Kelechi Ogueji
Improving Multilingual Math Reasoning for African Languages
May 26, 2025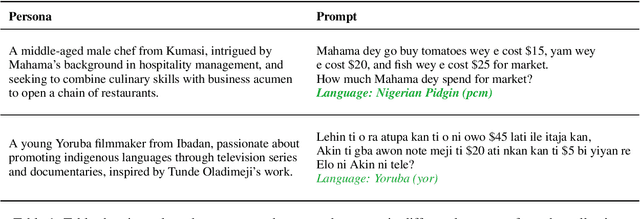
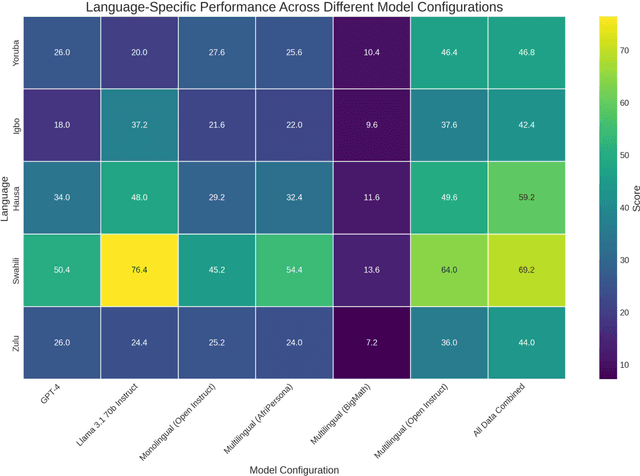
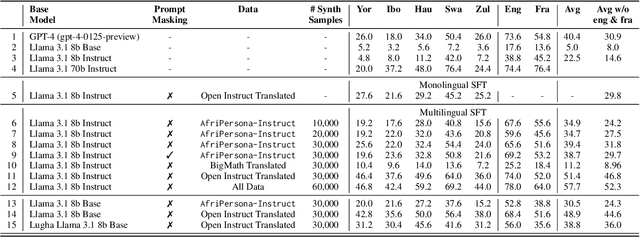
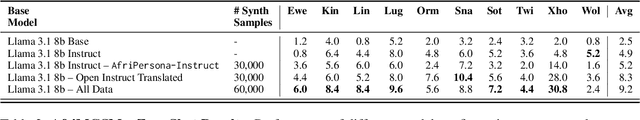
Abstract:Researchers working on low-resource languages face persistent challenges due to limited data availability and restricted access to computational resources. Although most large language models (LLMs) are predominantly trained in high-resource languages, adapting them to low-resource contexts, particularly African languages, requires specialized techniques. Several strategies have emerged for adapting models to low-resource languages in todays LLM landscape, defined by multi-stage pre-training and post-training paradigms. However, the most effective approaches remain uncertain. This work systematically investigates which adaptation strategies yield the best performance when extending existing LLMs to African languages. We conduct extensive experiments and ablation studies to evaluate different combinations of data types (translated versus synthetically generated), training stages (pre-training versus post-training), and other model adaptation configurations. Our experiments focuses on mathematical reasoning tasks, using the Llama 3.1 model family as our base model.
Multi-Reference Preference Optimization for Large Language Models
May 26, 2024



Abstract:How can Large Language Models (LLMs) be aligned with human intentions and values? A typical solution is to gather human preference on model outputs and finetune the LLMs accordingly while ensuring that updates do not deviate too far from a reference model. Recent approaches, such as direct preference optimization (DPO), have eliminated the need for unstable and sluggish reinforcement learning optimization by introducing close-formed supervised losses. However, a significant limitation of the current approach is its design for a single reference model only, neglecting to leverage the collective power of numerous pretrained LLMs. To overcome this limitation, we introduce a novel closed-form formulation for direct preference optimization using multiple reference models. The resulting algorithm, Multi-Reference Preference Optimization (MRPO), leverages broader prior knowledge from diverse reference models, substantially enhancing preference learning capabilities compared to the single-reference DPO. Our experiments demonstrate that LLMs finetuned with MRPO generalize better in various preference data, regardless of data scarcity or abundance. Furthermore, MRPO effectively finetunes LLMs to exhibit superior performance in several downstream natural language processing tasks such as GSM8K and TruthfulQA.
Curry-DPO: Enhancing Alignment using Curriculum Learning & Ranked Preferences
Mar 12, 2024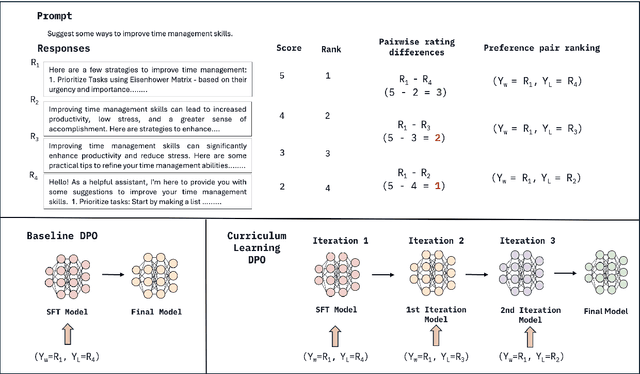
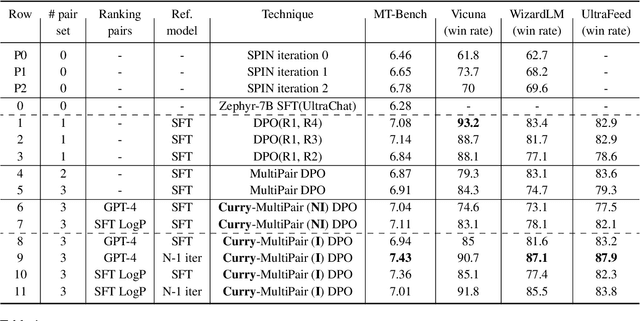
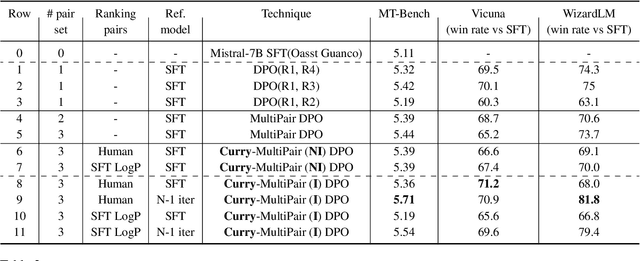

Abstract:Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) is an effective technique that leverages pairwise preference data (usually one chosen and rejected response pair per user prompt) to align LLMs to human preferences. In practice, multiple responses can exist for a given prompt with varying quality relative to each other. With availability of such quality ratings for multiple responses, we propose utilizing these responses to create multiple preference pairs for a given prompt. Our work focuses on systematically using the constructed multiple preference pair in DPO training via curriculum learning methodology. In particular, we order these multiple pairs of preference data from easy to hard (emulating curriculum training) according to various criteria. We show detailed comparisons of our proposed approach to the standard single-pair DPO setting. Our method, which we call Curry-DPO consistently shows increased performance gains on MTbench, Vicuna, WizardLM, and the UltraFeedback test set, highlighting its effectiveness. More specifically, Curry-DPO achieves a score of 7.43 on MT-bench with Zephy-7B model outperforming majority of existing LLMs with similar parameter size. Curry-DPO also achieves the highest adjusted win rates on Vicuna, WizardLM, and UltraFeedback test datasets (90.7%, 87.1%, and 87.9% respectively) in our experiments, with notable gains of upto 7.5% when compared to standard DPO technique.
How good are Large Language Models on African Languages?
Nov 14, 2023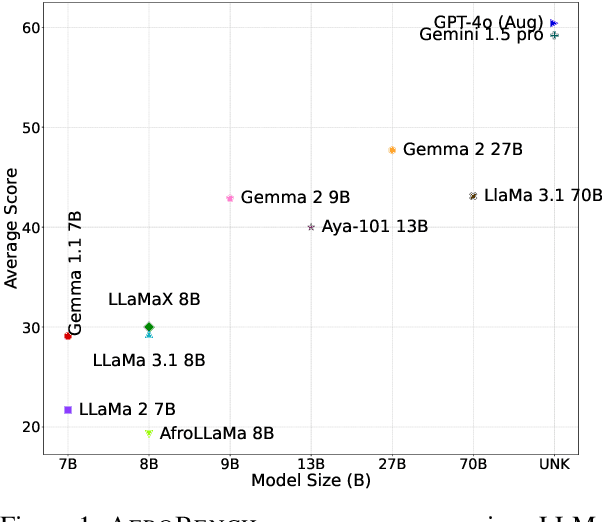



Abstract:Recent advancements in natural language processing have led to the proliferation of large language models (LLMs). These models have been shown to yield good performance, using in-context learning, even on unseen tasks and languages. Additionally, they have been widely adopted as language-model-as-a-service commercial APIs like GPT-4 API. However, their performance on African languages is largely unknown. We present an analysis of three popular large language models (mT0, LLaMa 2, and GPT-4) on five tasks (news topic classification, sentiment classification, machine translation, question answering, and named entity recognition) across 30 African languages, spanning different language families and geographical regions. Our results suggest that all LLMs produce below-par performance on African languages, and there is a large gap in performance compared to high-resource languages like English most tasks. We find that GPT-4 has an average or impressive performance on classification tasks but very poor results on generative tasks like machine translation. Surprisingly, we find that mT0 had the best overall on cross-lingual QA, better than the state-of-the-art supervised model (i.e. fine-tuned mT5) and GPT-4 on African languages. Overall, LLaMa 2 records the worst performance due to its limited multilingual capabilities and English-centric pre-training corpus. In general, our findings present a call-to-action to ensure African languages are well represented in large language models, given their growing popularity.
How Good are Commercial Large Language Models on African Languages?
May 11, 2023


Abstract:Recent advancements in Natural Language Processing (NLP) has led to the proliferation of large pretrained language models. These models have been shown to yield good performance, using in-context learning, even on unseen tasks and languages. They have also been exposed as commercial APIs as a form of language-model-as-a-service, with great adoption. However, their performance on African languages is largely unknown. We present a preliminary analysis of commercial large language models on two tasks (machine translation and text classification) across eight African languages, spanning different language families and geographical areas. Our results suggest that commercial language models produce below-par performance on African languages. We also find that they perform better on text classification than machine translation. In general, our findings present a call-to-action to ensure African languages are well represented in commercial large language models, given their growing popularity.
Intriguing Properties of Compression on Multilingual Models
Nov 04, 2022



Abstract:Multilingual models are often particularly dependent on scaling to generalize to a growing number of languages. Compression techniques are widely relied upon to reconcile the growth in model size with real world resource constraints, but compression can have a disparate effect on model performance for low-resource languages. It is thus crucial to understand the trade-offs between scale, multilingualism, and compression. In this work, we propose an experimental framework to characterize the impact of sparsifying multilingual pre-trained language models during fine-tuning. Applying this framework to mBERT named entity recognition models across 40 languages, we find that compression confers several intriguing and previously unknown generalization properties. In contrast to prior findings, we find that compression may improve model robustness over dense models. We additionally observe that under certain sparsification regimes compression may aid, rather than disproportionately impact the performance of low-resource languages.
What a Creole Wants, What a Creole Needs
Jun 01, 2022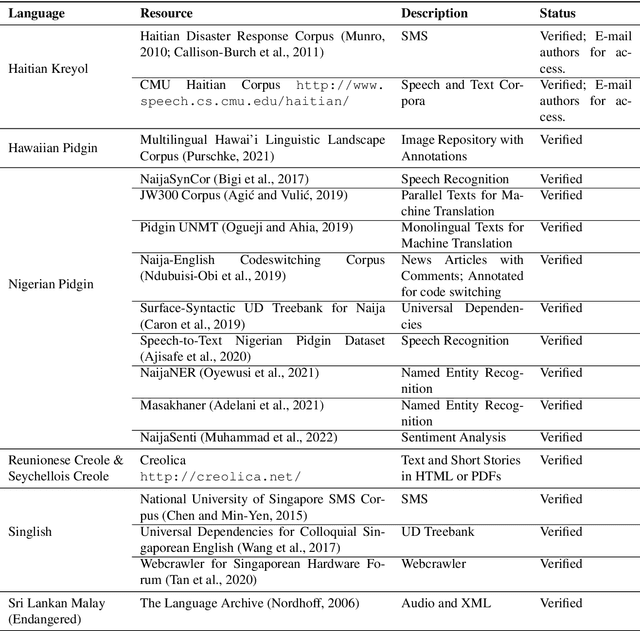
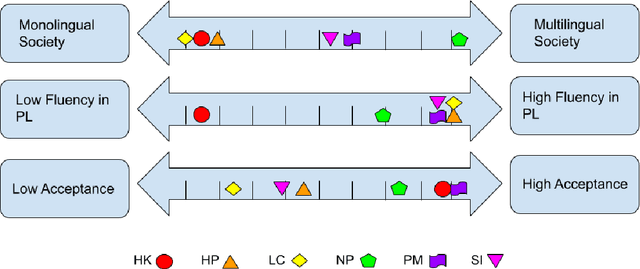
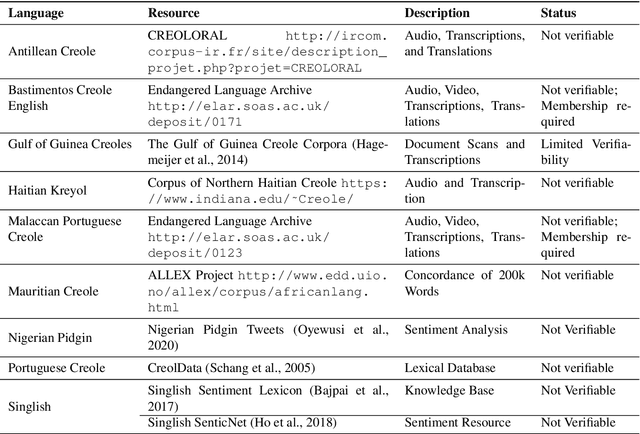
Abstract:In recent years, the natural language processing (NLP) community has given increased attention to the disparity of efforts directed towards high-resource languages over low-resource ones. Efforts to remedy this delta often begin with translations of existing English datasets into other languages. However, this approach ignores that different language communities have different needs. We consider a group of low-resource languages, Creole languages. Creoles are both largely absent from the NLP literature, and also often ignored by society at large due to stigma, despite these languages having sizable and vibrant communities. We demonstrate, through conversations with Creole experts and surveys of Creole-speaking communities, how the things needed from language technology can change dramatically from one language to another, even when the languages are considered to be very similar to each other, as with Creoles. We discuss the prominent themes arising from these conversations, and ultimately demonstrate that useful language technology cannot be built without involving the relevant community.
Towards Best Practices for Training Multilingual Dense Retrieval Models
Apr 05, 2022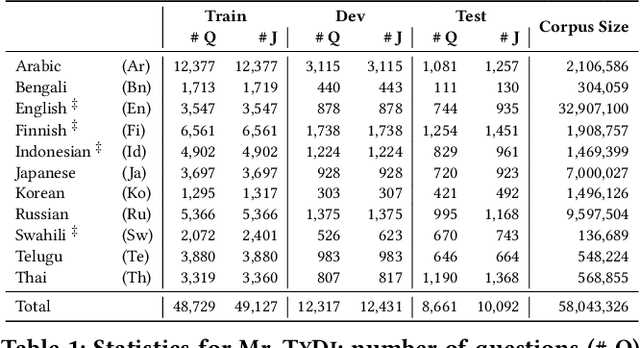
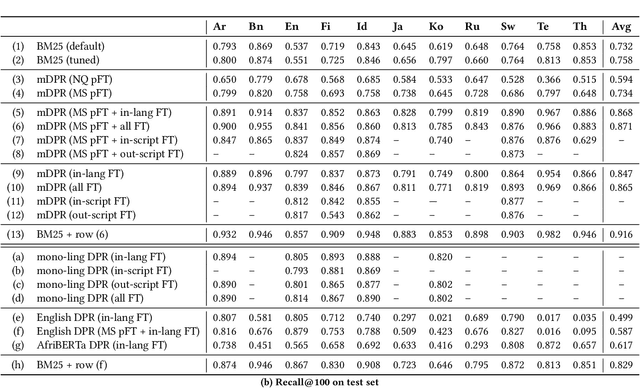
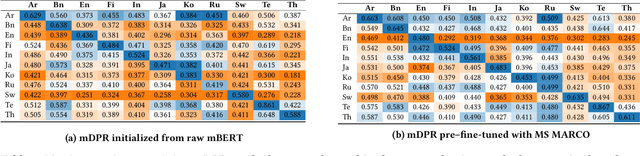
Abstract:Dense retrieval models using a transformer-based bi-encoder design have emerged as an active area of research. In this work, we focus on the task of monolingual retrieval in a variety of typologically diverse languages using one such design. Although recent work with multilingual transformers demonstrates that they exhibit strong cross-lingual generalization capabilities, there remain many open research questions, which we tackle here. Our study is organized as a "best practices" guide for training multilingual dense retrieval models, broken down into three main scenarios: where a multilingual transformer is available, but relevance judgments are not available in the language of interest; where both models and training data are available; and, where training data are available not but models. In considering these scenarios, we gain a better understanding of the role of multi-stage fine-tuning, the strength of cross-lingual transfer under various conditions, the usefulness of out-of-language data, and the advantages of multilingual vs. monolingual transformers. Our recommendations offer a guide for practitioners building search applications, particularly for low-resource languages, and while our work leaves open a number of research questions, we provide a solid foundation for future work.
Quality at a Glance: An Audit of Web-Crawled Multilingual Datasets
Mar 22, 2021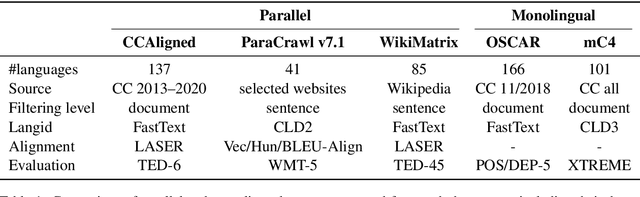
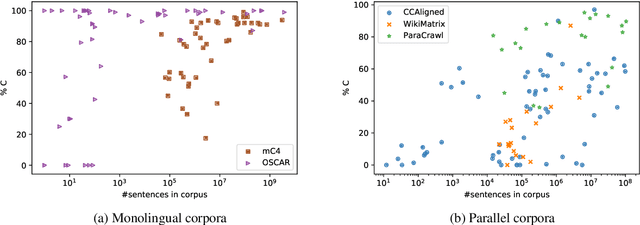
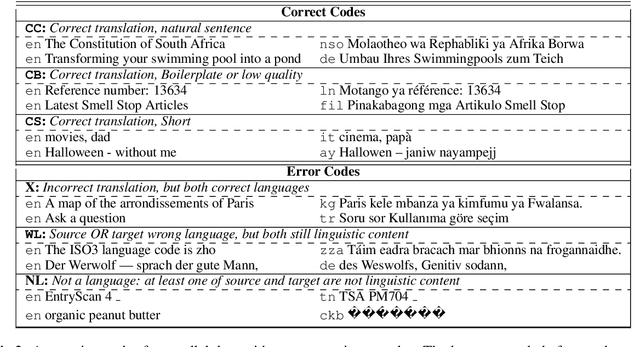
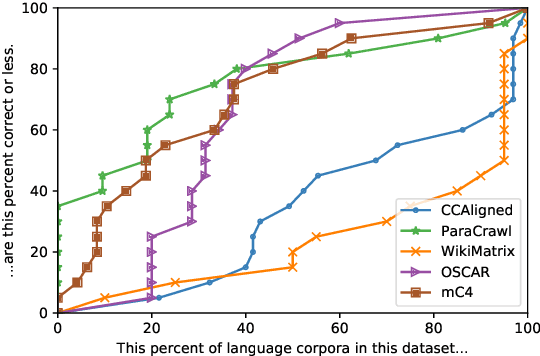
Abstract:With the success of large-scale pre-training and multilingual modeling in Natural Language Processing (NLP), recent years have seen a proliferation of large, web-mined text datasets covering hundreds of languages. However, to date there has been no systematic analysis of the quality of these publicly available datasets, or whether the datasets actually contain content in the languages they claim to represent. In this work, we manually audit the quality of 205 language-specific corpora released with five major public datasets (CCAligned, ParaCrawl, WikiMatrix, OSCAR, mC4), and audit the correctness of language codes in a sixth (JW300). We find that lower-resource corpora have systematic issues: at least 15 corpora are completely erroneous, and a significant fraction contains less than 50% sentences of acceptable quality. Similarly, we find 82 corpora that are mislabeled or use nonstandard/ambiguous language codes. We demonstrate that these issues are easy to detect even for non-speakers of the languages in question, and supplement the human judgements with automatic analyses. Inspired by our analysis, we recommend techniques to evaluate and improve multilingual corpora and discuss the risks that come with low-quality data releases.
MasakhaNER: Named Entity Recognition for African Languages
Mar 22, 2021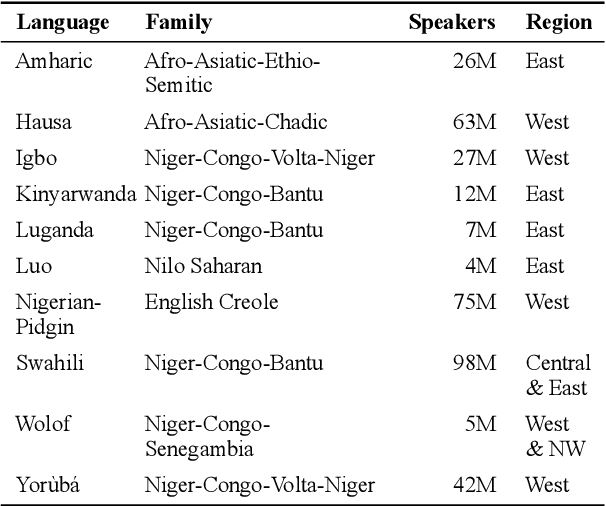

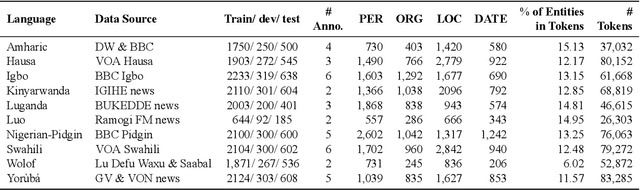
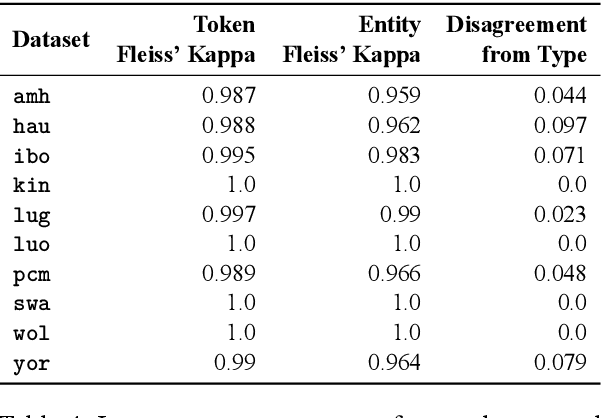
Abstract:We take a step towards addressing the under-representation of the African continent in NLP research by creating the first large publicly available high-quality dataset for named entity recognition (NER) in ten African languages, bringing together a variety of stakeholders. We detail characteristics of the languages to help researchers understand the challenges that these languages pose for NER. We analyze our datasets and conduct an extensive empirical evaluation of state-of-the-art methods across both supervised and transfer learning settings. We release the data, code, and models in order to inspire future research on African NLP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge