Xinyu Zhang
School of Electronics and Information, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi'an, China, Chongqing Institute for Brain and Intelligence, Guangyang Bay Laboratory, Chongqing, China
Qwen3-ASR Technical Report
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce Qwen3-ASR family, which includes two powerful all-in-one speech recognition models and a novel non-autoregressive speech forced alignment model. Qwen3-ASR-1.7B and Qwen3-ASR-0.6B are ASR models that support language identification and ASR for 52 languages and dialects. Both of them leverage large-scale speech training data and the strong audio understanding ability of their foundation model Qwen3-Omni. We conduct comprehensive internal evaluation besides the open-sourced benchmarks as ASR models might differ little on open-sourced benchmark scores but exhibit significant quality differences in real-world scenarios. The experiments reveal that the 1.7B version achieves SOTA performance among open-sourced ASR models and is competitive with the strongest proprietary APIs while the 0.6B version offers the best accuracy-efficiency trade-off. Qwen3-ASR-0.6B can achieve an average TTFT as low as 92ms and transcribe 2000 seconds speech in 1 second at a concurrency of 128. Qwen3-ForcedAligner-0.6B is an LLM based NAR timestamp predictor that is able to align text-speech pairs in 11 languages. Timestamp accuracy experiments show that the proposed model outperforms the three strongest force alignment models and takes more advantages in efficiency and versatility. To further accelerate the community research of ASR and audio understanding, we release these models under the Apache 2.0 license.
A Unified SPD Token Transformer Framework for EEG Classification: Systematic Comparison of Geometric Embeddings
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Spatial covariance matrices of EEG signals are Symmetric Positive Definite (SPD) and lie on a Riemannian manifold, yet the theoretical connection between embedding geometry and optimization dynamics remains unexplored. We provide a formal analysis linking embedding choice to gradient conditioning and numerical stability for SPD manifolds, establishing three theoretical results: (1) BWSPD's $\sqrtκ$ gradient conditioning (vs $κ$ for Log-Euclidean) via Daleckii-Kreĭn matrices provides better gradient conditioning on high-dimensional inputs ($d \geq 22$), with this advantage reducing on low-dimensional inputs ($d \leq 8$) where eigendecomposition overhead dominates; (2) Embedding-Space Batch Normalization (BN-Embed) approximates Riemannian normalization up to $O(\varepsilon^2)$ error, yielding $+26\%$ accuracy on 56-channel ERP data but negligible effect on 8-channel SSVEP data, matching the channel-count-dependent prediction; (3) bi-Lipschitz bounds prove BWSPD tokens preserve manifold distances with distortion governed solely by the condition ratio $κ$. We validate these predictions via a unified Transformer framework comparing BWSPD, Log-Euclidean, and Euclidean embeddings within identical architecture across 1,500+ runs on three EEG paradigms (motor imagery, ERP, SSVEP; 36 subjects). Our Log-Euclidean Transformer achieves state-of-the-art performance on all datasets, substantially outperforming classical Riemannian classifiers and recent SPD baselines, while BWSPD offers competitive accuracy with similar training time.
Qwen3-TTS Technical Report
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:In this report, we present the Qwen3-TTS series, a family of advanced multilingual, controllable, robust, and streaming text-to-speech models. Qwen3-TTS supports state-of-the-art 3-second voice cloning and description-based control, allowing both the creation of entirely novel voices and fine-grained manipulation over the output speech. Trained on over 5 million hours of speech data spanning 10 languages, Qwen3-TTS adopts a dual-track LM architecture for real-time synthesis, coupled with two speech tokenizers: 1) Qwen-TTS-Tokenizer-25Hz is a single-codebook codec emphasizing semantic content, which offers seamlessly integration with Qwen-Audio and enables streaming waveform reconstruction via a block-wise DiT. 2) Qwen-TTS-Tokenizer-12Hz achieves extreme bitrate reduction and ultra-low-latency streaming, enabling immediate first-packet emission ($97\,\mathrm{ms}$) through its 12.5 Hz, 16-layer multi-codebook design and a lightweight causal ConvNet. Extensive experiments indicate state-of-the-art performance across diverse objective and subjective benchmark (e.g., TTS multilingual test set, InstructTTSEval, and our long speech test set). To facilitate community research and development, we release both tokenizers and models under the Apache 2.0 license.
Process In-Context Learning: Enhancing Mathematical Reasoning via Dynamic Demonstration Insertion
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) has proven highly effective across diverse large language model (LLM) tasks. However, its potential for enhancing tasks that demand step-by-step logical deduction, such as mathematical reasoning, remains underexplored. A core limitation of existing ICL approaches is their static use of demonstrations: examples are pre-selected before inference and remain fixed, failing to adapt to the dynamic confusion points that often arise during multi-step reasoning such as ambiguous calculations or logical gaps. These unresolved confusion points can lead to cascading errors that degrade final accuracy. To tackle this issue, we propose Process In-Context Learning (PICL), a dynamic demonstration integration framework designed to boost mathematical reasoning by responding to real-time inference needs. PICL operates in two stages: 1)~it identifies potential confusion points by analyzing semantics and entropy in the reasoning process and summarizes their core characteristics; 2)~upon encountering these points, it retrieves relevant demonstrations from the demonstration pool that match the confusion context and inserts them directly into the ongoing reasoning process to guide subsequent steps. Experiments show that PICL outperforms baseline methods by mitigating mid-inference confusion, highlighting the value of adaptive demonstration insertion in complex mathematical reasoning.
Towards Efficient 3D Object Detection for Vehicle-Infrastructure Collaboration via Risk-Intent Selection
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Vehicle-Infrastructure Collaborative Perception (VICP) is pivotal for resolving occlusion in autonomous driving, yet the trade-off between communication bandwidth and feature redundancy remains a critical bottleneck. While intermediate fusion mitigates data volume compared to raw sharing, existing frameworks typically rely on spatial compression or static confidence maps, which inefficiently transmit spatially redundant features from non-critical background regions. To address this, we propose Risk-intent Selective detection (RiSe), an interaction-aware framework that shifts the paradigm from identifying visible regions to prioritizing risk-critical ones. Specifically, we introduce a Potential Field-Trajectory Correlation Model (PTCM) grounded in potential field theory to quantitatively assess kinematic risks. Complementing this, an Intention-Driven Area Prediction Module (IDAPM) leverages ego-motion priors to proactively predict and filter key Bird's-Eye-View (BEV) areas essential for decision-making. By integrating these components, RiSe implements a semantic-selective fusion scheme that transmits high-fidelity features only from high-interaction regions, effectively acting as a feature denoiser. Extensive experiments on the DeepAccident dataset demonstrate that our method reduces communication volume to 0.71\% of full feature sharing while maintaining state-of-the-art detection accuracy, establishing a competitive Pareto frontier between bandwidth efficiency and perception performance.
Adaptive Dependency-aware Prompt Optimization Framework for Multi-Step LLM Pipeline
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Multi-step LLM pipelines invoke large language models multiple times in a structured sequence and can effectively solve complex tasks, but their performance heavily depends on the prompts used at each step. Jointly optimizing these prompts is difficult due to missing step-level supervision and inter-step dependencies. Existing end-to-end prompt optimization methods struggle under these conditions and often yield suboptimal or unstable updates. We propose ADOPT, an Adaptive Dependency-aware Prompt Optimization framework for multi-step LLM pipelines. ADOPT explicitly models the dependency between each LLM step and the final task outcome, enabling precise text-gradient estimation analogous to computing analytical derivatives. It decouples textual gradient estimation from gradient updates, reducing multi-prompt optimization to flexible single-prompt optimization steps, and employs a Shapley-based mechanism to adaptively allocate optimization resources. Experiments on real-world datasets and diverse pipeline structures show that ADOPT is effective and robust, consistently outperforming state-of-the-art prompt optimization baselines.
MUSON: A Reasoning-oriented Multimodal Dataset for Socially Compliant Navigation in Urban Environments
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Socially compliant navigation requires structured reasoning over dynamic pedestrians and physical constraints to ensure safe and interpretable decisions. However, existing social navigation datasets often lack explicit reasoning supervision and exhibit highly long-tailed action distributions, limiting models' ability to learn safety-critical behaviors. To address these issues, we introduce MUSON, a multimodal dataset for short-horizon social navigation collected across diverse indoor and outdoor campus scenes. MUSON adopts a structured five-step Chain-of-Thought annotation consisting of perception, prediction, reasoning, action, and explanation, with explicit modeling of static physical constraints and a rationally balanced discrete action space. Compared to SNEI, MUSON provides consistent reasoning, action, and explanation. Benchmarking multiple state-of-the-art Small Vision Language Models on MUSON shows that Qwen2.5-VL-3B achieves the highest decision accuracy of 0.8625, demonstrating that MUSON serves as an effective and reusable benchmark for socially compliant navigation. The dataset is publicly available at https://huggingface.co/datasets/MARSLab/MUSON
MAction-SocialNav: Multi-Action Socially Compliant Navigation via Reasoning-enhanced Prompt Tuning
Dec 25, 2025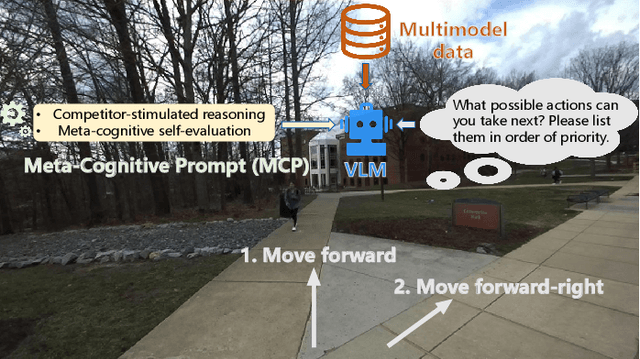
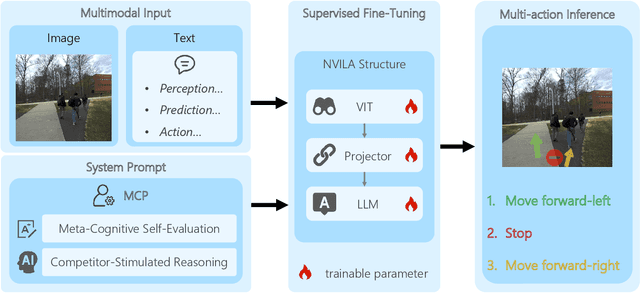

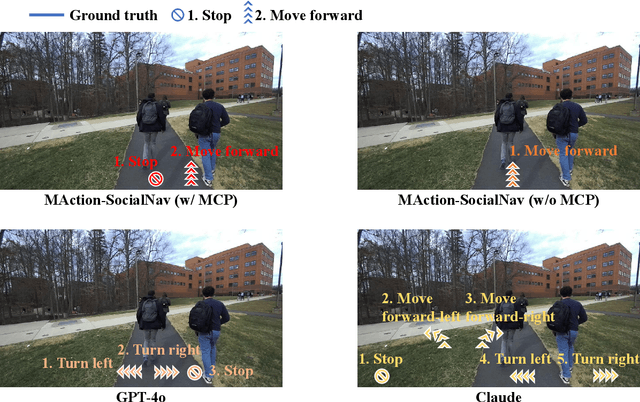
Abstract:Socially compliant navigation requires robots to move safely and appropriately in human-centered environments by respecting social norms. However, social norms are often ambiguous, and in a single scenario, multiple actions may be equally acceptable. Most existing methods simplify this problem by assuming a single correct action, which limits their ability to handle real-world social uncertainty. In this work, we propose MAction-SocialNav, an efficient vision language model for socially compliant navigation that explicitly addresses action ambiguity, enabling generating multiple plausible actions within one scenario. To enhance the model's reasoning capability, we introduce a novel meta-cognitive prompt (MCP) method. Furthermore, to evaluate the proposed method, we curate a multi-action socially compliant navigation dataset that accounts for diverse conditions, including crowd density, indoor and outdoor environments, and dual human annotations. The dataset contains 789 samples, each with three-turn conversation, split into 710 training samples and 79 test samples through random selection. We also design five evaluation metrics to assess high-level decision precision, safety, and diversity. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed MAction-SocialNav achieves strong social reasoning performance while maintaining high efficiency, highlighting its potential for real-world human robot navigation. Compared with zero-shot GPT-4o and Claude, our model achieves substantially higher decision quality (APG: 0.595 vs. 0.000/0.025) and safety alignment (ER: 0.264 vs. 0.642/0.668), while maintaining real-time efficiency (1.524 FPS, over 3x faster).
Driving in Corner Case: A Real-World Adversarial Closed-Loop Evaluation Platform for End-to-End Autonomous Driving
Dec 18, 2025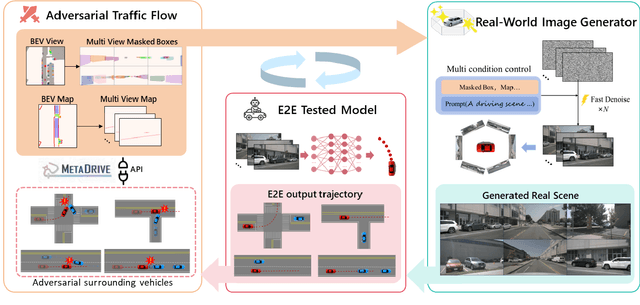
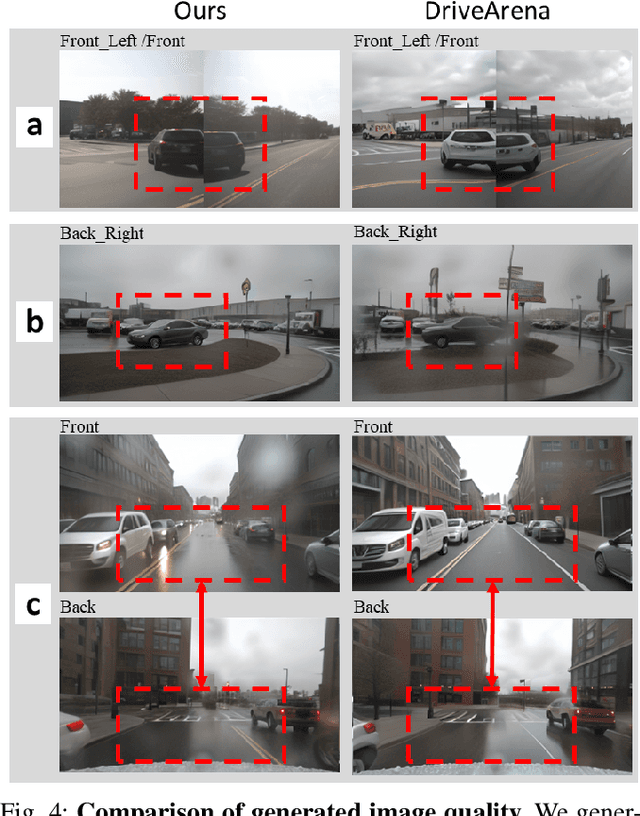
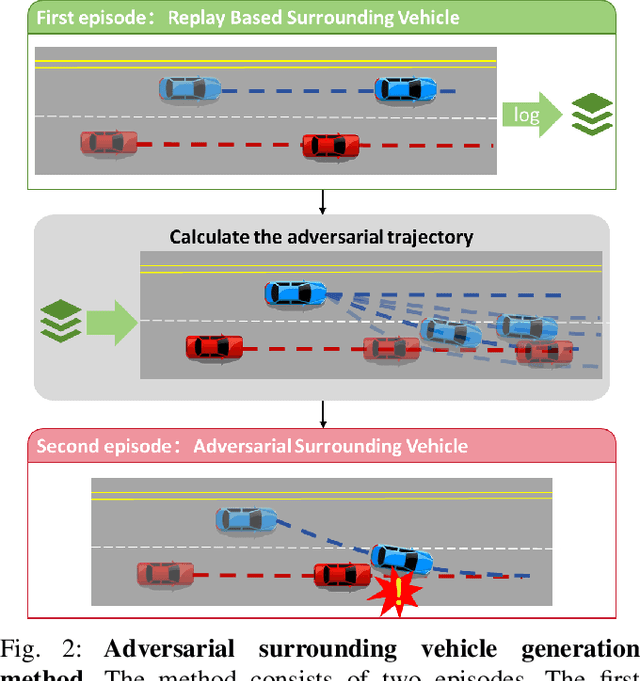
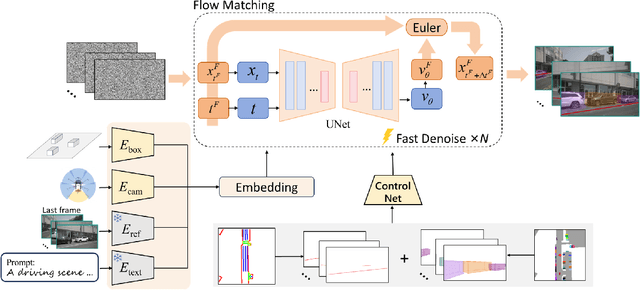

Abstract:Safety-critical corner cases, difficult to collect in the real world, are crucial for evaluating end-to-end autonomous driving. Adversarial interaction is an effective method to generate such safety-critical corner cases. While existing adversarial evaluation methods are built for models operating in simplified simulation environments, adversarial evaluation for real-world end-to-end autonomous driving has been little explored. To address this challenge, we propose a closed-loop evaluation platform for end-to-end autonomous driving, which can generate adversarial interactions in real-world scenes. In our platform, the real-world image generator cooperates with an adversarial traffic policy to evaluate various end-to-end models trained on real-world data. The generator, based on flow matching, efficiently and stably generates real-world images according to the traffic environment information. The efficient adversarial surrounding vehicle policy is designed to model challenging interactions and create corner cases that current autonomous driving systems struggle to handle. Experimental results demonstrate that the platform can generate realistic driving images efficiently. Through evaluating the end-to-end models such as UniAD and VAD, we demonstrate that based on the adversarial policy, our platform evaluates the performance degradation of the tested model in corner cases. This result indicates that this platform can effectively detect the model's potential issues, which will facilitate the safety and robustness of end-to-end autonomous driving.
SocialNav-MoE: A Mixture-of-Experts Vision Language Model for Socially Compliant Navigation with Reinforcement Fine-Tuning
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:For robots navigating in human-populated environments, safety and social compliance are equally critical, yet prior work has mostly emphasized safety. Socially compliant navigation that accounts for human comfort, social norms, and contextual appropriateness remains underexplored. Vision language models (VLMs) show promise for this task; however, large-scale models incur substantial computational overhead, leading to higher inference latency and energy consumption, which makes them unsuitable for real-time deployment on resource-constrained robotic platforms. To address this issue, we investigate the effectiveness of small VLM and propose SocialNav-MoE, an efficient Mixture-of-Experts vision language model for socially compliant navigation with reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT). We further introduce a semantic similarity reward (SSR) to effectively leverage RFT for enhancing the decision-making capabilities. Additionally, we study the effectiveness of different small language model types (Phi, Qwen, and StableLM), routing strategies, and vision encoders (CLIP vs. SigLIP, frozen vs. fine-tuned). Experiments on the SNEI dataset demonstrate that SocialNav-MoE achieves an excellent balance between navigation accuracy and efficiency. The proposed SSR function is more effective than hard-level and character-level rewards. Source code will be released upon acceptance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge