Ang Li
Bounding Probabilities of Causation with Partial Causal Diagrams
Feb 16, 2026Abstract:Probabilities of causation are fundamental to individual-level explanation and decision making, yet they are inherently counterfactual and not point-identifiable from data in general. Existing bounds either disregard available covariates, require complete causal graphs, or rely on restrictive binary settings, limiting their practical use. In real-world applications, causal information is often partial but nontrivial. This paper proposes a general framework for bounding probabilities of causation using partial causal information. We show how the available structural or statistical information can be systematically incorporated as constraints in a optimization programming formulation, yielding tighter and formally valid bounds without full identifiability. This approach extends the applicability of probabilities of causation to realistic settings where causal knowledge is incomplete but informative.
GUI-GENESIS: Automated Synthesis of Efficient Environments with Verifiable Rewards for GUI Agent Post-Training
Feb 15, 2026Abstract:Post-training GUI agents in interactive environments is critical for developing generalization and long-horizon planning capabilities. However, training on real-world applications is hindered by high latency, poor reproducibility, and unverifiable rewards relying on noisy visual proxies. To address the limitations, we present GUI-GENESIS, the first framework to automatically synthesize efficient GUI training environments with verifiable rewards. GUI-GENESIS reconstructs real-world applications into lightweight web environments using multimodal code models and equips them with code-native rewards, executable assertions that provide deterministic reward signals and eliminate visual estimation noise. Extensive experiments show that GUI-GENESIS reduces environment latency by 10 times and costs by over $28,000 per epoch compared to training on real applications. Notably, agents trained with GUI-GENESIS outperform the base model by 14.54% and even real-world RL baselines by 3.27% on held-out real-world tasks. Finally, we observe that models can synthesize environments they cannot yet solve, highlighting a pathway for self-improving agents.
Step 3.5 Flash: Open Frontier-Level Intelligence with 11B Active Parameters
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:We introduce Step 3.5 Flash, a sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model that bridges frontier-level agentic intelligence and computational efficiency. We focus on what matters most when building agents: sharp reasoning and fast, reliable execution. Step 3.5 Flash pairs a 196B-parameter foundation with 11B active parameters for efficient inference. It is optimized with interleaved 3:1 sliding-window/full attention and Multi-Token Prediction (MTP-3) to reduce the latency and cost of multi-round agentic interactions. To reach frontier-level intelligence, we design a scalable reinforcement learning framework that combines verifiable signals with preference feedback, while remaining stable under large-scale off-policy training, enabling consistent self-improvement across mathematics, code, and tool use. Step 3.5 Flash demonstrates strong performance across agent, coding, and math tasks, achieving 85.4% on IMO-AnswerBench, 86.4% on LiveCodeBench-v6 (2024.08-2025.05), 88.2% on tau2-Bench, 69.0% on BrowseComp (with context management), and 51.0% on Terminal-Bench 2.0, comparable to frontier models such as GPT-5.2 xHigh and Gemini 3.0 Pro. By redefining the efficiency frontier, Step 3.5 Flash provides a high-density foundation for deploying sophisticated agents in real-world industrial environments.
FedMOA: Federated GRPO for Personalized Reasoning LLMs under Heterogeneous Rewards
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) has recently emerged as an effective approach for improving the reasoning capabilities of large language models through online multi-objective reinforcement learning. While personalization on private data is increasingly vital, traditional Reinforcement Learning (RL) alignment is often memory-prohibitive for on-device federated learning due to the overhead of maintaining a separate critic network. GRPO's critic-free architecture enables feasible on-device training, yet transitioning to a federated setting introduces systemic challenges: heterogeneous reward definitions, imbalanced multi-objective optimization, and high training costs. We propose FedMOA, a federated GRPO framework for multi-objective alignment under heterogeneous rewards. FedMOA stabilizes local training through an online adaptive weighting mechanism via hypergradient descent, which prioritizes primary reasoning as auxiliary objectives saturate. On the server side, it utilizes a task- and accuracy-aware aggregation strategy to prioritize high-quality updates. Experiments on mathematical reasoning and code generation benchmarks demonstrate that FedMOA consistently outperforms federated averaging, achieving accuracy gains of up to 2.2% while improving global performance, personalization, and multi-objective balance.
Towards Building Non-Fine-Tunable Foundation Models
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Open-sourcing foundation models (FMs) enables broad reuse but also exposes model trainers to economic and safety risks from unrestricted downstream fine-tuning. We address this problem by building non-fine-tunable foundation models: models that remain broadly usable in their released form while yielding limited adaptation gains under task-agnostic unauthorized fine-tuning. We propose Private Mask Pre-Training (PMP), a pre-training framework that concentrates representation learning into a sparse subnetwork identified early in training. The binary mask defining this subnetwork is kept private, and only the final dense weights are released. This forces unauthorized fine-tuning without access to the mask to update parameters misaligned with pretraining subspace, inducing an intrinsic mismatch between the fine-tuning objective and the pre-training geometry. We provide theoretical analysis showing that this mismatch destabilizes gradient-based adaptation and bounds fine-tuning gains. Empirical results on large language models demonstrating that PMP preserves base model performance while consistently degrading unauthorized fine-tuning across a wide range of downstream tasks, with the strength of non-fine-tunability controlled by the mask ratio.
Causal-Driven Feature Evaluation for Cross-Domain Image Classification
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization remains a fundamental challenge in real-world classification, where test distributions often differ substantially from training data. Most existing approaches pursue domain-invariant representations, implicitly assuming that invariance implies reliability. However, features that are invariant across domains are not necessarily causally effective for prediction. In this work, we revisit OOD classification from a causal perspective and propose to evaluate learned representations based on their necessity and sufficiency under distribution shift. We introduce an explicit segment-level framework that directly measures causal effectiveness across domains, providing a more faithful criterion than invariance alone. Experiments on multi-domain benchmarks demonstrate consistent improvements in OOD performance, particularly under challenging domain shifts, highlighting the value of causal evaluation for robust generalization.
Decoupling Return-to-Go for Efficient Decision Transformer
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:The Decision Transformer (DT) has established a powerful sequence modeling approach to offline reinforcement learning. It conditions its action predictions on Return-to-Go (RTG), using it both to distinguish trajectory quality during training and to guide action generation at inference. In this work, we identify a critical redundancy in this design: feeding the entire sequence of RTGs into the Transformer is theoretically unnecessary, as only the most recent RTG affects action prediction. We show that this redundancy can impair DT's performance through experiments. To resolve this, we propose the Decoupled DT (DDT). DDT simplifies the architecture by processing only observation and action sequences through the Transformer, using the latest RTG to guide the action prediction. This streamlined approach not only improves performance but also reduces computational cost. Our experiments show that DDT significantly outperforms DT and establishes competitive performance against state-of-the-art DT variants across multiple offline RL tasks.
STEP3-VL-10B Technical Report
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:We present STEP3-VL-10B, a lightweight open-source foundation model designed to redefine the trade-off between compact efficiency and frontier-level multimodal intelligence. STEP3-VL-10B is realized through two strategic shifts: first, a unified, fully unfrozen pre-training strategy on 1.2T multimodal tokens that integrates a language-aligned Perception Encoder with a Qwen3-8B decoder to establish intrinsic vision-language synergy; and second, a scaled post-training pipeline featuring over 1k iterations of reinforcement learning. Crucially, we implement Parallel Coordinated Reasoning (PaCoRe) to scale test-time compute, allocating resources to scalable perceptual reasoning that explores and synthesizes diverse visual hypotheses. Consequently, despite its compact 10B footprint, STEP3-VL-10B rivals or surpasses models 10$\times$-20$\times$ larger (e.g., GLM-4.6V-106B, Qwen3-VL-235B) and top-tier proprietary flagships like Gemini 2.5 Pro and Seed-1.5-VL. Delivering best-in-class performance, it records 92.2% on MMBench and 80.11% on MMMU, while excelling in complex reasoning with 94.43% on AIME2025 and 75.95% on MathVision. We release the full model suite to provide the community with a powerful, efficient, and reproducible baseline.
Zeros can be Informative: Masked Binary U-Net for Image Segmentation on Tensor Cores
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Real-time image segmentation is a key enabler for AR/VR, robotics, drones, and autonomous systems, where tight accuracy, latency, and energy budgets must be met on resource-constrained edge devices. While U-Net offers a favorable balance of accuracy and efficiency compared to large transformer-based models, achieving real-time performance on high-resolution input remains challenging due to compute, memory, and power limits. Extreme quantization, particularly binary networks, is appealing for its hardware-friendly operations. However, two obstacles limit practicality: (1) severe accuracy degradation, and (2) a lack of end-to-end implementations that deliver efficiency on general-purpose GPUs. We make two empirical observations that guide our design. (1) An explicit zero state is essential: training with zero masking to binary U-Net weights yields noticeable sparsity. (2) Quantization sensitivity is uniform across layers. Motivated by these findings, we introduce Masked Binary U-Net (MBU-Net), obtained through a cost-aware masking strategy that prioritizes masking where it yields the highest accuracy-per-cost, reconciling accuracy with near-binary efficiency. To realize these gains in practice, we develop a GPU execution framework that maps MBU-Net to Tensor Cores via a subtractive bit-encoding scheme, efficiently implementing masked binary weights with binary activations. This design leverages native binary Tensor Core BMMA instructions, enabling high throughput and energy savings on widely available GPUs. Across 3 segmentation benchmarks, MBU-Net attains near full-precision accuracy (3% average drop) while delivering 2.04x speedup and 3.54x energy reductions over a 16-bit floating point U-Net.
Policy-Conditioned Policies for Multi-Agent Task Solving
Dec 24, 2025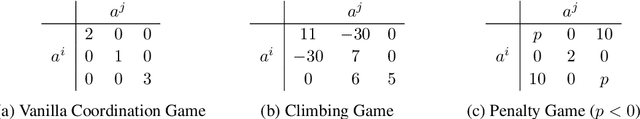
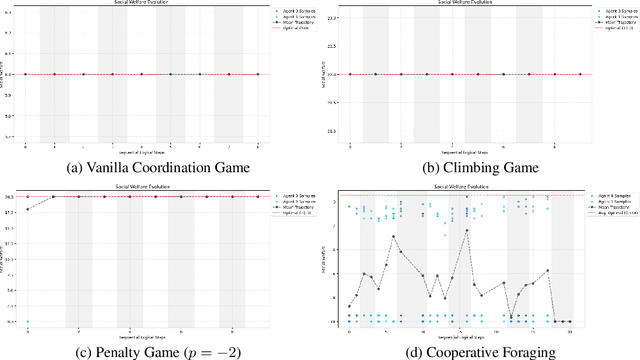
Abstract:In multi-agent tasks, the central challenge lies in the dynamic adaptation of strategies. However, directly conditioning on opponents' strategies is intractable in the prevalent deep reinforcement learning paradigm due to a fundamental ``representational bottleneck'': neural policies are opaque, high-dimensional parameter vectors that are incomprehensible to other agents. In this work, we propose a paradigm shift that bridges this gap by representing policies as human-interpretable source code and utilizing Large Language Models (LLMs) as approximate interpreters. This programmatic representation allows us to operationalize the game-theoretic concept of \textit{Program Equilibrium}. We reformulate the learning problem by utilizing LLMs to perform optimization directly in the space of programmatic policies. The LLM functions as a point-wise best-response operator that iteratively synthesizes and refines the ego agent's policy code to respond to the opponent's strategy. We formalize this process as \textit{Programmatic Iterated Best Response (PIBR)}, an algorithm where the policy code is optimized by textual gradients, using structured feedback derived from game utility and runtime unit tests. We demonstrate that this approach effectively solves several standard coordination matrix games and a cooperative Level-Based Foraging environment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge