Zihao Zhu
Towards Reliable Social A/B Testing: Spillover-Contained Clustering with Robust Post-Experiment Analysis
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:A/B testing is the foundation of decision-making in online platforms, yet social products often suffer from network interference: user interactions cause treatment effects to spill over into the control group. Such spillovers bias causal estimates and undermine experimental conclusions. Existing approaches face key limitations: user-level randomization ignores network structure, while cluster-based methods often rely on general-purpose clustering that is not tailored for spillover containment and has difficulty balancing unbiasedness and statistical power at scale. We propose a spillover-contained experimentation framework with two stages. In the pre-experiment stage, we build social interaction graphs and introduce a Balanced Louvain algorithm that produces stable, size-balanced clusters while minimizing cross-cluster edges, enabling reliable cluster-based randomization. In the post-experiment stage, we develop a tailored CUPAC estimator that leverages pre-experiment behavioral covariates to reduce the variance induced by cluster-level assignment, thereby improving statistical power. Together, these components provide both structural spillover containment and robust statistical inference. We validate our approach through large-scale social sharing experiments on Kuaishou, a platform serving hundreds of millions of users. Results show that our method substantially reduces spillover and yields more accurate assessments of social strategies than traditional user-level designs, establishing a reliable and scalable framework for networked A/B testing.
Agent Banana: High-Fidelity Image Editing with Agentic Thinking and Tooling
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:We study instruction-based image editing under professional workflows and identify three persistent challenges: (i) editors often over-edit, modifying content beyond the user's intent; (ii) existing models are largely single-turn, while multi-turn edits can alter object faithfulness; and (iii) evaluation at around 1K resolution is misaligned with real workflows that often operate on ultra high-definition images (e.g., 4K). We propose Agent Banana, a hierarchical agentic planner-executor framework for high-fidelity, object-aware, deliberative editing. Agent Banana introduces two key mechanisms: (1) Context Folding, which compresses long interaction histories into structured memory for stable long-horizon control; and (2) Image Layer Decomposition, which performs localized layer-based edits to preserve non-target regions while enabling native-resolution outputs. To support rigorous evaluation, we build HDD-Bench, a high-definition, dialogue-based benchmark featuring verifiable stepwise targets and native 4K images (11.8M pixels) for diagnosing long-horizon failures. On HDD-Bench, Agent Banana achieves the best multi-turn consistency and background fidelity (e.g., IC 0.871, SSIM-OM 0.84, LPIPS-OM 0.12) while remaining competitive on instruction following, and also attains strong performance on standard single-turn editing benchmarks. We hope this work advances reliable, professional-grade agentic image editing and its integration into real workflows.
Unveiling Covert Toxicity in Multimodal Data via Toxicity Association Graphs: A Graph-Based Metric and Interpretable Detection Framework
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Detecting toxicity in multimodal data remains a significant challenge, as harmful meanings often lurk beneath seemingly benign individual modalities: only emerging when modalities are combined and semantic associations are activated. To address this, we propose a novel detection framework based on Toxicity Association Graphs (TAGs), which systematically model semantic associations between innocuous entities and latent toxic implications. Leveraging TAGs, we introduce the first quantifiable metric for hidden toxicity, the Multimodal Toxicity Covertness (MTC), which measures the degree of concealment in toxic multimodal expressions. By integrating our detection framework with the MTC metric, our approach enables precise identification of covert toxicity while preserving full interpretability of the decision-making process, significantly enhancing transparency in multimodal toxicity detection. To validate our method, we construct the Covert Toxic Dataset, the first benchmark specifically designed to capture high-covertness toxic multimodal instances. This dataset encodes nuanced cross-modal associations and serves as a rigorous testbed for evaluating both the proposed metric and detection framework. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing methods across both low- and high-covertness toxicity regimes, while delivering clear, interpretable, and auditable detection outcomes. Together, our contributions advance the state of the art in explainable multimodal toxicity detection and lay the foundation for future context-aware and interpretable approaches. Content Warning: This paper contains examples of toxic multimodal content that may be offensive or disturbing to some readers. Reader discretion is advised.
SCOPE-DTI: Semi-Inductive Dataset Construction and Framework Optimization for Practical Usability Enhancement in Deep Learning-Based Drug Target Interaction Prediction
Mar 12, 2025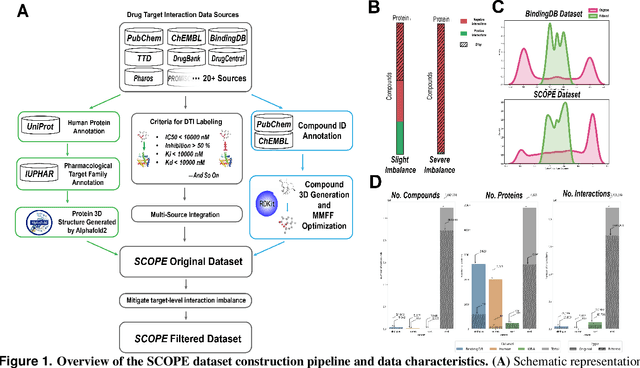
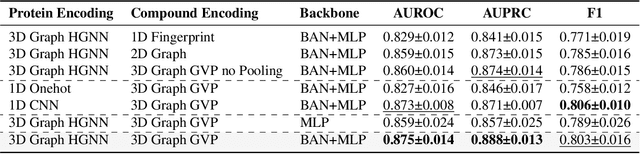
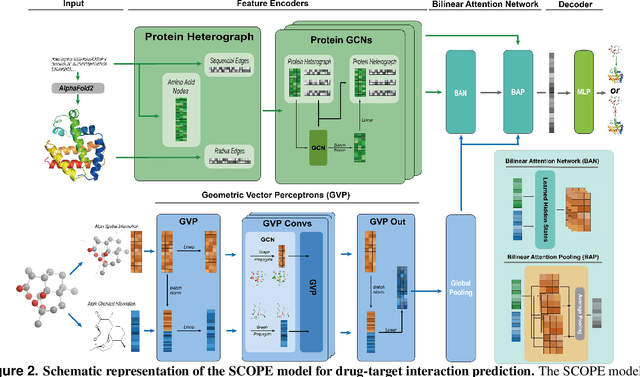
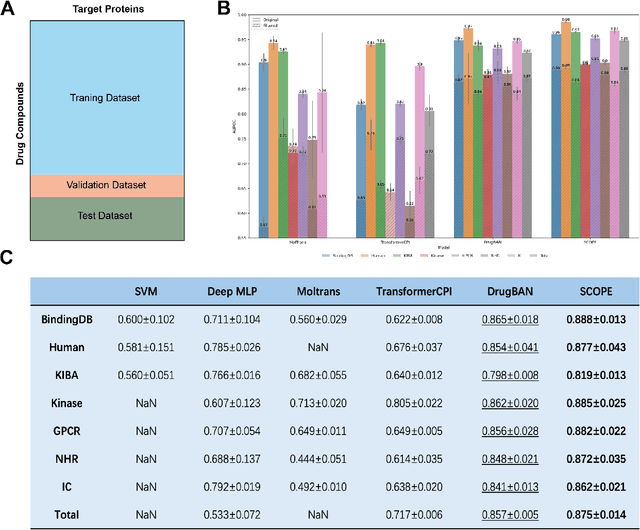
Abstract:Deep learning-based drug-target interaction (DTI) prediction methods have demonstrated strong performance; however, real-world applicability remains constrained by limited data diversity and modeling complexity. To address these challenges, we propose SCOPE-DTI, a unified framework combining a large-scale, balanced semi-inductive human DTI dataset with advanced deep learning modeling. Constructed from 13 public repositories, the SCOPE dataset expands data volume by up to 100-fold compared to common benchmarks such as the Human dataset. The SCOPE model integrates three-dimensional protein and compound representations, graph neural networks, and bilinear attention mechanisms to effectively capture cross domain interaction patterns, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art methods across various DTI prediction tasks. Additionally, SCOPE-DTI provides a user-friendly interface and database. We further validate its effectiveness by experimentally identifying anticancer targets of Ginsenoside Rh1. By offering comprehensive data, advanced modeling, and accessible tools, SCOPE-DTI accelerates drug discovery research.
AuxDepthNet: Real-Time Monocular 3D Object Detection with Depth-Sensitive Features
Jan 07, 2025



Abstract:Monocular 3D object detection is a challenging task in autonomous systems due to the lack of explicit depth information in single-view images. Existing methods often depend on external depth estimators or expensive sensors, which increase computational complexity and hinder real-time performance. To overcome these limitations, we propose AuxDepthNet, an efficient framework for real-time monocular 3D object detection that eliminates the reliance on external depth maps or pre-trained depth models. AuxDepthNet introduces two key components: the Auxiliary Depth Feature (ADF) module, which implicitly learns depth-sensitive features to improve spatial reasoning and computational efficiency, and the Depth Position Mapping (DPM) module, which embeds depth positional information directly into the detection process to enable accurate object localization and 3D bounding box regression. Leveraging the DepthFusion Transformer architecture, AuxDepthNet globally integrates visual and depth-sensitive features through depth-guided interactions, ensuring robust and efficient detection. Extensive experiments on the KITTI dataset show that AuxDepthNet achieves state-of-the-art performance, with $\text{AP}_{3D}$ scores of 24.72\% (Easy), 18.63\% (Moderate), and 15.31\% (Hard), and $\text{AP}_{\text{BEV}}$ scores of 34.11\% (Easy), 25.18\% (Moderate), and 21.90\% (Hard) at an IoU threshold of 0.7.
HMGIE: Hierarchical and Multi-Grained Inconsistency Evaluation for Vision-Language Data Cleansing
Dec 07, 2024Abstract:Visual-textual inconsistency (VTI) evaluation plays a crucial role in cleansing vision-language data. Its main challenges stem from the high variety of image captioning datasets, where differences in content can create a range of inconsistencies (\eg, inconsistencies in scene, entities, entity attributes, entity numbers, entity interactions). Moreover, variations in caption length can introduce inconsistencies at different levels of granularity as well. To tackle these challenges, we design an adaptive evaluation framework, called Hierarchical and Multi-Grained Inconsistency Evaluation (HMGIE), which can provide multi-grained evaluations covering both accuracy and completeness for various image-caption pairs. Specifically, the HMGIE framework is implemented by three consecutive modules. Firstly, the semantic graph generation module converts the image caption to a semantic graph for building a structural representation of all involved semantic items. Then, the hierarchical inconsistency evaluation module provides a progressive evaluation procedure with a dynamic question-answer generation and evaluation strategy guided by the semantic graph, producing a hierarchical inconsistency evaluation graph (HIEG). Finally, the quantitative evaluation module calculates the accuracy and completeness scores based on the HIEG, followed by a natural language explanation about the detection results. Moreover, to verify the efficacy and flexibility of the proposed framework on handling different image captioning datasets, we construct MVTID, an image-caption dataset with diverse types and granularities of inconsistencies. Extensive experiments on MVTID and other benchmark datasets demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed HMGIE to current state-of-the-art methods.
Reliable Poisoned Sample Detection against Backdoor Attacks Enhanced by Sharpness Aware Minimization
Nov 18, 2024



Abstract:Backdoor attack has been considered as a serious security threat to deep neural networks (DNNs). Poisoned sample detection (PSD) that aims at filtering out poisoned samples from an untrustworthy training dataset has shown very promising performance for defending against data poisoning based backdoor attacks. However, we observe that the detection performance of many advanced methods is likely to be unstable when facing weak backdoor attacks, such as low poisoning ratio or weak trigger strength. To further verify this observation, we make a statistical investigation among various backdoor attacks and poisoned sample detections, showing a positive correlation between backdoor effect and detection performance. It inspires us to strengthen the backdoor effect to enhance detection performance. Since we cannot achieve that goal via directly manipulating poisoning ratio or trigger strength, we propose to train one model using the Sharpness-Aware Minimization (SAM) algorithm, rather than the vanilla training algorithm. We also provide both empirical and theoretical analysis about how SAM training strengthens the backdoor effect. Then, this SAM trained model can be seamlessly integrated with any off-the-shelf PSD method that extracts discriminative features from the trained model for detection, called SAM-enhanced PSD. Extensive experiments on several benchmark datasets show the reliable detection performance of the proposed method against both weak and strong backdoor attacks, with significant improvements against various attacks ($+34.38\%$ TPR on average), over the conventional PSD methods (i.e., without SAM enhancement). Overall, this work provides new insights about PSD and proposes a novel approach that can complement existing detection methods, which may inspire more in-depth explorations in this field.
RiskAwareBench: Towards Evaluating Physical Risk Awareness for High-level Planning of LLM-based Embodied Agents
Aug 08, 2024



Abstract:The integration of large language models (LLMs) into robotics significantly enhances the capabilities of embodied agents in understanding and executing complex natural language instructions. However, the unmitigated deployment of LLM-based embodied systems in real-world environments may pose potential physical risks, such as property damage and personal injury. Existing security benchmarks for LLMs overlook risk awareness for LLM-based embodied agents. To address this gap, we propose RiskAwareBench, an automated framework designed to assess physical risks awareness in LLM-based embodied agents. RiskAwareBench consists of four modules: safety tips generation, risky scene generation, plan generation, and evaluation, enabling comprehensive risk assessment with minimal manual intervention. Utilizing this framework, we compile the PhysicalRisk dataset, encompassing diverse scenarios with associated safety tips, observations, and instructions. Extensive experiments reveal that most LLMs exhibit insufficient physical risk awareness, and baseline risk mitigation strategies yield limited enhancement, which emphasizes the urgency and cruciality of improving risk awareness in LLM-based embodied agents in the future.
LoCI-DiffCom: Longitudinal Consistency-Informed Diffusion Model for 3D Infant Brain Image Completion
May 17, 2024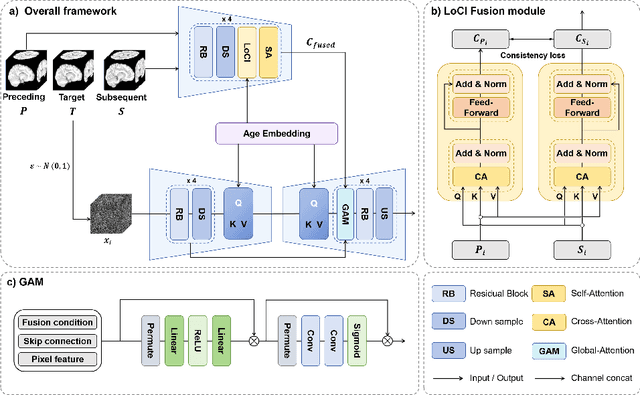
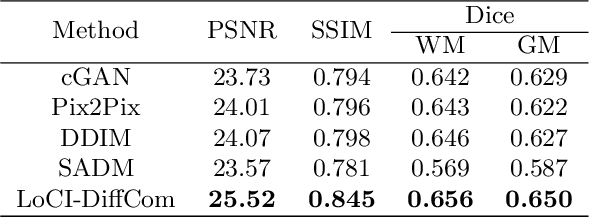
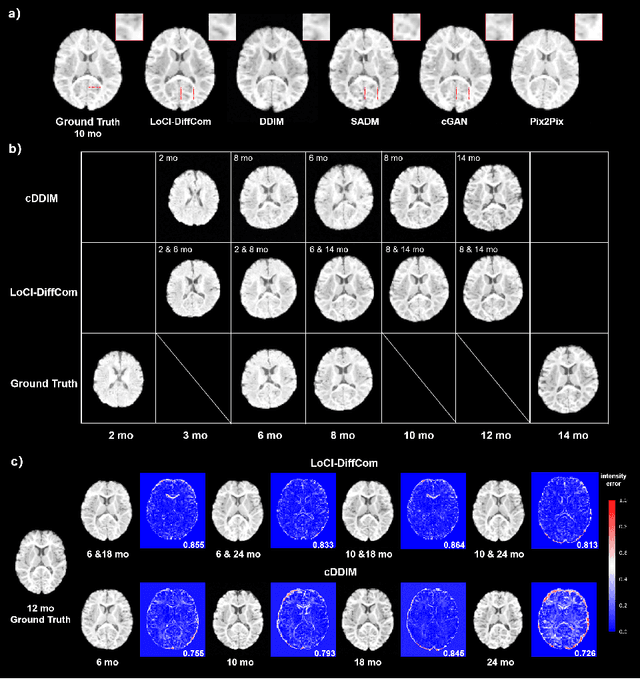
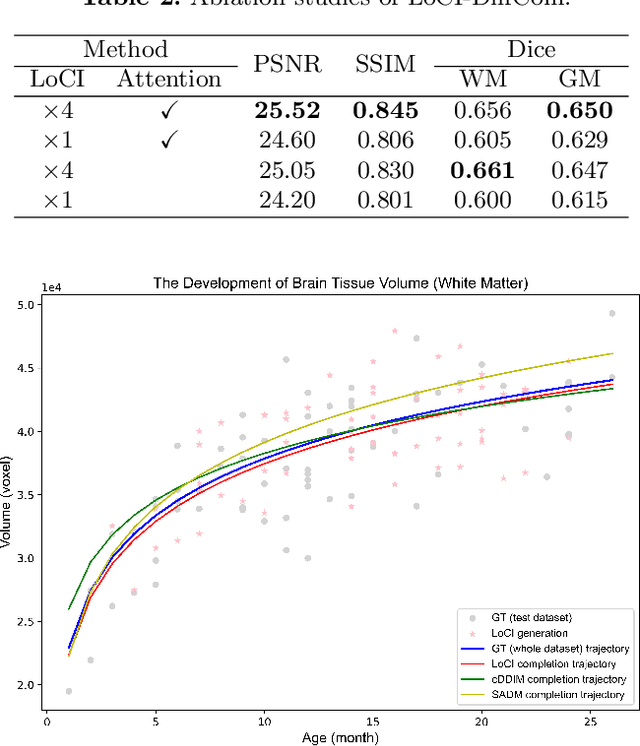
Abstract:The infant brain undergoes rapid development in the first few years after birth.Compared to cross-sectional studies, longitudinal studies can depict the trajectories of infants brain development with higher accuracy, statistical power and flexibility.However, the collection of infant longitudinal magnetic resonance (MR) data suffers a notorious dropout problem, resulting in incomplete datasets with missing time points. This limitation significantly impedes subsequent neuroscience and clinical modeling. Yet, existing deep generative models are facing difficulties in missing brain image completion, due to sparse data and the nonlinear, dramatic contrast/geometric variations in the developing brain. We propose LoCI-DiffCom, a novel Longitudinal Consistency-Informed Diffusion model for infant brain image Completion,which integrates the images from preceding and subsequent time points to guide a diffusion model for generating high-fidelity missing data. Our designed LoCI module can work on highly sparse sequences, relying solely on data from two temporal points. Despite wide separation and diversity between age time points, our approach can extract individualized developmental features while ensuring context-aware consistency. Our experiments on a large infant brain MR dataset demonstrate its effectiveness with consistent performance on missing infant brain MR completion even in big gap scenarios, aiding in better delineation of early developmental trajectories.
Dr.Hair: Reconstructing Scalp-Connected Hair Strands without Pre-training via Differentiable Rendering of Line Segments
Mar 29, 2024Abstract:In the film and gaming industries, achieving a realistic hair appearance typically involves the use of strands originating from the scalp. However, reconstructing these strands from observed surface images of hair presents significant challenges. The difficulty in acquiring Ground Truth (GT) data has led state-of-the-art learning-based methods to rely on pre-training with manually prepared synthetic CG data. This process is not only labor-intensive and costly but also introduces complications due to the domain gap when compared to real-world data. In this study, we propose an optimization-based approach that eliminates the need for pre-training. Our method represents hair strands as line segments growing from the scalp and optimizes them using a novel differentiable rendering algorithm. To robustly optimize a substantial number of slender explicit geometries, we introduce 3D orientation estimation utilizing global optimization, strand initialization based on Laplace's equation, and reparameterization that leverages geometric connectivity and spatial proximity. Unlike existing optimization-based methods, our method is capable of reconstructing internal hair flow in an absolute direction. Our method exhibits robust and accurate inverse rendering, surpassing the quality of existing methods and significantly improving processing speed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge