Mingda Zhang
FlowSteer: Interactive Agentic Workflow Orchestration via End-to-End Reinforcement Learning
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:In recent years, a variety of powerful agentic workflows have been applied to solve a wide range of human problems. However, existing workflow orchestration still faces key challenges, including high manual cost, reliance on specific operators/large language models (LLMs), and sparse reward signals. To address these challenges, we propose FlowSteer, an end-to-end reinforcement learning framework that takes a lightweight policy model as the agent and an executable canvas environment, automating workflow orchestration through multi-turn interaction. In this process, the policy model analyzes execution states and selects editing actions, while the canvas executes operators and returns feedback for iterative refinement. Moreover, FlowSteer provides a plug-and-play framework that supports diverse operator libraries and interchangeable LLM backends. To effectively train this interaction paradigm, we propose Canvas Workflow Relative Policy Optimization (CWRPO), which introduces diversity-constrained rewards with conditional release to stabilize learning and suppress shortcut behaviors. Experimental results on twelve datasets show that FlowSteer significantly outperforms baselines across various tasks.
A Semantic Segmentation Algorithm for Pleural Effusion Based on DBIF-AUNet
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:Pleural effusion semantic segmentation can significantly enhance the accuracy and timeliness of clinical diagnosis and treatment by precisely identifying disease severity and lesion areas. Currently, semantic segmentation of pleural effusion CT images faces multiple challenges. These include similar gray levels between effusion and surrounding tissues, blurred edges, and variable morphology. Existing methods often struggle with diverse image variations and complex edges, primarily because direct feature concatenation causes semantic gaps. To address these challenges, we propose the Dual-Branch Interactive Fusion Attention model (DBIF-AUNet). This model constructs a densely nested skip-connection network and innovatively refines the Dual-Domain Feature Disentanglement module (DDFD). The DDFD module orthogonally decouples the functions of dual-domain modules to achieve multi-scale feature complementarity and enhance characteristics at different levels. Concurrently, we design a Branch Interaction Attention Fusion module (BIAF) that works synergistically with the DDFD. This module dynamically weights and fuses global, local, and frequency band features, thereby improving segmentation robustness. Furthermore, we implement a nested deep supervision mechanism with hierarchical adaptive hybrid loss to effectively address class imbalance. Through validation on 1,622 pleural effusion CT images from Southwest Hospital, DBIF-AUNet achieved IoU and Dice scores of 80.1% and 89.0% respectively. These results outperform state-of-the-art medical image segmentation models U-Net++ and Swin-UNet by 5.7%/2.7% and 2.2%/1.5% respectively, demonstrating significant optimization in segmentation accuracy for complex pleural effusion CT images.
An Integrated Framework of Prompt Engineering and Multidimensional Knowledge Graphs for Legal Dispute Analysis
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:The rapid development of artificial intelligence has positioned large language models as fundamental components of intelligent legal systems. However, these models face significant limitations in legal dispute analysis, including insufficient legal knowledge representation, limited concept understanding, and reasoning deficiencies. This research proposes an enhanced framework integrating prompt engineering with multidimensional knowledge graphs. The framework introduces a three-stage hierarchical prompt structure comprising task definition, knowledge background, and reasoning guidance, supplemented by legal-specific reasoning templates and dynamic optimization mechanisms. A three-layer knowledge graph architecture is constructed with legal classification ontology, representation, and instance layers. Four complementary methods enable precise legal concept retrieval: direct legal norm code matching, domain-specific semantic vector similarity, ontology-based path reasoning, and specialized lexical segmentation. These components integrate with web search technology to establish a knowledge-enhanced framework for legal decision-making. Experimental results demonstrate significant performance improvements in legal dispute analysis, enabling accurate legal application analysis for complex cases while exhibiting nuanced understanding of judicial decision-making logic, providing a novel technical approach for implementing intelligent legal assistance systems.
A Method for the Architecture of a Medical Vertical Large Language Model Based on Deepseek R1
Apr 25, 2025Abstract:In recent years, despite foundation models like DeepSeek-R1 and ChatGPT demonstrating significant capabilities in general tasks, professional knowledge barriers, computational resource requirements, and deployment environment limitations have severely hindered their application in actual medical scenarios. Addressing these challenges, this paper proposes an efficient lightweight medical vertical large language model architecture method, systematically solving the lightweight problem of medical large models from three dimensions: knowledge acquisition, model compression, and computational optimization. At the knowledge acquisition level, a knowledge transfer pipeline is designed from the fine-tuned DeepSeek-R1-Distill-70B teacher model to the DeepSeek-R1-Distill-7B student model, and Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) technology is adopted to precisely adjust key attention layers. At the model compression level, compression techniques including 4-bit weight quantization are implemented while preserving the core representation ability for medical reasoning. At the computational optimization level, inference optimization techniques such as Flash Attention acceleration and continuous batching are integrated, and a professional prompt template system is constructed to adapt to different types of medical problems. Experimental results on medical question-answering datasets show that the method proposed in this paper maintains professional accuracy while reducing memory consumption by 64.7\% and inference latency by 12.4\%, providing an effective solution for the application of medical large models in resource-constrained environments such as edge computing devices.
Inference-Time Scaling for Diffusion Models beyond Scaling Denoising Steps
Jan 16, 2025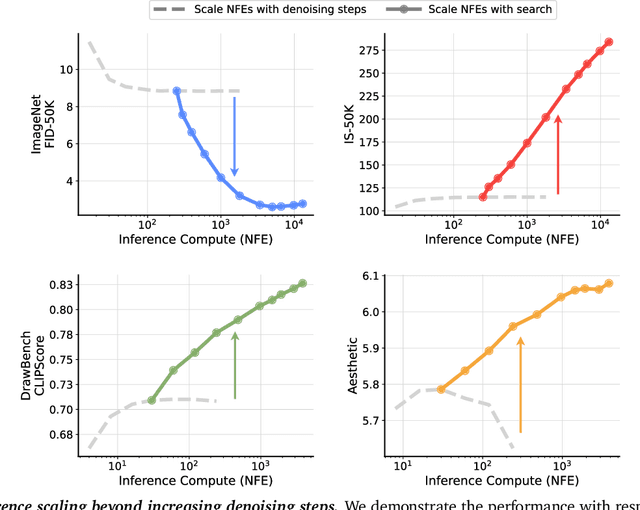
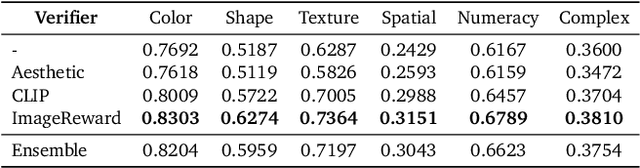
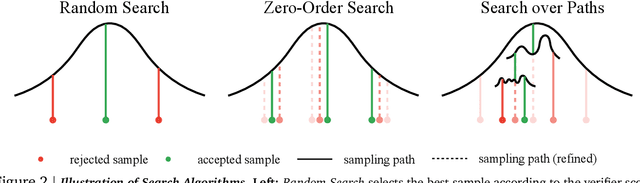
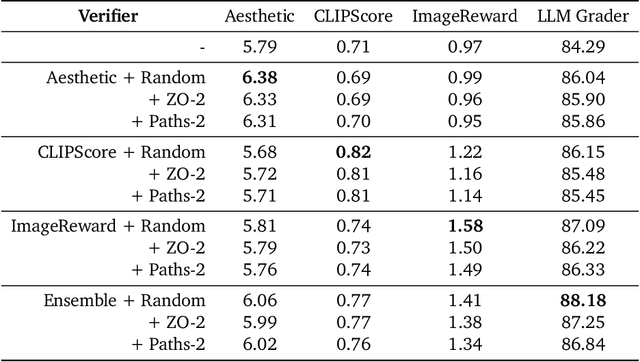
Abstract:Generative models have made significant impacts across various domains, largely due to their ability to scale during training by increasing data, computational resources, and model size, a phenomenon characterized by the scaling laws. Recent research has begun to explore inference-time scaling behavior in Large Language Models (LLMs), revealing how performance can further improve with additional computation during inference. Unlike LLMs, diffusion models inherently possess the flexibility to adjust inference-time computation via the number of denoising steps, although the performance gains typically flatten after a few dozen. In this work, we explore the inference-time scaling behavior of diffusion models beyond increasing denoising steps and investigate how the generation performance can further improve with increased computation. Specifically, we consider a search problem aimed at identifying better noises for the diffusion sampling process. We structure the design space along two axes: the verifiers used to provide feedback, and the algorithms used to find better noise candidates. Through extensive experiments on class-conditioned and text-conditioned image generation benchmarks, our findings reveal that increasing inference-time compute leads to substantial improvements in the quality of samples generated by diffusion models, and with the complicated nature of images, combinations of the components in the framework can be specifically chosen to conform with different application scenario.
Neptune: The Long Orbit to Benchmarking Long Video Understanding
Dec 12, 2024



Abstract:This paper describes a semi-automatic pipeline to generate challenging question-answer-decoy sets for understanding long videos. Many existing video datasets and models are focused on short clips (10s-30s). While some long video datasets do exist, they can often be solved by powerful image models applied per frame (and often to very few frames) in a video, and are usually manually annotated at high cost. In order to mitigate both these problems, we propose a scalable dataset creation pipeline which leverages large models (VLMs and LLMs), to automatically generate dense, time-aligned video captions, as well as tough question answer decoy sets for video segments (up to 15 minutes in length). Our dataset Neptune covers a broad range of long video reasoning abilities and consists of a subset that emphasizes multimodal reasoning. Since existing metrics for open-ended question answering are either rule-based or may rely on proprietary models, we provide a new open source model-based metric GEM to score open-ended responses on Neptune. Benchmark evaluations reveal that most current open-source long video models perform poorly on Neptune, particularly on questions testing temporal ordering, counting and state changes. Through Neptune, we aim to spur the development of more advanced models capable of understanding long videos. The dataset is available at https://github.com/google-deepmind/neptune
Reliable Poisoned Sample Detection against Backdoor Attacks Enhanced by Sharpness Aware Minimization
Nov 18, 2024



Abstract:Backdoor attack has been considered as a serious security threat to deep neural networks (DNNs). Poisoned sample detection (PSD) that aims at filtering out poisoned samples from an untrustworthy training dataset has shown very promising performance for defending against data poisoning based backdoor attacks. However, we observe that the detection performance of many advanced methods is likely to be unstable when facing weak backdoor attacks, such as low poisoning ratio or weak trigger strength. To further verify this observation, we make a statistical investigation among various backdoor attacks and poisoned sample detections, showing a positive correlation between backdoor effect and detection performance. It inspires us to strengthen the backdoor effect to enhance detection performance. Since we cannot achieve that goal via directly manipulating poisoning ratio or trigger strength, we propose to train one model using the Sharpness-Aware Minimization (SAM) algorithm, rather than the vanilla training algorithm. We also provide both empirical and theoretical analysis about how SAM training strengthens the backdoor effect. Then, this SAM trained model can be seamlessly integrated with any off-the-shelf PSD method that extracts discriminative features from the trained model for detection, called SAM-enhanced PSD. Extensive experiments on several benchmark datasets show the reliable detection performance of the proposed method against both weak and strong backdoor attacks, with significant improvements against various attacks ($+34.38\%$ TPR on average), over the conventional PSD methods (i.e., without SAM enhancement). Overall, this work provides new insights about PSD and proposes a novel approach that can complement existing detection methods, which may inspire more in-depth explorations in this field.
OmnixR: Evaluating Omni-modality Language Models on Reasoning across Modalities
Oct 16, 2024Abstract:We introduce OmnixR, an evaluation suite designed to benchmark SoTA Omni-modality Language Models, such as GPT-4o and Gemini. Evaluating OLMs, which integrate multiple modalities such as text, vision, and audio, presents unique challenges. Particularly, the user message might often consist of multiple modalities, such that OLMs have to establish holistic understanding and reasoning across modalities to accomplish the task. Existing benchmarks are limited to single modality or dual-modality tasks, overlooking comprehensive multi-modal assessments of model reasoning. To address this, OmnixR offers two evaluation variants: (1)synthetic subset: a synthetic dataset generated automatically by translating text into multiple modalities--audio, images, video, and hybrids (Omnify). (2)realistic subset: a real-world dataset, manually curated and annotated by experts, for evaluating cross-modal reasoning in natural settings. OmnixR presents a unique evaluation towards assessing OLMs over a diverse mix of modalities, such as a question that involves video, audio, and text, providing a rigorous cross-modal reasoning testbed unlike any existing benchmarks. Our experiments find that all state-of-the-art OLMs struggle with OmnixR questions that require integrating information from multiple modalities to answer. Further analysis highlights differences in reasoning behavior, underscoring the challenges of omni-modal AI alignment.
BackdoorBench: A Comprehensive Benchmark and Analysis of Backdoor Learning
Jan 26, 2024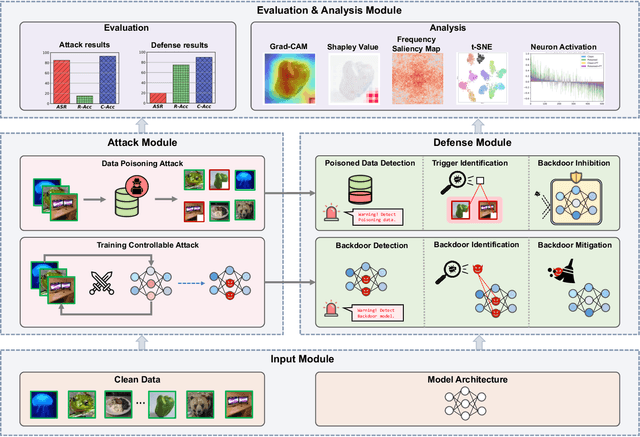
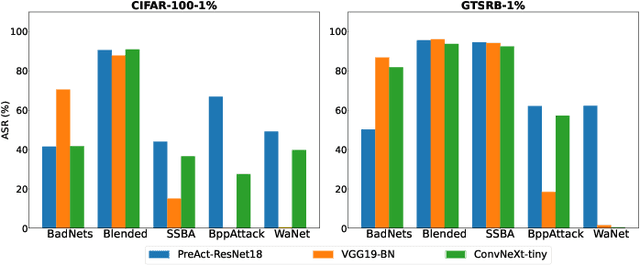
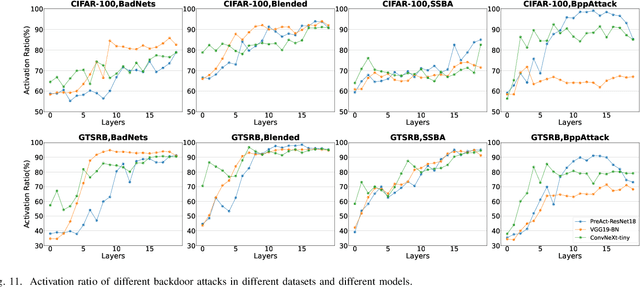
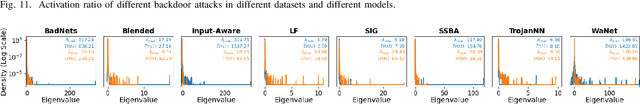
Abstract:As an emerging and vital topic for studying deep neural networks' vulnerability (DNNs), backdoor learning has attracted increasing interest in recent years, and many seminal backdoor attack and defense algorithms are being developed successively or concurrently, in the status of a rapid arms race. However, mainly due to the diverse settings, and the difficulties of implementation and reproducibility of existing works, there is a lack of a unified and standardized benchmark of backdoor learning, causing unfair comparisons, and unreliable conclusions (e.g., misleading, biased or even false conclusions). Consequently, it is difficult to evaluate the current progress and design the future development roadmap of this literature. To alleviate this dilemma, we build a comprehensive benchmark of backdoor learning called BackdoorBench. Our benchmark makes three valuable contributions to the research community. 1) We provide an integrated implementation of state-of-the-art (SOTA) backdoor learning algorithms (currently including 16 attack and 27 defense algorithms), based on an extensible modular-based codebase. 2) We conduct comprehensive evaluations of 12 attacks against 16 defenses, with 5 poisoning ratios, based on 4 models and 4 datasets, thus 11,492 pairs of evaluations in total. 3) Based on above evaluations, we present abundant analysis from 8 perspectives via 18 useful analysis tools, and provide several inspiring insights about backdoor learning. We hope that our efforts could build a solid foundation of backdoor learning to facilitate researchers to investigate existing algorithms, develop more innovative algorithms, and explore the intrinsic mechanism of backdoor learning. Finally, we have created a user-friendly website at http://backdoorbench.com, which collects all important information of BackdoorBench, including codebase, docs, leaderboard, and model Zoo.
Defenses in Adversarial Machine Learning: A Survey
Dec 13, 2023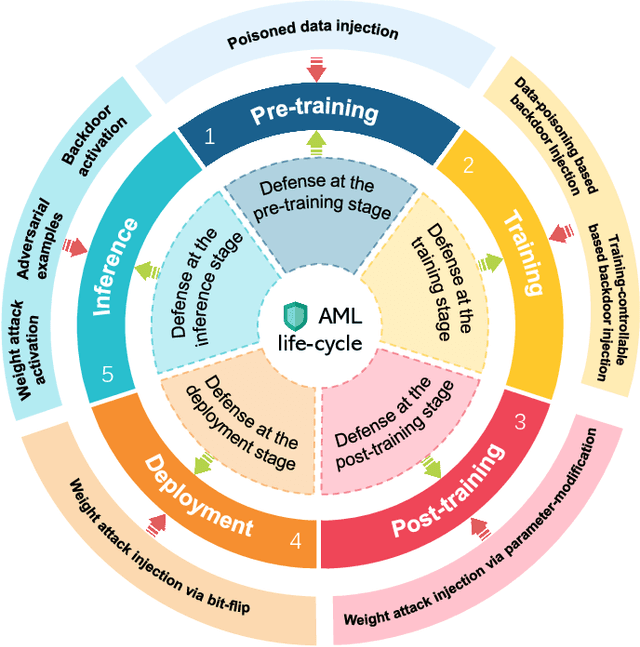
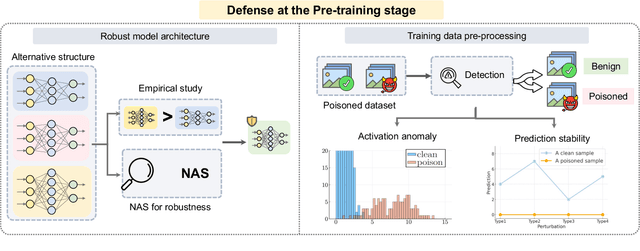
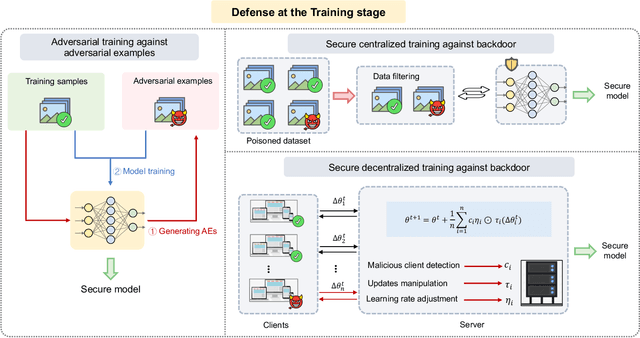
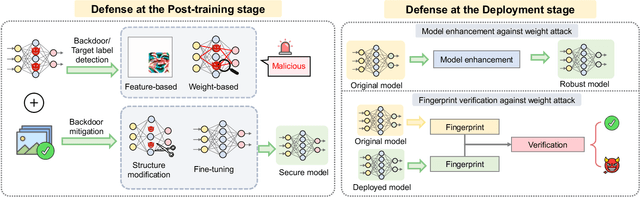
Abstract:Adversarial phenomenon has been widely observed in machine learning (ML) systems, especially in those using deep neural networks, describing that ML systems may produce inconsistent and incomprehensible predictions with humans at some particular cases. This phenomenon poses a serious security threat to the practical application of ML systems, and several advanced attack paradigms have been developed to explore it, mainly including backdoor attacks, weight attacks, and adversarial examples. For each individual attack paradigm, various defense paradigms have been developed to improve the model robustness against the corresponding attack paradigm. However, due to the independence and diversity of these defense paradigms, it is difficult to examine the overall robustness of an ML system against different kinds of attacks.This survey aims to build a systematic review of all existing defense paradigms from a unified perspective. Specifically, from the life-cycle perspective, we factorize a complete machine learning system into five stages, including pre-training, training, post-training, deployment, and inference stages, respectively. Then, we present a clear taxonomy to categorize and review representative defense methods at each individual stage. The unified perspective and presented taxonomies not only facilitate the analysis of the mechanism of each defense paradigm but also help us to understand connections and differences among different defense paradigms, which may inspire future research to develop more advanced, comprehensive defenses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge