Heather Pon-Barry
Dialogue with Robots: Proposals for Broadening Participation and Research in the SLIVAR Community
Apr 01, 2024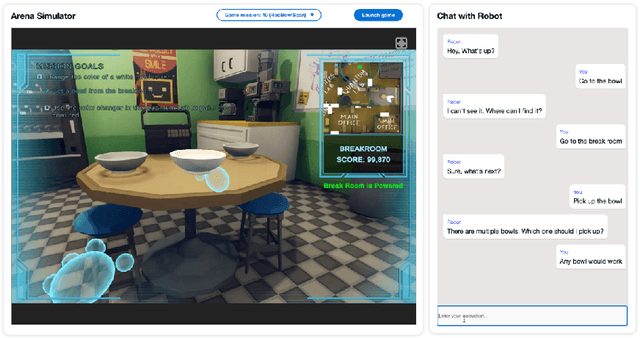
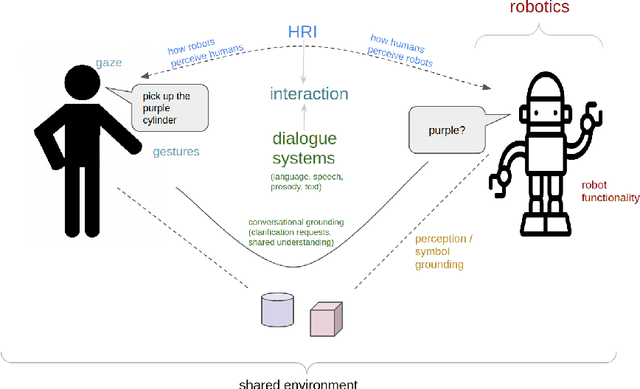
Abstract:The ability to interact with machines using natural human language is becoming not just commonplace, but expected. The next step is not just text interfaces, but speech interfaces and not just with computers, but with all machines including robots. In this paper, we chronicle the recent history of this growing field of spoken dialogue with robots and offer the community three proposals, the first focused on education, the second on benchmarks, and the third on the modeling of language when it comes to spoken interaction with robots. The three proposals should act as white papers for any researcher to take and build upon.
Finding Eyewitness Tweets During Crises
Mar 07, 2014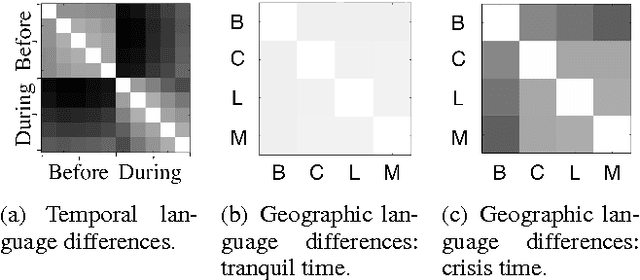
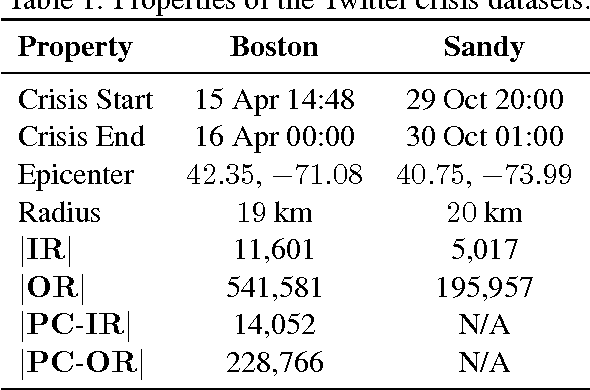
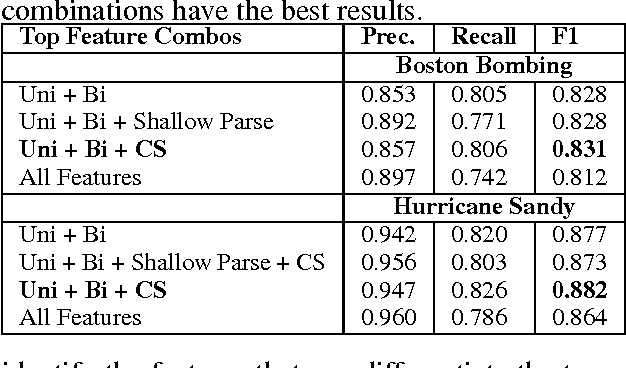
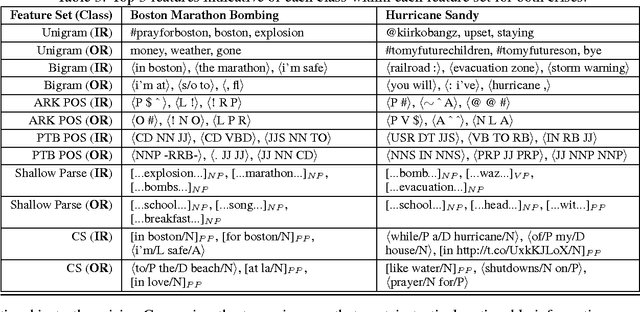
Abstract:Disaster response agencies have started to incorporate social media as a source of fast-breaking information to understand the needs of people affected by the many crises that occur around the world. These agencies look for tweets from within the region affected by the crisis to get the latest updates of the status of the affected region. However only 1% of all tweets are geotagged with explicit location information. First responders lose valuable information because they cannot assess the origin of many of the tweets they collect. In this work we seek to identify non-geotagged tweets that originate from within the crisis region. Towards this, we address three questions: (1) is there a difference between the language of tweets originating within a crisis region and tweets originating outside the region, (2) what are the linguistic patterns that can be used to differentiate within-region and outside-region tweets, and (3) for non-geotagged tweets, can we automatically identify those originating within the crisis region in real-time?
Recognizing Uncertainty in Speech
Mar 09, 2011



Abstract:We address the problem of inferring a speaker's level of certainty based on prosodic information in the speech signal, which has application in speech-based dialogue systems. We show that using phrase-level prosodic features centered around the phrases causing uncertainty, in addition to utterance-level prosodic features, improves our model's level of certainty classification. In addition, our models can be used to predict which phrase a person is uncertain about. These results rely on a novel method for eliciting utterances of varying levels of certainty that allows us to compare the utility of contextually-based feature sets. We elicit level of certainty ratings from both the speakers themselves and a panel of listeners, finding that there is often a mismatch between speakers' internal states and their perceived states, and highlighting the importance of this distinction.
* 11 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge