Jessica Ojo
InkubaLM: A small language model for low-resource African languages
Sep 03, 2024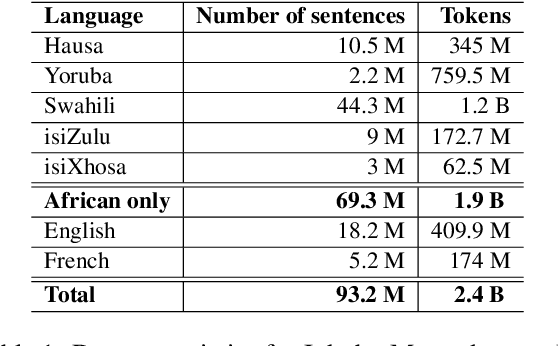
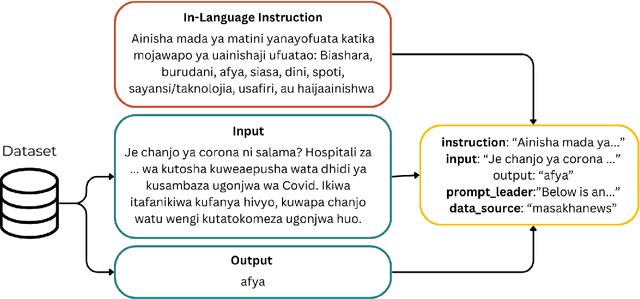
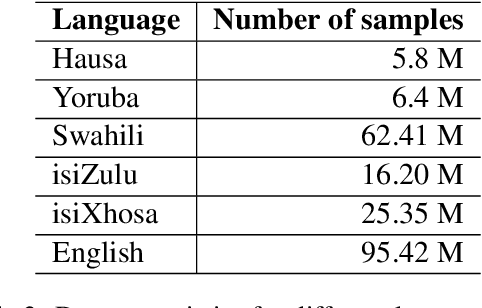
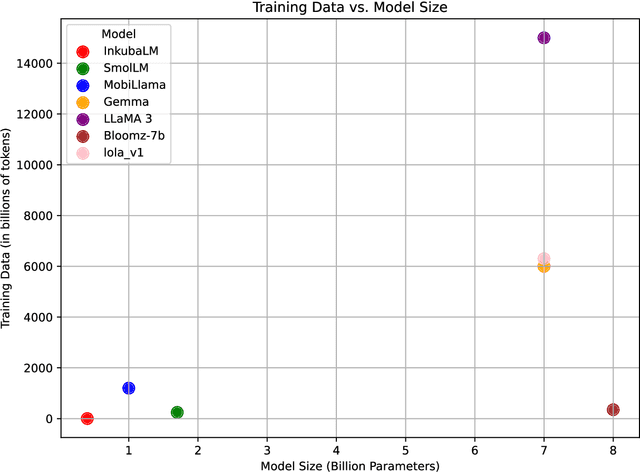
Abstract:High-resource language models often fall short in the African context, where there is a critical need for models that are efficient, accessible, and locally relevant, even amidst significant computing and data constraints. This paper introduces InkubaLM, a small language model with 0.4 billion parameters, which achieves performance comparable to models with significantly larger parameter counts and more extensive training data on tasks such as machine translation, question-answering, AfriMMLU, and the AfriXnli task. Notably, InkubaLM outperforms many larger models in sentiment analysis and demonstrates remarkable consistency across multiple languages. This work represents a pivotal advancement in challenging the conventional paradigm that effective language models must rely on substantial resources. Our model and datasets are publicly available at https://huggingface.co/lelapa to encourage research and development on low-resource languages.
IrokoBench: A New Benchmark for African Languages in the Age of Large Language Models
Jun 05, 2024
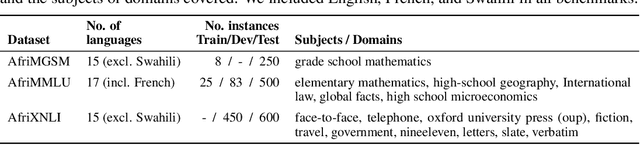
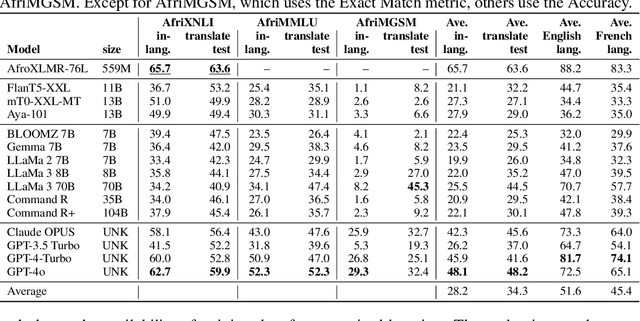
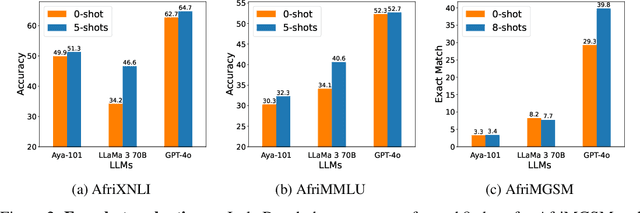
Abstract:Despite the widespread adoption of Large language models (LLMs), their remarkable capabilities remain limited to a few high-resource languages. Additionally, many low-resource languages (e.g. African languages) are often evaluated only on basic text classification tasks due to the lack of appropriate or comprehensive benchmarks outside of high-resource languages. In this paper, we introduce IrokoBench -- a human-translated benchmark dataset for 16 typologically-diverse low-resource African languages covering three tasks: natural language inference~(AfriXNLI), mathematical reasoning~(AfriMGSM), and multi-choice knowledge-based QA~(AfriMMLU). We use IrokoBench to evaluate zero-shot, few-shot, and translate-test settings~(where test sets are translated into English) across 10 open and four proprietary LLMs. Our evaluation reveals a significant performance gap between high-resource languages~(such as English and French) and low-resource African languages. We observe a significant performance gap between open and proprietary models, with the highest performing open model, Aya-101 only at 58\% of the best-performing proprietary model GPT-4o performance. Machine translating the test set to English before evaluation helped to close the gap for larger models that are English-centric, like LLaMa 3 70B. These findings suggest that more efforts are needed to develop and adapt LLMs for African languages.
AfriMTE and AfriCOMET: Empowering COMET to Embrace Under-resourced African Languages
Nov 16, 2023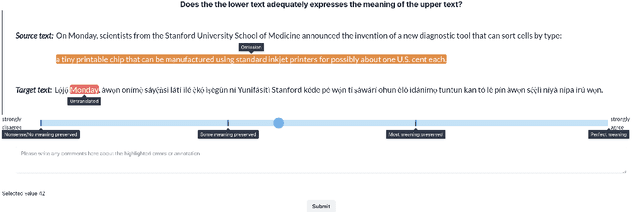
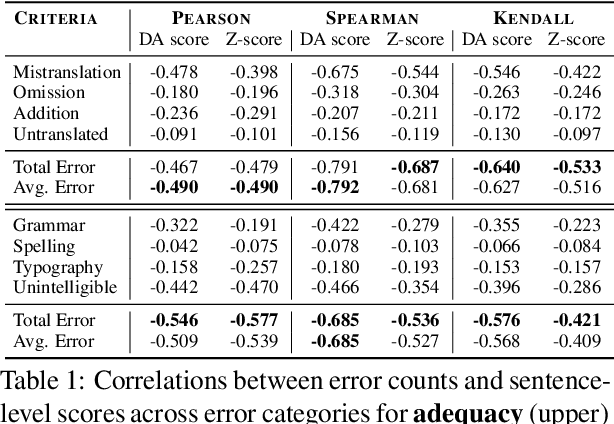
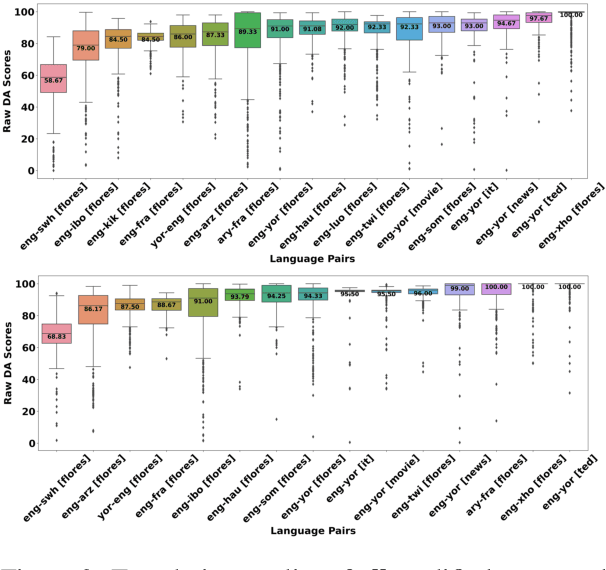
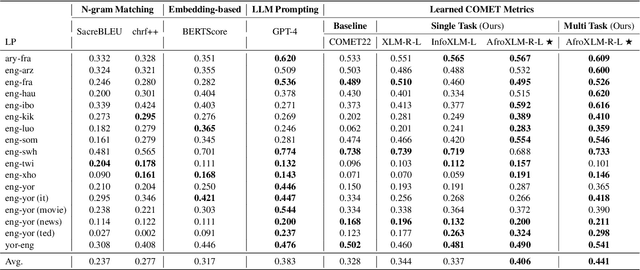
Abstract:Despite the progress we have recorded in scaling multilingual machine translation (MT) models and evaluation data to several under-resourced African languages, it is difficult to measure accurately the progress we have made on these languages because evaluation is often performed on n-gram matching metrics like BLEU that often have worse correlation with human judgments. Embedding-based metrics such as COMET correlate better; however, lack of evaluation data with human ratings for under-resourced languages, complexity of annotation guidelines like Multidimensional Quality Metrics (MQM), and limited language coverage of multilingual encoders have hampered their applicability to African languages. In this paper, we address these challenges by creating high-quality human evaluation data with a simplified MQM guideline for error-span annotation and direct assessment (DA) scoring for 13 typologically diverse African languages. Furthermore, we develop AfriCOMET, a COMET evaluation metric for African languages by leveraging DA training data from high-resource languages and African-centric multilingual encoder (AfroXLM-Roberta) to create the state-of-the-art evaluation metric for African languages MT with respect to Spearman-rank correlation with human judgments (+0.406).
How good are Large Language Models on African Languages?
Nov 14, 2023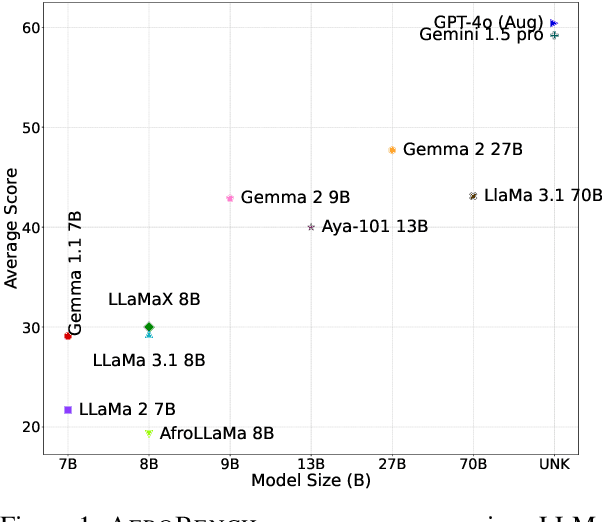



Abstract:Recent advancements in natural language processing have led to the proliferation of large language models (LLMs). These models have been shown to yield good performance, using in-context learning, even on unseen tasks and languages. Additionally, they have been widely adopted as language-model-as-a-service commercial APIs like GPT-4 API. However, their performance on African languages is largely unknown. We present an analysis of three popular large language models (mT0, LLaMa 2, and GPT-4) on five tasks (news topic classification, sentiment classification, machine translation, question answering, and named entity recognition) across 30 African languages, spanning different language families and geographical regions. Our results suggest that all LLMs produce below-par performance on African languages, and there is a large gap in performance compared to high-resource languages like English most tasks. We find that GPT-4 has an average or impressive performance on classification tasks but very poor results on generative tasks like machine translation. Surprisingly, we find that mT0 had the best overall on cross-lingual QA, better than the state-of-the-art supervised model (i.e. fine-tuned mT5) and GPT-4 on African languages. Overall, LLaMa 2 records the worst performance due to its limited multilingual capabilities and English-centric pre-training corpus. In general, our findings present a call-to-action to ensure African languages are well represented in large language models, given their growing popularity.
How Good are Commercial Large Language Models on African Languages?
May 11, 2023


Abstract:Recent advancements in Natural Language Processing (NLP) has led to the proliferation of large pretrained language models. These models have been shown to yield good performance, using in-context learning, even on unseen tasks and languages. They have also been exposed as commercial APIs as a form of language-model-as-a-service, with great adoption. However, their performance on African languages is largely unknown. We present a preliminary analysis of commercial large language models on two tasks (machine translation and text classification) across eight African languages, spanning different language families and geographical areas. Our results suggest that commercial language models produce below-par performance on African languages. We also find that they perform better on text classification than machine translation. In general, our findings present a call-to-action to ensure African languages are well represented in commercial large language models, given their growing popularity.
MasakhaNEWS: News Topic Classification for African languages
Apr 19, 2023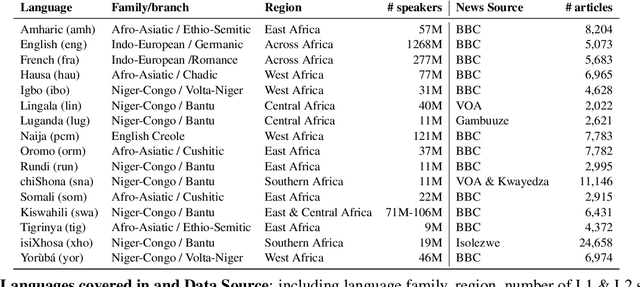
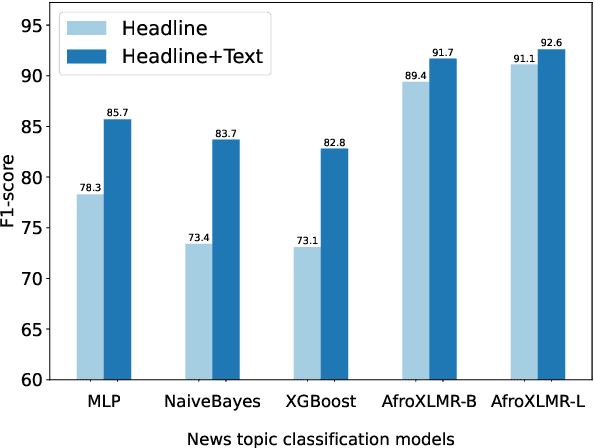
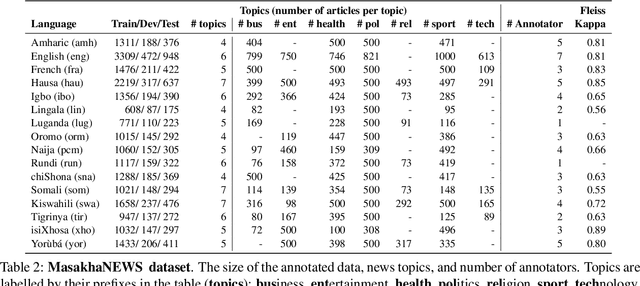
Abstract:African languages are severely under-represented in NLP research due to lack of datasets covering several NLP tasks. While there are individual language specific datasets that are being expanded to different tasks, only a handful of NLP tasks (e.g. named entity recognition and machine translation) have standardized benchmark datasets covering several geographical and typologically-diverse African languages. In this paper, we develop MasakhaNEWS -- a new benchmark dataset for news topic classification covering 16 languages widely spoken in Africa. We provide an evaluation of baseline models by training classical machine learning models and fine-tuning several language models. Furthermore, we explore several alternatives to full fine-tuning of language models that are better suited for zero-shot and few-shot learning such as cross-lingual parameter-efficient fine-tuning (like MAD-X), pattern exploiting training (PET), prompting language models (like ChatGPT), and prompt-free sentence transformer fine-tuning (SetFit and Cohere Embedding API). Our evaluation in zero-shot setting shows the potential of prompting ChatGPT for news topic classification in low-resource African languages, achieving an average performance of 70 F1 points without leveraging additional supervision like MAD-X. In few-shot setting, we show that with as little as 10 examples per label, we achieved more than 90\% (i.e. 86.0 F1 points) of the performance of full supervised training (92.6 F1 points) leveraging the PET approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge