Dezhi Yu
AdaMixup: A Dynamic Defense Framework for Membership Inference Attack Mitigation
Jan 04, 2025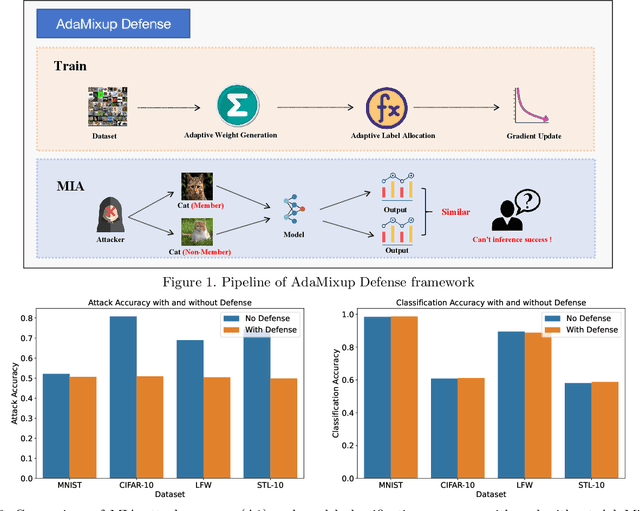
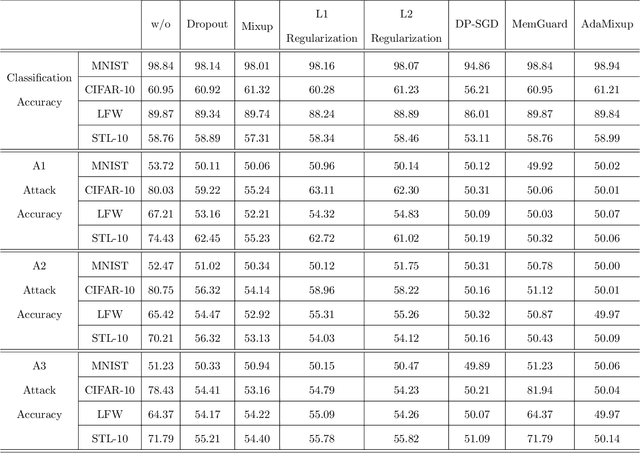
Abstract:Membership inference attacks have emerged as a significant privacy concern in the training of deep learning models, where attackers can infer whether a data point was part of the training set based on the model's outputs. To address this challenge, we propose a novel defense mechanism, AdaMixup. AdaMixup employs adaptive mixup techniques to enhance the model's robustness against membership inference attacks by dynamically adjusting the mixup strategy during training. This method not only improves the model's privacy protection but also maintains high performance. Experimental results across multiple datasets demonstrate that AdaMixup significantly reduces the risk of membership inference attacks while achieving a favorable trade-off between defensive efficiency and model accuracy. This research provides an effective solution for data privacy protection and lays the groundwork for future advancements in mixup training methods.
ROSE: A Reward-Oriented Data Selection Framework for LLM Task-Specific Instruction Tuning
Dec 01, 2024



Abstract:Instruction tuning has underscored the significant potential of large language models (LLMs) in producing more human-controllable and effective outputs in various domains. In this work, we focus on the data selection problem for task-specific instruction tuning of LLMs. Prevailing methods primarily rely on the crafted similarity metrics to select training data that aligns with the test data distribution. The goal is to minimize instruction tuning loss on the test data, ultimately improving performance on the target task. However, it has been widely observed that instruction tuning loss (i.e., cross-entropy loss for next token prediction) in LLMs often fails to exhibit a monotonic relationship with actual task performance. This misalignment undermines the effectiveness of current data selection methods for task-specific instruction tuning. To address this issue, we introduce ROSE, a novel Reward-Oriented inStruction data sElection method which leverages pairwise preference loss as a reward signal to optimize data selection for task-specific instruction tuning. Specifically, ROSE adapts an influence formulation to approximate the influence of training data points relative to a few-shot preference validation set to select the most task-related training data points. Experimental results show that by selecting just 5% of the training data using ROSE, our approach can achieve competitive results compared to fine-tuning with the full training dataset, and it surpasses other state-of-the-art data selection methods for task-specific instruction tuning. Our qualitative analysis further confirms the robust generalizability of our method across multiple benchmark datasets and diverse model architectures.
Research on reinforcement learning based warehouse robot navigation algorithm in complex warehouse layout
Nov 09, 2024
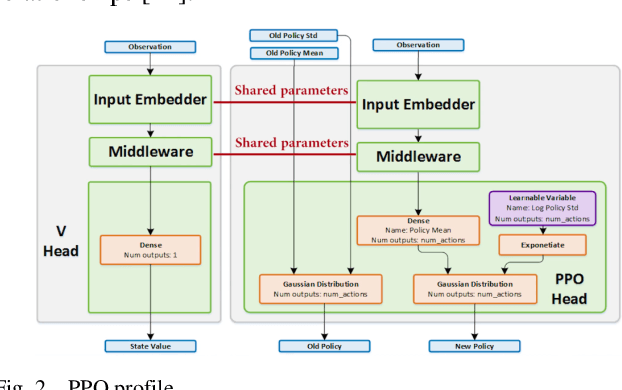
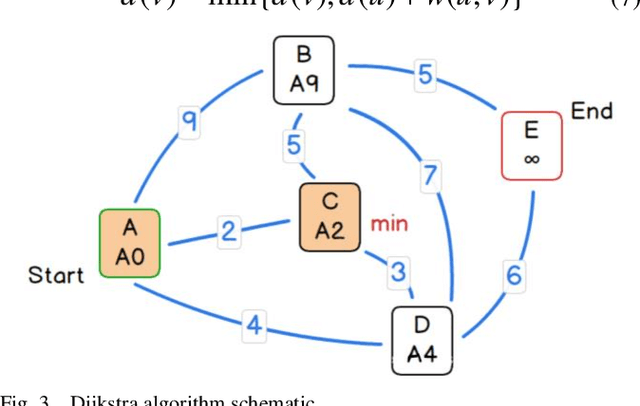
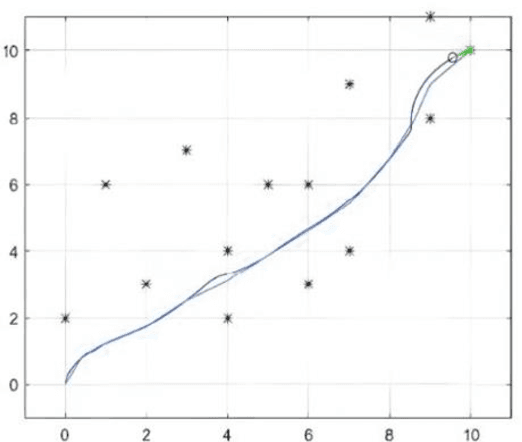
Abstract:In this paper, how to efficiently find the optimal path in complex warehouse layout and make real-time decision is a key problem. This paper proposes a new method of Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) and Dijkstra's algorithm, Proximal policy-Dijkstra (PP-D). PP-D method realizes efficient strategy learning and real-time decision making through PPO, and uses Dijkstra algorithm to plan the global optimal path, thus ensuring high navigation accuracy and significantly improving the efficiency of path planning. Specifically, PPO enables robots to quickly adapt and optimize action strategies in dynamic environments through its stable policy updating mechanism. Dijkstra's algorithm ensures global optimal path planning in static environment. Finally, through the comparison experiment and analysis of the proposed framework with the traditional algorithm, the results show that the PP-D method has significant advantages in improving the accuracy of navigation prediction and enhancing the robustness of the system. Especially in complex warehouse layout, PP-D method can find the optimal path more accurately and reduce collision and stagnation. This proves the reliability and effectiveness of the robot in the study of complex warehouse layout navigation algorithm.
Predicting 30-Day Hospital Readmission in Medicare Patients: Insights from an LSTM Deep Learning Model
Oct 23, 2024Abstract:Readmissions among Medicare beneficiaries are a major problem for the US healthcare system from a perspective of both healthcare operations and patient caregiving outcomes. Our study analyzes Medicare hospital readmissions using LSTM networks with feature engineering to assess feature contributions. We selected variables from admission-level data, inpatient medical history and patient demography. The LSTM model is designed to capture temporal dynamics from admission-level and patient-level data. On a case study on the MIMIC dataset, the LSTM model outperformed the logistic regression baseline, accurately leveraging temporal features to predict readmission. The major features were the Charlson Comorbidity Index, hospital length of stay, the hospital admissions over the past 6 months, while demographic variables were less impactful. This work suggests that LSTM networks offers a more promising approach to improve Medicare patient readmission prediction. It captures temporal interactions in patient databases, enhancing current prediction models for healthcare providers. Adoption of predictive models into clinical practice may be more effective in identifying Medicare patients to provide early and targeted interventions to improve patient outcomes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge