Zelin Zhou
KG-TRICK: Unifying Textual and Relational Information Completion of Knowledge for Multilingual Knowledge Graphs
Jan 07, 2025



Abstract:Multilingual knowledge graphs (KGs) provide high-quality relational and textual information for various NLP applications, but they are often incomplete, especially in non-English languages. Previous research has shown that combining information from KGs in different languages aids either Knowledge Graph Completion (KGC), the task of predicting missing relations between entities, or Knowledge Graph Enhancement (KGE), the task of predicting missing textual information for entities. Although previous efforts have considered KGC and KGE as independent tasks, we hypothesize that they are interdependent and mutually beneficial. To this end, we introduce KG-TRICK, a novel sequence-to-sequence framework that unifies the tasks of textual and relational information completion for multilingual KGs. KG-TRICK demonstrates that: i) it is possible to unify the tasks of KGC and KGE into a single framework, and ii) combining textual information from multiple languages is beneficial to improve the completeness of a KG. As part of our contributions, we also introduce WikiKGE10++, the largest manually-curated benchmark for textual information completion of KGs, which features over 25,000 entities across 10 diverse languages.
Do Large Language Models Have an English Accent? Evaluating and Improving the Naturalness of Multilingual LLMs
Oct 21, 2024



Abstract:Current Large Language Models (LLMs) are predominantly designed with English as the primary language, and even the few that are multilingual tend to exhibit strong English-centric biases. Much like speakers who might produce awkward expressions when learning a second language, LLMs often generate unnatural outputs in non-English languages, reflecting English-centric patterns in both vocabulary and grammar. Despite the importance of this issue, the naturalness of multilingual LLM outputs has received limited attention. In this paper, we address this gap by introducing novel automatic corpus-level metrics to assess the lexical and syntactic naturalness of LLM outputs in a multilingual context. Using our new metrics, we evaluate state-of-the-art LLMs on a curated benchmark in French and Chinese, revealing a tendency towards English-influenced patterns. To mitigate this issue, we also propose a simple and effective alignment method to improve the naturalness of an LLM in a target language and domain, achieving consistent improvements in naturalness without compromising the performance on general-purpose benchmarks. Our work highlights the importance of developing multilingual metrics, resources and methods for the new wave of multilingual LLMs.
BLAT: Bootstrapping Language-Audio Pre-training based on AudioSet Tag-guided Synthetic Data
Mar 14, 2023Abstract:Compared with ample visual-text pre-training research, few works explore audio-text pre-training, mostly due to the lack of sufficient parallel audio-text data. Most existing methods incorporate the visual modality as a pivot for audio-text pre-training, which inevitably induces data noise. In this paper, we propose BLAT: Bootstrapping Language-Audio pre-training based on Tag-guided synthetic data. We utilize audio captioning to generate text directly from audio, without the aid of the visual modality so that potential noise from modality mismatch is eliminated. Furthermore, we propose caption generation under the guidance of AudioSet tags, leading to more accurate captions. With the above two improvements, we curate high-quality, large-scale parallel audio-text data, based on which we perform audio-text pre-training. Evaluation on a series of downstream tasks indicates that BLAT achieves SOTA zero-shot classification performance on most datasets and significant performance improvement when fine-tuned on downstream tasks, suggesting the effectiveness of our synthetic data.
Can Audio Captions Be Evaluated with Image Caption Metrics?
Oct 10, 2021

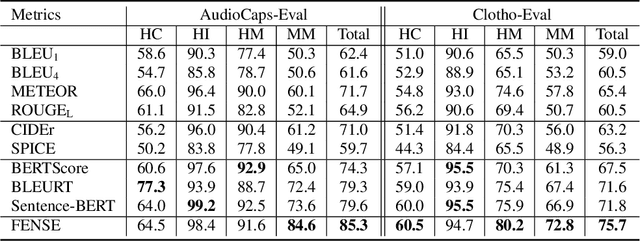

Abstract:Automated audio captioning aims at generating textual descriptions for an audio clip. To evaluate the quality of generated audio captions, previous works directly adopt image captioning metrics like SPICE and CIDEr, without justifying their suitability in this new domain, which may mislead the development of advanced models. This problem is still unstudied due to the lack of human judgment datasets on caption quality. Therefore, we firstly construct two evaluation benchmarks, AudioCaps-Eval and Clotho-Eval. They are established with pairwise comparison instead of absolute rating to achieve better inter-annotator agreement. Current metrics are found in poor correlation with human annotations on these datasets. To overcome their limitations, we propose a metric named FENSE, where we combine the strength of Sentence-BERT in capturing similarity, and a novel Error Detector to penalize erroneous sentences for robustness. On the newly established benchmarks, FENSE outperforms current metrics by 14-25% accuracy. Code, data and web demo available at: https://github.com/blmoistawinde/fense
Enriching Ontology with Temporal Commonsense for Low-Resource Audio Tagging
Oct 03, 2021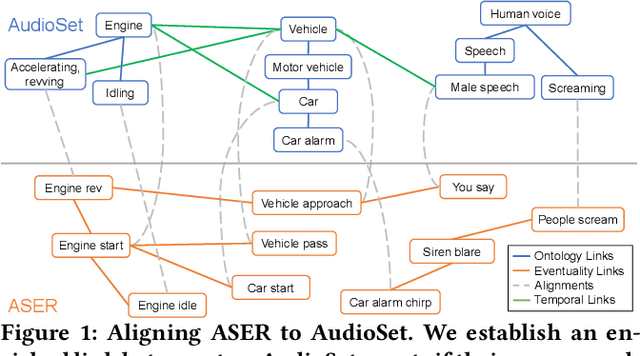
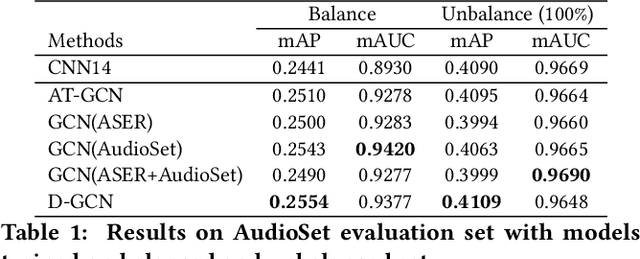
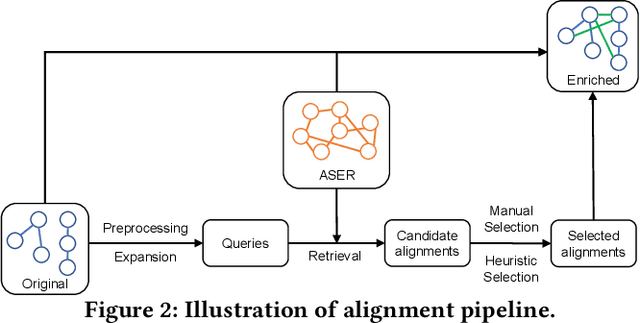
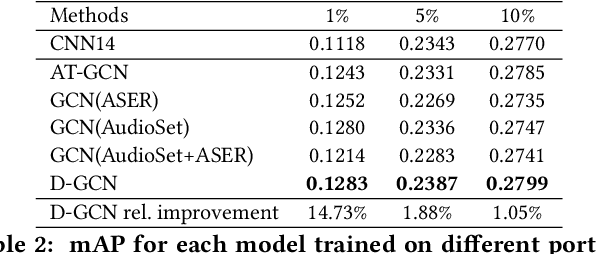
Abstract:Audio tagging aims at predicting sound events occurred in a recording. Traditional models require enormous laborious annotations, otherwise performance degeneration will be the norm. Therefore, we investigate robust audio tagging models in low-resource scenarios with the enhancement of knowledge graphs. Besides existing ontological knowledge, we further propose a semi-automatic approach that can construct temporal knowledge graphs on diverse domain-specific label sets. Moreover, we leverage a variant of relation-aware graph neural network, D-GCN, to combine the strength of the two knowledge types. Experiments on AudioSet and SONYC urban sound tagging datasets suggest the effectiveness of the introduced temporal knowledge, and the advantage of the combined KGs with D-GCN over single knowledge source.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge