Haifeng Tang
Is Your Image a Good Storyteller?
Dec 29, 2024Abstract:Quantifying image complexity at the entity level is straightforward, but the assessment of semantic complexity has been largely overlooked. In fact, there are differences in semantic complexity across images. Images with richer semantics can tell vivid and engaging stories and offer a wide range of application scenarios. For example, the Cookie Theft picture is such a kind of image and is widely used to assess human language and cognitive abilities due to its higher semantic complexity. Additionally, semantically rich images can benefit the development of vision models, as images with limited semantics are becoming less challenging for them. However, such images are scarce, highlighting the need for a greater number of them. For instance, there is a need for more images like Cookie Theft to cater to people from different cultural backgrounds and eras. Assessing semantic complexity requires human experts and empirical evidence. Automatic evaluation of how semantically rich an image will be the first step of mining or generating more images with rich semantics, and benefit human cognitive assessment, Artificial Intelligence, and various other applications. In response, we propose the Image Semantic Assessment (ISA) task to address this problem. We introduce the first ISA dataset and a novel method that leverages language to solve this vision problem. Experiments on our dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. Our data and code are available at: https://github.com/xiujiesong/ISA.
LoCI-DiffCom: Longitudinal Consistency-Informed Diffusion Model for 3D Infant Brain Image Completion
May 17, 2024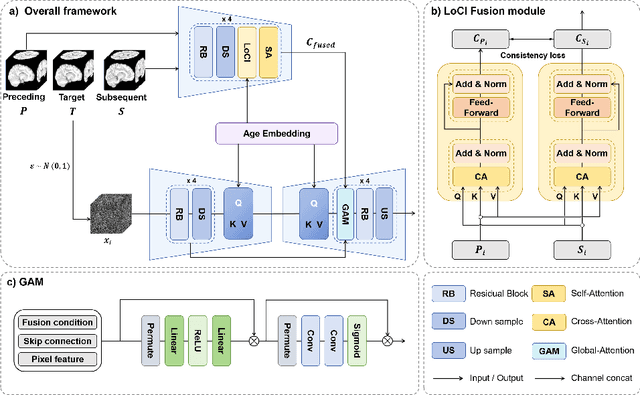
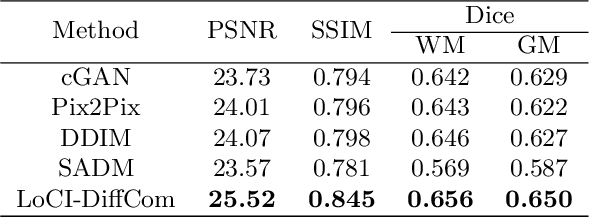
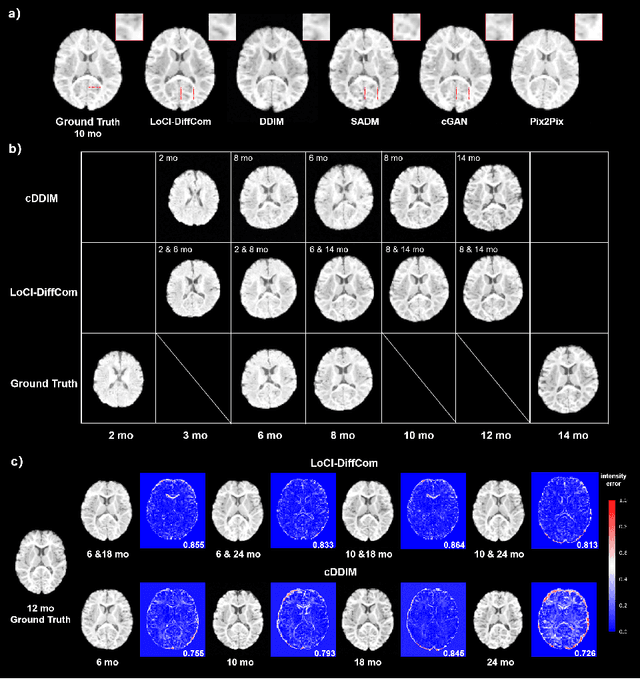
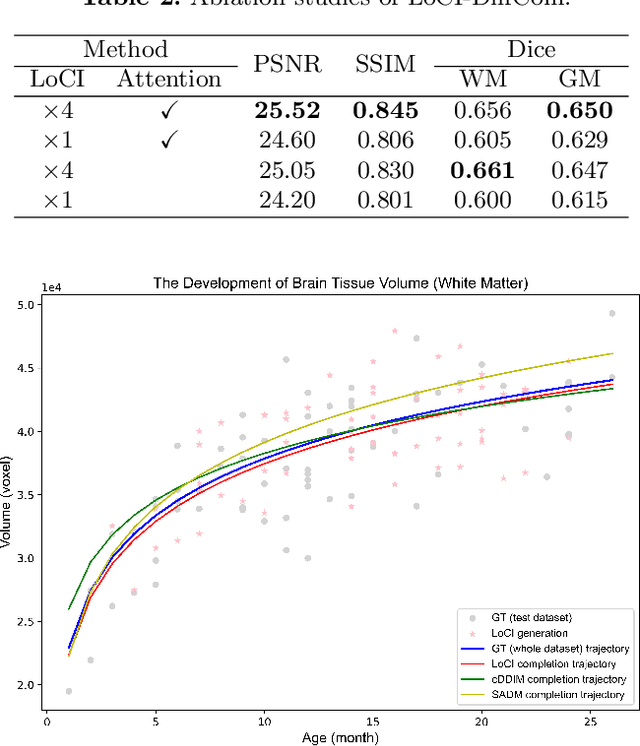
Abstract:The infant brain undergoes rapid development in the first few years after birth.Compared to cross-sectional studies, longitudinal studies can depict the trajectories of infants brain development with higher accuracy, statistical power and flexibility.However, the collection of infant longitudinal magnetic resonance (MR) data suffers a notorious dropout problem, resulting in incomplete datasets with missing time points. This limitation significantly impedes subsequent neuroscience and clinical modeling. Yet, existing deep generative models are facing difficulties in missing brain image completion, due to sparse data and the nonlinear, dramatic contrast/geometric variations in the developing brain. We propose LoCI-DiffCom, a novel Longitudinal Consistency-Informed Diffusion model for infant brain image Completion,which integrates the images from preceding and subsequent time points to guide a diffusion model for generating high-fidelity missing data. Our designed LoCI module can work on highly sparse sequences, relying solely on data from two temporal points. Despite wide separation and diversity between age time points, our approach can extract individualized developmental features while ensuring context-aware consistency. Our experiments on a large infant brain MR dataset demonstrate its effectiveness with consistent performance on missing infant brain MR completion even in big gap scenarios, aiding in better delineation of early developmental trajectories.
Cas-DiffCom: Cascaded diffusion model for infant longitudinal super-resolution 3D medical image completion
Feb 21, 2024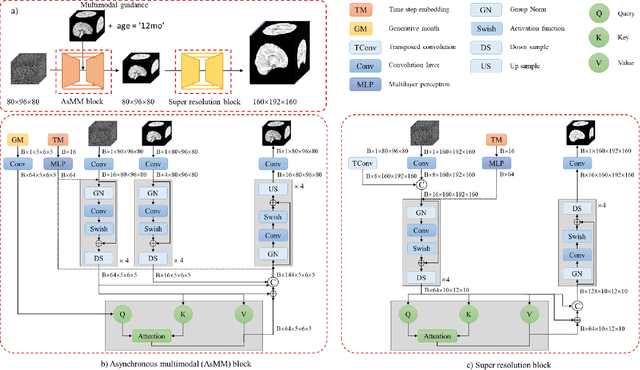
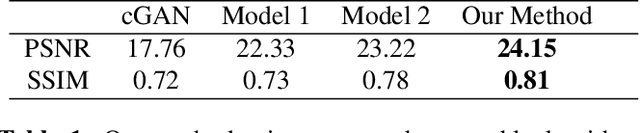
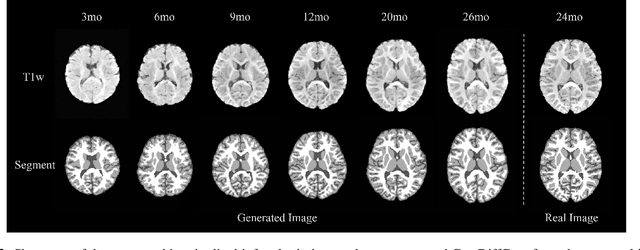
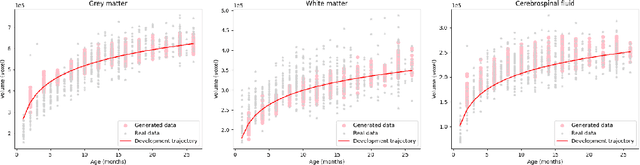
Abstract:Early infancy is a rapid and dynamic neurodevelopmental period for behavior and neurocognition. Longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an effective tool to investigate such a crucial stage by capturing the developmental trajectories of the brain structures. However, longitudinal MRI acquisition always meets a serious data-missing problem due to participant dropout and failed scans, making longitudinal infant brain atlas construction and developmental trajectory delineation quite challenging. Thanks to the development of an AI-based generative model, neuroimage completion has become a powerful technique to retain as much available data as possible. However, current image completion methods usually suffer from inconsistency within each individual subject in the time dimension, compromising the overall quality. To solve this problem, our paper proposed a two-stage cascaded diffusion model, Cas-DiffCom, for dense and longitudinal 3D infant brain MRI completion and super-resolution. We applied our proposed method to the Baby Connectome Project (BCP) dataset. The experiment results validate that Cas-DiffCom achieves both individual consistency and high fidelity in longitudinal infant brain image completion. We further applied the generated infant brain images to two downstream tasks, brain tissue segmentation and developmental trajectory delineation, to declare its task-oriented potential in the neuroscience field.
Reducing Sensitivity on Speaker Names for Text Generation from Dialogues
May 23, 2023



Abstract:Changing speaker names consistently throughout a dialogue should not affect its meaning and corresponding outputs for text generation from dialogues. However, pre-trained language models, serving as the backbone for dialogue-processing tasks, have shown to be sensitive to nuances. This may result in unfairness in real-world applications. No comprehensive analysis of this problem has been done in the past. In this work, we propose to quantitatively measure a model's sensitivity on speaker names, and comprehensively evaluate a number of known methods for reducing speaker name sensitivity, including a novel approach of our own. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets provide a benchmark for this problem and show the favorable performance of our approach in sensitivity reduction and quality of generation.
In-sample Curriculum Learning by Sequence Completion for Natural Language Generation
Nov 21, 2022



Abstract:Curriculum learning has shown promising improvements in multiple domains by training machine learning models from easy samples to hard ones. Previous works which either design rules or train models for scoring the difficulty highly rely on task-specific expertise, and cannot generalize. Inspired by the ``easy-to-hard'' intuition, we propose to do in-sample curriculum learning for natural language generation tasks. Our learning strategy starts training the model to generate the last few words, i.e., do sequence completion, and gradually extends to generate the whole output sequence. Comprehensive experiments show that it generalizes well to different tasks and achieves significant improvements over strong baselines.
Post-Training Dialogue Summarization using Pseudo-Paraphrasing
Apr 28, 2022


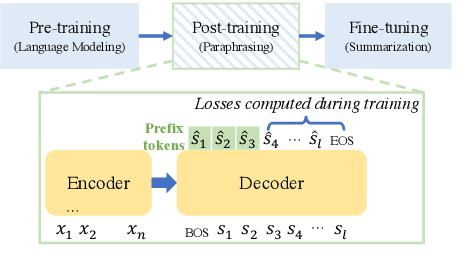
Abstract:Previous dialogue summarization techniques adapt large language models pretrained on the narrative text by injecting dialogue-specific features into the models. These features either require additional knowledge to recognize or make the resulting models harder to tune. To bridge the format gap between dialogues and narrative summaries in dialogue summarization tasks, we propose to post-train pretrained language models (PLMs) to rephrase from dialogue to narratives. After that, the model is fine-tuned for dialogue summarization as usual. Comprehensive experiments show that our approach significantly improves vanilla PLMs on dialogue summarization and outperforms other SOTA models by the summary quality and implementation costs.
Enriching Ontology with Temporal Commonsense for Low-Resource Audio Tagging
Oct 03, 2021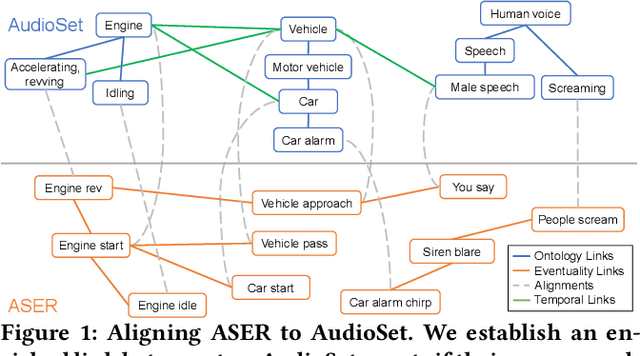
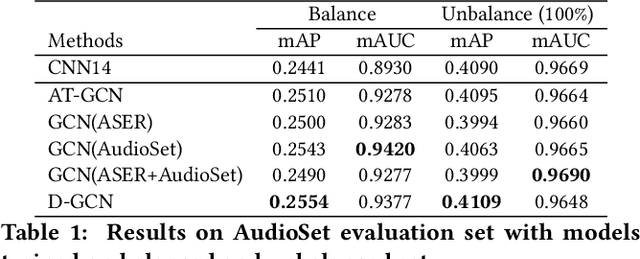
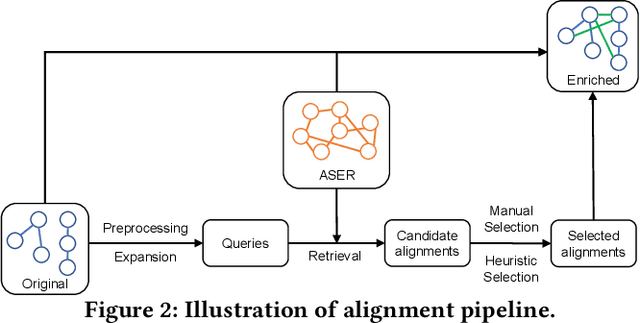
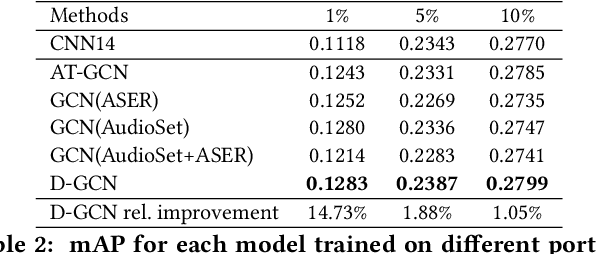
Abstract:Audio tagging aims at predicting sound events occurred in a recording. Traditional models require enormous laborious annotations, otherwise performance degeneration will be the norm. Therefore, we investigate robust audio tagging models in low-resource scenarios with the enhancement of knowledge graphs. Besides existing ontological knowledge, we further propose a semi-automatic approach that can construct temporal knowledge graphs on diverse domain-specific label sets. Moreover, we leverage a variant of relation-aware graph neural network, D-GCN, to combine the strength of the two knowledge types. Experiments on AudioSet and SONYC urban sound tagging datasets suggest the effectiveness of the introduced temporal knowledge, and the advantage of the combined KGs with D-GCN over single knowledge source.
Multi-turn Response Selection using Dialogue Dependency Relations
Oct 04, 2020
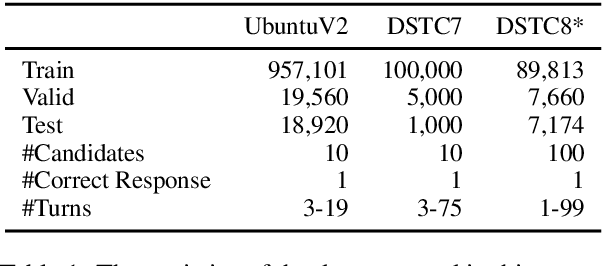
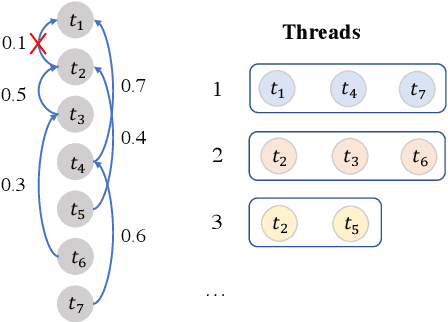
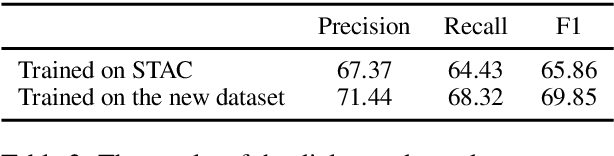
Abstract:Multi-turn response selection is a task designed for developing dialogue agents. The performance on this task has a remarkable improvement with pre-trained language models. However, these models simply concatenate the turns in dialogue history as the input and largely ignore the dependencies between the turns. In this paper, we propose a dialogue extraction algorithm to transform a dialogue history into threads based on their dependency relations. Each thread can be regarded as a self-contained sub-dialogue. We also propose Thread-Encoder model to encode threads and candidates into compact representations by pre-trained Transformers and finally get the matching score through an attention layer. The experiments show that dependency relations are helpful for dialogue context understanding, and our model outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines on both DSTC7 and DSTC8*, with competitive results on UbuntuV2.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge