Johannes Bjerva
Characterizing Memorization in Diffusion Language Models: Generalized Extraction and Sampling Effects
Mar 02, 2026Abstract:Autoregressive language models (ARMs) have been shown to memorize and occasionally reproduce training data verbatim, raising concerns about privacy and copyright liability. Diffusion language models (DLMs) have recently emerged as a competitive alternative, yet their memorization behavior remains largely unexplored due to fundamental differences in generation dynamics. To address this gap, we present a systematic theoretical and empirical characterization of memorization in DLMs. We propose a generalized probabilistic extraction framework that unifies prefix-conditioned decoding and diffusion-based generation under arbitrary masking patterns and stochastic sampling trajectories. Theorem 4.3 establishes a monotonic relationship between sampling resolution and memorization: increasing resolution strictly increases the probability of exact training data extraction, implying that autoregressive decoding corresponds to a limiting case of diffusion-based generation by setting the sampling resolution maximal. Extensive experiments across model scales and sampling strategies validate our theoretical predictions. Under aligned prefix-conditioned evaluations, we further demonstrate that DLMs exhibit substantially lower memorization-based leakage of personally identifiable information (PII) compared to ARMs.
Semantic Leakage from Image Embeddings
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Image embeddings are generally assumed to pose limited privacy risk. We challenge this assumption by formalizing semantic leakage as the ability to recover semantic structures from compressed image embeddings. Surprisingly, we show that semantic leakage does not require exact reconstruction of the original image. Preserving local semantic neighborhoods under embedding alignment is sufficient to expose the intrinsic vulnerability of image embeddings. Crucially, this preserved neighborhood structure allows semantic information to propagate through a sequence of lossy mappings. Based on this conjecture, we propose Semantic Leakage from Image Embeddings (SLImE), a lightweight inference framework that reveals semantic information from standalone compressed image embeddings, incorporating a locally trained semantic retriever with off-the-shelf models, without training task-specific decoders. We thoroughly validate each step of the framework empirically, from aligned embeddings to retrieved tags, symbolic representations, and grammatical and coherent descriptions. We evaluate SLImE across a range of open and closed embedding models, including GEMINI, COHERE, NOMIC, and CLIP, and demonstrate consistent recovery of semantic information across diverse inference tasks. Our results reveal a fundamental vulnerability in image embeddings, whereby the preservation of semantic neighborhoods under alignment enables semantic leakage, highlighting challenges for privacy preservation.1
Do LLMs Really Memorize Personally Identifiable Information? Revisiting PII Leakage with a Cue-Controlled Memorization Framework
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have been reported to "leak" Personally Identifiable Information (PII), with successful PII reconstruction often interpreted as evidence of memorization. We propose a principled revision of memorization evaluation for LLMs, arguing that PII leakage should be evaluated under low lexical cue conditions, where target PII cannot be reconstructed through prompt-induced generalization or pattern completion. We formalize Cue-Resistant Memorization (CRM) as a cue-controlled evaluation framework and a necessary condition for valid memorization evaluation, explicitly conditioning on prompt-target overlap cues. Using CRM, we conduct a large-scale multilingual re-evaluation of PII leakage across 32 languages and multiple memorization paradigms. Revisiting reconstruction-based settings, including verbatim prefix-suffix completion and associative reconstruction, we find that their apparent effectiveness is driven primarily by direct surface-form cues rather than by true memorization. When such cues are controlled for, reconstruction success diminishes substantially. We further examine cue-free generation and membership inference, both of which exhibit extremely low true positive rates. Overall, our results suggest that previously reported PII leakage is better explained by cue-driven behavior than by genuine memorization, highlighting the importance of cue-controlled evaluation for reliably quantifying privacy-relevant memorization in LLMs.
Limited-Resource Adapters Are Regularizers, Not Linguists
May 30, 2025Abstract:Cross-lingual transfer from related high-resource languages is a well-established strategy to enhance low-resource language technologies. Prior work has shown that adapters show promise for, e.g., improving low-resource machine translation (MT). In this work, we investigate an adapter souping method combined with cross-attention fine-tuning of a pre-trained MT model to leverage language transfer for three low-resource Creole languages, which exhibit relatedness to different language groups across distinct linguistic dimensions. Our approach improves performance substantially over baselines. However, we find that linguistic relatedness -- or even a lack thereof -- does not covary meaningfully with adapter performance. Surprisingly, our cross-attention fine-tuning approach appears equally effective with randomly initialized adapters, implying that the benefit of adapters in this setting lies in parameter regularization, and not in meaningful information transfer. We provide analysis supporting this regularization hypothesis. Our findings underscore the reality that neural language processing involves many success factors, and that not all neural methods leverage linguistic knowledge in intuitive ways.
Shared Path: Unraveling Memorization in Multilingual LLMs through Language Similarities
May 21, 2025Abstract:We present the first comprehensive study of Memorization in Multilingual Large Language Models (MLLMs), analyzing 95 languages using models across diverse model scales, architectures, and memorization definitions. As MLLMs are increasingly deployed, understanding their memorization behavior has become critical. Yet prior work has focused primarily on monolingual models, leaving multilingual memorization underexplored, despite the inherently long-tailed nature of training corpora. We find that the prevailing assumption, that memorization is highly correlated with training data availability, fails to fully explain memorization patterns in MLLMs. We hypothesize that treating languages in isolation - ignoring their similarities - obscures the true patterns of memorization. To address this, we propose a novel graph-based correlation metric that incorporates language similarity to analyze cross-lingual memorization. Our analysis reveals that among similar languages, those with fewer training tokens tend to exhibit higher memorization, a trend that only emerges when cross-lingual relationships are explicitly modeled. These findings underscore the importance of a language-aware perspective in evaluating and mitigating memorization vulnerabilities in MLLMs. This also constitutes empirical evidence that language similarity both explains Memorization in MLLMs and underpins Cross-lingual Transferability, with broad implications for multilingual NLP.
LAGO: Few-shot Crosslingual Embedding Inversion Attacks via Language Similarity-Aware Graph Optimization
May 21, 2025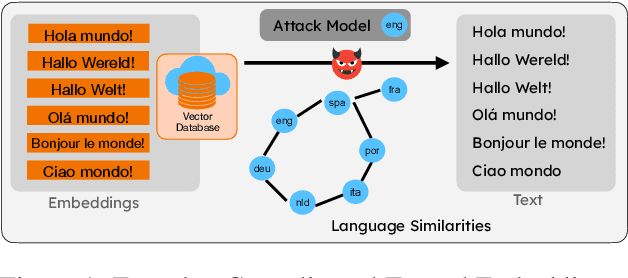
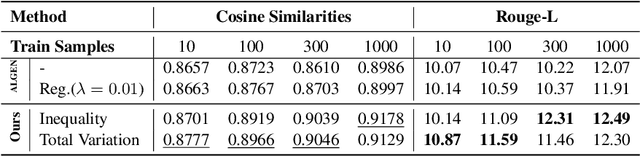
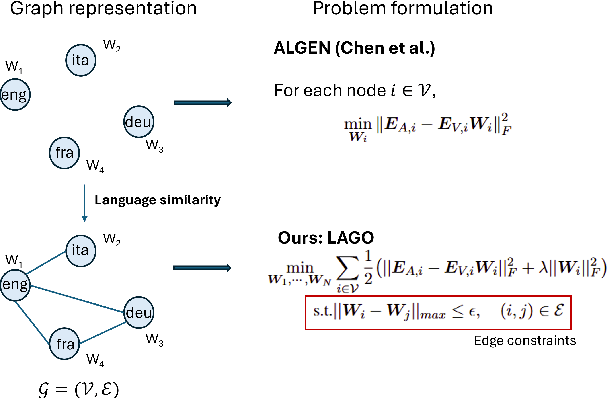
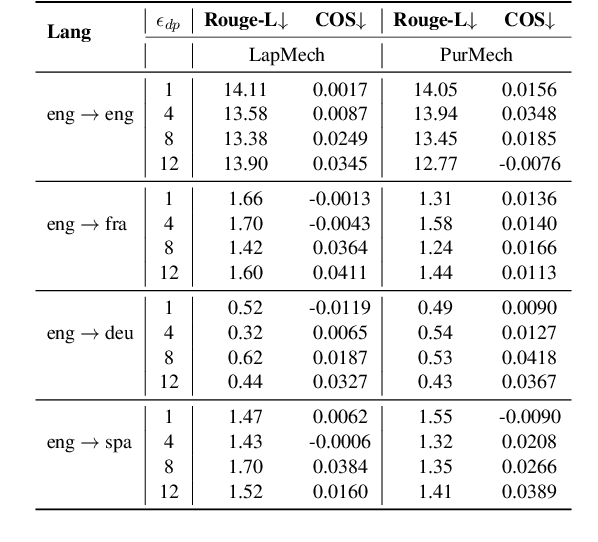
Abstract:We propose LAGO - Language Similarity-Aware Graph Optimization - a novel approach for few-shot cross-lingual embedding inversion attacks, addressing critical privacy vulnerabilities in multilingual NLP systems. Unlike prior work in embedding inversion attacks that treat languages independently, LAGO explicitly models linguistic relationships through a graph-based constrained distributed optimization framework. By integrating syntactic and lexical similarity as edge constraints, our method enables collaborative parameter learning across related languages. Theoretically, we show this formulation generalizes prior approaches, such as ALGEN, which emerges as a special case when similarity constraints are relaxed. Our framework uniquely combines Frobenius-norm regularization with linear inequality or total variation constraints, ensuring robust alignment of cross-lingual embedding spaces even with extremely limited data (as few as 10 samples per language). Extensive experiments across multiple languages and embedding models demonstrate that LAGO substantially improves the transferability of attacks with 10-20% increase in Rouge-L score over baselines. This work establishes language similarity as a critical factor in inversion attack transferability, urging renewed focus on language-aware privacy-preserving multilingual embeddings.
MultiHal: Multilingual Dataset for Knowledge-Graph Grounded Evaluation of LLM Hallucinations
May 20, 2025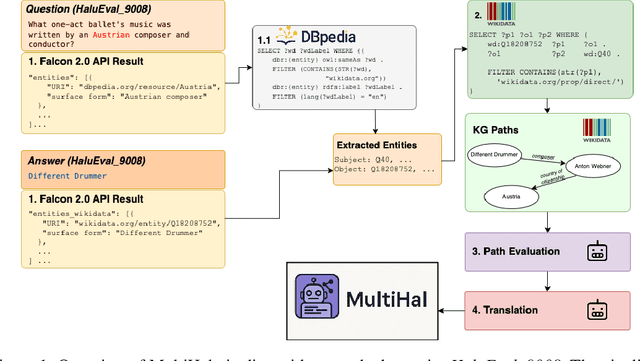
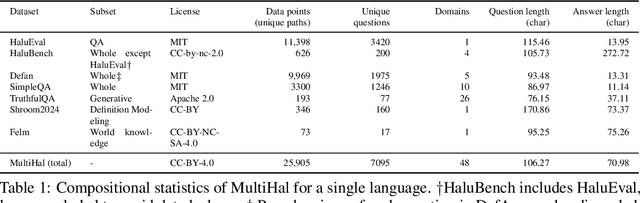
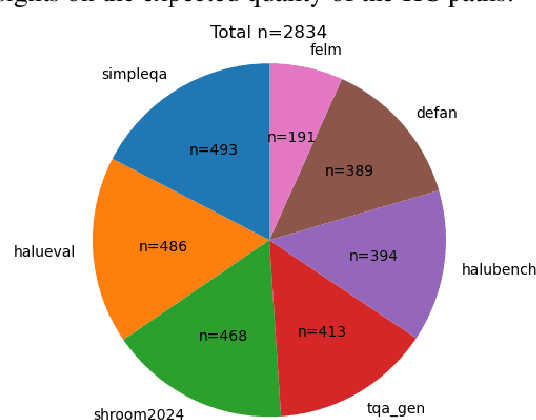
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have inherent limitations of faithfulness and factuality, commonly referred to as hallucinations. Several benchmarks have been developed that provide a test bed for factuality evaluation within the context of English-centric datasets, while relying on supplementary informative context like web links or text passages but ignoring the available structured factual resources. To this end, Knowledge Graphs (KGs) have been identified as a useful aid for hallucination mitigation, as they provide a structured way to represent the facts about entities and their relations with minimal linguistic overhead. We bridge the lack of KG paths and multilinguality for factual language modeling within the existing hallucination evaluation benchmarks and propose a KG-based multilingual, multihop benchmark called \textbf{MultiHal} framed for generative text evaluation. As part of our data collection pipeline, we mined 140k KG-paths from open-domain KGs, from which we pruned noisy KG-paths, curating a high-quality subset of 25.9k. Our baseline evaluation shows an absolute scale increase by approximately 0.12 to 0.36 points for the semantic similarity score in KG-RAG over vanilla QA across multiple languages and multiple models, demonstrating the potential of KG integration. We anticipate MultiHal will foster future research towards several graph-based hallucination mitigation and fact-checking tasks.
Scaling Reasoning can Improve Factuality in Large Language Models
May 16, 2025Abstract:Recent studies on large language model (LLM) reasoning capabilities have demonstrated promising improvements in model performance by leveraging a lengthy thinking process and additional computational resources during inference, primarily in tasks involving mathematical reasoning (Muennighoff et al., 2025). However, it remains uncertain if longer reasoning chains inherently enhance factual accuracy, particularly beyond mathematical contexts. In this work, we thoroughly examine LLM reasoning within complex open-domain question-answering (QA) scenarios. We initially distill reasoning traces from advanced, large-scale reasoning models (QwQ-32B and DeepSeek-R1-671B), then fine-tune a variety of models ranging from smaller, instruction-tuned variants to larger architectures based on Qwen2.5. To enrich reasoning traces, we introduce factual information from knowledge graphs in the form of paths into our reasoning traces. Our experimental setup includes four baseline approaches and six different instruction-tuned models evaluated across a benchmark of six datasets, encompassing over 22.6K questions. Overall, we carry out 168 experimental runs and analyze approximately 1.7 million reasoning traces. Our findings indicate that, within a single run, smaller reasoning models achieve noticeable improvements in factual accuracy compared to their original instruction-tuned counterparts. Moreover, our analysis demonstrates that adding test-time compute and token budgets factual accuracy consistently improves by 2-8%, further confirming the effectiveness of test-time scaling for enhancing performance and consequently improving reasoning accuracy in open-domain QA tasks. We release all the experimental artifacts for further research.
NLP Security and Ethics, in the Wild
Apr 09, 2025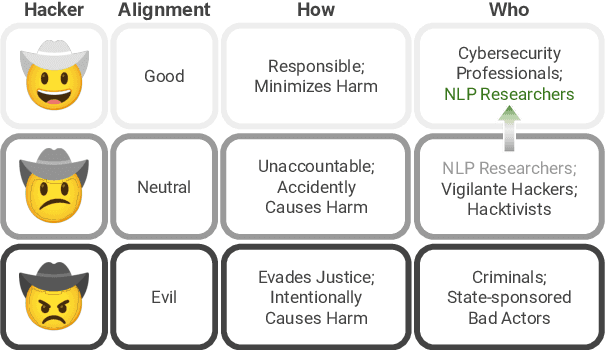
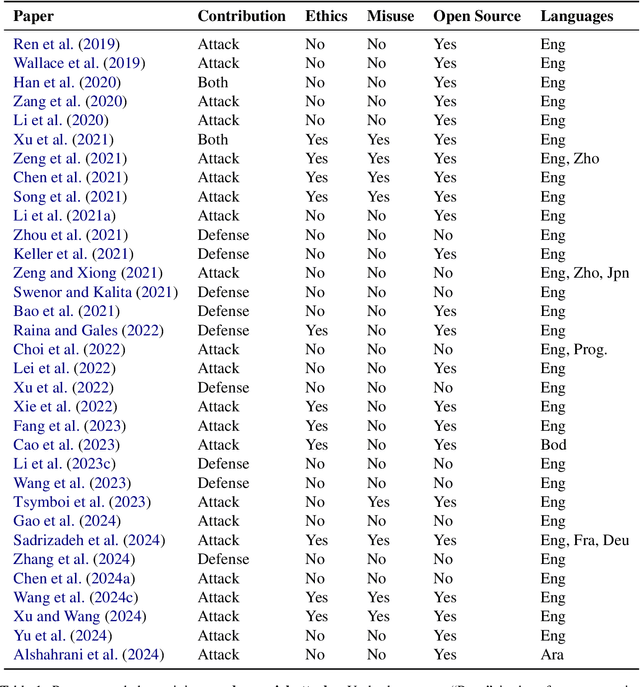
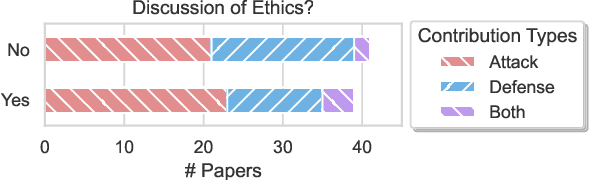
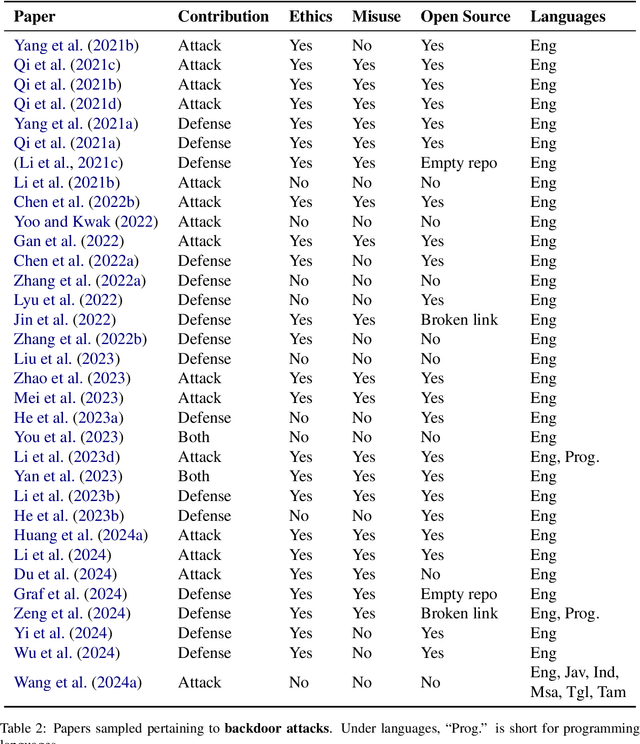
Abstract:As NLP models are used by a growing number of end-users, an area of increasing importance is NLP Security (NLPSec): assessing the vulnerability of models to malicious attacks and developing comprehensive countermeasures against them. While work at the intersection of NLP and cybersecurity has the potential to create safer NLP for all, accidental oversights can result in tangible harm (e.g., breaches of privacy or proliferation of malicious models). In this emerging field, however, the research ethics of NLP have not yet faced many of the long-standing conundrums pertinent to cybersecurity, until now. We thus examine contemporary works across NLPSec, and explore their engagement with cybersecurity's ethical norms. We identify trends across the literature, ultimately finding alarming gaps on topics like harm minimization and responsible disclosure. To alleviate these concerns, we provide concrete recommendations to help NLP researchers navigate this space more ethically, bridging the gap between traditional cybersecurity and NLP ethics, which we frame as ``white hat NLP''. The goal of this work is to help cultivate an intentional culture of ethical research for those working in NLP Security.
Trustworthy Machine Learning via Memorization and the Granular Long-Tail: A Survey on Interactions, Tradeoffs, and Beyond
Mar 10, 2025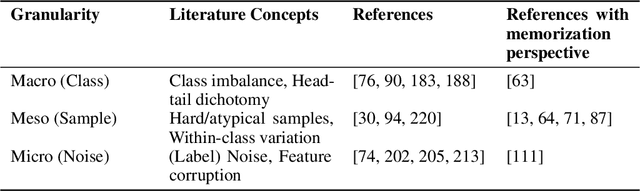

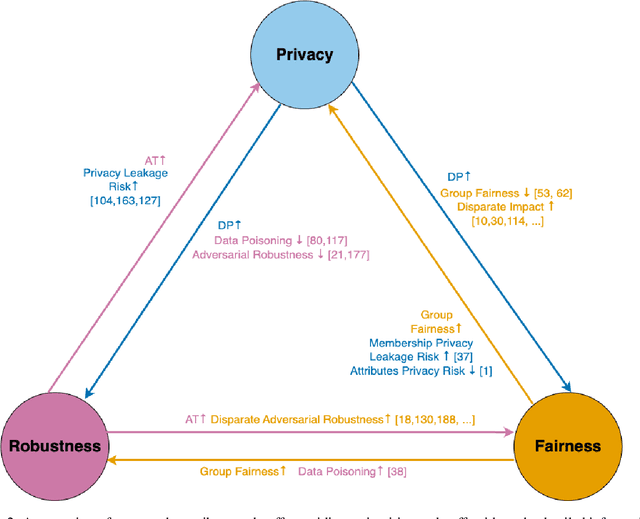
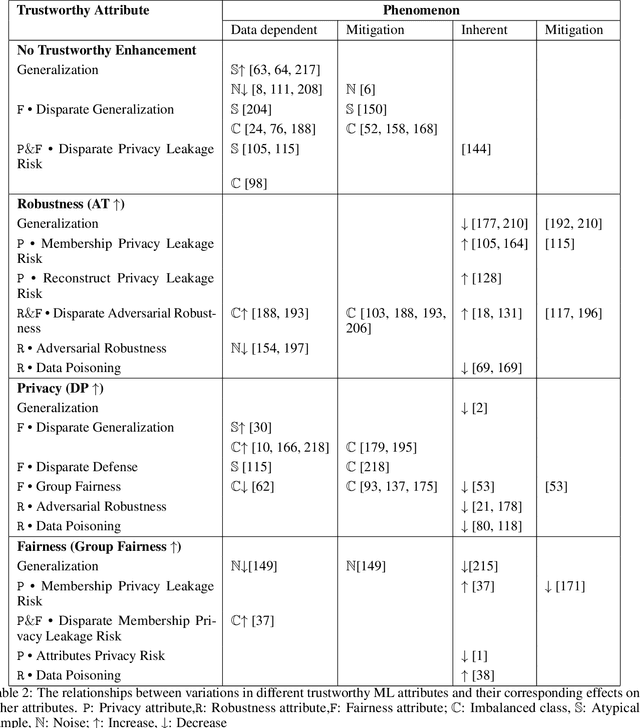
Abstract:The role of memorization in machine learning (ML) has garnered significant attention, particularly as modern models are empirically observed to memorize fragments of training data. Previous theoretical analyses, such as Feldman's seminal work, attribute memorization to the prevalence of long-tail distributions in training data, proving it unavoidable for samples that lie in the tail of the distribution. However, the intersection of memorization and trustworthy ML research reveals critical gaps. While prior research in memorization in trustworthy ML has solely focused on class imbalance, recent work starts to differentiate class-level rarity from atypical samples, which are valid and rare intra-class instances. However, a critical research gap remains: current frameworks conflate atypical samples with noisy and erroneous data, neglecting their divergent impacts on fairness, robustness, and privacy. In this work, we conduct a thorough survey of existing research and their findings on trustworthy ML and the role of memorization. More and beyond, we identify and highlight uncharted gaps and propose new revenues in this research direction. Since existing theoretical and empirical analyses lack the nuances to disentangle memorization's duality as both a necessity and a liability, we formalize three-level long-tail granularity - class imbalance, atypicality, and noise - to reveal how current frameworks misapply these levels, perpetuating flawed solutions. By systematizing this granularity, we draw a roadmap for future research. Trustworthy ML must reconcile the nuanced trade-offs between memorizing atypicality for fairness assurance and suppressing noise for robustness and privacy guarantee. Redefining memorization via this granularity reshapes the theoretical foundation for trustworthy ML, and further affords an empirical prerequisite for models that align performance with societal trust.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge