Xuan Yang
Silhouette Score Efficient Radio Frequency Fingerprint Feature Extraction
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Radio frequency fingerprint (RFF) identification technology, which exploits relatively stable hardware imperfections, is highly susceptible to constantly changing channel effects. Although various channel-robust RFF feature extraction methods have been proposed, they predominantly rely on experimental comparisons rather than theoretical analyses. This limitation hinders the progress of channel-robust RFF feature extraction and impedes the establishment of theoretical guidance for its design. In this paper, we establish a unified theoretical performance analysis framework for different RFF feature extraction methods using the silhouette score as an evaluation metric, and propose a precoding-based channel-robust RFF feature extraction method that enhances the silhouette score without requiring channel estimation. First, we employ the silhouette score as an evaluation metric and obtain the theoretical performance of various RFF feature extraction methods using the Taylor series expansion. Next, we mitigate channel effects by computing the reciprocal of the received signal in the frequency domain at the device under authentication. We then compare these methods across three different scenarios: the deterministic channel scenario, the independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) stochastic channel scenario, and the non-i.i.d. stochastic channel scenario. Finally, simulation and experimental results demonstrate that the silhouette score is an efficient metric to evaluate classification accuracy. Furthermore, the results indicate that the proposed precoding-based channel-robust RFF feature extraction method achieves the highest silhouette score and classification accuracy under channel variations.
Intra-Class Subdivision for Pixel Contrastive Learning: Application to Semi-supervised Cardiac Image Segmentation
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:We propose an intra-class subdivision pixel contrastive learning (SPCL) framework for cardiac image segmentation to address representation contamination at boundaries. The novel concept ``Unconcerned sample'' is proposed to distinguish pixel representations at the inner and boundary regions within the same class, facilitating a clearer characterization of intra-class variations. A novel boundary contrastive loss for boundary representations is proposed to enhance representation discrimination across boundaries. The advantages of the unconcerned sample and boundary contrastive loss are analyzed theoretically. Experimental results in public cardiac datasets demonstrate that SPCL significantly improves segmentation performance, outperforming existing methods with respect to segmentation quality and boundary precision. Our code is available at https://github.com/Jrstud203/SPCL.
Building Digital Twins of Different Human Organs for Personalized Healthcare
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical entities and are poised to transform personalized medicine through the real-time simulation and prediction of human physiology. Translating this paradigm from engineering to biomedicine requires overcoming profound challenges, including anatomical variability, multi-scale biological processes, and the integration of multi-physics phenomena. This survey systematically reviews methodologies for building digital twins of human organs, structured around a pipeline decoupled into anatomical twinning (capturing patient-specific geometry and structure) and functional twinning (simulating multi-scale physiology from cellular to organ-level function). We categorize approaches both by organ-specific properties and by technical paradigm, with particular emphasis on multi-scale and multi-physics integration. A key focus is the role of artificial intelligence (AI), especially physics-informed AI, in enhancing model fidelity, scalability, and personalization. Furthermore, we discuss the critical challenges of clinical validation and translational pathways. This study not only charts a roadmap for overcoming current bottlenecks in single-organ twins but also outlines the promising, albeit ambitious, future of interconnected multi-organ digital twins for whole-body precision healthcare.
Batch-of-Thought: Cross-Instance Learning for Enhanced LLM Reasoning
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Current Large Language Model reasoning systems process queries independently, discarding valuable cross-instance signals such as shared reasoning patterns and consistency constraints. We introduce Batch-of-Thought (BoT), a training-free method that processes related queries jointly to enable cross-instance learning. By performing comparative analysis across batches, BoT identifies high-quality reasoning templates, detects errors through consistency checks, and amortizes computational costs. We instantiate BoT within a multi-agent reflection architecture (BoT-R), where a Reflector performs joint evaluation to unlock mutual information gain unavailable in isolated processing. Experiments across three model families and six benchmarks demonstrate that BoT-R consistently improves accuracy and confidence calibration while reducing inference costs by up to 61%. Our theoretical and experimental analysis reveals when and why batch-aware reasoning benefits LLM systems.
Division-based Receiver-agnostic RFF Identification in WiFi Systems
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:In physical-layer security schemes, radio frequency fingerprint (RFF) identification of WiFi devices is susceptible to receiver differences, which can significantly degrade classification performance when a model is trained on one receiver but tested on another. In this paper, we propose a division-based receiver-agnostic RFF extraction method for WiFi systems, which removes the receivers' effects by dividing different preambles in the frequency domain. The proposed method requires only a single receiver for training and does not rely on additional calibration or stacking processes. First, for flat fading channel scenarios, the legacy short training field (L-STF) and legacy long training field (L-LTF) of the unknown device are divided by those of the reference device in the frequency domain. The receiver-dependent effects can be eliminated with the requirement of only a single receiver for training, and the higher-dimensional RFF features can be extracted. Second, for frequency-selective fading channel scenarios, the high-throughput long training field (HT-LTF) is divided by the L-LTF in the frequency domain. Only a single receiver is required for training and the higher-dimensional RFF features that are both channel-invariant and receiver-agnostic are extracted. Finally, simulation and experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method effectively mitigate the impacts of channel variations and receiver differences. The classification results show that, even when training on a single receiver and testing on a different one, the proposed method achieves classification accuracy improvements of 15.5% and 28.45% over the state-of-the-art approach in flat fading and frequency-selective fading channel scenarios, respectively.
Hybrid Quantum-Classical Neural Networks for Few-Shot Credit Risk Assessment
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:Quantum Machine Learning (QML) offers a new paradigm for addressing complex financial problems intractable for classical methods. This work specifically tackles the challenge of few-shot credit risk assessment, a critical issue in inclusive finance where data scarcity and imbalance limit the effectiveness of conventional models. To address this, we design and implement a novel hybrid quantum-classical workflow. The methodology first employs an ensemble of classical machine learning models (Logistic Regression, Random Forest, XGBoost) for intelligent feature engineering and dimensionality reduction. Subsequently, a Quantum Neural Network (QNN), trained via the parameter-shift rule, serves as the core classifier. This framework was evaluated through numerical simulations and deployed on the Quafu Quantum Cloud Platform's ScQ-P21 superconducting processor. On a real-world credit dataset of 279 samples, our QNN achieved a robust average AUC of 0.852 +/- 0.027 in simulations and yielded an impressive AUC of 0.88 in the hardware experiment. This performance surpasses a suite of classical benchmarks, with a particularly strong result on the recall metric. This study provides a pragmatic blueprint for applying quantum computing to data-constrained financial scenarios in the NISQ era and offers valuable empirical evidence supporting its potential in high-stakes applications like inclusive finance.
Unified Autoregressive Visual Generation and Understanding with Continuous Tokens
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:We present UniFluid, a unified autoregressive framework for joint visual generation and understanding leveraging continuous visual tokens. Our unified autoregressive architecture processes multimodal image and text inputs, generating discrete tokens for text and continuous tokens for image. We find though there is an inherent trade-off between the image generation and understanding task, a carefully tuned training recipe enables them to improve each other. By selecting an appropriate loss balance weight, the unified model achieves results comparable to or exceeding those of single-task baselines on both tasks. Furthermore, we demonstrate that employing stronger pre-trained LLMs and random-order generation during training is important to achieve high-fidelity image generation within this unified framework. Built upon the Gemma model series, UniFluid exhibits competitive performance across both image generation and understanding, demonstrating strong transferability to various downstream tasks, including image editing for generation, as well as visual captioning and question answering for understanding.
Inference-Time Scaling for Diffusion Models beyond Scaling Denoising Steps
Jan 16, 2025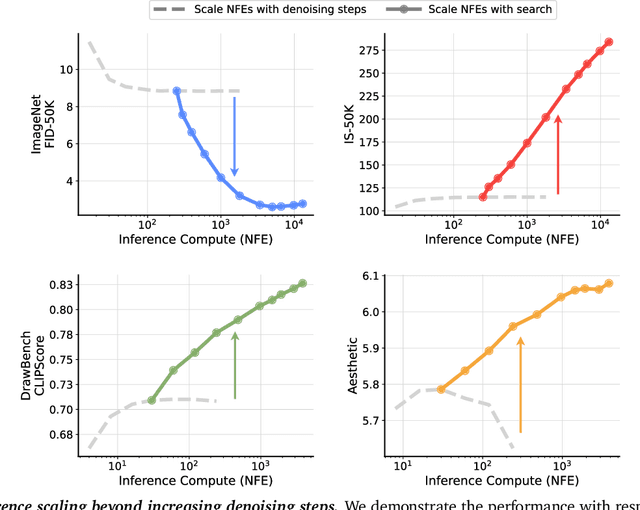
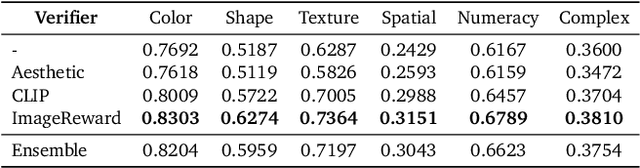
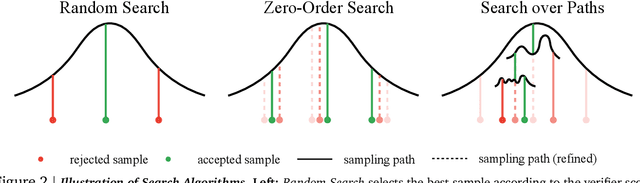
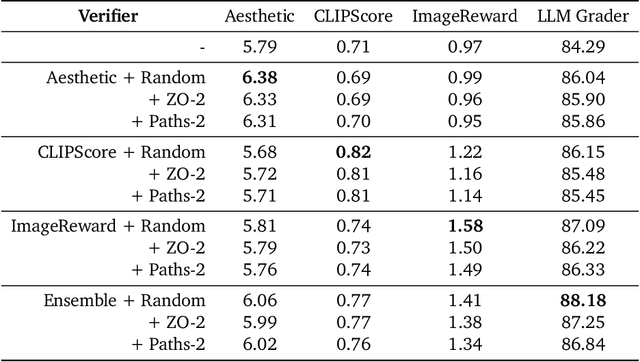
Abstract:Generative models have made significant impacts across various domains, largely due to their ability to scale during training by increasing data, computational resources, and model size, a phenomenon characterized by the scaling laws. Recent research has begun to explore inference-time scaling behavior in Large Language Models (LLMs), revealing how performance can further improve with additional computation during inference. Unlike LLMs, diffusion models inherently possess the flexibility to adjust inference-time computation via the number of denoising steps, although the performance gains typically flatten after a few dozen. In this work, we explore the inference-time scaling behavior of diffusion models beyond increasing denoising steps and investigate how the generation performance can further improve with increased computation. Specifically, we consider a search problem aimed at identifying better noises for the diffusion sampling process. We structure the design space along two axes: the verifiers used to provide feedback, and the algorithms used to find better noise candidates. Through extensive experiments on class-conditioned and text-conditioned image generation benchmarks, our findings reveal that increasing inference-time compute leads to substantial improvements in the quality of samples generated by diffusion models, and with the complicated nature of images, combinations of the components in the framework can be specifically chosen to conform with different application scenario.
STNMamba: Mamba-based Spatial-Temporal Normality Learning for Video Anomaly Detection
Dec 28, 2024Abstract:Video anomaly detection (VAD) has been extensively researched due to its potential for intelligent video systems. However, most existing methods based on CNNs and transformers still suffer from substantial computational burdens and have room for improvement in learning spatial-temporal normality. Recently, Mamba has shown great potential for modeling long-range dependencies with linear complexity, providing an effective solution to the above dilemma. To this end, we propose a lightweight and effective Mamba-based network named STNMamba, which incorporates carefully designed Mamba modules to enhance the learning of spatial-temporal normality. Firstly, we develop a dual-encoder architecture, where the spatial encoder equipped with Multi-Scale Vision Space State Blocks (MS-VSSB) extracts multi-scale appearance features, and the temporal encoder employs Channel-Aware Vision Space State Blocks (CA-VSSB) to capture significant motion patterns. Secondly, a Spatial-Temporal Interaction Module (STIM) is introduced to integrate spatial and temporal information across multiple levels, enabling effective modeling of intrinsic spatial-temporal consistency. Within this module, the Spatial-Temporal Fusion Block (STFB) is proposed to fuse the spatial and temporal features into a unified feature space, and the memory bank is utilized to store spatial-temporal prototypes of normal patterns, restricting the model's ability to represent anomalies. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that our STNMamba achieves competitive performance with fewer parameters and lower computational costs than existing methods.
LLM-RG4: Flexible and Factual Radiology Report Generation across Diverse Input Contexts
Dec 16, 2024Abstract:Drafting radiology reports is a complex task requiring flexibility, where radiologists tail content to available information and particular clinical demands. However, most current radiology report generation (RRG) models are constrained to a fixed task paradigm, such as predicting the full ``finding'' section from a single image, inherently involving a mismatch between inputs and outputs. The trained models lack the flexibility for diverse inputs and could generate harmful, input-agnostic hallucinations. To bridge the gap between current RRG models and the clinical demands in practice, we first develop a data generation pipeline to create a new MIMIC-RG4 dataset, which considers four common radiology report drafting scenarios and has perfectly corresponded input and output. Secondly, we propose a novel large language model (LLM) based RRG framework, namely LLM-RG4, which utilizes LLM's flexible instruction-following capabilities and extensive general knowledge. We further develop an adaptive token fusion module that offers flexibility to handle diverse scenarios with different input combinations, while minimizing the additional computational burden associated with increased input volumes. Besides, we propose a token-level loss weighting strategy to direct the model's attention towards positive and uncertain descriptions. Experimental results demonstrate that LLM-RG4 achieves state-of-the-art performance in both clinical efficiency and natural language generation on the MIMIC-RG4 and MIMIC-CXR datasets. We quantitatively demonstrate that our model has minimal input-agnostic hallucinations, whereas current open-source models commonly suffer from this problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge