Subramanian Ramamoorthy
The University of Edinburgh
Heuristic Adaptation of Potentially Misspecified Domain Support for Likelihood-Free Inference in Stochastic Dynamical Systems
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:In robotics, likelihood-free inference (LFI) can provide the domain distribution that adapts a learnt agent in a parametric set of deployment conditions. LFI assumes an arbitrary support for sampling, which remains constant as the initial generic prior is iteratively refined to more descriptive posteriors. However, a potentially misspecified support can lead to suboptimal, yet falsely certain, posteriors. To address this issue, we propose three heuristic LFI variants: EDGE, MODE, and CENTRE. Each interprets the posterior mode shift over inference steps in its own way and, when integrated into an LFI step, adapts the support alongside posterior inference. We first expose the support misspecification issue and evaluate our heuristics using stochastic dynamical benchmarks. We then evaluate the impact of heuristic support adaptation on parameter inference and policy learning for a dynamic deformable linear object (DLO) manipulation task. Inference results in a finer length and stiffness classification for a parametric set of DLOs. When the resulting posteriors are used as domain distributions for sim-based policy learning, they lead to more robust object-centric agent performance.
ROOM: A Physics-Based Continuum Robot Simulator for Photorealistic Medical Datasets Generation
Sep 16, 2025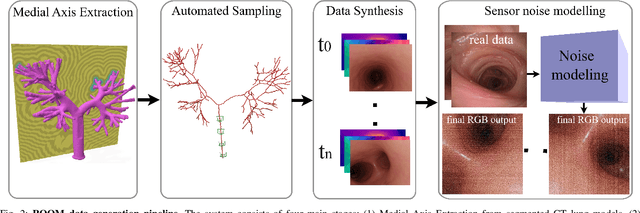



Abstract:Continuum robots are advancing bronchoscopy procedures by accessing complex lung airways and enabling targeted interventions. However, their development is limited by the lack of realistic training and test environments: Real data is difficult to collect due to ethical constraints and patient safety concerns, and developing autonomy algorithms requires realistic imaging and physical feedback. We present ROOM (Realistic Optical Observation in Medicine), a comprehensive simulation framework designed for generating photorealistic bronchoscopy training data. By leveraging patient CT scans, our pipeline renders multi-modal sensor data including RGB images with realistic noise and light specularities, metric depth maps, surface normals, optical flow and point clouds at medically relevant scales. We validate the data generated by ROOM in two canonical tasks for medical robotics -- multi-view pose estimation and monocular depth estimation, demonstrating diverse challenges that state-of-the-art methods must overcome to transfer to these medical settings. Furthermore, we show that the data produced by ROOM can be used to fine-tune existing depth estimation models to overcome these challenges, also enabling other downstream applications such as navigation. We expect that ROOM will enable large-scale data generation across diverse patient anatomies and procedural scenarios that are challenging to capture in clinical settings. Code and data: https://github.com/iamsalvatore/room.
ContactFusion: Stochastic Poisson Surface Maps from Visual and Contact Sensing
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:Robust and precise robotic assembly entails insertion of constituent components. Insertion success is hindered when noise in scene understanding exceeds tolerance limits, especially when fabricated with tight tolerances. In this work, we propose ContactFusion which combines global mapping with local contact information, fusing point clouds with force sensing. Our method entails a Rejection Sampling based contact occupancy sensing procedure which estimates contact locations on the end-effector from Force/Torque sensing at the wrist. We demonstrate how to fuse contact with visual information into a Stochastic Poisson Surface Map (SPSMap) - a map representation that can be updated with the Stochastic Poisson Surface Reconstruction (SPSR) algorithm. We first validate the contact occupancy sensor in simulation and show its ability to detect the contact location on the robot from force sensing information. Then, we evaluate our method in a peg-in-hole task, demonstrating an improvement in the hole pose estimate with the fusion of the contact information with the SPSMap.
A Distributional Treatment of Real2Sim2Real for Vision-Driven Deformable Linear Object Manipulation
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:We present an integrated (or end-to-end) framework for the Real2Sim2Real problem of manipulating deformable linear objects (DLOs) based on visual perception. Working with a parameterised set of DLOs, we use likelihood-free inference (LFI) to compute the posterior distributions for the physical parameters using which we can approximately simulate the behaviour of each specific DLO. We use these posteriors for domain randomisation while training, in simulation, object-specific visuomotor policies for a visuomotor DLO reaching task, using model-free reinforcement learning. We demonstrate the utility of this approach by deploying sim-trained DLO manipulation policies in the real world in a zero-shot manner, i.e. without any further fine-tuning. In this context, we evaluate the capacity of a prominent LFI method to perform fine classification over the parametric set of DLOs, using only visual and proprioceptive data obtained in a dynamic manipulation trajectory. We then study the implications of the resulting domain distributions in sim-based policy learning and real-world performance.
Learning Visually Grounded Domain Ontologies via Embodied Conversation and Explanation
Dec 13, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we offer a learning framework in which the agent's knowledge gaps are overcome through corrective feedback from a teacher whenever the agent explains its (incorrect) predictions. We test it in a low-resource visual processing scenario, in which the agent must learn to recognize distinct types of toy truck. The agent starts the learning process with no ontology about what types of trucks exist nor which parts they have, and a deficient model for recognizing those parts from visual input. The teacher's feedback to the agent's explanations addresses its lack of relevant knowledge in the ontology via a generic rule (e.g., "dump trucks have dumpers"), whereas an inaccurate part recognition is corrected by a deictic statement (e.g., "this is not a dumper"). The learner utilizes this feedback not only to improve its estimate of the hypothesis space of possible domain ontologies and probability distributions over them, but also to use those estimates to update its visual interpretation of the scene. Our experiments demonstrate that teacher-learner pairs utilizing explanations and corrections are more data-efficient than those without such a faculty.
Learning a Neural Association Network for Self-supervised Multi-Object Tracking
Nov 18, 2024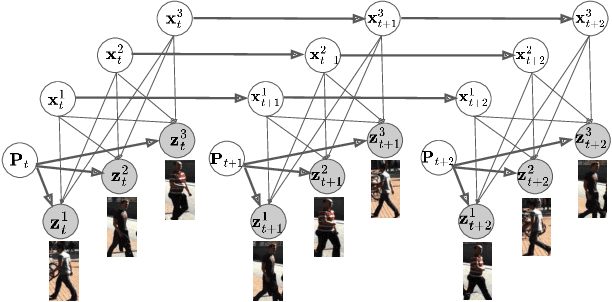
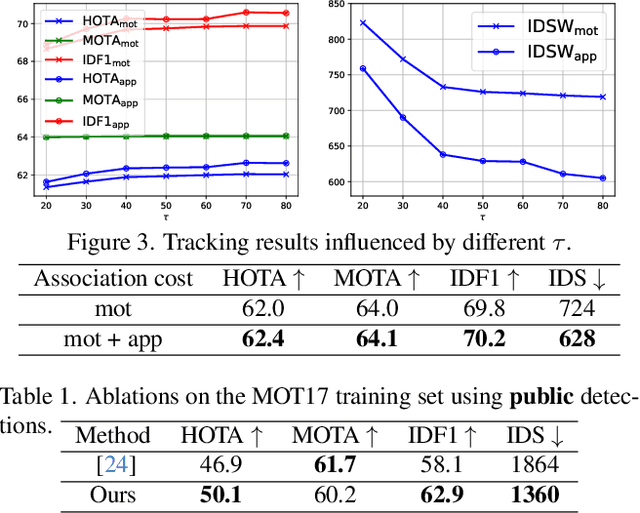
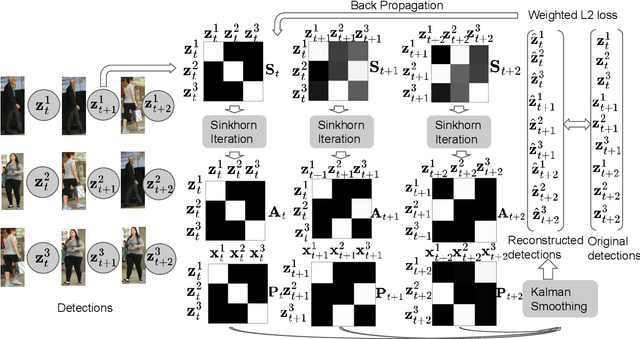
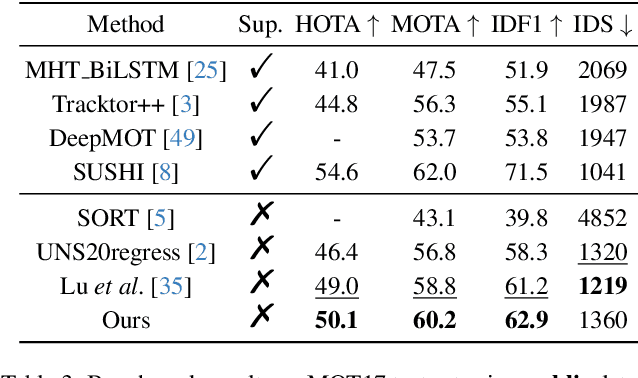
Abstract:This paper introduces a novel framework to learn data association for multi-object tracking in a self-supervised manner. Fully-supervised learning methods are known to achieve excellent tracking performances, but acquiring identity-level annotations is tedious and time-consuming. Motivated by the fact that in real-world scenarios object motion can be usually represented by a Markov process, we present a novel expectation maximization (EM) algorithm that trains a neural network to associate detections for tracking, without requiring prior knowledge of their temporal correspondences. At the core of our method lies a neural Kalman filter, with an observation model conditioned on associations of detections parameterized by a neural network. Given a batch of frames as input, data associations between detections from adjacent frames are predicted by a neural network followed by a Sinkhorn normalization that determines the assignment probabilities of detections to states. Kalman smoothing is then used to obtain the marginal probability of observations given the inferred states, producing a training objective to maximize this marginal probability using gradient descent. The proposed framework is fully differentiable, allowing the underlying neural model to be trained end-to-end. We evaluate our approach on the challenging MOT17 and MOT20 datasets and achieve state-of-the-art results in comparison to self-supervised trackers using public detections. We furthermore demonstrate the capability of the learned model to generalize across datasets.
Generating Driving Simulations via Conversation
Oct 13, 2024Abstract:Cyber-physical systems like autonomous vehicles are tested in simulation before deployment, using domain-specific programs for scenario specification. To aid the testing of autonomous vehicles in simulation, we design a natural language interface, using an instruction-following large language model, to assist a non-coding domain expert in synthesising the desired scenarios and vehicle behaviours. We show that using it to convert utterances to the symbolic program is feasible, despite the very small training dataset. Human experiments show that dialogue is critical to successful simulation generation, leading to a 4.5 times higher success rate than a generation without engaging in extended conversation.
Learning from Demonstration with Implicit Nonlinear Dynamics Models
Sep 27, 2024Abstract:Learning from Demonstration (LfD) is a useful paradigm for training policies that solve tasks involving complex motions. In practice, the successful application of LfD requires overcoming error accumulation during policy execution, i.e. the problem of drift due to errors compounding over time and the consequent out-of-distribution behaviours. Existing works seek to address this problem through scaling data collection, correcting policy errors with a human-in-the-loop, temporally ensembling policy predictions or through learning the parameters of a dynamical system model. In this work, we propose and validate an alternative approach to overcoming this issue. Inspired by reservoir computing, we develop a novel neural network layer that includes a fixed nonlinear dynamical system with tunable dynamical properties. We validate the efficacy of our neural network layer on the task of reproducing human handwriting motions using the LASA Human Handwriting Dataset. Through empirical experiments we demonstrate that incorporating our layer into existing neural network architectures addresses the issue of compounding errors in LfD. Furthermore, we perform a comparative evaluation against existing approaches including a temporal ensemble of policy predictions and an Echo State Networks (ESNs) implementation. We find that our approach yields greater policy precision and robustness on the handwriting task while also generalising to multiple dynamics regimes and maintaining competitive latency scores.
SECURE: Semantics-aware Embodied Conversation under Unawareness for Lifelong Robot Learning
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:This paper addresses a challenging interactive task learning scenario we call rearrangement under unawareness: to manipulate a rigid-body environment in a context where the robot is unaware of a concept that's key to solving the instructed task. We propose SECURE, an interactive task learning framework designed to solve such problems by fixing a deficient domain model using embodied conversation. Through dialogue, the robot discovers and then learns to exploit unforeseen possibilities. Using SECURE, the robot not only learns from the user's corrective feedback when it makes a mistake, but it also learns to make strategic dialogue decisions for revealing useful evidence about novel concepts for solving the instructed task. Together, these abilities allow the robot to generalise to subsequent tasks using newly acquired knowledge. We demonstrate that a robot that is semantics-aware -- that is, it exploits the logical consequences of both sentence and discourse semantics in the learning and inference process -- learns to solve rearrangement under unawareness more effectively than a robot that lacks such capabilities.
OPPH: A Vision-Based Operator for Measuring Body Movements for Personal Healthcare
Aug 18, 2024



Abstract:Vision-based motion estimation methods show promise in accurately and unobtrusively estimating human body motion for healthcare purposes. However, these methods are not specifically designed for healthcare purposes and face challenges in real-world applications. Human pose estimation methods often lack the accuracy needed for detecting fine-grained, subtle body movements, while optical flow-based methods struggle with poor lighting conditions and unseen real-world data. These issues result in human body motion estimation errors, particularly during critical medical situations where the body is motionless, such as during unconsciousness. To address these challenges and improve the accuracy of human body motion estimation for healthcare purposes, we propose the OPPH operator designed to enhance current vision-based motion estimation methods. This operator, which considers human body movement and noise properties, functions as a multi-stage filter. Results tested on two real-world and one synthetic human motion dataset demonstrate that the operator effectively removes real-world noise, significantly enhances the detection of motionless states, maintains the accuracy of estimating active body movements, and maintains long-term body movement trends. This method could be beneficial for analyzing both critical medical events and chronic medical conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge