Jiajing Chen
PRISM: Product Retrieval In Shopping Carts using Hybrid Matching
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Compared to traditional image retrieval tasks, product retrieval in retail settings is even more challenging. Products of the same type from different brands may have highly similar visual appearances, and the query image may be taken from an angle that differs significantly from view angles of the stored catalog images. Foundational models, such as CLIP and SigLIP, often struggle to distinguish these subtle but important local differences. Pixel-wise matching methods, on the other hand, are computationally expensive and incur prohibitively high matching times. In this paper, we propose a new, hybrid method, called PRISM, for product retrieval in retail settings by leveraging the advantages of both vision-language model-based and pixel-wise matching approaches. To provide both efficiency/speed and finegrained retrieval accuracy, PRISM consists of three stages: 1) A vision-language model (SigLIP) is employed first to retrieve the top 35 most semantically similar products from a fixed gallery, thereby narrowing the search space significantly; 2) a segmentation model (YOLO-E) is applied to eliminate background clutter; 3) fine-grained pixel-level matching is performed using LightGlue across the filtered candidates. This framework enables more accurate discrimination between products with high inter-class similarity by focusing on subtle visual cues often missed by global models. Experiments performed on the ABV dataset show that our proposed PRISM outperforms the state-of-the-art image retrieval methods by 4.21% in top-1 accuracy while still remaining within the bounds of real-time processing for practical retail deployments.
AdaMixup: A Dynamic Defense Framework for Membership Inference Attack Mitigation
Jan 04, 2025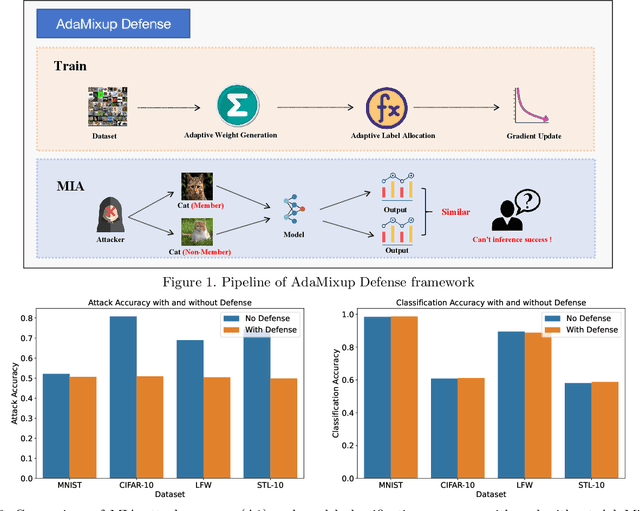
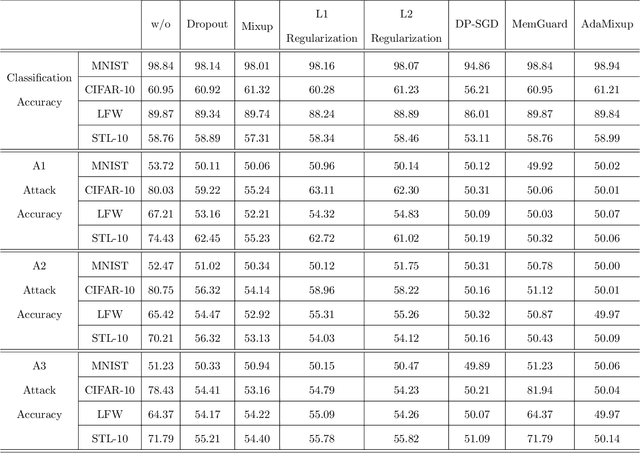
Abstract:Membership inference attacks have emerged as a significant privacy concern in the training of deep learning models, where attackers can infer whether a data point was part of the training set based on the model's outputs. To address this challenge, we propose a novel defense mechanism, AdaMixup. AdaMixup employs adaptive mixup techniques to enhance the model's robustness against membership inference attacks by dynamically adjusting the mixup strategy during training. This method not only improves the model's privacy protection but also maintains high performance. Experimental results across multiple datasets demonstrate that AdaMixup significantly reduces the risk of membership inference attacks while achieving a favorable trade-off between defensive efficiency and model accuracy. This research provides an effective solution for data privacy protection and lays the groundwork for future advancements in mixup training methods.
Optimizing Multi-Task Learning for Enhanced Performance in Large Language Models
Dec 09, 2024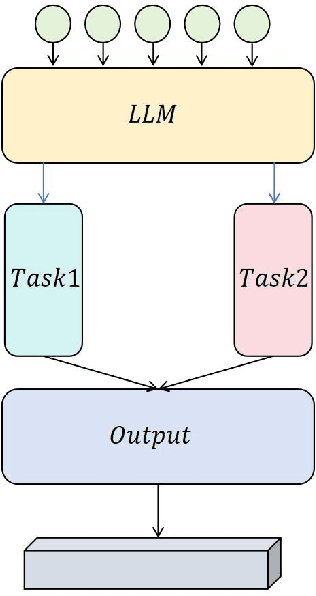
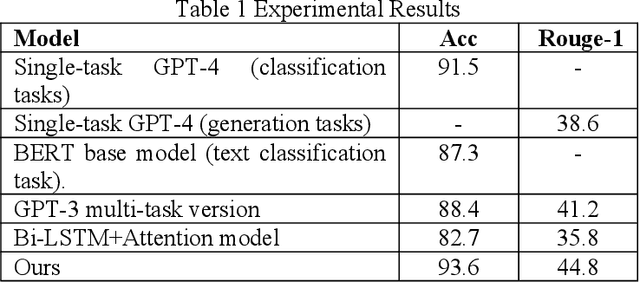

Abstract:This study aims to explore the performance improvement method of large language models based on GPT-4 under the multi-task learning framework and conducts experiments on two tasks: text classification and automatic summary generation. Through the combined design of shared feature extractors and task-specific modules, we achieve knowledge-sharing and optimization of multiple tasks in the same model. The experiment uses multiple subtasks of the GLUE dataset to compare the performance of the multi-task model with the single-task GPT-4, the multi-task version of GPT-3, the BERT basic model, and the classic Bi-LSTM with Attention model. The results show that the proposed multi-task learning model outperforms other comparison models in terms of text classification accuracy and ROUGE value of summary generation, demonstrating the advantages of multi-task learning in improving model generalization ability and collaborative learning between tasks. The model maintains a stable loss convergence rate during training, showing good learning efficiency and adaptability to the test set. This study verifies the applicability of the multi-task learning framework in large language models, especially in improving the model's ability to balance different tasks. In the future, with the combination of large language models and multimodal data and the application of dynamic task adjustment technology, the framework based on multi-task learning is expected to play a greater role in practical applications across fields and provide new ideas for the development of general artificial intelligence.
Adaptive Optimization for Enhanced Efficiency in Large-Scale Language Model Training
Dec 06, 2024



Abstract:With the rapid development of natural language processing technology, large-scale language models (LLM) have achieved remarkable results in a variety of tasks. However, how to effectively train these huge models and improve their performance and computational efficiency remains an important challenge. This paper proposes an improved method based on adaptive optimization algorithm, aiming to improve the training efficiency and final performance of LLM. Through comparative experiments on the SQuAD and GLUE data sets, the experimental results show that compared with traditional optimization algorithms (such as SGD, Momentum, AdaGrad, RMSProp and Adam), the adaptive optimization algorithm we proposed has better accuracy and F1 score. Both have achieved significant improvements, especially showed stronger training capabilities when processed large-scale texts and complex tasks. The research results verify the advantages of adaptive optimization algorithms in large-scale language model training and provide new ideas and directions for future optimization methods.
Few-Shot Learning with Adaptive Weight Masking in Conditional GANs
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:Deep learning has revolutionized various fields, yet its efficacy is hindered by overfitting and the requirement of extensive annotated data, particularly in few-shot learning scenarios where limited samples are available. This paper introduces a novel approach to few-shot learning by employing a Residual Weight Masking Conditional Generative Adversarial Network (RWM-CGAN) for data augmentation. The proposed model integrates residual units within the generator to enhance network depth and sample quality, coupled with a weight mask regularization technique in the discriminator to improve feature learning from small-sample categories. This method addresses the core issues of robustness and generalization in few-shot learning by providing a controlled and clear augmentation of the sample space. Extensive experiments demonstrate that RWM-CGAN not only expands the sample space effectively but also enriches the diversity and quality of generated samples, leading to significant improvements in detection and classification accuracy on public datasets. The paper contributes to the advancement of few-shot learning by offering a practical solution to the challenges posed by data scarcity and the need for rapid generalization to new tasks or categories.
A Combined Encoder and Transformer Approach for Coherent and High-Quality Text Generation
Nov 19, 2024


Abstract:This research introduces a novel text generation model that combines BERT's semantic interpretation strengths with GPT-4's generative capabilities, establishing a high standard in generating coherent, contextually accurate language. Through the combined architecture, the model enhances semantic depth and maintains smooth, human-like text flow, overcoming limitations seen in prior models. Experimental benchmarks reveal that BERT-GPT-4 surpasses traditional models, including GPT-3, T5, BART, Transformer-XL, and CTRL, in key metrics like Perplexity and BLEU, showcasing its superior natural language generation performance. By fully utilizing contextual information, this hybrid model generates text that is not only logically coherent but also aligns closely with human language patterns, providing an advanced solution for text generation tasks. This research highlights the potential of integrating semantic understanding with advanced generative models, contributing new insights for NLP, and setting a foundation for broader applications of large-scale generative architectures in areas such as automated writing, question-answer systems, and adaptive conversational agents.
Research on reinforcement learning based warehouse robot navigation algorithm in complex warehouse layout
Nov 09, 2024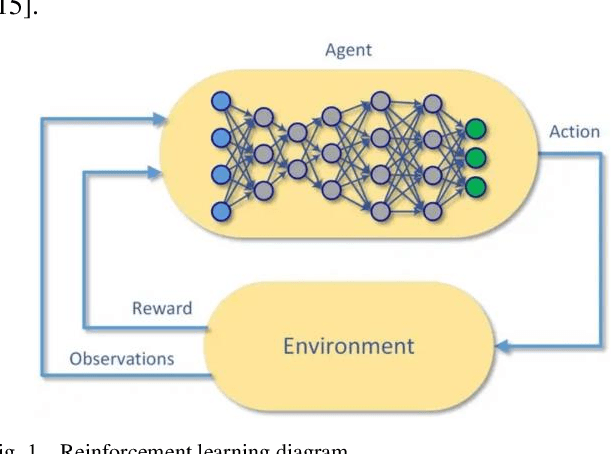
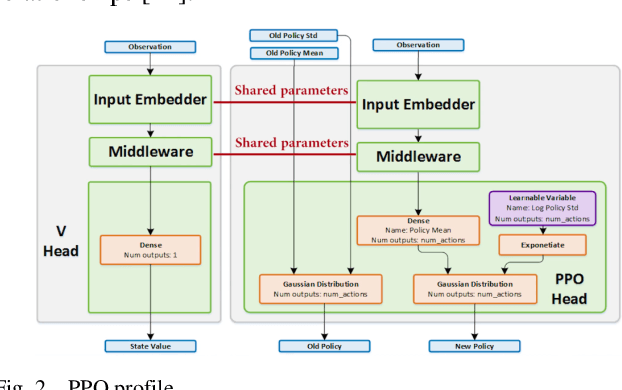
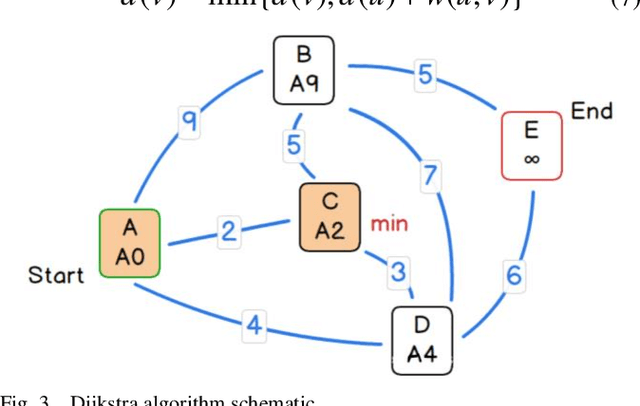
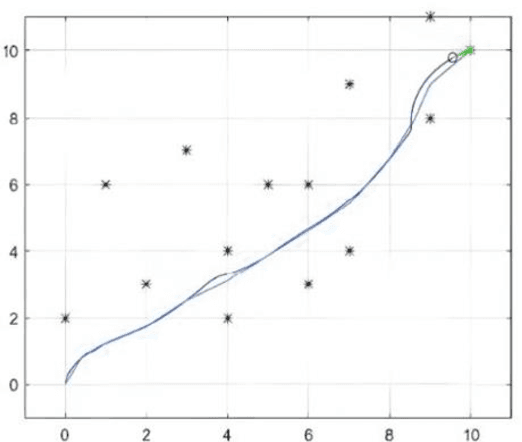
Abstract:In this paper, how to efficiently find the optimal path in complex warehouse layout and make real-time decision is a key problem. This paper proposes a new method of Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) and Dijkstra's algorithm, Proximal policy-Dijkstra (PP-D). PP-D method realizes efficient strategy learning and real-time decision making through PPO, and uses Dijkstra algorithm to plan the global optimal path, thus ensuring high navigation accuracy and significantly improving the efficiency of path planning. Specifically, PPO enables robots to quickly adapt and optimize action strategies in dynamic environments through its stable policy updating mechanism. Dijkstra's algorithm ensures global optimal path planning in static environment. Finally, through the comparison experiment and analysis of the proposed framework with the traditional algorithm, the results show that the PP-D method has significant advantages in improving the accuracy of navigation prediction and enhancing the robustness of the system. Especially in complex warehouse layout, PP-D method can find the optimal path more accurately and reduce collision and stagnation. This proves the reliability and effectiveness of the robot in the study of complex warehouse layout navigation algorithm.
Advanced RAG Models with Graph Structures: Optimizing Complex Knowledge Reasoning and Text Generation
Nov 06, 2024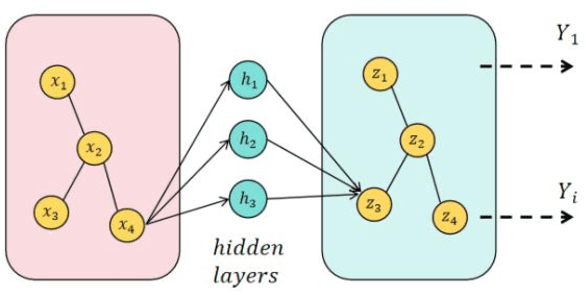
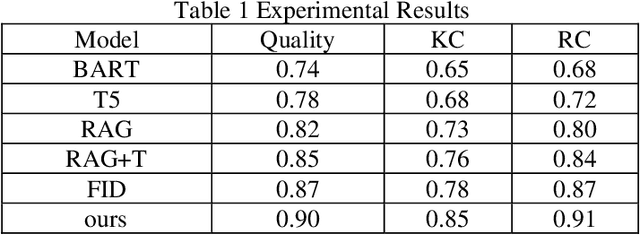
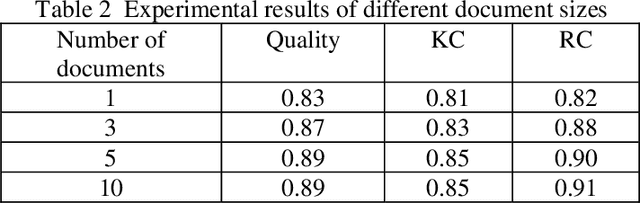
Abstract:This study aims to optimize the existing retrieval-augmented generation model (RAG) by introducing a graph structure to improve the performance of the model in dealing with complex knowledge reasoning tasks. The traditional RAG model has the problem of insufficient processing efficiency when facing complex graph structure information (such as knowledge graphs, hierarchical relationships, etc.), which affects the quality and consistency of the generated results. This study proposes a scheme to process graph structure data by combining graph neural network (GNN), so that the model can capture the complex relationship between entities, thereby improving the knowledge consistency and reasoning ability of the generated text. The experiment used the Natural Questions (NQ) dataset and compared it with multiple existing generation models. The results show that the graph-based RAG model proposed in this paper is superior to the traditional generation model in terms of quality, knowledge consistency, and reasoning ability, especially when dealing with tasks that require multi-dimensional reasoning. Through the combination of the enhancement of the retrieval module and the graph neural network, the model in this study can better handle complex knowledge background information and has broad potential value in multiple practical application scenarios.
Optimizing Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Elasticsearch for Enhanced Question-Answering Systems
Oct 18, 2024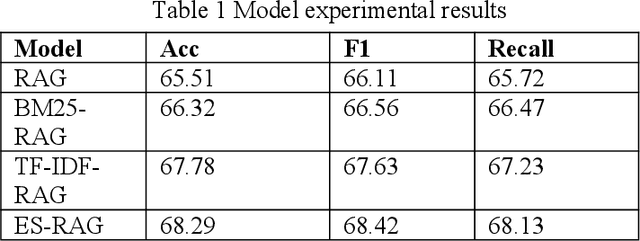
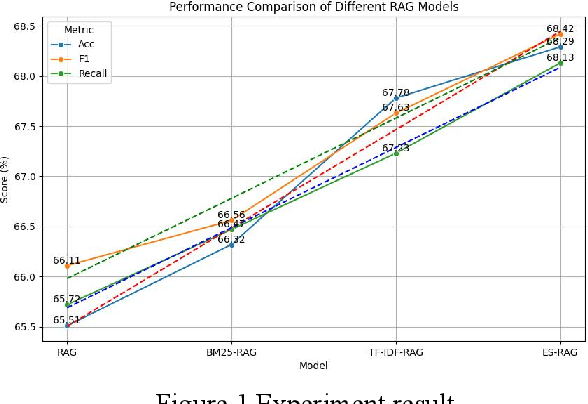
Abstract:This study aims to improve the accuracy and quality of large-scale language models (LLMs) in answering questions by integrating Elasticsearch into the Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) framework. The experiment uses the Stanford Question Answering Dataset (SQuAD) version 2.0 as the test dataset and compares the performance of different retrieval methods, including traditional methods based on keyword matching or semantic similarity calculation, BM25-RAG and TF-IDF- RAG, and the newly proposed ES-RAG scheme. The results show that ES-RAG not only has obvious advantages in retrieval efficiency but also performs well in key indicators such as accuracy, which is 0.51 percentage points higher than TF-IDF-RAG. In addition, Elasticsearch's powerful search capabilities and rich configuration options enable the entire question-answering system to better handle complex queries and provide more flexible and efficient responses based on the diverse needs of users. Future research directions can further explore how to optimize the interaction mechanism between Elasticsearch and LLM, such as introducing higher-level semantic understanding and context-awareness capabilities, to achieve a more intelligent and humanized question-answering experience.
Automated Genre-Aware Article Scoring and Feedback Using Large Language Models
Oct 18, 2024



Abstract:This paper focuses on the development of an advanced intelligent article scoring system that not only assesses the overall quality of written work but also offers detailed feature-based scoring tailored to various article genres. By integrating the pre-trained BERT model with the large language model Chat-GPT, the system gains a deep understanding of both the content and structure of the text, enabling it to provide a thorough evaluation along with targeted suggestions for improvement. Experimental results demonstrate that this system outperforms traditional scoring methods across multiple public datasets, particularly in feature-based assessments, offering a more accurate reflection of the quality of different article types. Moreover, the system generates personalized feedback to assist users in enhancing their writing skills, underscoring the potential and practical value of automated scoring technologies in educational contexts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge