Xiaozhong Liu
P2S: Probabilistic Process Supervision for General-Domain Reasoning Question Answering
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:While reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) has advanced LLM reasoning in structured domains like mathematics and programming, its application to general-domain reasoning tasks remains challenging due to the absence of verifiable reward signals. To this end, methods like Reinforcement Learning with Reference Probability Reward (RLPR) have emerged, leveraging the probability of generating the final answer as a reward signal. However, these outcome-focused approaches neglect crucial step-by-step supervision of the reasoning process itself. To address this gap, we introduce Probabilistic Process Supervision (P2S), a novel self-supervision framework that provides fine-grained process rewards without requiring a separate reward model or human-annotated reasoning steps. During reinforcement learning, P2S synthesizes and filters a high-quality reference reasoning chain (gold-CoT). The core of our method is to calculate a Path Faithfulness Reward (PFR) for each reasoning step, which is derived from the conditional probability of generating the gold-CoT's suffix, given the model's current reasoning prefix. Crucially, this PFR can be flexibly integrated with any outcome-based reward, directly tackling the reward sparsity problem by providing dense guidance. Extensive experiments on reading comprehension and medical Question Answering benchmarks show that P2S significantly outperforms strong baselines.
VitalDiagnosis: AI-Driven Ecosystem for 24/7 Vital Monitoring and Chronic Disease Management
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Chronic diseases have become the leading cause of death worldwide, a challenge intensified by strained medical resources and an aging population. Individually, patients often struggle to interpret early signs of deterioration or maintain adherence to care plans. In this paper, we introduce VitalDiagnosis, an LLM-driven ecosystem designed to shift chronic disease management from passive monitoring to proactive, interactive engagement. By integrating continuous data from wearable devices with the reasoning capabilities of LLMs, the system addresses both acute health anomalies and routine adherence. It analyzes triggers through context-aware inquiries, produces provisional insights within a collaborative patient-clinician workflow, and offers personalized guidance. This approach aims to promote a more proactive and cooperative care paradigm, with the potential to enhance patient self-management and reduce avoidable clinical workload.
Human-in-the-Loop Interactive Report Generation for Chronic Disease Adherence
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Chronic disease management requires regular adherence feedback to prevent avoidable hospitalizations, yet clinicians lack time to produce personalized patient communications. Manual authoring preserves clinical accuracy but does not scale; AI generation scales but can undermine trust in patient-facing contexts. We present a clinician-in-the-loop interface that constrains AI to data organization and preserves physician oversight through recognition-based review. A single-page editor pairs AI-generated section drafts with time-aligned visualizations, enabling inline editing with visual evidence for each claim. This division of labor (AI organizes, clinician decides) targets both efficiency and accountability. In a pilot with three physicians reviewing 24 cases, AI successfully generated clinically personalized drafts matching physicians' manual authoring practice (overall mean 4.86/10 vs. 5.0/10 baseline), requiring minimal physician editing (mean 8.3\% content modification) with zero safety-critical issues, demonstrating effective automation of content generation. However, review time remained comparable to manual practice, revealing an accountability paradox: in high-stakes clinical contexts, professional responsibility requires complete verification regardless of AI accuracy. We contribute three interaction patterns for clinical AI collaboration: bounded generation with recognition-based review via chart-text pairing, automated urgency flagging that analyzes vital trends and adherence patterns with fail-safe escalation for missed critical monitoring tasks, and progressive disclosure controls that reduce cognitive load while maintaining oversight. These patterns indicate that clinical AI efficiency requires not only accurate models, but also mechanisms for selective verification that preserve accountability.
Teaching According to Students' Aptitude: Personalized Mathematics Tutoring via Persona-, Memory-, and Forgetting-Aware LLMs
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly integrated into intelligent tutoring systems to provide human-like and adaptive instruction. However, most existing approaches fail to capture how students' knowledge evolves dynamically across their proficiencies, conceptual gaps, and forgetting patterns. This challenge is particularly acute in mathematics tutoring, where effective instruction requires fine-grained scaffolding precisely calibrated to each student's mastery level and cognitive retention. To address this issue, we propose TASA (Teaching According to Students' Aptitude), a student-aware tutoring framework that integrates persona, memory, and forgetting dynamics for personalized mathematics learning. Specifically, TASA maintains a structured student persona capturing proficiency profiles and an event memory recording prior learning interactions. By incorporating a continuous forgetting curve with knowledge tracing, TASA dynamically updates each student's mastery state and generates contextually appropriate, difficulty-calibrated questions and explanations. Empirical results demonstrate that TASA achieves superior learning outcomes and more adaptive tutoring behavior compared to representative baselines, underscoring the importance of modeling temporal forgetting and learner profiles in LLM-based tutoring systems.
Active Domain Knowledge Acquisition with \$100 Budget: Enhancing LLMs via Cost-Efficient, Expert-Involved Interaction in Sensitive Domains
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated an impressive level of general knowledge. However, they often struggle in highly specialized and cost-sensitive domains such as drug discovery and rare disease research due to the lack of expert knowledge. In this paper, we propose a novel framework (PU-ADKA) designed to efficiently enhance domain-specific LLMs by actively engaging domain experts within a fixed budget. Unlike traditional fine-tuning approaches, PU-ADKA selectively identifies and queries the most appropriate expert from a team, taking into account each expert's availability, knowledge boundaries, and consultation costs. We train PU-ADKA using simulations on PubMed data and validate it through both controlled expert interactions and real-world deployment with a drug development team, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing LLM performance in specialized domains under strict budget constraints. In addition to outlining our methodological innovations and experimental results, we introduce a new benchmark dataset, CKAD, for cost-effective LLM domain knowledge acquisition to foster further research in this challenging area.
LeCoDe: A Benchmark Dataset for Interactive Legal Consultation Dialogue Evaluation
May 26, 2025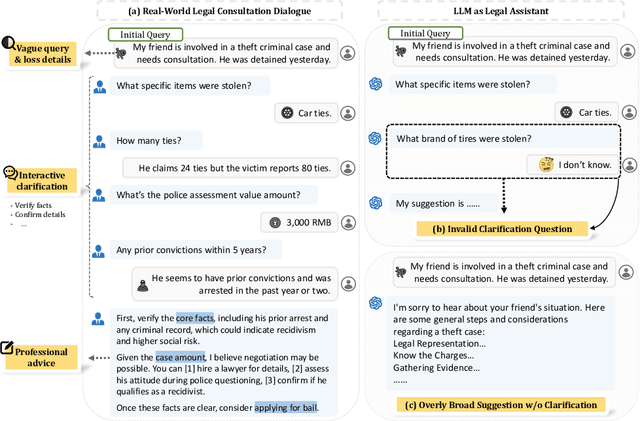
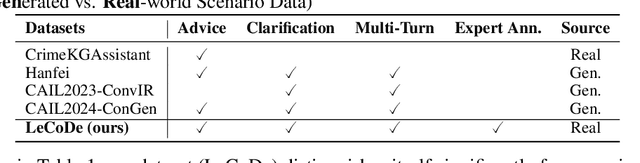

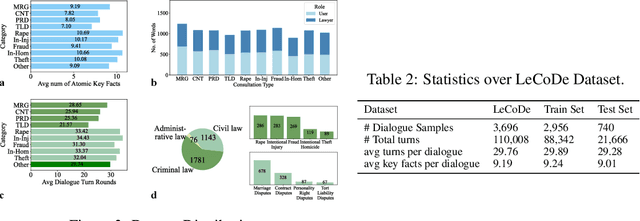
Abstract:Legal consultation is essential for safeguarding individual rights and ensuring access to justice, yet remains costly and inaccessible to many individuals due to the shortage of professionals. While recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) offer a promising path toward scalable, low-cost legal assistance, current systems fall short in handling the interactive and knowledge-intensive nature of real-world consultations. To address these challenges, we introduce LeCoDe, a real-world multi-turn benchmark dataset comprising 3,696 legal consultation dialogues with 110,008 dialogue turns, designed to evaluate and improve LLMs' legal consultation capability. With LeCoDe, we innovatively collect live-streamed consultations from short-video platforms, providing authentic multi-turn legal consultation dialogues. The rigorous annotation by legal experts further enhances the dataset with professional insights and expertise. Furthermore, we propose a comprehensive evaluation framework that assesses LLMs' consultation capabilities in terms of (1) clarification capability and (2) professional advice quality. This unified framework incorporates 12 metrics across two dimensions. Through extensive experiments on various general and domain-specific LLMs, our results reveal significant challenges in this task, with even state-of-the-art models like GPT-4 achieving only 39.8% recall for clarification and 59% overall score for advice quality, highlighting the complexity of professional consultation scenarios. Based on these findings, we further explore several strategies to enhance LLMs' legal consultation abilities. Our benchmark contributes to advancing research in legal domain dialogue systems, particularly in simulating more real-world user-expert interactions.
CLaDMoP: Learning Transferrable Models from Successful Clinical Trials via LLMs
May 24, 2025Abstract:Many existing models for clinical trial outcome prediction are optimized using task-specific loss functions on trial phase-specific data. While this scheme may boost prediction for common diseases and drugs, it can hinder learning of generalizable representations, leading to more false positives/negatives. To address this limitation, we introduce CLaDMoP, a new pre-training approach for clinical trial outcome prediction, alongside the Successful Clinical Trials dataset(SCT), specifically designed for this task. CLaDMoP leverages a Large Language Model-to encode trials' eligibility criteria-linked to a lightweight Drug-Molecule branch through a novel multi-level fusion technique. To efficiently fuse long embeddings across levels, we incorporate a grouping block, drastically reducing computational overhead. CLaDMoP avoids reliance on task-specific objectives by pre-training on a "pair matching" proxy task. Compared to established zero-shot and few-shot baselines, our method significantly improves both PR-AUC and ROC-AUC, especially for phase I and phase II trials. We further evaluate and perform ablation on CLaDMoP after Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning, comparing it to state-of-the-art supervised baselines, including MEXA-CTP, on the Trial Outcome Prediction(TOP) benchmark. CLaDMoP achieves up to 10.5% improvement in PR-AUC and 3.6% in ROC-AUC, while attaining comparable F1 score to MEXA-CTP, highlighting its potential for clinical trial outcome prediction. Code and SCT dataset can be downloaded from https://github.com/murai-lab/CLaDMoP.
AppealCase: A Dataset and Benchmark for Civil Case Appeal Scenarios
May 22, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in LegalAI have primarily focused on individual case judgment analysis, often overlooking the critical appellate process within the judicial system. Appeals serve as a core mechanism for error correction and ensuring fair trials, making them highly significant both in practice and in research. To address this gap, we present the AppealCase dataset, consisting of 10,000 pairs of real-world, matched first-instance and second-instance documents across 91 categories of civil cases. The dataset also includes detailed annotations along five dimensions central to appellate review: judgment reversals, reversal reasons, cited legal provisions, claim-level decisions, and whether there is new information in the second instance. Based on these annotations, we propose five novel LegalAI tasks and conduct a comprehensive evaluation across 20 mainstream models. Experimental results reveal that all current models achieve less than 50% F1 scores on the judgment reversal prediction task, highlighting the complexity and challenge of the appeal scenario. We hope that the AppealCase dataset will spur further research in LegalAI for appellate case analysis and contribute to improving consistency in judicial decision-making.
KEDRec-LM: A Knowledge-distilled Explainable Drug Recommendation Large Language Model
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Drug discovery is a critical task in biomedical natural language processing (NLP), yet explainable drug discovery remains underexplored. Meanwhile, large language models (LLMs) have shown remarkable abilities in natural language understanding and generation. Leveraging LLMs for explainable drug discovery has the potential to improve downstream tasks and real-world applications. In this study, we utilize open-source drug knowledge graphs, clinical trial data, and PubMed publications to construct a comprehensive dataset for the explainable drug discovery task, named \textbf{expRxRec}. Furthermore, we introduce \textbf{KEDRec-LM}, an instruction-tuned LLM which distills knowledge from rich medical knowledge corpus for drug recommendation and rationale generation. To encourage further research in this area, we will publicly release\footnote{A copy is attached with this submission} both the dataset and KEDRec-LM.
Auto-Drafting Police Reports from Noisy ASR Outputs: A Trust-Centered LLM Approach
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Achieving a delicate balance between fostering trust in law en- forcement and protecting the rights of both officers and civilians continues to emerge as a pressing research and product challenge in the world today. In the pursuit of fairness and transparency, this study presents an innovative AI-driven system designed to generate police report drafts from complex, noisy, and multi-role dialogue data. Our approach intelligently extracts key elements of law enforcement interactions and includes them in the draft, producing structured narratives that are not only high in quality but also reinforce accountability and procedural clarity. This frame- work holds the potential to transform the reporting process, ensur- ing greater oversight, consistency, and fairness in future policing practices. A demonstration video of our system can be accessed at https://drive.google.com/file/d/1kBrsGGR8e3B5xPSblrchRGj-Y-kpCHNO/view?usp=sharing
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge