Mikhail Sirotenko
MINERVA: Evaluating Complex Video Reasoning
May 01, 2025Abstract:Multimodal LLMs are turning their focus to video benchmarks, however most video benchmarks only provide outcome supervision, with no intermediate or interpretable reasoning steps. This makes it challenging to assess if models are truly able to combine perceptual and temporal information to reason about videos, or simply get the correct answer by chance or by exploiting linguistic biases. To remedy this, we provide a new video reasoning dataset called MINERVA for modern multimodal models. Each question in the dataset comes with 5 answer choices, as well as detailed, hand-crafted reasoning traces. Our dataset is multimodal, diverse in terms of video domain and length, and consists of complex multi-step questions. Extensive benchmarking shows that our dataset provides a challenge for frontier open-source and proprietary models. We perform fine-grained error analysis to identify common failure modes across various models, and create a taxonomy of reasoning errors. We use this to explore both human and LLM-as-a-judge methods for scoring video reasoning traces, and find that failure modes are primarily related to temporal localization, followed by visual perception errors, as opposed to logical or completeness errors. The dataset, along with questions, answer candidates and reasoning traces will be publicly available under https://github.com/google-deepmind/neptune?tab=readme-ov-file\#minerva.
Neptune: The Long Orbit to Benchmarking Long Video Understanding
Dec 12, 2024



Abstract:This paper describes a semi-automatic pipeline to generate challenging question-answer-decoy sets for understanding long videos. Many existing video datasets and models are focused on short clips (10s-30s). While some long video datasets do exist, they can often be solved by powerful image models applied per frame (and often to very few frames) in a video, and are usually manually annotated at high cost. In order to mitigate both these problems, we propose a scalable dataset creation pipeline which leverages large models (VLMs and LLMs), to automatically generate dense, time-aligned video captions, as well as tough question answer decoy sets for video segments (up to 15 minutes in length). Our dataset Neptune covers a broad range of long video reasoning abilities and consists of a subset that emphasizes multimodal reasoning. Since existing metrics for open-ended question answering are either rule-based or may rely on proprietary models, we provide a new open source model-based metric GEM to score open-ended responses on Neptune. Benchmark evaluations reveal that most current open-source long video models perform poorly on Neptune, particularly on questions testing temporal ordering, counting and state changes. Through Neptune, we aim to spur the development of more advanced models capable of understanding long videos. The dataset is available at https://github.com/google-deepmind/neptune
Extending Video Masked Autoencoders to 128 frames
Nov 20, 2024



Abstract:Video understanding has witnessed significant progress with recent video foundation models demonstrating strong performance owing to self-supervised pre-training objectives; Masked Autoencoders (MAE) being the design of choice. Nevertheless, the majority of prior works that leverage MAE pre-training have focused on relatively short video representations (16 / 32 frames in length) largely due to hardware memory and compute limitations that scale poorly with video length due to the dense memory-intensive self-attention decoding. One natural strategy to address these challenges is to subsample tokens to reconstruct during decoding (or decoder masking). In this work, we propose an effective strategy for prioritizing tokens which allows training on longer video sequences (128 frames) and gets better performance than, more typical, random and uniform masking strategies. The core of our approach is an adaptive decoder masking strategy that prioritizes the most important tokens and uses quantized tokens as reconstruction objectives. Our adaptive strategy leverages a powerful MAGVIT-based tokenizer that jointly learns the tokens and their priority. We validate our design choices through exhaustive ablations and observe improved performance of the resulting long-video (128 frames) encoders over short-video (32 frames) counterparts. With our long-video masked autoencoder (LVMAE) strategy, we surpass state-of-the-art on Diving48 by 3.9 points and EPIC-Kitchens-100 verb classification by 2.5 points while relying on a simple core architecture and video-only pre-training (unlike some of the prior works that require millions of labeled video-text pairs or specialized encoders).
VideoPrism: A Foundational Visual Encoder for Video Understanding
Feb 20, 2024
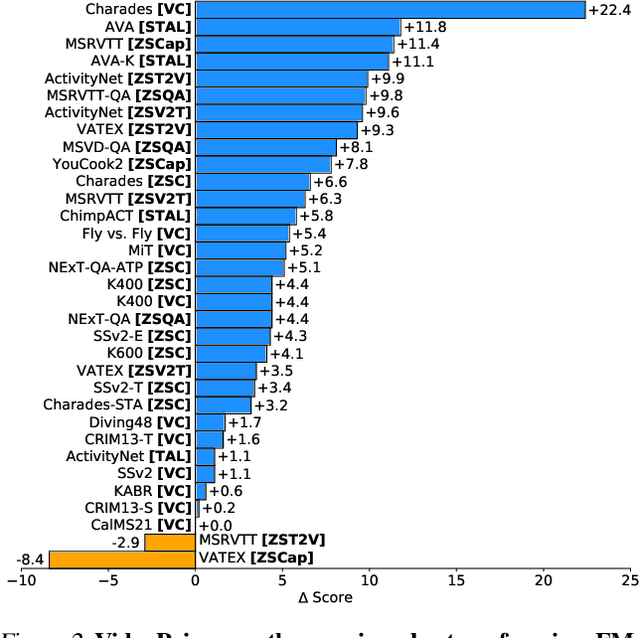
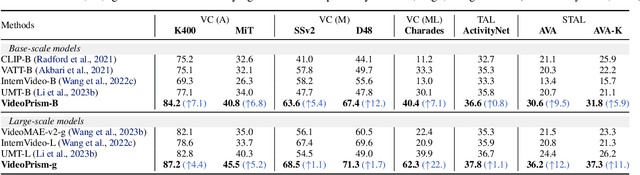
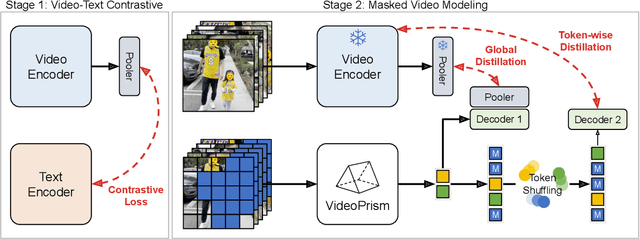
Abstract:We introduce VideoPrism, a general-purpose video encoder that tackles diverse video understanding tasks with a single frozen model. We pretrain VideoPrism on a heterogeneous corpus containing 36M high-quality video-caption pairs and 582M video clips with noisy parallel text (e.g., ASR transcripts). The pretraining approach improves upon masked autoencoding by global-local distillation of semantic video embeddings and a token shuffling scheme, enabling VideoPrism to focus primarily on the video modality while leveraging the invaluable text associated with videos. We extensively test VideoPrism on four broad groups of video understanding tasks, from web video question answering to CV for science, achieving state-of-the-art performance on 30 out of 33 video understanding benchmarks.
VideoPoet: A Large Language Model for Zero-Shot Video Generation
Dec 21, 2023



Abstract:We present VideoPoet, a language model capable of synthesizing high-quality video, with matching audio, from a large variety of conditioning signals. VideoPoet employs a decoder-only transformer architecture that processes multimodal inputs -- including images, videos, text, and audio. The training protocol follows that of Large Language Models (LLMs), consisting of two stages: pretraining and task-specific adaptation. During pretraining, VideoPoet incorporates a mixture of multimodal generative objectives within an autoregressive Transformer framework. The pretrained LLM serves as a foundation that can be adapted for a range of video generation tasks. We present empirical results demonstrating the model's state-of-the-art capabilities in zero-shot video generation, specifically highlighting VideoPoet's ability to generate high-fidelity motions. Project page: http://sites.research.google/videopoet/
PolyMaX: General Dense Prediction with Mask Transformer
Nov 09, 2023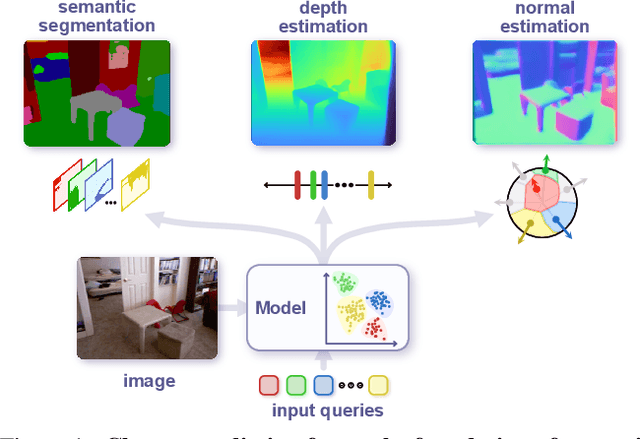
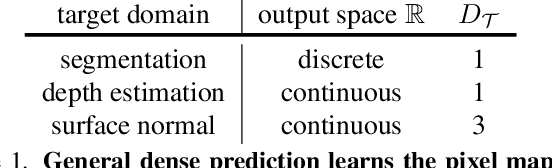
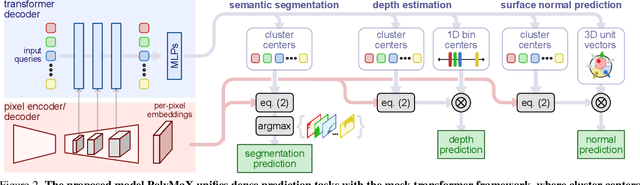
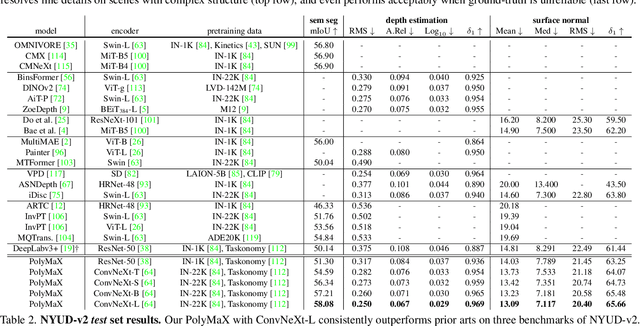
Abstract:Dense prediction tasks, such as semantic segmentation, depth estimation, and surface normal prediction, can be easily formulated as per-pixel classification (discrete outputs) or regression (continuous outputs). This per-pixel prediction paradigm has remained popular due to the prevalence of fully convolutional networks. However, on the recent frontier of segmentation task, the community has been witnessing a shift of paradigm from per-pixel prediction to cluster-prediction with the emergence of transformer architectures, particularly the mask transformers, which directly predicts a label for a mask instead of a pixel. Despite this shift, methods based on the per-pixel prediction paradigm still dominate the benchmarks on the other dense prediction tasks that require continuous outputs, such as depth estimation and surface normal prediction. Motivated by the success of DORN and AdaBins in depth estimation, achieved by discretizing the continuous output space, we propose to generalize the cluster-prediction based method to general dense prediction tasks. This allows us to unify dense prediction tasks with the mask transformer framework. Remarkably, the resulting model PolyMaX demonstrates state-of-the-art performance on three benchmarks of NYUD-v2 dataset. We hope our simple yet effective design can inspire more research on exploiting mask transformers for more dense prediction tasks. Code and model will be made available.
SANPO: A Scene Understanding, Accessibility, Navigation, Pathfinding, Obstacle Avoidance Dataset
Sep 21, 2023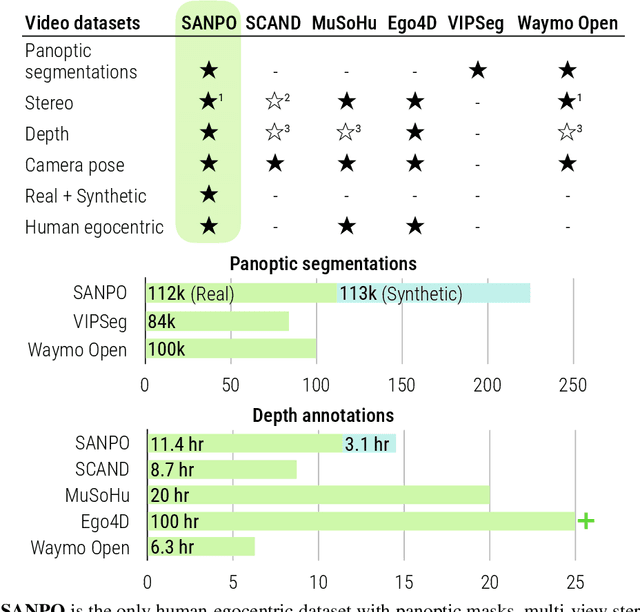
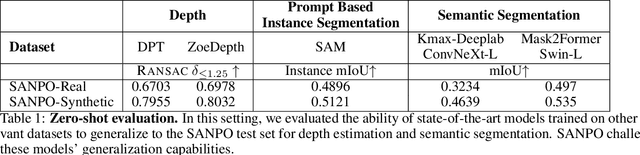
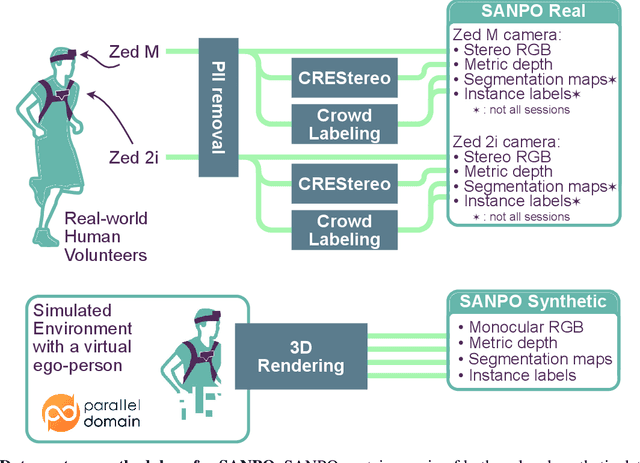
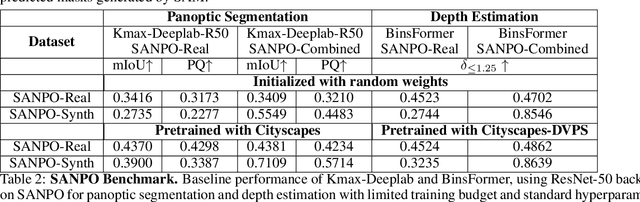
Abstract:We introduce SANPO, a large-scale egocentric video dataset focused on dense prediction in outdoor environments. It contains stereo video sessions collected across diverse outdoor environments, as well as rendered synthetic video sessions. (Synthetic data was provided by Parallel Domain.) All sessions have (dense) depth and odometry labels. All synthetic sessions and a subset of real sessions have temporally consistent dense panoptic segmentation labels. To our knowledge, this is the first human egocentric video dataset with both large scale dense panoptic segmentation and depth annotations. In addition to the dataset we also provide zero-shot baselines and SANPO benchmarks for future research. We hope that the challenging nature of SANPO will help advance the state-of-the-art in video segmentation, depth estimation, multi-task visual modeling, and synthetic-to-real domain adaptation, while enabling human navigation systems. SANPO is available here: https://google-research-datasets.github.io/sanpo_dataset/
VideoGLUE: Video General Understanding Evaluation of Foundation Models
Jul 06, 2023



Abstract:We evaluate existing foundation models video understanding capabilities using a carefully designed experiment protocol consisting of three hallmark tasks (action recognition, temporal localization, and spatiotemporal localization), eight datasets well received by the community, and four adaptation methods tailoring a foundation model (FM) for a downstream task. Moreover, we propose a scalar VideoGLUE score (VGS) to measure an FMs efficacy and efficiency when adapting to general video understanding tasks. Our main findings are as follows. First, task-specialized models significantly outperform the six FMs studied in this work, in sharp contrast to what FMs have achieved in natural language and image understanding. Second,video-native FMs, whose pretraining data contains the video modality, are generally better than image-native FMs in classifying motion-rich videos, localizing actions in time, and understanding a video of more than one action. Third, the video-native FMs can perform well on video tasks under light adaptations to downstream tasks(e.g., freezing the FM backbones), while image-native FMs win in full end-to-end finetuning. The first two observations reveal the need and tremendous opportunities to conduct research on video-focused FMs, and the last confirms that both tasks and adaptation methods matter when it comes to the evaluation of FMs.
Efficient Image Representation Learning with Federated Sampled Softmax
Mar 09, 2022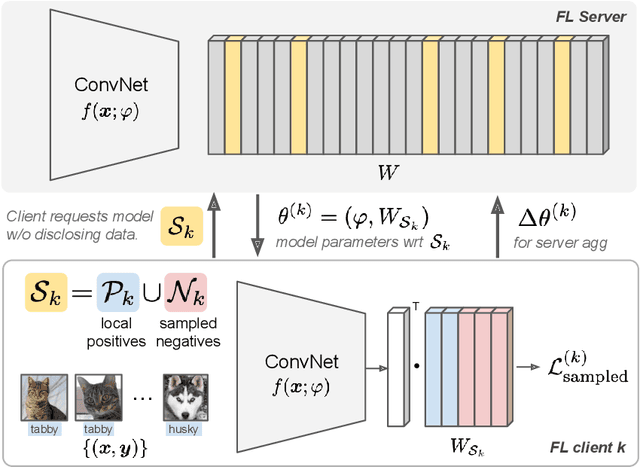
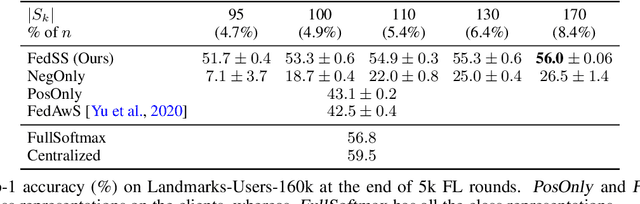
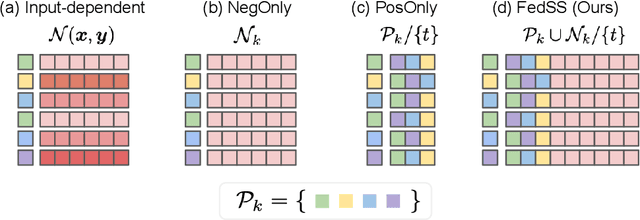
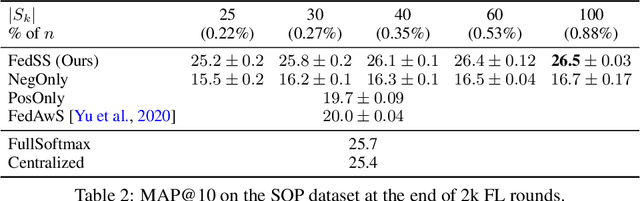
Abstract:Learning image representations on decentralized data can bring many benefits in cases where data cannot be aggregated across data silos. Softmax cross entropy loss is highly effective and commonly used for learning image representations. Using a large number of classes has proven to be particularly beneficial for the descriptive power of such representations in centralized learning. However, doing so on decentralized data with Federated Learning is not straightforward as the demand on FL clients' computation and communication increases proportionally to the number of classes. In this work we introduce federated sampled softmax (FedSS), a resource-efficient approach for learning image representation with Federated Learning. Specifically, the FL clients sample a set of classes and optimize only the corresponding model parameters with respect to a sampled softmax objective that approximates the global full softmax objective. We examine the loss formulation and empirically show that our method significantly reduces the number of parameters transferred to and optimized by the client devices, while performing on par with the standard full softmax method. This work creates a possibility for efficiently learning image representations on decentralized data with a large number of classes under the federated setting.
Fashionpedia: Ontology, Segmentation, and an Attribute Localization Dataset
Apr 26, 2020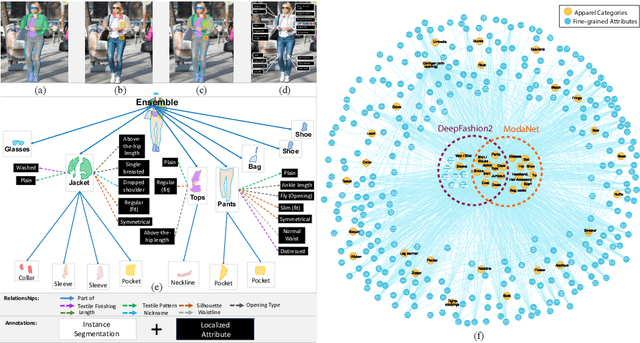
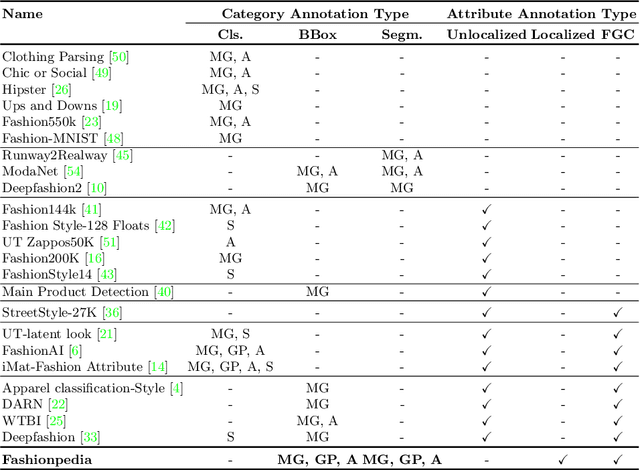

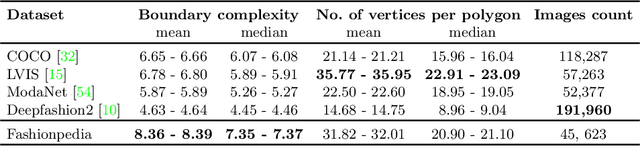
Abstract:In this work we explore the task of instance segmentation with attribute localization, which unifies instance segmentation (detect and segment each object instance) and fine-grained visual attribute categorization (recognize one or multiple attributes). The proposed task requires both localizing an object and describing its properties. To illustrate the various aspects of this task, we focus on the domain of fashion and introduce Fashionpedia as a step toward mapping out the visual aspects of the fashion world. Fashionpedia consists of two parts: (1) an ontology built by fashion experts containing 27 main apparel categories, 19 apparel parts, 294 fine-grained attributes and their relationships; (2) a dataset with everyday and celebrity event fashion images annotated with segmentation masks and their associated per-mask fine-grained attributes, built upon the Fashionpedia ontology. In order to solve this challenging task, we propose a novel Attribute-Mask RCNN model to jointly perform instance segmentation and localized attribute recognition, and provide a novel evaluation metric for the task. We also demonstrate instance segmentation models pre-trained on Fashionpedia achieve better transfer learning performance on other fashion datasets than ImageNet pre-training. Fashionpedia is available at: https://fashionpedia.github.io/home/index.html.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge