Yiquan Wu
SIGHT: Reinforcement Learning with Self-Evidence and Information-Gain Diverse Branching for Search Agent
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) has empowered Large Language Models (LLMs) to master autonomous search for complex question answering. However, particularly within multi-turn search scenarios, this interaction introduces a critical challenge: search results often suffer from high redundancy and low signal-to-noise ratios. Consequently, agents easily fall into "Tunnel Vision," where the forced interpretation of early noisy retrievals leads to irreversible error accumulation. To address these challenges, we propose SIGHT, a framework that enhances search-based reasoning through Self-Evidence Support (SES) and Information-Gain Driven Diverse Branching. SIGHT distills search results into high-fidelity evidence via SES and calculates an Information Gain score to pinpoint pivotal states where observations maximally reduce uncertainty. This score guides Dynamic Prompting Interventions - including de-duplication, reflection, or adaptive branching - to spawn new branches with SES. Finally, by integrating SES and correctness rewards via Group Relative Policy Optimization, SIGHT internalizes robust exploration strategies without external verifiers. Experiments on single-hop and multi-hop QA benchmarks demonstrate that SIGHT significantly outperforms existing approaches, particularly in complex reasoning scenarios, using fewer search steps.
P2S: Probabilistic Process Supervision for General-Domain Reasoning Question Answering
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:While reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) has advanced LLM reasoning in structured domains like mathematics and programming, its application to general-domain reasoning tasks remains challenging due to the absence of verifiable reward signals. To this end, methods like Reinforcement Learning with Reference Probability Reward (RLPR) have emerged, leveraging the probability of generating the final answer as a reward signal. However, these outcome-focused approaches neglect crucial step-by-step supervision of the reasoning process itself. To address this gap, we introduce Probabilistic Process Supervision (P2S), a novel self-supervision framework that provides fine-grained process rewards without requiring a separate reward model or human-annotated reasoning steps. During reinforcement learning, P2S synthesizes and filters a high-quality reference reasoning chain (gold-CoT). The core of our method is to calculate a Path Faithfulness Reward (PFR) for each reasoning step, which is derived from the conditional probability of generating the gold-CoT's suffix, given the model's current reasoning prefix. Crucially, this PFR can be flexibly integrated with any outcome-based reward, directly tackling the reward sparsity problem by providing dense guidance. Extensive experiments on reading comprehension and medical Question Answering benchmarks show that P2S significantly outperforms strong baselines.
Universal Legal Article Prediction via Tight Collaboration between Supervised Classification Model and LLM
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Legal Article Prediction (LAP) is a critical task in legal text classification, leveraging natural language processing (NLP) techniques to automatically predict relevant legal articles based on the fact descriptions of cases. As a foundational step in legal decision-making, LAP plays a pivotal role in determining subsequent judgments, such as charges and penalties. Despite its importance, existing methods face significant challenges in addressing the complexities of LAP. Supervised classification models (SCMs), such as CNN and BERT, struggle to fully capture intricate fact patterns due to their inherent limitations. Conversely, large language models (LLMs), while excelling in generative tasks, perform suboptimally in predictive scenarios due to the abstract and ID-based nature of legal articles. Furthermore, the diversity of legal systems across jurisdictions exacerbates the issue, as most approaches are tailored to specific countries and lack broader applicability. To address these limitations, we propose Uni-LAP, a universal framework for legal article prediction that integrates the strengths of SCMs and LLMs through tight collaboration. Specifically, in Uni-LAP, the SCM is enhanced with a novel Top-K loss function to generate accurate candidate articles, while the LLM employs syllogism-inspired reasoning to refine the final predictions. We evaluated Uni-LAP on datasets from multiple jurisdictions, and empirical results demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms existing baselines, showcasing its effectiveness and generalizability.
ClaimGen-CN: A Large-scale Chinese Dataset for Legal Claim Generation
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:Legal claims refer to the plaintiff's demands in a case and are essential to guiding judicial reasoning and case resolution. While many works have focused on improving the efficiency of legal professionals, the research on helping non-professionals (e.g., plaintiffs) remains unexplored. This paper explores the problem of legal claim generation based on the given case's facts. First, we construct ClaimGen-CN, the first dataset for Chinese legal claim generation task, from various real-world legal disputes. Additionally, we design an evaluation metric tailored for assessing the generated claims, which encompasses two essential dimensions: factuality and clarity. Building on this, we conduct a comprehensive zero-shot evaluation of state-of-the-art general and legal-domain large language models. Our findings highlight the limitations of the current models in factual precision and expressive clarity, pointing to the need for more targeted development in this domain. To encourage further exploration of this important task, we will make the dataset publicly available.
AppealCase: A Dataset and Benchmark for Civil Case Appeal Scenarios
May 22, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in LegalAI have primarily focused on individual case judgment analysis, often overlooking the critical appellate process within the judicial system. Appeals serve as a core mechanism for error correction and ensuring fair trials, making them highly significant both in practice and in research. To address this gap, we present the AppealCase dataset, consisting of 10,000 pairs of real-world, matched first-instance and second-instance documents across 91 categories of civil cases. The dataset also includes detailed annotations along five dimensions central to appellate review: judgment reversals, reversal reasons, cited legal provisions, claim-level decisions, and whether there is new information in the second instance. Based on these annotations, we propose five novel LegalAI tasks and conduct a comprehensive evaluation across 20 mainstream models. Experimental results reveal that all current models achieve less than 50% F1 scores on the judgment reversal prediction task, highlighting the complexity and challenge of the appeal scenario. We hope that the AppealCase dataset will spur further research in LegalAI for appellate case analysis and contribute to improving consistency in judicial decision-making.
Intelligent Legal Assistant: An Interactive Clarification System for Legal Question Answering
Feb 11, 2025



Abstract:The rise of large language models has opened new avenues for users seeking legal advice. However, users often lack professional legal knowledge, which can lead to questions that omit critical information. This deficiency makes it challenging for traditional legal question-answering systems to accurately identify users' actual needs, often resulting in imprecise or generalized advice. In this work, we develop a legal question-answering system called Intelligent Legal Assistant, which interacts with users to precisely capture their needs. When a user poses a question, the system requests that the user select their geographical location to pinpoint the applicable laws. It then generates clarifying questions and options based on the key information missing from the user's initial question. This allows the user to select and provide the necessary details. Once all necessary information is provided, the system produces an in-depth legal analysis encompassing three aspects: overall conclusion, jurisprudential analysis, and resolution suggestions.
Xinyu: An Efficient LLM-based System for Commentary Generation
Aug 21, 2024



Abstract:Commentary provides readers with a deep understanding of events by presenting diverse arguments and evidence. However, creating commentary is a time-consuming task, even for skilled commentators. Large language models (LLMs) have simplified the process of natural language generation, but their direct application in commentary creation still faces challenges due to unique task requirements. These requirements can be categorized into two levels: 1) fundamental requirements, which include creating well-structured and logically consistent narratives, and 2) advanced requirements, which involve generating quality arguments and providing convincing evidence. In this paper, we introduce Xinyu, an efficient LLM-based system designed to assist commentators in generating Chinese commentaries. To meet the fundamental requirements, we deconstruct the generation process into sequential steps, proposing targeted strategies and supervised fine-tuning (SFT) for each step. To address the advanced requirements, we present an argument ranking model for arguments and establish a comprehensive evidence database that includes up-to-date events and classic books, thereby strengthening the substantiation of the evidence with retrieval augmented generation (RAG) technology. To evaluate the generated commentaries more fairly, corresponding to the two-level requirements, we introduce a comprehensive evaluation metric that considers five distinct perspectives in commentary generation. Our experiments confirm the effectiveness of our proposed system. We also observe a significant increase in the efficiency of commentators in real-world scenarios, with the average time spent on creating a commentary dropping from 4 hours to 20 minutes. Importantly, such an increase in efficiency does not compromise the quality of the commentaries.
From Graph to Word Bag: Introducing Domain Knowledge to Confusing Charge Prediction
Mar 14, 2024



Abstract:Confusing charge prediction is a challenging task in legal AI, which involves predicting confusing charges based on fact descriptions. While existing charge prediction methods have shown impressive performance, they face significant challenges when dealing with confusing charges, such as Snatch and Robbery. In the legal domain, constituent elements play a pivotal role in distinguishing confusing charges. Constituent elements are fundamental behaviors underlying criminal punishment and have subtle distinctions among charges. In this paper, we introduce a novel From Graph to Word Bag (FWGB) approach, which introduces domain knowledge regarding constituent elements to guide the model in making judgments on confusing charges, much like a judge's reasoning process. Specifically, we first construct a legal knowledge graph containing constituent elements to help select keywords for each charge, forming a word bag. Subsequently, to guide the model's attention towards the differentiating information for each charge within the context, we expand the attention mechanism and introduce a new loss function with attention supervision through words in the word bag. We construct the confusing charges dataset from real-world judicial documents. Experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, especially in maintaining exceptional performance in imbalanced label distributions.
Enhancing Court View Generation with Knowledge Injection and Guidance
Mar 07, 2024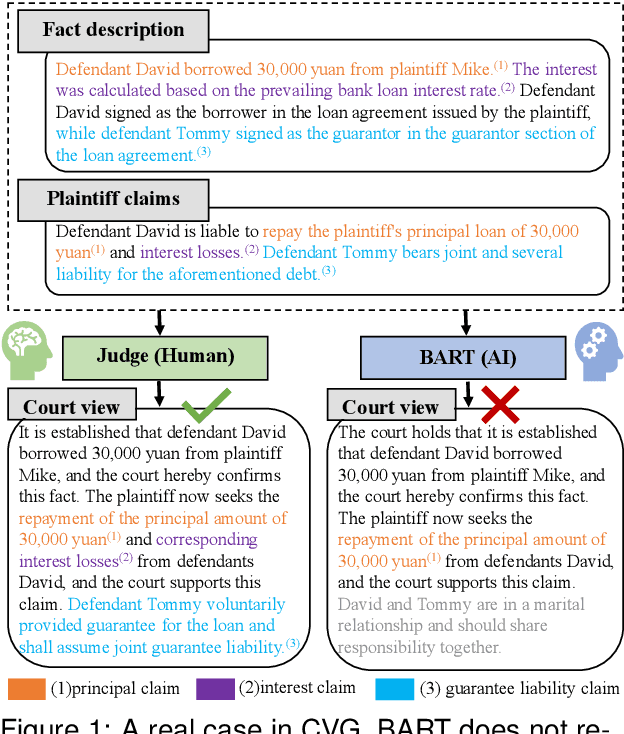

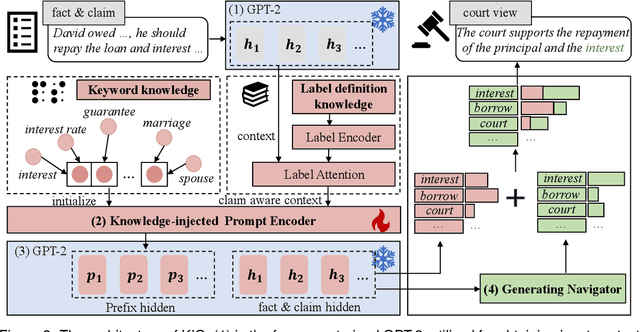

Abstract:Court View Generation (CVG) is a challenging task in the field of Legal Artificial Intelligence (LegalAI), which aims to generate court views based on the plaintiff claims and the fact descriptions. While Pretrained Language Models (PLMs) have showcased their prowess in natural language generation, their application to the complex, knowledge-intensive domain of CVG often reveals inherent limitations. In this paper, we present a novel approach, named Knowledge Injection and Guidance (KIG), designed to bolster CVG using PLMs. To efficiently incorporate domain knowledge during the training stage, we introduce a knowledge-injected prompt encoder for prompt tuning, thereby reducing computational overhead. Moreover, to further enhance the model's ability to utilize domain knowledge, we employ a generating navigator, which dynamically guides the text generation process in the inference stage without altering the model's architecture, making it readily transferable. Comprehensive experiments on real-world data demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach compared to several established baselines, especially in the responsivity of claims, where it outperforms the best baseline by 11.87%.
Adversarial Masking Contrastive Learning for vein recognition
Jan 16, 2024Abstract:Vein recognition has received increasing attention due to its high security and privacy. Recently, deep neural networks such as Convolutional neural networks (CNN) and Transformers have been introduced for vein recognition and achieved state-of-the-art performance. Despite the recent advances, however, existing solutions for finger-vein feature extraction are still not optimal due to scarce training image samples. To overcome this problem, in this paper, we propose an adversarial masking contrastive learning (AMCL) approach, that generates challenging samples to train a more robust contrastive learning model for the downstream palm-vein recognition task, by alternatively optimizing the encoder in the contrastive learning model and a set of latent variables. First, a huge number of masks are generated to train a robust generative adversarial network (GAN). The trained generator transforms a latent variable from the latent variable space into a mask space. Then, we combine the trained generator with a contrastive learning model to obtain our AMCL, where the generator produces challenging masking images to increase the contrastive loss and the contrastive learning model is trained based on the harder images to learn a more robust feature representation. After training, the trained encoder in the contrastive learning model is combined with a classification layer to build a classifier, which is further fine-tuned on labeled training data for vein recognition. The experimental results on three databases demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing contrastive learning approaches in terms of improving identification accuracy of vein classifiers and achieves state-of-the-art recognition results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge