Shenglei Huang
KG-TRICK: Unifying Textual and Relational Information Completion of Knowledge for Multilingual Knowledge Graphs
Jan 07, 2025



Abstract:Multilingual knowledge graphs (KGs) provide high-quality relational and textual information for various NLP applications, but they are often incomplete, especially in non-English languages. Previous research has shown that combining information from KGs in different languages aids either Knowledge Graph Completion (KGC), the task of predicting missing relations between entities, or Knowledge Graph Enhancement (KGE), the task of predicting missing textual information for entities. Although previous efforts have considered KGC and KGE as independent tasks, we hypothesize that they are interdependent and mutually beneficial. To this end, we introduce KG-TRICK, a novel sequence-to-sequence framework that unifies the tasks of textual and relational information completion for multilingual KGs. KG-TRICK demonstrates that: i) it is possible to unify the tasks of KGC and KGE into a single framework, and ii) combining textual information from multiple languages is beneficial to improve the completeness of a KG. As part of our contributions, we also introduce WikiKGE10++, the largest manually-curated benchmark for textual information completion of KGs, which features over 25,000 entities across 10 diverse languages.
Multi-scale Neural Networks for Retinal Blood Vessels Segmentation
Apr 11, 2018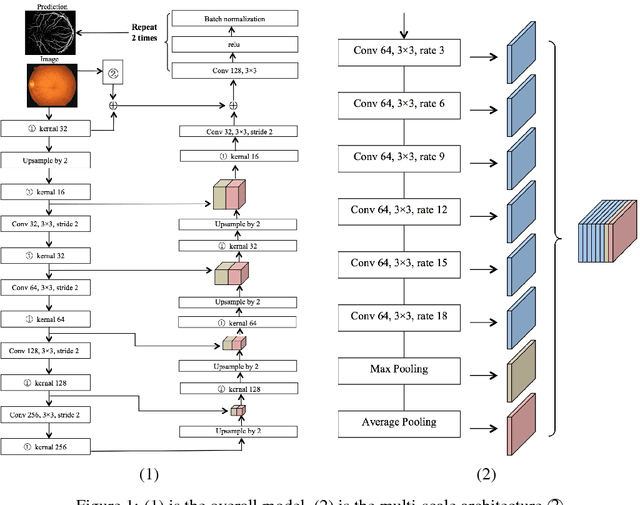
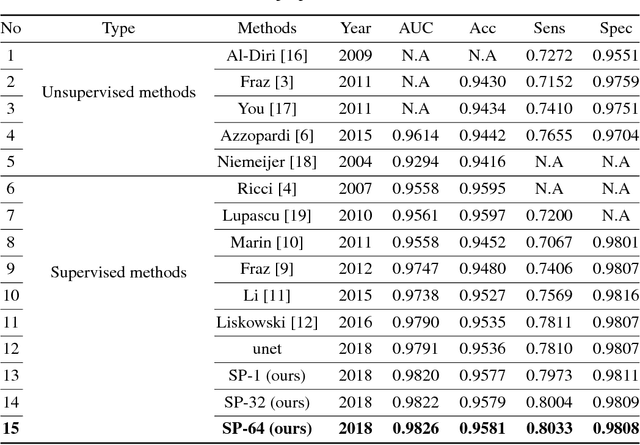
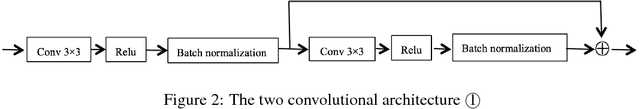
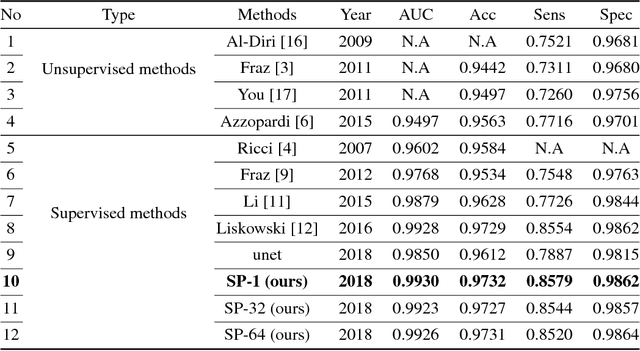
Abstract:Existing supervised approaches didn't make use of the low-level features which are actually effective to this task. And another deficiency is that they didn't consider the relation between pixels, which means effective features are not extracted. In this paper, we proposed a novel convolutional neural network which make sufficient use of low-level features together with high-level features and involves atrous convolution to get multi-scale features which should be considered as effective features. Our model is tested on three standard benchmarks - DRIVE, STARE, and CHASE databases. The results presents that our model significantly outperforms existing approaches in terms of accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, the area under the ROC curve and the highest prediction speed. Our work provides evidence of the power of wide and deep neural networks in retinal blood vessels segmentation task which could be applied on other medical images tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge