate an adapter souping method combined with cross-attention fine-tuning of a pre-trained MT model to leverage language transfer for three low-resource Creole languages, which exhibit relatedness to different language groups across distinct linguistic dimensions. Our approach improves performance substantially over baselines. However, we find that linguistic relatedness -- or even a lack thereof -- does not covary meaningfully with adapter performance. Surprisingly, our cross-attention fine-tuning approach appears equally effective with randomly initialized adapters, implying that the benefit of adapters in this setting lies in parameter regularization, and not in meaningful information transfer. We provide analysis supporting this regularization hypothesis. Our findings underscore the reality that neural language processing involves many success factors, and that not all neural methods leverage linguistic knowledge in intuitive ways.
NLP Security and Ethics, in the Wild
Apr 09, 2025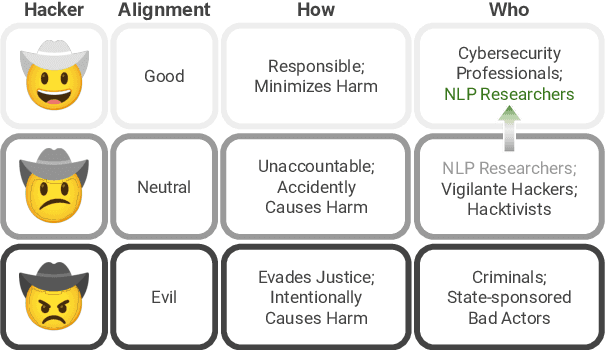
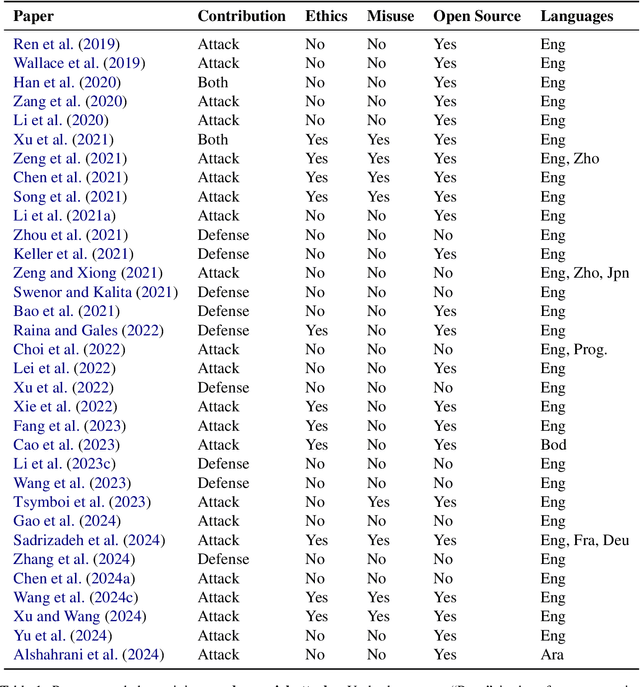
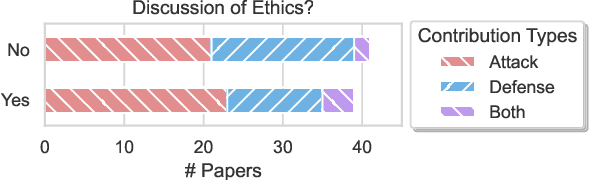
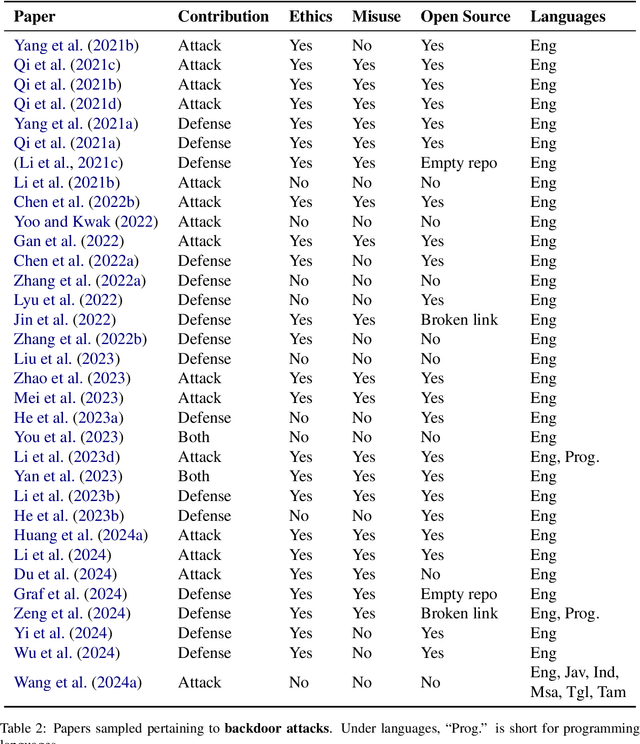
Abstract:As NLP models are used by a growing number of end-users, an area of increasing importance is NLP Security (NLPSec): assessing the vulnerability of models to malicious attacks and developing comprehensive countermeasures against them. While work at the intersection of NLP and cybersecurity has the potential to create safer NLP for all, accidental oversights can result in tangible harm (e.g., breaches of privacy or proliferation of malicious models). In this emerging field, however, the research ethics of NLP have not yet faced many of the long-standing conundrums pertinent to cybersecurity, until now. We thus examine contemporary works across NLPSec, and explore their engagement with cybersecurity's ethical norms. We identify trends across the literature, ultimately finding alarming gaps on topics like harm minimization and responsible disclosure. To alleviate these concerns, we provide concrete recommendations to help NLP researchers navigate this space more ethically, bridging the gap between traditional cybersecurity and NLP ethics, which we frame as ``white hat NLP''. The goal of this work is to help cultivate an intentional culture of ethical research for those working in NLP Security.
How Good is Your Wikipedia?
Nov 08, 2024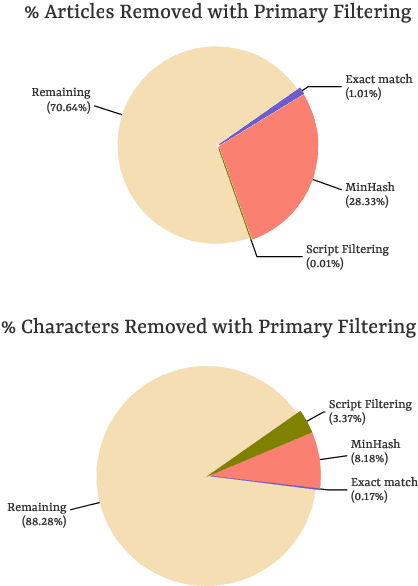
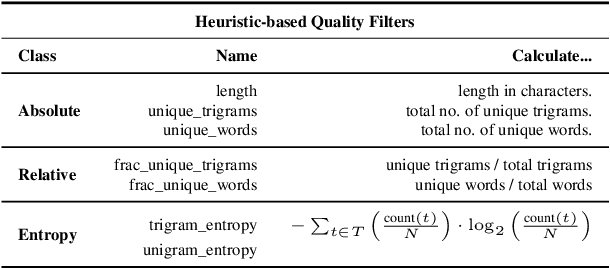
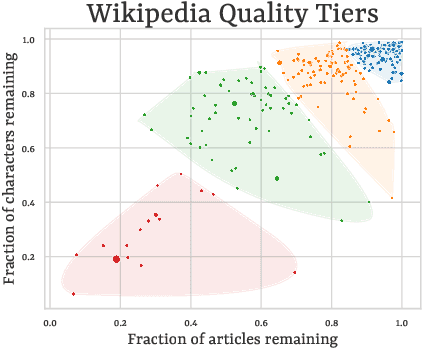
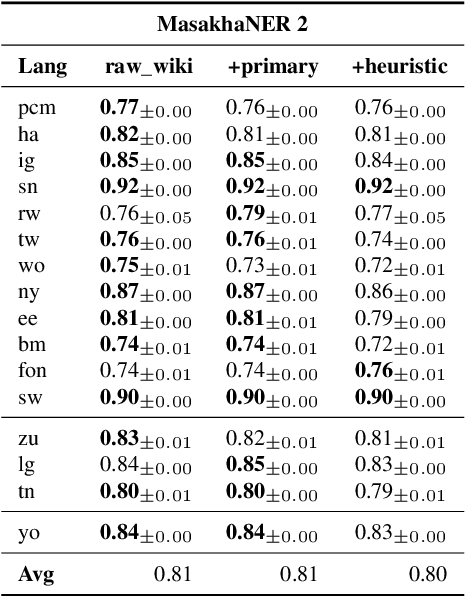
Abstract:Wikipedia's perceived high quality and broad language coverage have established it as a fundamental resource in multilingual NLP. In the context of low-resource languages, however, these quality assumptions are increasingly being scrutinised. This paper critically examines the data quality of Wikipedia in a non-English setting by subjecting it to various quality filtering techniques, revealing widespread issues such as a high percentage of one-line articles and duplicate articles. We evaluate the downstream impact of quality filtering on Wikipedia and find that data quality pruning is an effective means for resource-efficient training without hurting performance, especially for low-resource languages. Moreover, we advocate for a shift in perspective from seeking a general definition of data quality towards a more language- and task-specific one. Ultimately, we aim for this study to serve as a guide to using Wikipedia for pretraining in a multilingual setting.
Against All Odds: Overcoming Typology, Script, and Language Confusion in Multilingual Embedding Inversion Attacks
Aug 21, 2024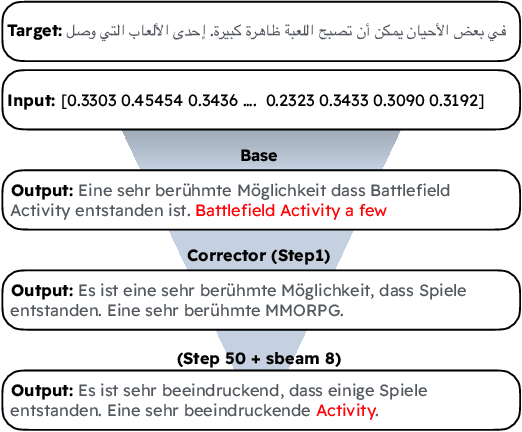
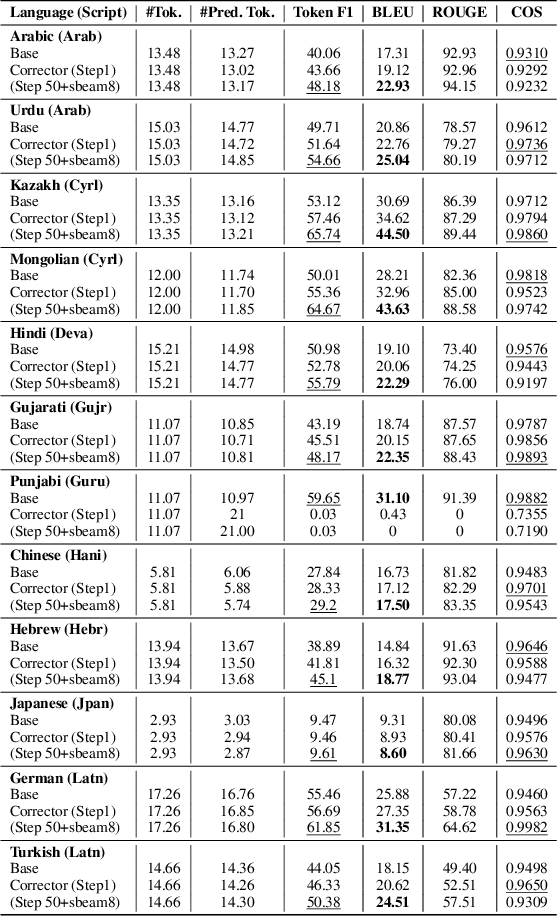

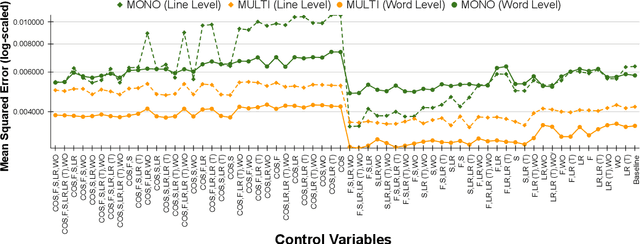
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are susceptible to malicious influence by cyber attackers through intrusions such as adversarial, backdoor, and embedding inversion attacks. In response, the burgeoning field of LLM Security aims to study and defend against such threats. Thus far, the majority of works in this area have focused on monolingual English models, however, emerging research suggests that multilingual LLMs may be more vulnerable to various attacks than their monolingual counterparts. While previous work has investigated embedding inversion over a small subset of European languages, it is challenging to extrapolate these findings to languages from different linguistic families and with differing scripts. To this end, we explore the security of multilingual LLMs in the context of embedding inversion attacks and investigate cross-lingual and cross-script inversion across 20 languages, spanning over 8 language families and 12 scripts. Our findings indicate that languages written in Arabic script and Cyrillic script are particularly vulnerable to embedding inversion, as are languages within the Indo-Aryan language family. We further observe that inversion models tend to suffer from language confusion, sometimes greatly reducing the efficacy of an attack. Accordingly, we systematically explore this bottleneck for inversion models, uncovering predictable patterns which could be leveraged by attackers. Ultimately, this study aims to further the field's understanding of the outstanding security vulnerabilities facing multilingual LLMs and raise awareness for the languages most at risk of negative impact from these attacks.
Sociolinguistically Informed Interpretability: A Case Study on Hinglish Emotion Classification
Feb 05, 2024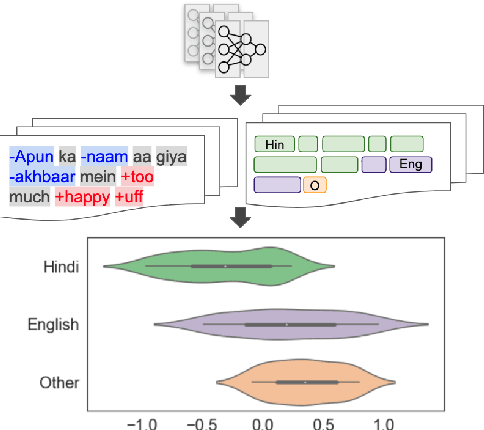
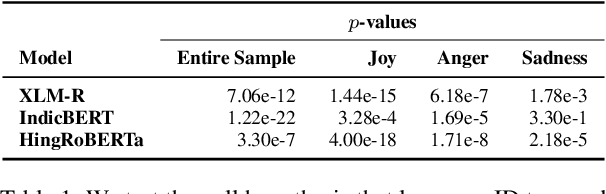
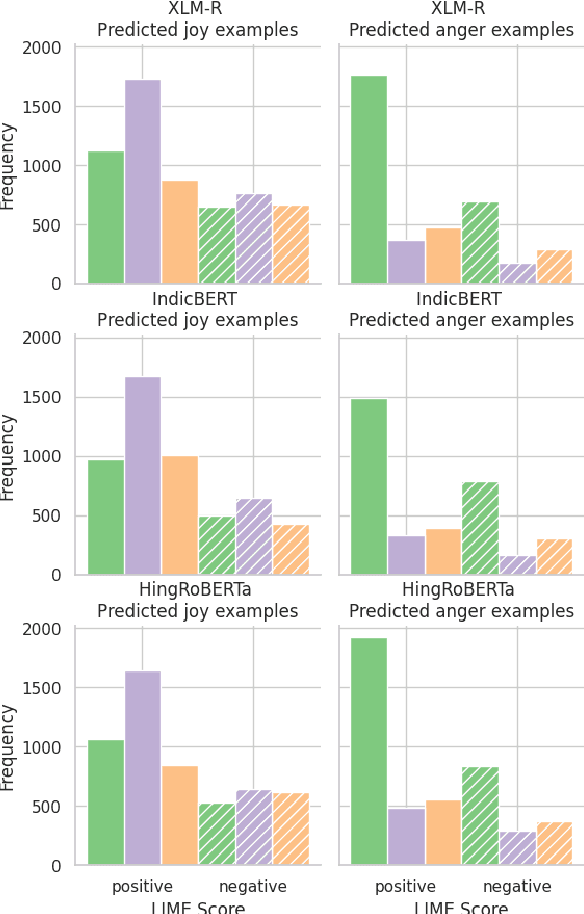

Abstract:Emotion classification is a challenging task in NLP due to the inherent idiosyncratic and subjective nature of linguistic expression, especially with code-mixed data. Pre-trained language models (PLMs) have achieved high performance for many tasks and languages, but it remains to be seen whether these models learn and are robust to the differences in emotional expression across languages. Sociolinguistic studies have shown that Hinglish speakers switch to Hindi when expressing negative emotions and to English when expressing positive emotions. To understand if language models can learn these associations, we study the effect of language on emotion prediction across 3 PLMs on a Hinglish emotion classification dataset. Using LIME and token level language ID, we find that models do learn these associations between language choice and emotional expression. Moreover, having code-mixed data present in the pre-training can augment that learning when task-specific data is scarce. We also conclude from the misclassifications that the models may overgeneralise this heuristic to other infrequent examples where this sociolinguistic phenomenon does not apply.
Text Embedding Inversion Attacks on Multilingual Language Models
Jan 22, 2024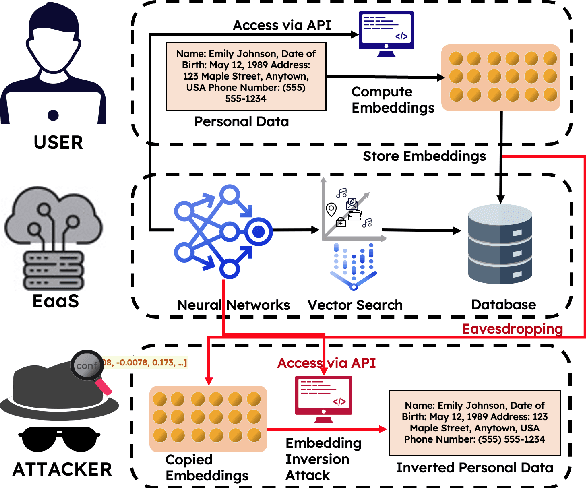
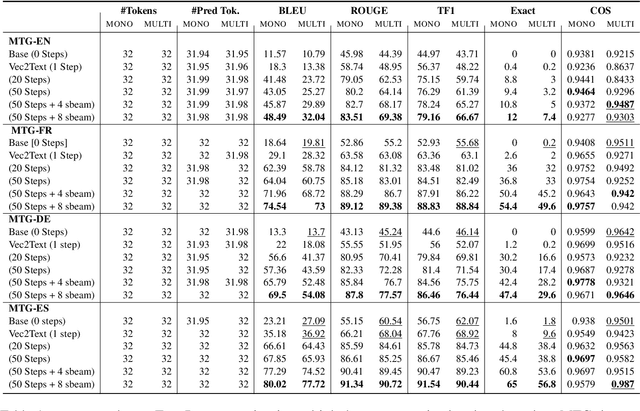
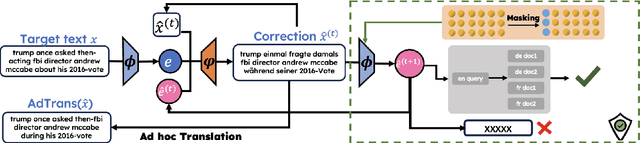
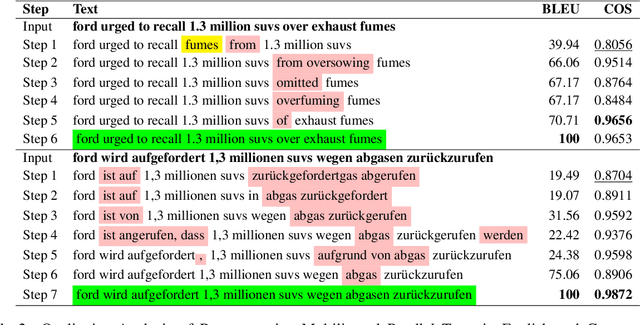
Abstract:Representing textual information as real-numbered embeddings has become the norm in NLP. Moreover, with the rise of public interest in large language models (LLMs), Embeddings as a Service (EaaS) has rapidly gained traction as a business model. This is not without outstanding security risks, as previous research has demonstrated that sensitive data can be reconstructed from embeddings, even without knowledge of the underlying model that generated them. However, such work is limited by its sole focus on English, leaving all other languages vulnerable to attacks by malicious actors. %As many international and multilingual companies leverage EaaS, there is an urgent need for research into multilingual LLM security. To this end, this work investigates LLM security from the perspective of multilingual embedding inversion. Concretely, we define the problem of black-box multilingual and cross-lingual inversion attacks, with special attention to a cross-domain scenario. Our findings reveal that multilingual models are potentially more vulnerable to inversion attacks than their monolingual counterparts. This stems from the reduced data requirements for achieving comparable inversion performance in settings where the underlying language is not known a-priori. To our knowledge, this work is the first to delve into multilinguality within the context of inversion attacks, and our findings highlight the need for further investigation and enhanced defenses in the area of NLP Security.
CreoleVal: Multilingual Multitask Benchmarks for Creoles
Oct 30, 2023Abstract:Creoles represent an under-explored and marginalized group of languages, with few available resources for NLP research. While the genealogical ties between Creoles and other highly-resourced languages imply a significant potential for transfer learning, this potential is hampered due to this lack of annotated data. In this work we present CreoleVal, a collection of benchmark datasets spanning 8 different NLP tasks, covering up to 28 Creole languages; it is an aggregate of brand new development datasets for machine comprehension, relation classification, and machine translation for Creoles, in addition to a practical gateway to a handful of preexisting benchmarks. For each benchmark, we conduct baseline experiments in a zero-shot setting in order to further ascertain the capabilities and limitations of transfer learning for Creoles. Ultimately, the goal of CreoleVal is to empower research on Creoles in NLP and computational linguistics. We hope this resource will contribute to technological inclusion for Creole language users around the globe.
Ancestor-to-Creole Transfer is Not a Walk in the Park
Jun 09, 2022
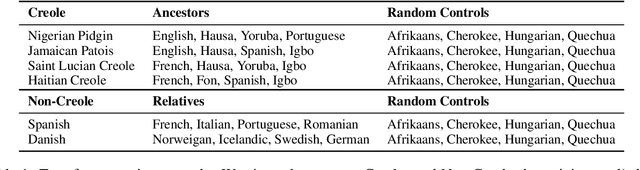
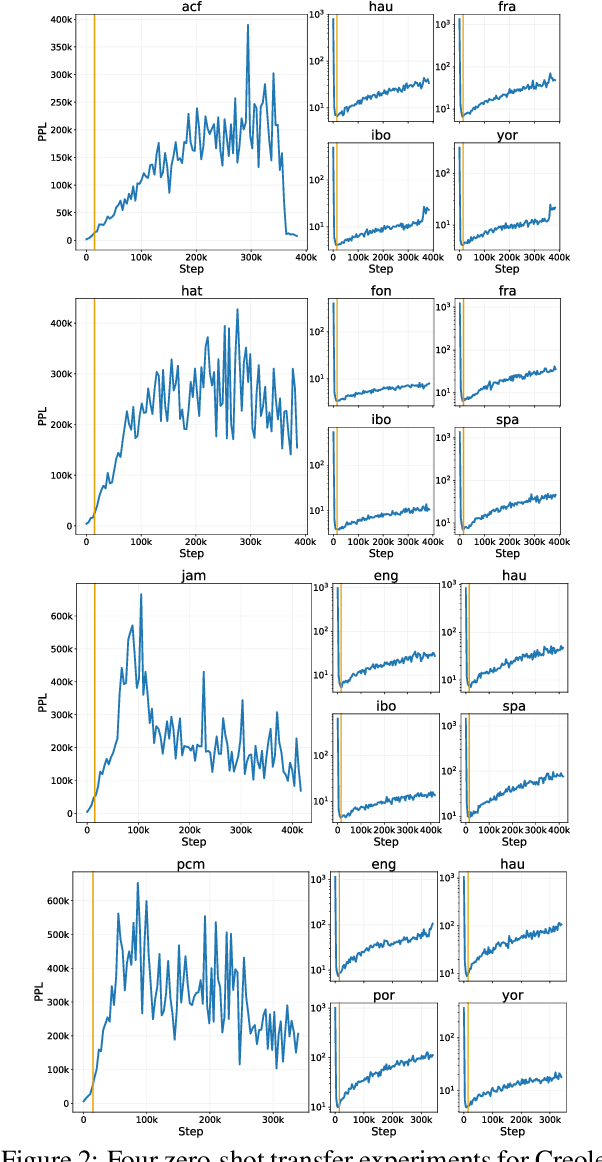
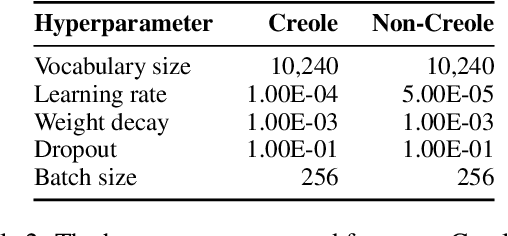
Abstract:We aim to learn language models for Creole languages for which large volumes of data are not readily available, and therefore explore the potential transfer from ancestor languages (the 'Ancestry Transfer Hypothesis'). We find that standard transfer methods do not facilitate ancestry transfer. Surprisingly, different from other non-Creole languages, a very distinct two-phase pattern emerges for Creoles: As our training losses plateau, and language models begin to overfit on their source languages, perplexity on the Creoles drop. We explore if this compression phase can lead to practically useful language models (the 'Ancestry Bottleneck Hypothesis'), but also falsify this. Moreover, we show that Creoles even exhibit this two-phase pattern even when training on random, unrelated languages. Thus Creoles seem to be typological outliers and we speculate whether there is a link between the two observations.
What a Creole Wants, What a Creole Needs
Jun 01, 2022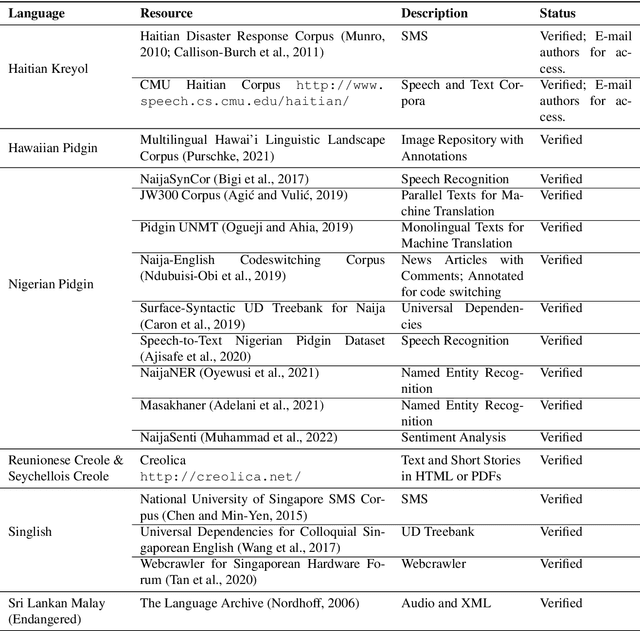
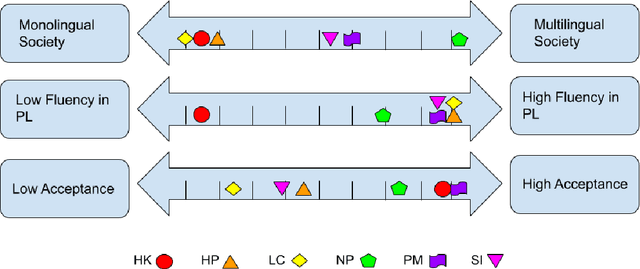
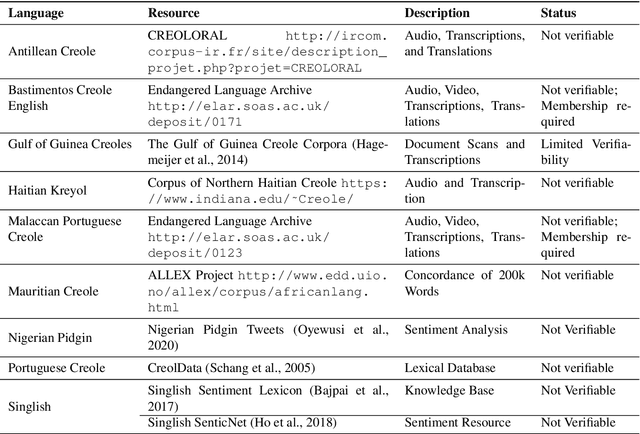
Abstract:In recent years, the natural language processing (NLP) community has given increased attention to the disparity of efforts directed towards high-resource languages over low-resource ones. Efforts to remedy this delta often begin with translations of existing English datasets into other languages. However, this approach ignores that different language communities have different needs. We consider a group of low-resource languages, Creole languages. Creoles are both largely absent from the NLP literature, and also often ignored by society at large due to stigma, despite these languages having sizable and vibrant communities. We demonstrate, through conversations with Creole experts and surveys of Creole-speaking communities, how the things needed from language technology can change dramatically from one language to another, even when the languages are considered to be very similar to each other, as with Creoles. We discuss the prominent themes arising from these conversations, and ultimately demonstrate that useful language technology cannot be built without involving the relevant community.
Challenges and Strategies in Cross-Cultural NLP
Mar 18, 2022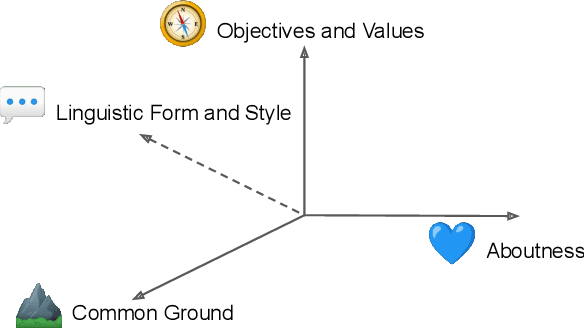
Abstract:Various efforts in the Natural Language Processing (NLP) community have been made to accommodate linguistic diversity and serve speakers of many different languages. However, it is important to acknowledge that speakers and the content they produce and require, vary not just by language, but also by culture. Although language and culture are tightly linked, there are important differences. Analogous to cross-lingual and multilingual NLP, cross-cultural and multicultural NLP considers these differences in order to better serve users of NLP systems. We propose a principled framework to frame these efforts, and survey existing and potential strategies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge