Eirikur Agustsson
Extending Video Masked Autoencoders to 128 frames
Nov 20, 2024



Abstract:Video understanding has witnessed significant progress with recent video foundation models demonstrating strong performance owing to self-supervised pre-training objectives; Masked Autoencoders (MAE) being the design of choice. Nevertheless, the majority of prior works that leverage MAE pre-training have focused on relatively short video representations (16 / 32 frames in length) largely due to hardware memory and compute limitations that scale poorly with video length due to the dense memory-intensive self-attention decoding. One natural strategy to address these challenges is to subsample tokens to reconstruct during decoding (or decoder masking). In this work, we propose an effective strategy for prioritizing tokens which allows training on longer video sequences (128 frames) and gets better performance than, more typical, random and uniform masking strategies. The core of our approach is an adaptive decoder masking strategy that prioritizes the most important tokens and uses quantized tokens as reconstruction objectives. Our adaptive strategy leverages a powerful MAGVIT-based tokenizer that jointly learns the tokens and their priority. We validate our design choices through exhaustive ablations and observe improved performance of the resulting long-video (128 frames) encoders over short-video (32 frames) counterparts. With our long-video masked autoencoder (LVMAE) strategy, we surpass state-of-the-art on Diving48 by 3.9 points and EPIC-Kitchens-100 verb classification by 2.5 points while relying on a simple core architecture and video-only pre-training (unlike some of the prior works that require millions of labeled video-text pairs or specialized encoders).
Finite Scalar Quantization: VQ-VAE Made Simple
Oct 12, 2023



Abstract:We propose to replace vector quantization (VQ) in the latent representation of VQ-VAEs with a simple scheme termed finite scalar quantization (FSQ), where we project the VAE representation down to a few dimensions (typically less than 10). Each dimension is quantized to a small set of fixed values, leading to an (implicit) codebook given by the product of these sets. By appropriately choosing the number of dimensions and values each dimension can take, we obtain the same codebook size as in VQ. On top of such discrete representations, we can train the same models that have been trained on VQ-VAE representations. For example, autoregressive and masked transformer models for image generation, multimodal generation, and dense prediction computer vision tasks. Concretely, we employ FSQ with MaskGIT for image generation, and with UViM for depth estimation, colorization, and panoptic segmentation. Despite the much simpler design of FSQ, we obtain competitive performance in all these tasks. We emphasize that FSQ does not suffer from codebook collapse and does not need the complex machinery employed in VQ (commitment losses, codebook reseeding, code splitting, entropy penalties, etc.) to learn expressive discrete representations.
High-Fidelity Image Compression with Score-based Generative Models
May 26, 2023



Abstract:Despite the tremendous success of diffusion generative models in text-to-image generation, replicating this success in the domain of image compression has proven difficult. In this paper, we demonstrate that diffusion can significantly improve perceptual quality at a given bit-rate, outperforming state-of-the-art approaches PO-ELIC and HiFiC as measured by FID score. This is achieved using a simple but theoretically motivated two-stage approach combining an autoencoder targeting MSE followed by a further score-based decoder. However, as we will show, implementation details matter and the optimal design decisions can differ greatly from typical text-to-image models.
M2T: Masking Transformers Twice for Faster Decoding
Apr 14, 2023Abstract:We show how bidirectional transformers trained for masked token prediction can be applied to neural image compression to achieve state-of-the-art results. Such models were previously used for image generation by progressivly sampling groups of masked tokens according to uncertainty-adaptive schedules. Unlike these works, we demonstrate that predefined, deterministic schedules perform as well or better for image compression. This insight allows us to use masked attention during training in addition to masked inputs, and activation caching during inference, to significantly speed up our models (~4 higher inference speed) at a small increase in bitrate.
Multi-Realism Image Compression with a Conditional Generator
Dec 28, 2022Abstract:By optimizing the rate-distortion-realism trade-off, generative compression approaches produce detailed, realistic images, even at low bit rates, instead of the blurry reconstructions produced by rate-distortion optimized models. However, previous methods do not explicitly control how much detail is synthesized, which results in a common criticism of these methods: users might be worried that a misleading reconstruction far from the input image is generated. In this work, we alleviate these concerns by training a decoder that can bridge the two regimes and navigate the distortion-realism trade-off. From a single compressed representation, the receiver can decide to either reconstruct a low mean squared error reconstruction that is close to the input, a realistic reconstruction with high perceptual quality, or anything in between. With our method, we set a new state-of-the-art in distortion-realism, pushing the frontier of achievable distortion-realism pairs, i.e., our method achieves better distortions at high realism and better realism at low distortion than ever before.
VCT: A Video Compression Transformer
Jun 15, 2022


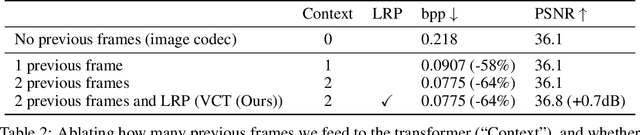
Abstract:We show how transformers can be used to vastly simplify neural video compression. Previous methods have been relying on an increasing number of architectural biases and priors, including motion prediction and warping operations, resulting in complex models. Instead, we independently map input frames to representations and use a transformer to model their dependencies, letting it predict the distribution of future representations given the past. The resulting video compression transformer outperforms previous methods on standard video compression data sets. Experiments on synthetic data show that our model learns to handle complex motion patterns such as panning, blurring and fading purely from data. Our approach is easy to implement, and we release code to facilitate future research.
Towards Generative Video Compression
Jul 26, 2021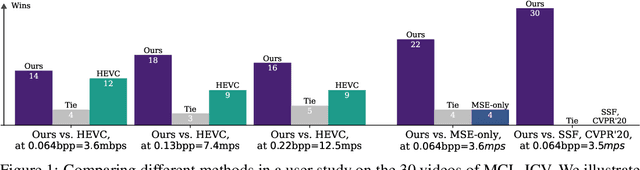
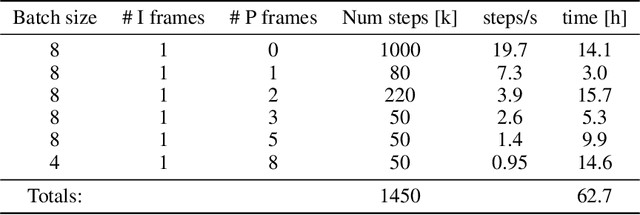
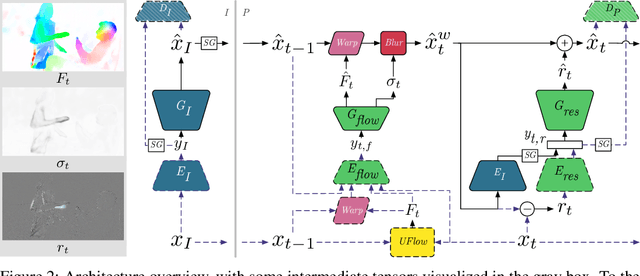
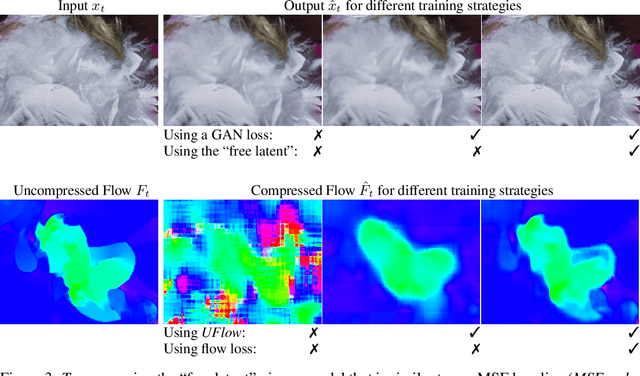
Abstract:We present a neural video compression method based on generative adversarial networks (GANs) that outperforms previous neural video compression methods and is comparable to HEVC in a user study. We propose a technique to mitigate temporal error accumulation caused by recursive frame compression that uses randomized shifting and un-shifting, motivated by a spectral analysis. We present in detail the network design choices, their relative importance, and elaborate on the challenges of evaluating video compression methods in user studies.
On the advantages of stochastic encoders
Feb 18, 2021


Abstract:Stochastic encoders have been used in rate-distortion theory and neural compression because they can be easier to handle. However, in performance comparisons with deterministic encoders they often do worse, suggesting that noise in the encoding process may generally be a bad idea. It is poorly understood if and when stochastic encoders do better than deterministic encoders. In this paper we provide one illustrative example which shows that stochastic encoders can significantly outperform the best deterministic encoders. Our toy example suggests that stochastic encoders may be particularly useful in the regime of "perfect perceptual quality".
High-Fidelity Generative Image Compression
Jul 10, 2020
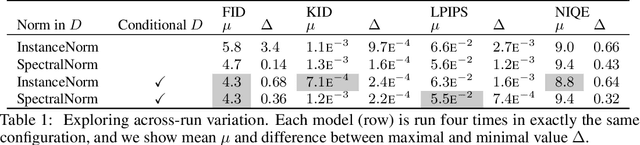
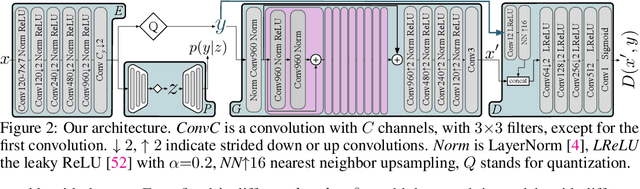
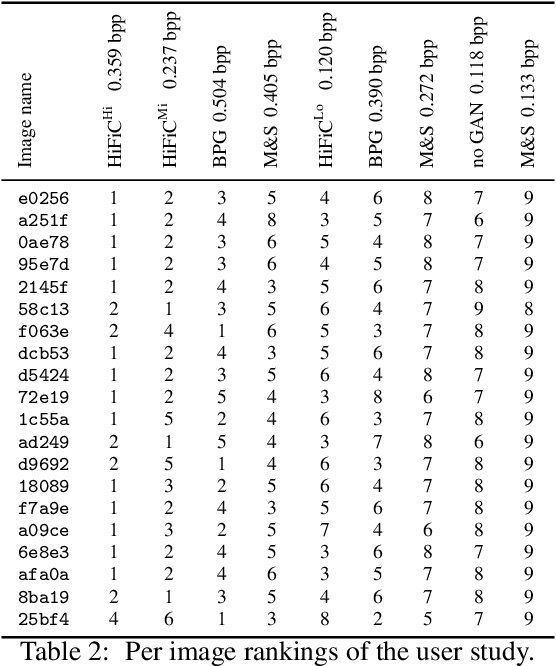
Abstract:We extensively study how to combine Generative Adversarial Networks and learned compression to obtain a state-of-the-art generative lossy compression system. In particular, we investigate normalization layers, generator and discriminator architectures, training strategies, as well as perceptual losses. In contrast to previous work, i) we obtain visually pleasing reconstructions that are perceptually similar to the input, ii) we operate in a broad range of bitrates, and iii) our approach can be applied to high-resolution images. We bridge the gap between rate-distortion-perception theory and practice by evaluating our approach both quantitatively with various perceptual metrics and a user study. The study shows that our method is preferred to previous approaches even if they use more than 2x the bitrate.
Universally Quantized Neural Compression
Jun 17, 2020



Abstract:A popular approach to learning encoders for lossy compression is to use additive uniform noise during training as a differentiable approximation to test-time quantization. We demonstrate that a uniform noise channel can also be implemented at test time using universal quantization (Ziv, 1985). This allows us to eliminate the mismatch between training and test phases while maintaining a completely differentiable loss function. Implementing the uniform noise channel is a special case of a more general problem to communicate a sample, which we prove is computationally hard if we do not make assumptions about its distribution. However, the uniform special case is efficient as well as easy to implement and thus of great interest from a practical point of view. Finally, we show that quantization can be obtained as a limiting case of a soft quantizer applied to the uniform noise channel, bridging compression with and without quantization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge