Jonghyuk Park
MatteViT: High-Frequency-Aware Document Shadow Removal with Shadow Matte Guidance
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Document shadow removal is essential for enhancing the clarity of digitized documents. Preserving high-frequency details (e.g., text edges and lines) is critical in this process because shadows often obscure or distort fine structures. This paper proposes a matte vision transformer (MatteViT), a novel shadow removal framework that applies spatial and frequency-domain information to eliminate shadows while preserving fine-grained structural details. To effectively retain these details, we employ two preservation strategies. First, our method introduces a lightweight high-frequency amplification module (HFAM) that decomposes and adaptively amplifies high-frequency components. Second, we present a continuous luminance-based shadow matte, generated using a custom-built matte dataset and shadow matte generator, which provides precise spatial guidance from the earliest processing stage. These strategies enable the model to accurately identify fine-grained regions and restore them with high fidelity. Extensive experiments on public benchmarks (RDD and Kligler) demonstrate that MatteViT achieves state-of-the-art performance, providing a robust and practical solution for real-world document shadow removal. Furthermore, the proposed method better preserves text-level details in downstream tasks, such as optical character recognition, improving recognition performance over prior methods.
Refining Visual Artifacts in Diffusion Models via Explainable AI-based Flaw Activation Maps
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have achieved remarkable success in image synthesis. However, addressing artifacts and unrealistic regions remains a critical challenge. We propose self-refining diffusion, a novel framework that enhances image generation quality by detecting these flaws. The framework employs an explainable artificial intelligence (XAI)-based flaw highlighter to produce flaw activation maps (FAMs) that identify artifacts and unrealistic regions. These FAMs improve reconstruction quality by amplifying noise in flawed regions during the forward process and by focusing on these regions during the reverse process. The proposed approach achieves up to a 27.3% improvement in Fréchet inception distance across various diffusion-based models, demonstrating consistently strong performance on diverse datasets. It also shows robust effectiveness across different tasks, including image generation, text-to-image generation, and inpainting. These results demonstrate that explainable AI techniques can extend beyond interpretability to actively contribute to image refinement. The proposed framework offers a versatile and effective approach applicable to various diffusion models and tasks, significantly advancing the field of image synthesis.
Learning Visually Grounded Domain Ontologies via Embodied Conversation and Explanation
Dec 13, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we offer a learning framework in which the agent's knowledge gaps are overcome through corrective feedback from a teacher whenever the agent explains its (incorrect) predictions. We test it in a low-resource visual processing scenario, in which the agent must learn to recognize distinct types of toy truck. The agent starts the learning process with no ontology about what types of trucks exist nor which parts they have, and a deficient model for recognizing those parts from visual input. The teacher's feedback to the agent's explanations addresses its lack of relevant knowledge in the ontology via a generic rule (e.g., "dump trucks have dumpers"), whereas an inaccurate part recognition is corrected by a deictic statement (e.g., "this is not a dumper"). The learner utilizes this feedback not only to improve its estimate of the hypothesis space of possible domain ontologies and probability distributions over them, but also to use those estimates to update its visual interpretation of the scene. Our experiments demonstrate that teacher-learner pairs utilizing explanations and corrections are more data-efficient than those without such a faculty.
Interactive Acquisition of Fine-grained Visual Concepts by Exploiting Semantics of Generic Characterizations in Discourse
May 05, 2023Abstract:Interactive Task Learning (ITL) concerns learning about unforeseen domain concepts via natural interactions with human users. The learner faces a number of significant constraints: learning should be online, incremental and few-shot, as it is expected to perform tangible belief updates right after novel words denoting unforeseen concepts are introduced. In this work, we explore a challenging symbol grounding task--discriminating among object classes that look very similar--within the constraints imposed by ITL. We demonstrate empirically that more data-efficient grounding results from exploiting the truth-conditions of the teacher's generic statements (e.g., "Xs have attribute Z.") and their implicatures in context (e.g., as an answer to "How are Xs and Ys different?", one infers Y lacks attribute Z).
Improving 3D Imaging with Pre-Trained Perpendicular 2D Diffusion Models
Mar 15, 2023


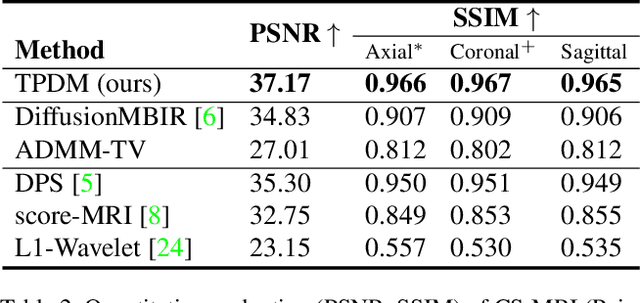
Abstract:Diffusion models have become a popular approach for image generation and reconstruction due to their numerous advantages. However, most diffusion-based inverse problem-solving methods only deal with 2D images, and even recently published 3D methods do not fully exploit the 3D distribution prior. To address this, we propose a novel approach using two perpendicular pre-trained 2D diffusion models to solve the 3D inverse problem. By modeling the 3D data distribution as a product of 2D distributions sliced in different directions, our method effectively addresses the curse of dimensionality. Our experimental results demonstrate that our method is highly effective for 3D medical image reconstruction tasks, including MRI Z-axis super-resolution, compressed sensing MRI, and sparse-view CT. Our method can generate high-quality voxel volumes suitable for medical applications.
HintPose
Mar 04, 2020
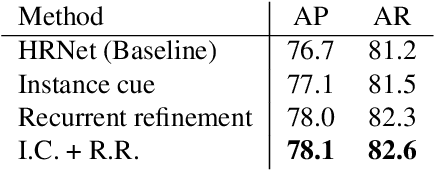
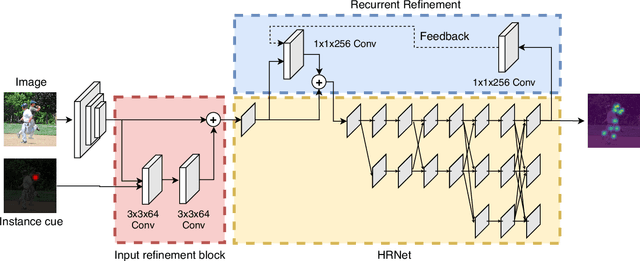
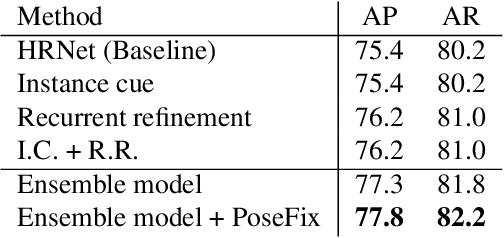
Abstract:Most of the top-down pose estimation models assume that there exists only one person in a bounding box. However, the assumption is not always correct. In this technical report, we introduce two ideas, instance cue and recurrent refinement, to an existing pose estimator so that the model is able to handle detection boxes with multiple persons properly. When we evaluated our model on the COCO17 keypoints dataset, it showed non-negligible improvement compared to its baseline model. Our model achieved 76.2 mAP as a single model and 77.3 mAP as an ensemble on the test-dev set without additional training data. After additional post-processing with a separate refinement network, our final predictions achieved 77.8 mAP on the COCO test-dev set.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge