Joschka Boedecker
Does TabPFN Understand Causal Structures?
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Causal discovery is fundamental for multiple scientific domains, yet extracting causal information from real world data remains a significant challenge. Given the recent success on real data, we investigate whether TabPFN, a transformer-based tabular foundation model pre-trained on synthetic datasets generated from structural causal models, encodes causal information in its internal representations. We develop an adapter framework using a learnable decoder and causal tokens that extract causal signals from TabPFN's frozen embeddings and decode them into adjacency matrices for causal discovery. Our evaluations demonstrate that TabPFN's embeddings contain causal information, outperforming several traditional causal discovery algorithms, with such causal information being concentrated in mid-range layers. These findings establish a new direction for interpretable and adaptable foundation models and demonstrate the potential for leveraging pre-trained tabular models for causal discovery.
Fitting Reinforcement Learning Model to Behavioral Data under Bandits
Nov 06, 2025


Abstract:We consider the problem of fitting a reinforcement learning (RL) model to some given behavioral data under a multi-armed bandit environment. These models have received much attention in recent years for characterizing human and animal decision making behavior. We provide a generic mathematical optimization problem formulation for the fitting problem of a wide range of RL models that appear frequently in scientific research applications, followed by a detailed theoretical analysis of its convexity properties. Based on the theoretical results, we introduce a novel solution method for the fitting problem of RL models based on convex relaxation and optimization. Our method is then evaluated in several simulated bandit environments to compare with some benchmark methods that appear in the literature. Numerical results indicate that our method achieves comparable performance to the state-of-the-art, while significantly reducing computation time. We also provide an open-source Python package for our proposed method to empower researchers to apply it in the analysis of their datasets directly, without prior knowledge of convex optimization.
Fast ECoT: Efficient Embodied Chain-of-Thought via Thoughts Reuse
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Embodied Chain-of-Thought (ECoT) reasoning enhances vision-language-action (VLA) models by improving performance and interpretability through intermediate reasoning steps. However, its sequential autoregressive token generation introduces significant inference latency, limiting real-time deployment. We propose Fast ECoT, an inference-time acceleration method that exploits the structured and repetitive nature of ECoT to (1) cache and reuse high-level reasoning across timesteps and (2) parallelise the generation of modular reasoning steps. Additionally, we introduce an asynchronous scheduler that decouples reasoning from action decoding, further boosting responsiveness. Fast ECoT requires no model changes or additional training and integrates easily into existing VLA pipelines. Experiments in both simulation (LIBERO) and real-world robot tasks show up to a 7.5% reduction in latency with comparable or improved task success rate and reasoning faithfulness, bringing ECoT policies closer to practical real-time deployment.
The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Discrete-Time Gaussian Process Mixtures for Robot Policy Learning
May 06, 2025Abstract:We present Mixture of Discrete-time Gaussian Processes (MiDiGap), a novel approach for flexible policy representation and imitation learning in robot manipulation. MiDiGap enables learning from as few as five demonstrations using only camera observations and generalizes across a wide range of challenging tasks. It excels at long-horizon behaviors such as making coffee, highly constrained motions such as opening doors, dynamic actions such as scooping with a spatula, and multimodal tasks such as hanging a mug. MiDiGap learns these tasks on a CPU in less than a minute and scales linearly to large datasets. We also develop a rich suite of tools for inference-time steering using evidence such as collision signals and robot kinematic constraints. This steering enables novel generalization capabilities, including obstacle avoidance and cross-embodiment policy transfer. MiDiGap achieves state-of-the-art performance on diverse few-shot manipulation benchmarks. On constrained RLBench tasks, it improves policy success by 76 percentage points and reduces trajectory cost by 67%. On multimodal tasks, it improves policy success by 48 percentage points and increases sample efficiency by a factor of 20. In cross-embodiment transfer, it more than doubles policy success. We make the code publicly available at https://midigap.cs.uni-freiburg.de.
Multi-convex Programming for Discrete Latent Factor Models Prototyping
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:Discrete latent factor models (DLFMs) are widely used in various domains such as machine learning, economics, neuroscience, psychology, etc. Currently, fitting a DLFM to some dataset relies on a customized solver for individual models, which requires lots of effort to implement and is limited to the targeted specific instance of DLFMs. In this paper, we propose a generic framework based on CVXPY, which allows users to specify and solve the fitting problem of a wide range of DLFMs, including both regression and classification models, within a very short script. Our framework is flexible and inherently supports the integration of regularization terms and constraints on the DLFM parameters and latent factors, such that the users can easily prototype the DLFM structure according to their dataset and application scenario. We introduce our open-source Python implementation and illustrate the framework in several examples.
Synthesis of Model Predictive Control and Reinforcement Learning: Survey and Classification
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:The fields of MPC and RL consider two successful control techniques for Markov decision processes. Both approaches are derived from similar fundamental principles, and both are widely used in practical applications, including robotics, process control, energy systems, and autonomous driving. Despite their similarities, MPC and RL follow distinct paradigms that emerged from diverse communities and different requirements. Various technical discrepancies, particularly the role of an environment model as part of the algorithm, lead to methodologies with nearly complementary advantages. Due to their orthogonal benefits, research interest in combination methods has recently increased significantly, leading to a large and growing set of complex ideas leveraging MPC and RL. This work illuminates the differences, similarities, and fundamentals that allow for different combination algorithms and categorizes existing work accordingly. Particularly, we focus on the versatile actor-critic RL approach as a basis for our categorization and examine how the online optimization approach of MPC can be used to improve the overall closed-loop performance of a policy.
Solving Inverse Problem for Multi-armed Bandits via Convex Optimization
Jan 31, 2025Abstract:We consider the inverse problem of multi-armed bandits (IMAB) that are widely used in neuroscience and psychology research for behavior modelling. We first show that the IMAB problem is not convex in general, but can be relaxed to a convex problem via variable transformation. Based on this result, we propose a two-step sequential heuristic for (approximately) solving the IMAB problem. We discuss a condition where our method provides global solution to the IMAB problem with certificate, as well as approximations to further save computing time. Numerical experiments indicate that our heuristic method is more robust than directly solving the IMAB problem via repeated local optimization, and can achieve the performance of Monte Carlo methods within a significantly decreased running time. We provide the implementation of our method based on CVXPY, which allows straightforward application by users not well versed in convex optimization.
Inverse Reinforcement Learning via Convex Optimization
Jan 27, 2025

Abstract:We consider the inverse reinforcement learning (IRL) problem, where an unknown reward function of some Markov decision process is estimated based on observed expert demonstrations. In most existing approaches, IRL is formulated and solved as a nonconvex optimization problem, posing challenges in scenarios where robustness and reproducibility are critical. We discuss a convex formulation of the IRL problem (CIRL) initially proposed by Ng and Russel, and reformulate the problem such that the domain-specific language CVXPY can be applied directly to specify and solve the convex problem. We also extend the CIRL problem to scenarios where the expert policy is not given analytically but by trajectory as state-action pairs, which can be strongly inconsistent with optimality, by augmenting some of the constraints. Theoretical analysis and practical implementation for hyperparameter auto-selection are introduced. This note helps the users to easily apply CIRL for their problems, without background knowledge on convex optimization.
SR-Reward: Taking The Path More Traveled
Jan 04, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel method for learning reward functions directly from offline demonstrations. Unlike traditional inverse reinforcement learning (IRL), our approach decouples the reward function from the learner's policy, eliminating the adversarial interaction typically required between the two. This results in a more stable and efficient training process. Our reward function, called \textit{SR-Reward}, leverages successor representation (SR) to encode a state based on expected future states' visitation under the demonstration policy and transition dynamics. By utilizing the Bellman equation, SR-Reward can be learned concurrently with most reinforcement learning (RL) algorithms without altering the existing training pipeline. We also introduce a negative sampling strategy to mitigate overestimation errors by reducing rewards for out-of-distribution data, thereby enhancing robustness. This strategy inherently introduces a conservative bias into RL algorithms that employ the learned reward. We evaluate our method on the D4RL benchmark, achieving competitive results compared to offline RL algorithms with access to true rewards and imitation learning (IL) techniques like behavioral cloning. Moreover, our ablation studies on data size and quality reveal the advantages and limitations of SR-Reward as a proxy for true rewards.
The Surprising Ineffectiveness of Pre-Trained Visual Representations for Model-Based Reinforcement Learning
Nov 15, 2024
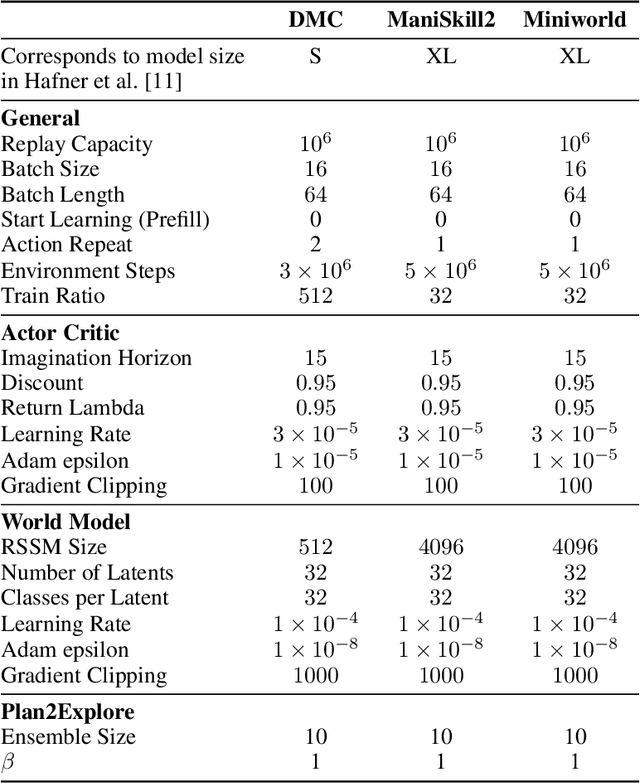

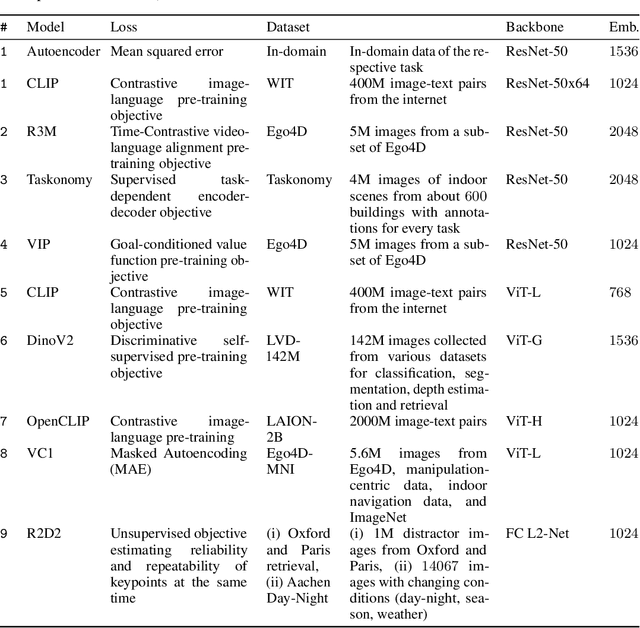
Abstract:Visual Reinforcement Learning (RL) methods often require extensive amounts of data. As opposed to model-free RL, model-based RL (MBRL) offers a potential solution with efficient data utilization through planning. Additionally, RL lacks generalization capabilities for real-world tasks. Prior work has shown that incorporating pre-trained visual representations (PVRs) enhances sample efficiency and generalization. While PVRs have been extensively studied in the context of model-free RL, their potential in MBRL remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we benchmark a set of PVRs on challenging control tasks in a model-based RL setting. We investigate the data efficiency, generalization capabilities, and the impact of different properties of PVRs on the performance of model-based agents. Our results, perhaps surprisingly, reveal that for MBRL current PVRs are not more sample efficient than learning representations from scratch, and that they do not generalize better to out-of-distribution (OOD) settings. To explain this, we analyze the quality of the trained dynamics model. Furthermore, we show that data diversity and network architecture are the most important contributors to OOD generalization performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge