Doreen Nixdorf
Text Categorization Can Enhance Domain-Agnostic Stopword Extraction
Jan 24, 2024Abstract:This paper investigates the role of text categorization in streamlining stopword extraction in natural language processing (NLP), specifically focusing on nine African languages alongside French. By leveraging the MasakhaNEWS, African Stopwords Project, and MasakhaPOS datasets, our findings emphasize that text categorization effectively identifies domain-agnostic stopwords with over 80% detection success rate for most examined languages. Nevertheless, linguistic variances result in lower detection rates for certain languages. Interestingly, we find that while over 40% of stopwords are common across news categories, less than 15% are unique to a single category. Uncommon stopwords add depth to text but their classification as stopwords depends on context. Therefore combining statistical and linguistic approaches creates comprehensive stopword lists, highlighting the value of our hybrid method. This research enhances NLP for African languages and underscores the importance of text categorization in stopword extraction.
MasakhaNEWS: News Topic Classification for African languages
Apr 19, 2023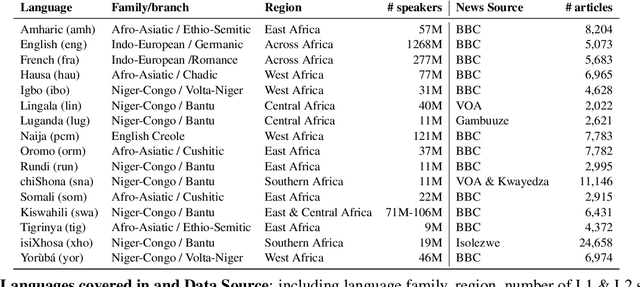
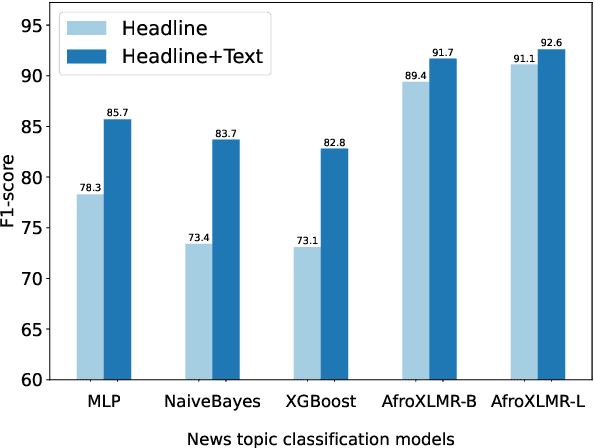
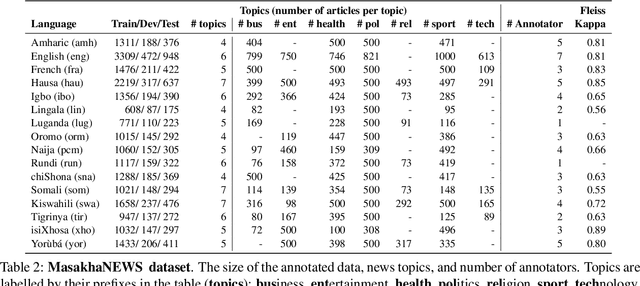
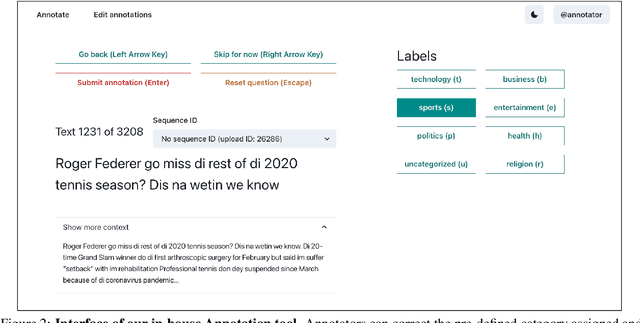
Abstract:African languages are severely under-represented in NLP research due to lack of datasets covering several NLP tasks. While there are individual language specific datasets that are being expanded to different tasks, only a handful of NLP tasks (e.g. named entity recognition and machine translation) have standardized benchmark datasets covering several geographical and typologically-diverse African languages. In this paper, we develop MasakhaNEWS -- a new benchmark dataset for news topic classification covering 16 languages widely spoken in Africa. We provide an evaluation of baseline models by training classical machine learning models and fine-tuning several language models. Furthermore, we explore several alternatives to full fine-tuning of language models that are better suited for zero-shot and few-shot learning such as cross-lingual parameter-efficient fine-tuning (like MAD-X), pattern exploiting training (PET), prompting language models (like ChatGPT), and prompt-free sentence transformer fine-tuning (SetFit and Cohere Embedding API). Our evaluation in zero-shot setting shows the potential of prompting ChatGPT for news topic classification in low-resource African languages, achieving an average performance of 70 F1 points without leveraging additional supervision like MAD-X. In few-shot setting, we show that with as little as 10 examples per label, we achieved more than 90\% (i.e. 86.0 F1 points) of the performance of full supervised training (92.6 F1 points) leveraging the PET approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge