Ruotong Wang
BadVideo: Stealthy Backdoor Attack against Text-to-Video Generation
Apr 23, 2025Abstract:Text-to-video (T2V) generative models have rapidly advanced and found widespread applications across fields like entertainment, education, and marketing. However, the adversarial vulnerabilities of these models remain rarely explored. We observe that in T2V generation tasks, the generated videos often contain substantial redundant information not explicitly specified in the text prompts, such as environmental elements, secondary objects, and additional details, providing opportunities for malicious attackers to embed hidden harmful content. Exploiting this inherent redundancy, we introduce BadVideo, the first backdoor attack framework tailored for T2V generation. Our attack focuses on designing target adversarial outputs through two key strategies: (1) Spatio-Temporal Composition, which combines different spatiotemporal features to encode malicious information; (2) Dynamic Element Transformation, which introduces transformations in redundant elements over time to convey malicious information. Based on these strategies, the attacker's malicious target seamlessly integrates with the user's textual instructions, providing high stealthiness. Moreover, by exploiting the temporal dimension of videos, our attack successfully evades traditional content moderation systems that primarily analyze spatial information within individual frames. Extensive experiments demonstrate that BadVideo achieves high attack success rates while preserving original semantics and maintaining excellent performance on clean inputs. Overall, our work reveals the adversarial vulnerability of T2V models, calling attention to potential risks and misuse. Our project page is at https://wrt2000.github.io/BadVideo2025/.
StructVPR++: Distill Structural and Semantic Knowledge with Weighting Samples for Visual Place Recognition
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Visual place recognition is a challenging task for autonomous driving and robotics, which is usually considered as an image retrieval problem. A commonly used two-stage strategy involves global retrieval followed by re-ranking using patch-level descriptors. Most deep learning-based methods in an end-to-end manner cannot extract global features with sufficient semantic information from RGB images. In contrast, re-ranking can utilize more explicit structural and semantic information in one-to-one matching process, but it is time-consuming. To bridge the gap between global retrieval and re-ranking and achieve a good trade-off between accuracy and efficiency, we propose StructVPR++, a framework that embeds structural and semantic knowledge into RGB global representations via segmentation-guided distillation. Our key innovation lies in decoupling label-specific features from global descriptors, enabling explicit semantic alignment between image pairs without requiring segmentation during deployment. Furthermore, we introduce a sample-wise weighted distillation strategy that prioritizes reliable training pairs while suppressing noisy ones. Experiments on four benchmarks demonstrate that StructVPR++ surpasses state-of-the-art global methods by 5-23% in Recall@1 and even outperforms many two-stage approaches, achieving real-time efficiency with a single RGB input.
Automated Genre-Aware Article Scoring and Feedback Using Large Language Models
Oct 18, 2024



Abstract:This paper focuses on the development of an advanced intelligent article scoring system that not only assesses the overall quality of written work but also offers detailed feature-based scoring tailored to various article genres. By integrating the pre-trained BERT model with the large language model Chat-GPT, the system gains a deep understanding of both the content and structure of the text, enabling it to provide a thorough evaluation along with targeted suggestions for improvement. Experimental results demonstrate that this system outperforms traditional scoring methods across multiple public datasets, particularly in feature-based assessments, offering a more accurate reflection of the quality of different article types. Moreover, the system generates personalized feedback to assist users in enhancing their writing skills, underscoring the potential and practical value of automated scoring technologies in educational contexts.
Integration of Mamba and Transformer -- MAT for Long-Short Range Time Series Forecasting with Application to Weather Dynamics
Sep 13, 2024
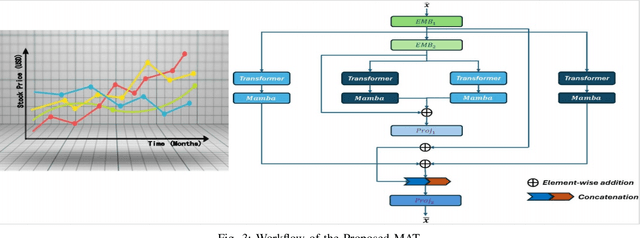
Abstract:Long-short range time series forecasting is essential for predicting future trends and patterns over extended periods. While deep learning models such as Transformers have made significant strides in advancing time series forecasting, they often encounter difficulties in capturing long-term dependencies and effectively managing sparse semantic features. The state-space model, Mamba, addresses these issues through its adept handling of selective input and parallel computing, striking a balance between computational efficiency and prediction accuracy. This article examines the advantages and disadvantages of both Mamba and Transformer models, and introduces a combined approach, MAT, which leverages the strengths of each model to capture unique long-short range dependencies and inherent evolutionary patterns in multivariate time series. Specifically, MAT harnesses the long-range dependency capabilities of Mamba and the short-range characteristics of Transformers. Experimental results on benchmark weather datasets demonstrate that MAT outperforms existing comparable methods in terms of prediction accuracy, scalability, and memory efficiency.
BackdoorBench: A Comprehensive Benchmark and Analysis of Backdoor Learning
Jan 26, 2024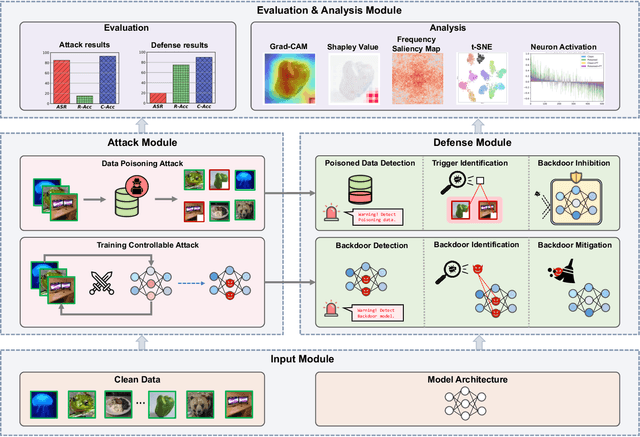
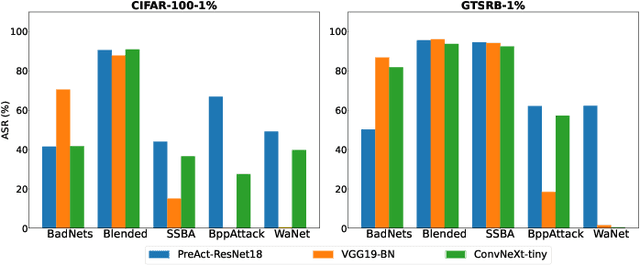
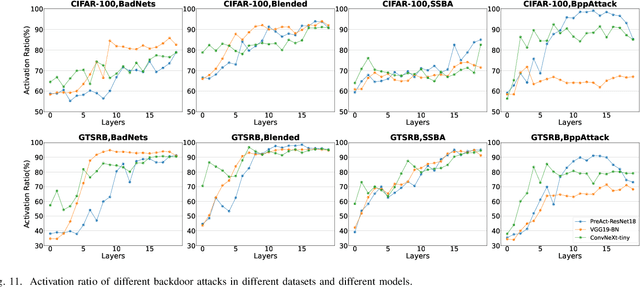
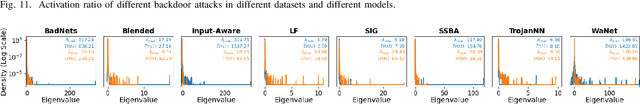
Abstract:As an emerging and vital topic for studying deep neural networks' vulnerability (DNNs), backdoor learning has attracted increasing interest in recent years, and many seminal backdoor attack and defense algorithms are being developed successively or concurrently, in the status of a rapid arms race. However, mainly due to the diverse settings, and the difficulties of implementation and reproducibility of existing works, there is a lack of a unified and standardized benchmark of backdoor learning, causing unfair comparisons, and unreliable conclusions (e.g., misleading, biased or even false conclusions). Consequently, it is difficult to evaluate the current progress and design the future development roadmap of this literature. To alleviate this dilemma, we build a comprehensive benchmark of backdoor learning called BackdoorBench. Our benchmark makes three valuable contributions to the research community. 1) We provide an integrated implementation of state-of-the-art (SOTA) backdoor learning algorithms (currently including 16 attack and 27 defense algorithms), based on an extensible modular-based codebase. 2) We conduct comprehensive evaluations of 12 attacks against 16 defenses, with 5 poisoning ratios, based on 4 models and 4 datasets, thus 11,492 pairs of evaluations in total. 3) Based on above evaluations, we present abundant analysis from 8 perspectives via 18 useful analysis tools, and provide several inspiring insights about backdoor learning. We hope that our efforts could build a solid foundation of backdoor learning to facilitate researchers to investigate existing algorithms, develop more innovative algorithms, and explore the intrinsic mechanism of backdoor learning. Finally, we have created a user-friendly website at http://backdoorbench.com, which collects all important information of BackdoorBench, including codebase, docs, leaderboard, and model Zoo.
Robust Backdoor Attack with Visible, Semantic, Sample-Specific, and Compatible Triggers
Jun 01, 2023Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) can be manipulated to exhibit specific behaviors when exposed to specific trigger patterns, without affecting their performance on normal samples. This type of attack is known as a backdoor attack. Recent research has focused on designing invisible triggers for backdoor attacks to ensure visual stealthiness. These triggers have demonstrated strong attack performance even under backdoor defense, which aims to eliminate or suppress the backdoor effect in the model. However, through experimental observations, we have noticed that these carefully designed invisible triggers are often susceptible to visual distortion during inference, such as Gaussian blurring or environmental variations in real-world scenarios. This phenomenon significantly undermines the effectiveness of attacks in practical applications. Unfortunately, this issue has not received sufficient attention and has not been thoroughly investigated. To address this limitation, we propose a novel approach called the Visible, Semantic, Sample-Specific, and Compatible trigger (VSSC-trigger), which leverages a recent powerful image method known as the stable diffusion model. In this approach, a text trigger is utilized as a prompt and combined with a benign image. The resulting combination is then processed by a pre-trained stable diffusion model, generating a corresponding semantic object. This object is seamlessly integrated with the original image, resulting in a new realistic image, referred to as the poisoned image. Extensive experimental results and analysis validate the effectiveness and robustness of our proposed attack method, even in the presence of visual distortion. We believe that the new trigger proposed in this work, along with the proposed idea to address the aforementioned issues, will have significant prospective implications for further advancements in this direction.
Mutilmodal Feature Extraction and Attention-based Fusion for Emotion Estimation in Videos
Mar 18, 2023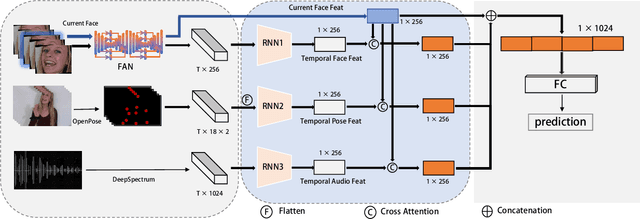
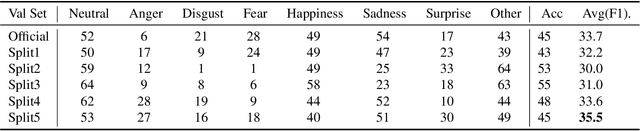
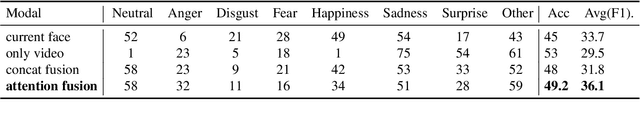
Abstract:The continuous improvement of human-computer interaction technology makes it possible to compute emotions. In this paper, we introduce our submission to the CVPR 2023 Competition on Affective Behavior Analysis in-the-wild (ABAW). Sentiment analysis in human-computer interaction should, as far as possible Start with multiple dimensions, fill in the single imperfect emotion channel, and finally determine the emotion tendency by fitting multiple results. Therefore, We exploited multimodal features extracted from video of different lengths from the competition dataset, including audio, pose and images. Well-informed emotion representations drive us to propose a Attention-based multimodal framework for emotion estimation. Our system achieves the performance of 0.361 on the validation dataset. The code is available at [https://github.com/xkwangcn/ABAW-5th-RT-IAI].
StructVPR: Distill Structural Knowledge with Weighting Samples for Visual Place Recognition
Dec 09, 2022Abstract:Visual place recognition (VPR) is usually considered as a specific image retrieval problem. Limited by existing training frameworks, most deep learning-based works cannot extract sufficiently stable global features from RGB images and rely on a time-consuming re-ranking step to exploit spatial structural information for better performance. In this paper, we propose StructVPR, a novel training architecture for VPR, to enhance structural knowledge in RGB global features and thus improve feature stability in a constantly changing environment. Specifically, StructVPR uses segmentation images as a more definitive source of structural knowledge input into a CNN network and applies knowledge distillation to avoid online segmentation and inference of seg-branch in testing. Considering that not all samples contain high-quality and helpful knowledge, and some even hurt the performance of distillation, we partition samples and weigh each sample's distillation loss to enhance the expected knowledge precisely. Finally, StructVPR achieves impressive performance on several benchmarks using only global retrieval and even outperforms many two-stage approaches by a large margin. After adding additional re-ranking, ours achieves state-of-the-art performance while maintaining a low computational cost.
TransVPR: Transformer-based place recognition with multi-level attention aggregation
Jan 06, 2022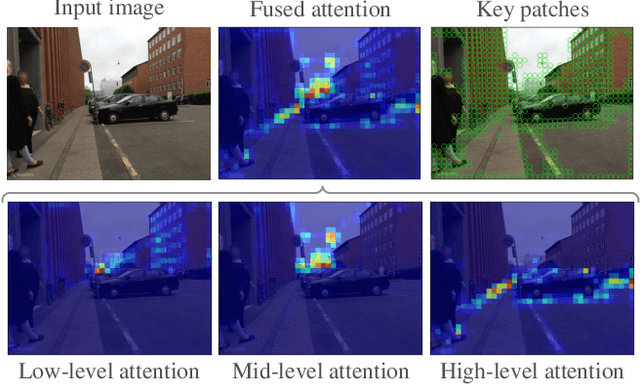
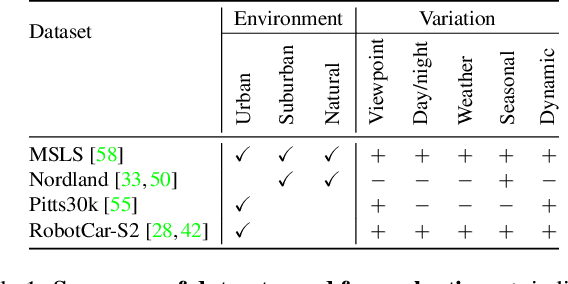
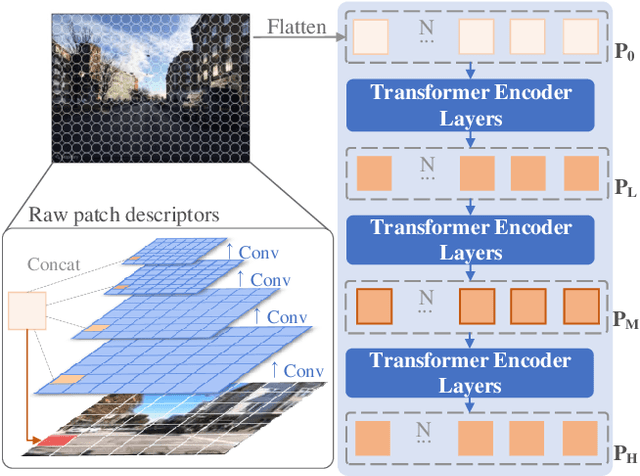
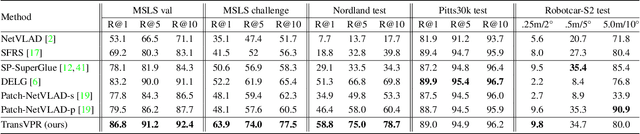
Abstract:Visual place recognition is a challenging task for applications such as autonomous driving navigation and mobile robot localization. Distracting elements presenting in complex scenes often lead to deviations in the perception of visual place. To address this problem, it is crucial to integrate information from only task-relevant regions into image representations. In this paper, we introduce a novel holistic place recognition model, TransVPR, based on vision Transformers. It benefits from the desirable property of the self-attention operation in Transformers which can naturally aggregate task-relevant features. Attentions from multiple levels of the Transformer, which focus on different regions of interest, are further combined to generate a global image representation. In addition, the output tokens from Transformer layers filtered by the fused attention mask are considered as key-patch descriptors, which are used to perform spatial matching to re-rank the candidates retrieved by the global image features. The whole model allows end-to-end training with a single objective and image-level supervision. TransVPR achieves state-of-the-art performance on several real-world benchmarks while maintaining low computational time and storage requirements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge