Jürgen Pfeffer
The Power of 10: New Rules for the Digital World
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:As artificial intelligence rapidly advances, society is increasingly captivated by promises of superhuman machines and seamless digital futures. Yet these visions often obscure mounting social, ethical, and psychological concerns tied to pervasive digital technologies - from surveillance to mental health crises. This article argues that a guiding ethos is urgently needed to navigate these transformations. Inspired by the lasting influence of the biblical Ten Commandments, a European interdisciplinary group has proposed "Ten Rules for the Digital World" - a novel ethical framework to help individuals and societies make prudent, human-centered decisions in the age of "supercharged" technology.
The Language of Trauma: Modeling Traumatic Event Descriptions Across Domains with Explainable AI
Aug 12, 2024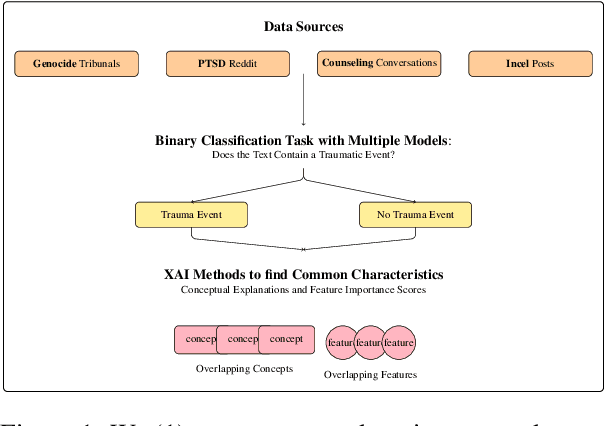

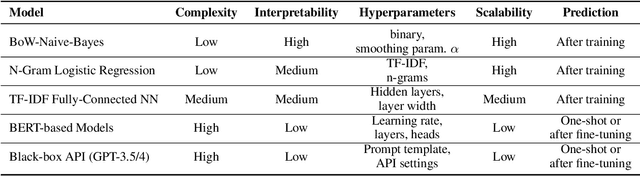
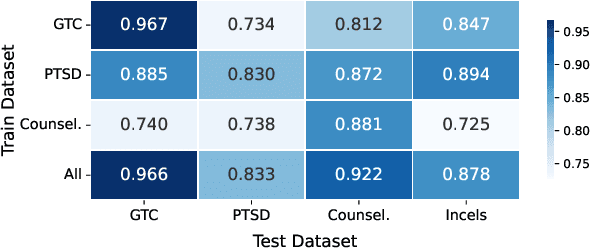
Abstract:Psychological trauma can manifest following various distressing events and is captured in diverse online contexts. However, studies traditionally focus on a single aspect of trauma, often neglecting the transferability of findings across different scenarios. We address this gap by training language models with progressing complexity on trauma-related datasets, including genocide-related court data, a Reddit dataset on post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), counseling conversations, and Incel forum posts. Our results show that the fine-tuned RoBERTa model excels in predicting traumatic events across domains, slightly outperforming large language models like GPT-4. Additionally, SLALOM-feature scores and conceptual explanations effectively differentiate and cluster trauma-related language, highlighting different trauma aspects and identifying sexual abuse and experiences related to death as a common traumatic event across all datasets. This transferability is crucial as it allows for the development of tools to enhance trauma detection and intervention in diverse populations and settings.
Can Smartphone Co-locations Detect Friendship? It Depends How You Model It
Aug 31, 2020
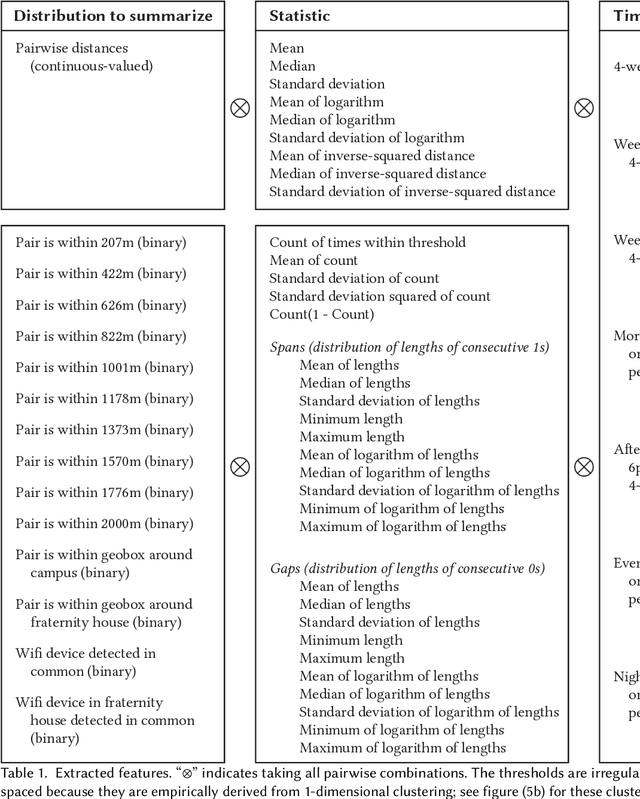
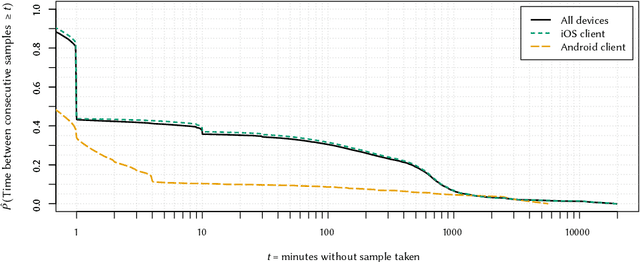
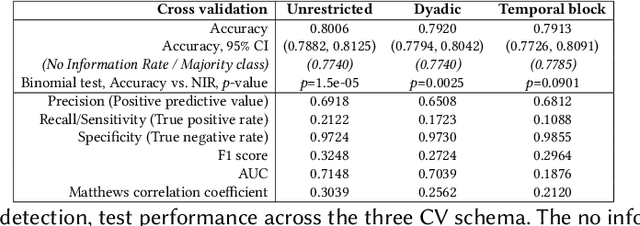
Abstract:We present a study to detect friendship, its strength, and its change from smartphone location data collectedamong members of a fraternity. We extract a rich set of co-location features and build classifiers that detectfriendships and close friendship at 30% above a random baseline. We design cross-validation schema to testour model performance in specific application settings, finding it robust to seeing new dyads and to temporalvariance.
Finding Eyewitness Tweets During Crises
Mar 07, 2014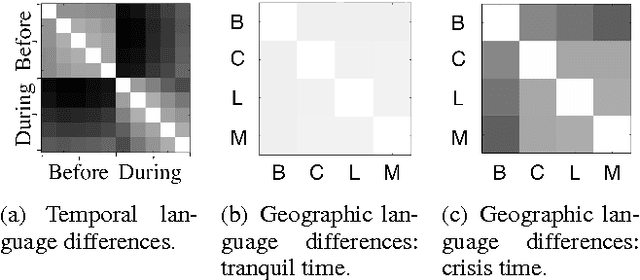
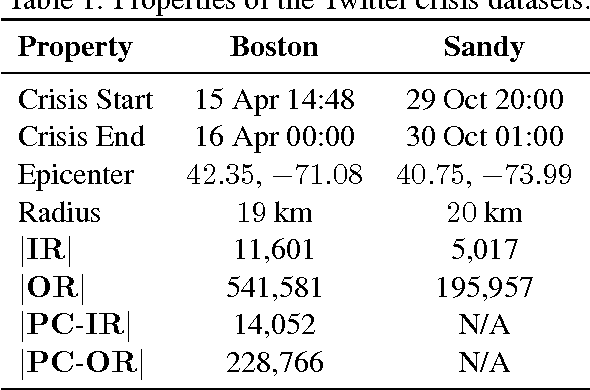
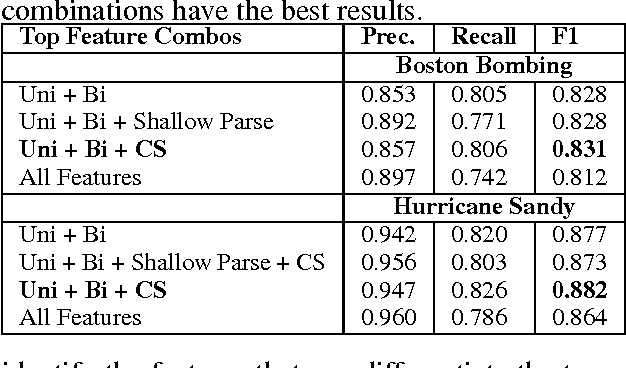
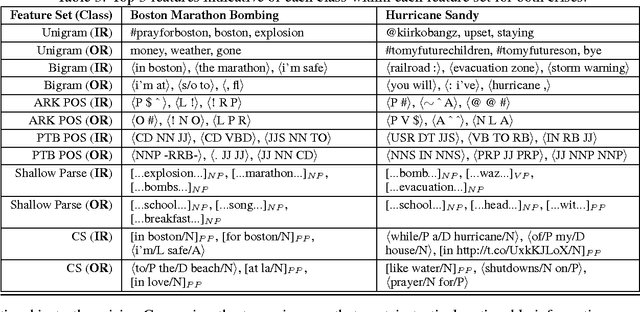
Abstract:Disaster response agencies have started to incorporate social media as a source of fast-breaking information to understand the needs of people affected by the many crises that occur around the world. These agencies look for tweets from within the region affected by the crisis to get the latest updates of the status of the affected region. However only 1% of all tweets are geotagged with explicit location information. First responders lose valuable information because they cannot assess the origin of many of the tweets they collect. In this work we seek to identify non-geotagged tweets that originate from within the crisis region. Towards this, we address three questions: (1) is there a difference between the language of tweets originating within a crisis region and tweets originating outside the region, (2) what are the linguistic patterns that can be used to differentiate within-region and outside-region tweets, and (3) for non-geotagged tweets, can we automatically identify those originating within the crisis region in real-time?
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge