Chris Xiaoxuan Lu
M4Human: A Large-Scale Multimodal mmWave Radar Benchmark for Human Mesh Reconstruction
Dec 17, 2025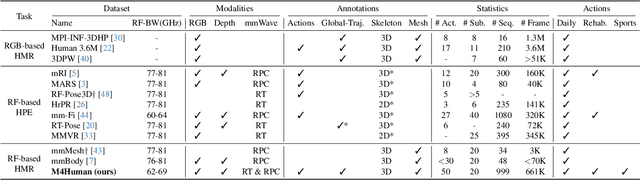
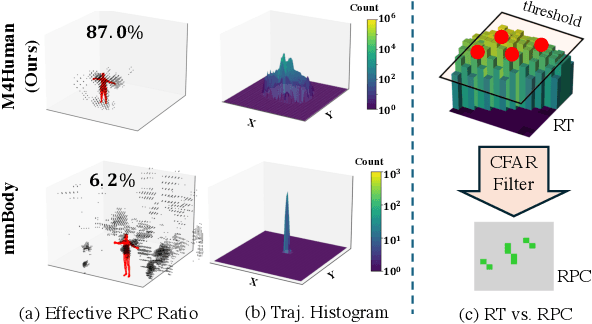
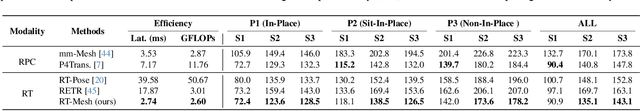
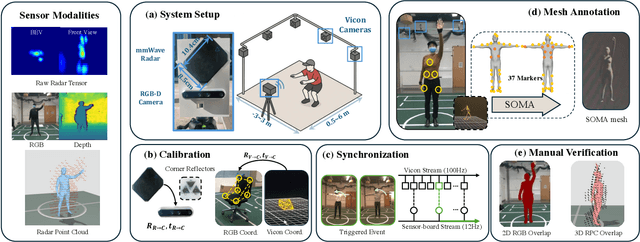
Abstract:Human mesh reconstruction (HMR) provides direct insights into body-environment interaction, which enables various immersive applications. While existing large-scale HMR datasets rely heavily on line-of-sight RGB input, vision-based sensing is limited by occlusion, lighting variation, and privacy concerns. To overcome these limitations, recent efforts have explored radio-frequency (RF) mmWave radar for privacy-preserving indoor human sensing. However, current radar datasets are constrained by sparse skeleton labels, limited scale, and simple in-place actions. To advance the HMR research community, we introduce M4Human, the current largest-scale (661K-frame) ($9\times$ prior largest) multimodal benchmark, featuring high-resolution mmWave radar, RGB, and depth data. M4Human provides both raw radar tensors (RT) and processed radar point clouds (RPC) to enable research across different levels of RF signal granularity. M4Human includes high-quality motion capture (MoCap) annotations with 3D meshes and global trajectories, and spans 20 subjects and 50 diverse actions, including in-place, sit-in-place, and free-space sports or rehabilitation movements. We establish benchmarks on both RT and RPC modalities, as well as multimodal fusion with RGB-D modalities. Extensive results highlight the significance of M4Human for radar-based human modeling while revealing persistent challenges under fast, unconstrained motion. The dataset and code will be released after the paper publication.
Attentive Feature Aggregation or: How Policies Learn to Stop Worrying about Robustness and Attend to Task-Relevant Visual Cues
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:The adoption of pre-trained visual representations (PVRs), leveraging features from large-scale vision models, has become a popular paradigm for training visuomotor policies. However, these powerful representations can encode a broad range of task-irrelevant scene information, making the resulting trained policies vulnerable to out-of-domain visual changes and distractors. In this work we address visuomotor policy feature pooling as a solution to the observed lack of robustness in perturbed scenes. We achieve this via Attentive Feature Aggregation (AFA), a lightweight, trainable pooling mechanism that learns to naturally attend to task-relevant visual cues, ignoring even semantically rich scene distractors. Through extensive experiments in both simulation and the real world, we demonstrate that policies trained with AFA significantly outperform standard pooling approaches in the presence of visual perturbations, without requiring expensive dataset augmentation or fine-tuning of the PVR. Our findings show that ignoring extraneous visual information is a crucial step towards deploying robust and generalisable visuomotor policies. Project Page: tsagkas.github.io/afa
InverTwin: Solving Inverse Problems via Differentiable Radio Frequency Digital Twin
Aug 19, 2025Abstract:Digital twins (DTs), virtual simulated replicas of physical scenes, are transforming various industries. However, their potential in radio frequency (RF) sensing applications has been limited by the unidirectional nature of conventional RF simulators. In this paper, we present InverTwin, an optimization-driven framework that creates RF digital twins by enabling bidirectional interaction between virtual and physical realms. InverTwin overcomes the fundamental differentiability challenges of RF optimization problems through novel design components, including path-space differentiation to address discontinuity in complex simulation functions, and a radar surrogate model to mitigate local non-convexity caused by RF signal periodicity. These techniques enable smooth gradient propagation and robust optimization of the DT model. Our implementation and experiments demonstrate InverTwin's versatility and effectiveness in augmenting both data-driven and model-driven RF sensing systems for DT reconstruction.
Fast ECoT: Efficient Embodied Chain-of-Thought via Thoughts Reuse
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Embodied Chain-of-Thought (ECoT) reasoning enhances vision-language-action (VLA) models by improving performance and interpretability through intermediate reasoning steps. However, its sequential autoregressive token generation introduces significant inference latency, limiting real-time deployment. We propose Fast ECoT, an inference-time acceleration method that exploits the structured and repetitive nature of ECoT to (1) cache and reuse high-level reasoning across timesteps and (2) parallelise the generation of modular reasoning steps. Additionally, we introduce an asynchronous scheduler that decouples reasoning from action decoding, further boosting responsiveness. Fast ECoT requires no model changes or additional training and integrates easily into existing VLA pipelines. Experiments in both simulation (LIBERO) and real-world robot tasks show up to a 7.5% reduction in latency with comparable or improved task success rate and reasoning faithfulness, bringing ECoT policies closer to practical real-time deployment.
When Pre-trained Visual Representations Fall Short: Limitations in Visuo-Motor Robot Learning
Feb 05, 2025Abstract:The integration of pre-trained visual representations (PVRs) into visuo-motor robot learning has emerged as a promising alternative to training visual encoders from scratch. However, PVRs face critical challenges in the context of policy learning, including temporal entanglement and an inability to generalise even in the presence of minor scene perturbations. These limitations hinder performance in tasks requiring temporal awareness and robustness to scene changes. This work identifies these shortcomings and proposes solutions to address them. First, we augment PVR features with temporal perception and a sense of task completion, effectively disentangling them in time. Second, we introduce a module that learns to selectively attend to task-relevant local features, enhancing robustness when evaluated on out-of-distribution scenes. Our experiments demonstrate significant performance improvements, particularly in PVRs trained with masking objectives, and validate the effectiveness of our enhancements in addressing PVR-specific limitations.
RadarOcc: Robust 3D Occupancy Prediction with 4D Imaging Radar
May 22, 2024Abstract:3D occupancy-based perception pipeline has significantly advanced autonomous driving by capturing detailed scene descriptions and demonstrating strong generalizability across various object categories and shapes. Current methods predominantly rely on LiDAR or camera inputs for 3D occupancy prediction. These methods are susceptible to adverse weather conditions, limiting the all-weather deployment of self-driving cars. To improve perception robustness, we leverage the recent advances in automotive radars and introduce a novel approach that utilizes 4D imaging radar sensors for 3D occupancy prediction. Our method, RadarOcc, circumvents the limitations of sparse radar point clouds by directly processing the 4D radar tensor, thus preserving essential scene details. RadarOcc innovatively addresses the challenges associated with the voluminous and noisy 4D radar data by employing Doppler bins descriptors, sidelobe-aware spatial sparsification, and range-wise self-attention mechanisms. To minimize the interpolation errors associated with direct coordinate transformations, we also devise a spherical-based feature encoding followed by spherical-to-Cartesian feature aggregation. We benchmark various baseline methods based on distinct modalities on the public K-Radar dataset. The results demonstrate RadarOcc's state-of-the-art performance in radar-based 3D occupancy prediction and promising results even when compared with LiDAR- or camera-based methods. Additionally, we present qualitative evidence of the superior performance of 4D radar in adverse weather conditions and explore the impact of key pipeline components through ablation studies.
Click to Grasp: Zero-Shot Precise Manipulation via Visual Diffusion Descriptors
Mar 21, 2024Abstract:Precise manipulation that is generalizable across scenes and objects remains a persistent challenge in robotics. Current approaches for this task heavily depend on having a significant number of training instances to handle objects with pronounced visual and/or geometric part ambiguities. Our work explores the grounding of fine-grained part descriptors for precise manipulation in a zero-shot setting by utilizing web-trained text-to-image diffusion-based generative models. We tackle the problem by framing it as a dense semantic part correspondence task. Our model returns a gripper pose for manipulating a specific part, using as reference a user-defined click from a source image of a visually different instance of the same object. We require no manual grasping demonstrations as we leverage the intrinsic object geometry and features. Practical experiments in a real-world tabletop scenario validate the efficacy of our approach, demonstrating its potential for advancing semantic-aware robotics manipulation. Web page: https://tsagkas.github.io/click2grasp
ThermoHands: A Benchmark for 3D Hand Pose Estimation from Egocentric Thermal Image
Mar 14, 2024Abstract:In this work, we present ThermoHands, a new benchmark for thermal image-based egocentric 3D hand pose estimation, aimed at overcoming challenges like varying lighting and obstructions (e.g., handwear). The benchmark includes a diverse dataset from 28 subjects performing hand-object and hand-virtual interactions, accurately annotated with 3D hand poses through an automated process. We introduce a bespoken baseline method, TheFormer, utilizing dual transformer modules for effective egocentric 3D hand pose estimation in thermal imagery. Our experimental results highlight TheFormer's leading performance and affirm thermal imaging's effectiveness in enabling robust 3D hand pose estimation in adverse conditions.
Self-Adapting Large Visual-Language Models to Edge Devices across Visual Modalities
Mar 07, 2024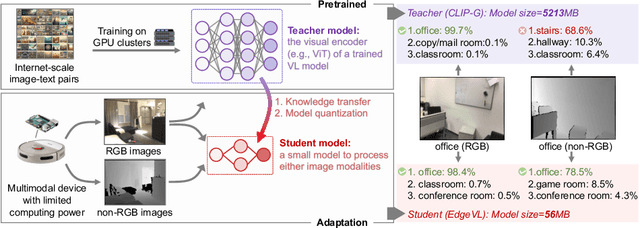
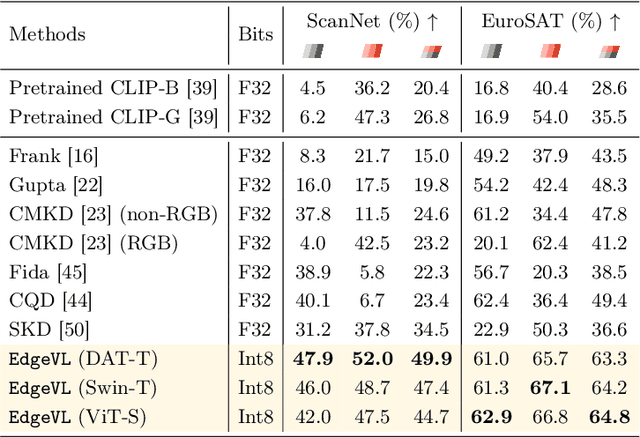
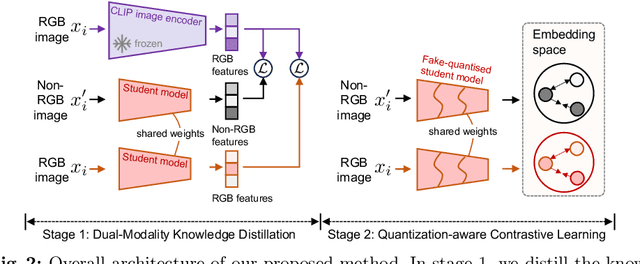

Abstract:Recent advancements in Vision-Language (VL) models have sparked interest in their deployment on edge devices, yet challenges in handling diverse visual modalities, manual annotation, and computational constraints remain. We introduce EdgeVL, a novel framework that bridges this gap by seamlessly integrating dual-modality knowledge distillation and quantization-aware contrastive learning. This approach enables the adaptation of large VL models, like CLIP, for efficient use with both RGB and non-RGB images on resource-limited devices without the need for manual annotations. EdgeVL not only transfers visual language alignment capabilities to compact models but also maintains feature quality post-quantization, significantly enhancing open-vocabulary classification performance across various visual modalities. Our work represents the first systematic effort to adapt large VL models for edge deployment, showcasing up to 15.4% accuracy improvements on multiple datasets and up to 93-fold reduction in model size.
Differentiable Radio Frequency Ray Tracing for Millimeter-Wave Sensing
Nov 22, 2023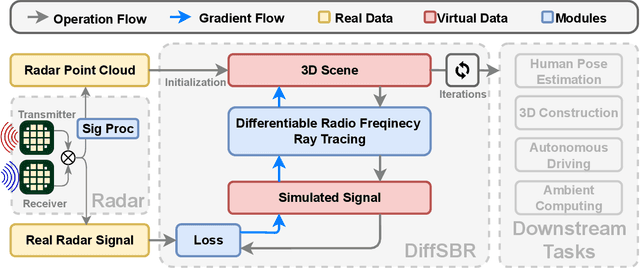
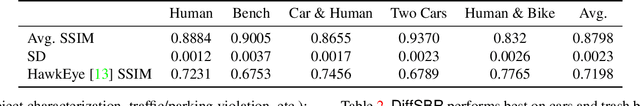
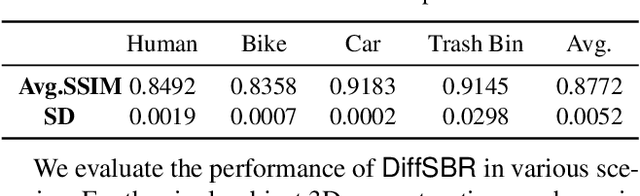
Abstract:Millimeter wave (mmWave) sensing is an emerging technology with applications in 3D object characterization and environment mapping. However, realizing precise 3D reconstruction from sparse mmWave signals remains challenging. Existing methods rely on data-driven learning, constrained by dataset availability and difficulty in generalization. We propose DiffSBR, a differentiable framework for mmWave-based 3D reconstruction. DiffSBR incorporates a differentiable ray tracing engine to simulate radar point clouds from virtual 3D models. A gradient-based optimizer refines the model parameters to minimize the discrepancy between simulated and real point clouds. Experiments using various radar hardware validate DiffSBR's capability for fine-grained 3D reconstruction, even for novel objects unseen by the radar previously. By integrating physics-based simulation with gradient optimization, DiffSBR transcends the limitations of data-driven approaches and pioneers a new paradigm for mmWave sensing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge