Svetha Venkatesh
Score-based Integrated Gradient for Root Cause Explanations of Outliers
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Identifying the root causes of outliers is a fundamental problem in causal inference and anomaly detection. Traditional approaches based on heuristics or counterfactual reasoning often struggle under uncertainty and high-dimensional dependencies. We introduce SIREN, a novel and scalable method that attributes the root causes of outliers by estimating the score functions of the data likelihood. Attribution is computed via integrated gradients that accumulate score contributions along paths from the outlier toward the normal data distribution. Our method satisfies three of the four classic Shapley value axioms - dummy, efficiency, and linearity - as well as an asymmetry axiom derived from the underlying causal structure. Unlike prior work, SIREN operates directly on the score function, enabling tractable and uncertainty-aware root cause attribution in nonlinear, high-dimensional, and heteroscedastic causal models. Extensive experiments on synthetic random graphs and real-world cloud service and supply chain datasets show that SIREN outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in both attribution accuracy and computational efficiency.
Federated Domain Generalization with Latent Space Inversion
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Federated domain generalization (FedDG) addresses distribution shifts among clients in a federated learning framework. FedDG methods aggregate the parameters of locally trained client models to form a global model that generalizes to unseen clients while preserving data privacy. While improving the generalization capability of the global model, many existing approaches in FedDG jeopardize privacy by sharing statistics of client data between themselves. Our solution addresses this problem by contributing new ways to perform local client training and model aggregation. To improve local client training, we enforce (domain) invariance across local models with the help of a novel technique, \textbf{latent space inversion}, which enables better client privacy. When clients are not \emph{i.i.d}, aggregating their local models may discard certain local adaptations. To overcome this, we propose an \textbf{important weight} aggregation strategy to prioritize parameters that significantly influence predictions of local models during aggregation. Our extensive experiments show that our approach achieves superior results over state-of-the-art methods with less communication overhead.
Uncertainty-Guided Checkpoint Selection for Reinforcement Finetuning of Large Language Models
Nov 13, 2025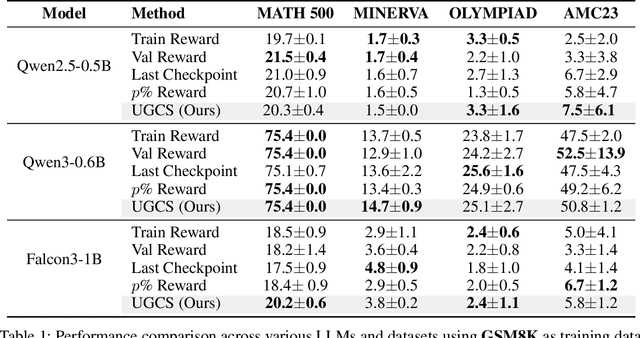
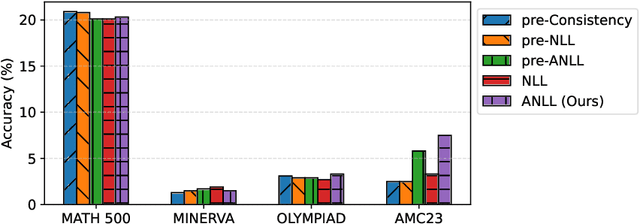
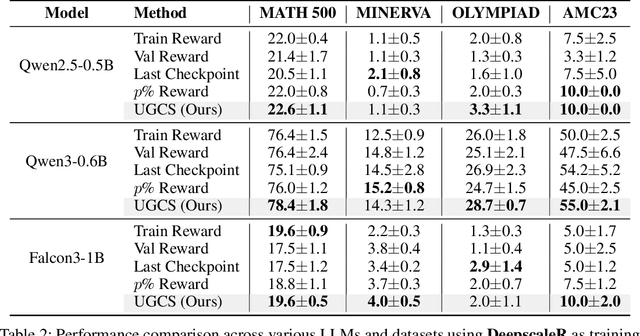
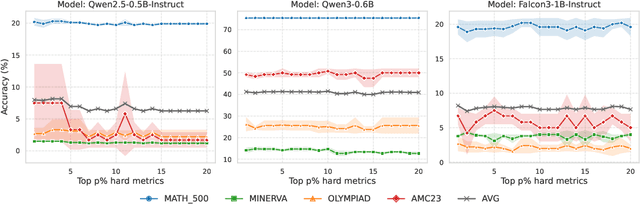
Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) finetuning is crucial to aligning large language models (LLMs), but the process is notoriously unstable and exhibits high variance across model checkpoints. In practice, selecting the best checkpoint is challenging: evaluating checkpoints on the validation set during training is computationally expensive and requires a good validation set, while relying on the final checkpoint provides no guarantee of good performance. We introduce an uncertainty-guided approach for checkpoint selection (UGCS) that avoids these pitfalls. Our method identifies hard question-answer pairs using per-sample uncertainty and ranks checkpoints by how well they handle these challenging cases. By averaging the rewards of the top-uncertain samples over a short training window, our method produces a stable and discriminative signal without additional forward passes or significant computation overhead. Experiments across three datasets and three LLMs demonstrate that it consistently identifies checkpoints with stronger generalization, outperforming traditional strategies such as relying on training or validation performance. These results highlight that models solving their hardest tasks with low uncertainty are the most reliable overall.
SPaRFT: Self-Paced Reinforcement Fine-Tuning for Large Language Models
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown strong reasoning capabilities when fine-tuned with reinforcement learning (RL). However, such methods require extensive data and compute, making them impractical for smaller models. Current approaches to curriculum learning or data selection are largely heuristic-driven or demand extensive computational resources, limiting their scalability and generalizability. We propose \textbf{SPaRFT}, a self-paced learning framework that enables efficient learning based on the capability of the model being trained through optimizing which data to use and when. First, we apply \emph{cluster-based data reduction} to partition training data by semantics and difficulty, extracting a compact yet diverse subset that reduces redundancy. Then, a \emph{multi-armed bandit} treats data clusters as arms, optimized to allocate training samples based on model current performance. Experiments across multiple reasoning benchmarks show that SPaRFT achieves comparable or better accuracy than state-of-the-art baselines while using up to \(100\times\) fewer samples. Ablation studies and analyses further highlight the importance of both data clustering and adaptive selection. Our results demonstrate that carefully curated, performance-driven training curricula can unlock strong reasoning abilities in LLMs with minimal resources.
Reasoning Under 1 Billion: Memory-Augmented Reinforcement Learning for Large Language Models
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) with reinforcement learning (RL) have shown promising improvements in complex reasoning tasks, particularly when paired with chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting. However, these successes have been largely demonstrated on large-scale models with billions of parameters, where a strong pretraining foundation ensures effective initial exploration. In contrast, RL remains challenging for tiny LLMs with 1 billion parameters or fewer because they lack the necessary pretraining strength to explore effectively, often leading to suboptimal reasoning patterns. This work introduces a novel intrinsic motivation approach that leverages episodic memory to address this challenge, improving tiny LLMs in CoT reasoning tasks. Inspired by human memory-driven learning, our method leverages successful reasoning patterns stored in memory while allowing for controlled exploration to generate novel responses. Intrinsic rewards are computed efficiently using a kNN-based episodic memory, allowing the model to discover new reasoning strategies while quickly adapting to effective past solutions. Experiments on fine-tuning GSM8K and AI-MO datasets demonstrate that our approach significantly enhances smaller LLMs' sample efficiency and generalization capability, making RL-based reasoning improvements more accessible in low-resource settings.
Finding the Trigger: Causal Abductive Reasoning on Video Events
Jan 16, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces a new problem, Causal Abductive Reasoning on Video Events (CARVE), which involves identifying causal relationships between events in a video and generating hypotheses about causal chains that account for the occurrence of a target event. To facilitate research in this direction, we create two new benchmark datasets with both synthetic and realistic videos, accompanied by trigger-target labels generated through a novel counterfactual synthesis approach. To explore the challenge of solving CARVE, we present a Causal Event Relation Network (CERN) that examines the relationships between video events in temporal and semantic spaces to efficiently determine the root-cause trigger events. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate the critical roles of event relational representation learning and interaction modeling in solving video causal reasoning challenges. The introduction of the CARVE task, along with the accompanying datasets and the CERN framework, will advance future research on video causal reasoning and significantly facilitate various applications, including video surveillance, root-cause analysis and movie content management.
Predicting the Reliability of an Image Classifier under Image Distortion
Dec 22, 2024Abstract:In image classification tasks, deep learning models are vulnerable to image distortions i.e. their accuracy significantly drops if the input images are distorted. An image-classifier is considered "reliable" if its accuracy on distorted images is above a user-specified threshold. For a quality control purpose, it is important to predict if the image-classifier is unreliable/reliable under a distortion level. In other words, we want to predict whether a distortion level makes the image-classifier "non-reliable" or "reliable". Our solution is to construct a training set consisting of distortion levels along with their "non-reliable" or "reliable" labels, and train a machine learning predictive model (called distortion-classifier) to classify unseen distortion levels. However, learning an effective distortion-classifier is a challenging problem as the training set is highly imbalanced. To address this problem, we propose two Gaussian process based methods to rebalance the training set. We conduct extensive experiments to show that our method significantly outperforms several baselines on six popular image datasets.
Efficient Symmetry-Aware Materials Generation via Hierarchical Generative Flow Networks
Nov 06, 2024



Abstract:Discovering new solid-state materials requires rapidly exploring the vast space of crystal structures and locating stable regions. Generating stable materials with desired properties and compositions is extremely difficult as we search for very small isolated pockets in the exponentially many possibilities, considering elements from the periodic table and their 3D arrangements in crystal lattices. Materials discovery necessitates both optimized solution structures and diversity in the generated material structures. Existing methods struggle to explore large material spaces and generate diverse samples with desired properties and requirements. We propose the Symmetry-aware Hierarchical Architecture for Flow-based Traversal (SHAFT), a novel generative model employing a hierarchical exploration strategy to efficiently exploit the symmetry of the materials space to generate crystal structures given desired properties. In particular, our model decomposes the exponentially large materials space into a hierarchy of subspaces consisting of symmetric space groups, lattice parameters, and atoms. We demonstrate that SHAFT significantly outperforms state-of-the-art iterative generative methods, such as Generative Flow Networks (GFlowNets) and Crystal Diffusion Variational AutoEncoders (CDVAE), in crystal structure generation tasks, achieving higher validity, diversity, and stability of generated structures optimized for target properties and requirements.
Generating Realistic Tabular Data with Large Language Models
Oct 29, 2024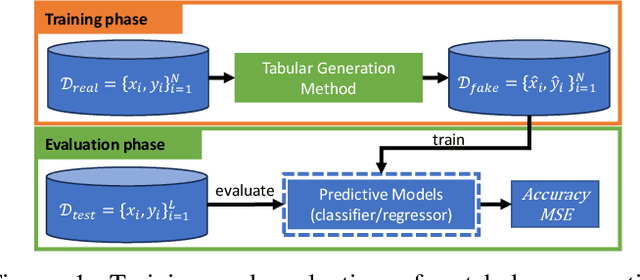

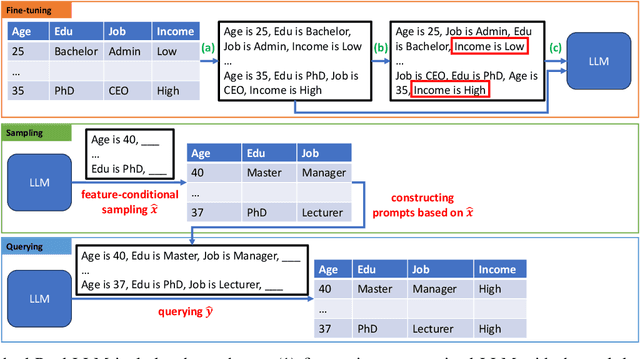
Abstract:While most generative models show achievements in image data generation, few are developed for tabular data generation. Recently, due to success of large language models (LLM) in diverse tasks, they have also been used for tabular data generation. However, these methods do not capture the correct correlation between the features and the target variable, hindering their applications in downstream predictive tasks. To address this problem, we propose a LLM-based method with three important improvements to correctly capture the ground-truth feature-class correlation in the real data. First, we propose a novel permutation strategy for the input data in the fine-tuning phase. Second, we propose a feature-conditional sampling approach to generate synthetic samples. Finally, we generate the labels by constructing prompts based on the generated samples to query our fine-tuned LLM. Our extensive experiments show that our method significantly outperforms 10 SOTA baselines on 20 datasets in downstream tasks. It also produces highly realistic synthetic samples in terms of quality and diversity. More importantly, classifiers trained with our synthetic data can even compete with classifiers trained with the original data on half of the benchmark datasets, which is a significant achievement in tabular data generation.
Stable Hadamard Memory: Revitalizing Memory-Augmented Agents for Reinforcement Learning
Oct 14, 2024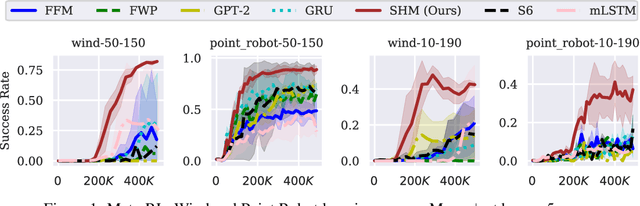
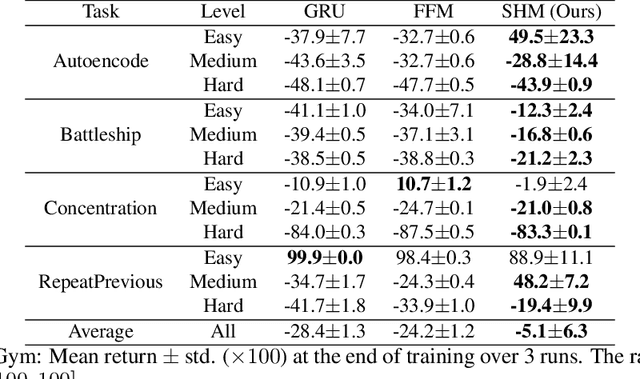
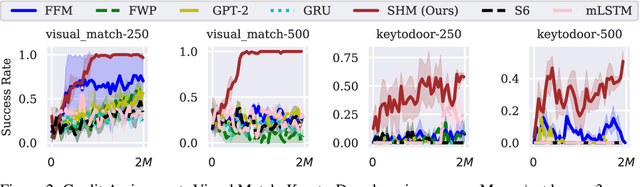

Abstract:Effective decision-making in partially observable environments demands robust memory management. Despite their success in supervised learning, current deep-learning memory models struggle in reinforcement learning environments that are partially observable and long-term. They fail to efficiently capture relevant past information, adapt flexibly to changing observations, and maintain stable updates over long episodes. We theoretically analyze the limitations of existing memory models within a unified framework and introduce the Stable Hadamard Memory, a novel memory model for reinforcement learning agents. Our model dynamically adjusts memory by erasing no longer needed experiences and reinforcing crucial ones computationally efficiently. To this end, we leverage the Hadamard product for calibrating and updating memory, specifically designed to enhance memory capacity while mitigating numerical and learning challenges. Our approach significantly outperforms state-of-the-art memory-based methods on challenging partially observable benchmarks, such as meta-reinforcement learning, long-horizon credit assignment, and POPGym, demonstrating superior performance in handling long-term and evolving contexts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge