A. Lee Swindlehurst
ASSENT: Learning-Based Association Optimization for Distributed Cell-Free ISAC
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) is a key emerging 6G technology. Despite progress, ISAC still lacks scalable methods for joint AP clustering and user/target scheduling in distributed deployments under fronthaul limits. Moreover, existing ISAC solutions largely rely on centralized processing and full channel state information, limiting scalability. This paper addresses joint access point (AP) clustering, user and target scheduling, and AP mode selection in distributed cell-free ISAC systems operating with constrained fronthaul capacity. We formulate the problem as a mixed-integer linear program (MILP) that jointly captures interference coupling, RF-chain limits, and sensing requirements, providing optimal but computationally demanding solutions. To enable real-time and scalable operation, we propose ASSENT (ASSociation and ENTity selection), a graph neural network (GNN) framework trained on MILP solutions to efficiently learn association and mode-selection policies directly from lightweight link statistics. Simulations show that ASSENT achieves near-optimal utility while accurately learning the underlying associations. Additionally, its single forward pass inference reduces decision latency compared to optimization-based methods. An open-source Python/PyTorch implementation with full datasets is provided to facilitate reproducible and extensible research in cell-free ISAC.
Optimal Interference Exploitation Waveform Design with Relaxed Block-Level Power Constraints
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates constructive interference (CI)-based waveform design for phase shift keying and quadrature amplitude modulation symbols under relaxed block-level power constraints in multi-user multiple-input single-output (MU-MIMO) communication systems. Existing linear CI-based precoding methods, including symbol-level precoding (SLP) and block-level precoding (BLP), suffer from performance limitations due to strict symbol-level power budgets or insufficient degrees of freedom over the block. To overcome these challenges, we propose a nonlinear waveform optimization framework that introduces additional optimization variables and maximizes the minimum CI metric across the transmission block. The optimal waveform is derived in closed form using the function and Karush Kuhn Tucker conditions, and the solution is explicitly expressed with respect to the dual variables. Moreover, the original problems are equivalently reformulated as tractable quadratic programming (QP) problems. To efficiently solve the derived QP problems, we develop an improved alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) algorithm by integrating a linear-time projection technique, which significantly enhances the computational efficiency. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithms substantially outperform the conventional CI-SLP and CI-BLP approaches, particularly under high-order modulations and large block lengths.
Semi-Blind Channel Estimation for Downlink Communications Based on Dynamic Metasurface Antennas
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Dynamic metasurface antennas (DMAs) are emerging as a promising technology to enable energy-efficient, large array-based multi-antenna systems. This paper presents a simple channel estimation scheme for the downlink of a multiple-input single-output orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (MISO-OFDM) communication system exploiting DMAs. The proposed scheme extracts separate estimates of the wireless channel and the unknown waveguide propagation vector using a simple iterative algorithm based on the parallel factor (PARAFAC) decomposition. Obtaining decoupled estimates of the wireless channel and inner waveguide vector enables the isolation and compensation for its effect when designing the DMA beamformer, regardless of the wireless channel state, which evolves much faster due to its shorter coherence time and bandwidth. Additionally, our solution operates in a data-aided manner, delivering estimates of useful data symbols jointly with channel estimates, without requiring sequential pilot and data stages. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to explore this CE approach. Numerical results corroborate the notable performance of the proposed scheme.
Near-Field Secure Beamfocusing With Receiver-Centered Protected Zone
May 26, 2025Abstract:This work studies near-field secure communications through transmit beamfocusing. We examine the benefit of having a protected eavesdropper-free zone around the legitimate receiver, and we determine the worst-case secrecy performance against a potential eavesdropper located anywhere outside the protected zone. A max-min optimization problem is formulated for the beamfocusing design with and without artificial noise transmission. Despite the NP-hardness of the problem, we develop a synchronous gradient descent-ascent framework that approximates the global maximin solution. A low-complexity solution is also derived that delivers excellent performance over a wide range of operating conditions. We further extend this study to a scenario where it is not possible to physically enforce a protected zone. To this end, we consider secure communications through the creation of a virtual protected zone using a full-duplex legitimate receiver. Numerical results demonstrate that exploiting either the physical or virtual receiver-centered protected zone with appropriately designed beamfocusing is an effective strategy for achieving secure near-field communications.
Simultaneously Exposing and Jamming Covert Communications via Disco Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces
May 18, 2025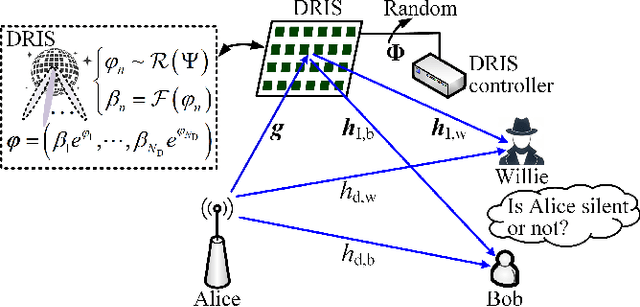
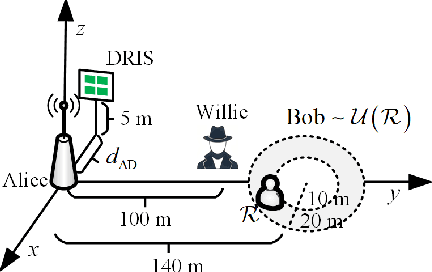
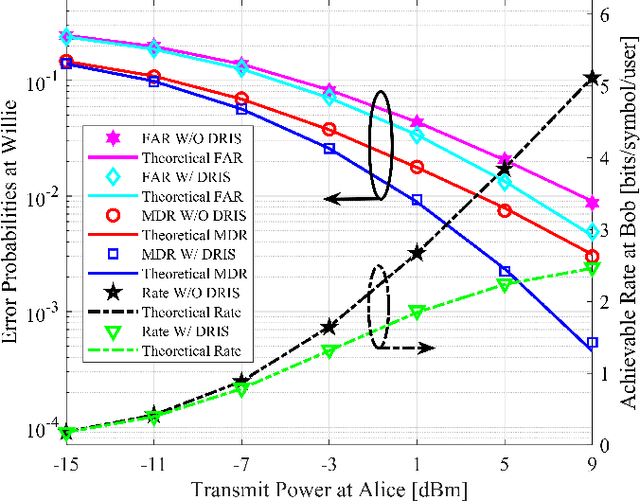
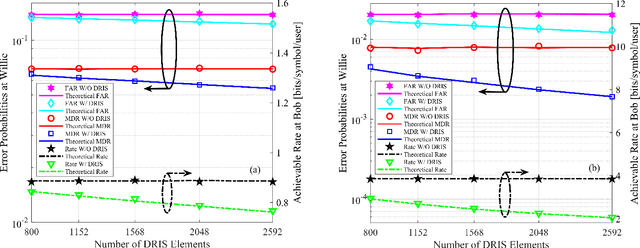
Abstract:Covert communications provide a stronger privacy protection than cryptography and physical-layer security (PLS). However, previous works on covert communications have implicitly assumed the validity of channel reciprocity, i.e., wireless channels remain constant or approximately constant during their coherence time. In this work, we investigate covert communications in the presence of a disco RIS (DRIS) deployed by the warden Willie, where the DRIS with random and time-varying reflective coefficients acts as a "disco ball", introducing timevarying fully-passive jamming (FPJ). Consequently, the channel reciprocity assumption no longer holds. The DRIS not only jams the covert transmissions between Alice and Bob, but also decreases the error probabilities of Willie's detections, without either Bob's channel knowledge or additional jamming power. To quantify the impact of the DRIS on covert communications, we first design a detection rule for the warden Willie in the presence of time-varying FPJ introduced by the DRIS. Then, we define the detection error probabilities, i.e., the false alarm rate (FAR) and the missed detection rate (MDR), as the monitoring performance metrics for Willie's detections, and the signal-to-jamming-plusnoise ratio (SJNR) as a communication performance metric for the covert transmissions between Alice and Bob. Based on the detection rule, we derive the detection threshold for the warden Willie to detect whether communications between Alice and Bob is ongoing, considering the time-varying DRIS-based FPJ. Moreover, we conduct theoretical analyses of the FAR and the MDR at the warden Willie, as well as SJNR at Bob, and then present unique properties of the DRIS-based FPJ in covert communications. We present numerical results to validate the derived theoretical analyses and evaluate the impact of DRIS on covert communications.
AI-Driven Optimization of Wave-Controlled Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces
May 11, 2025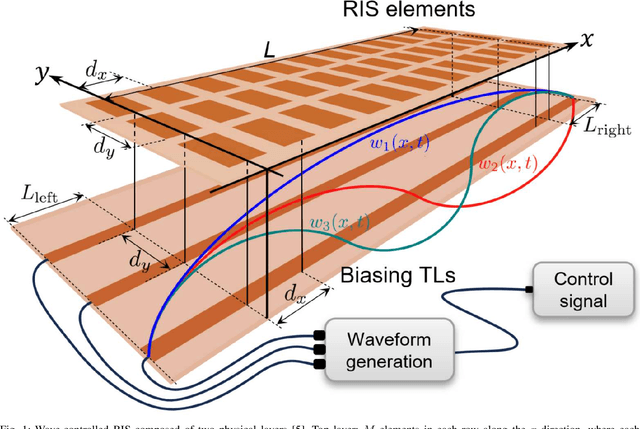
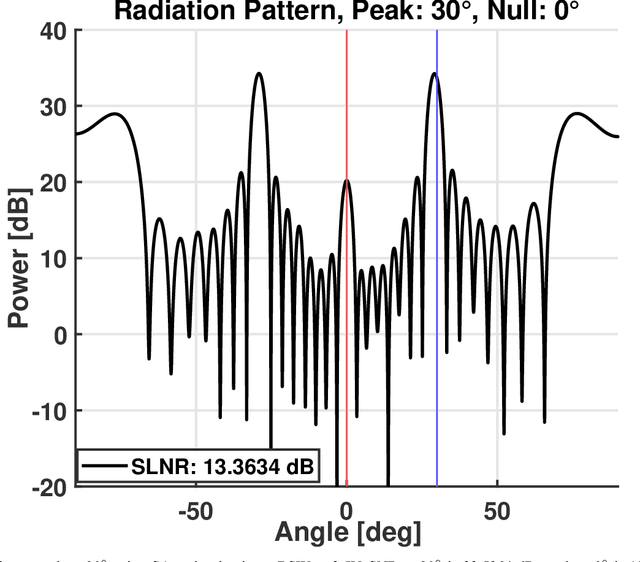
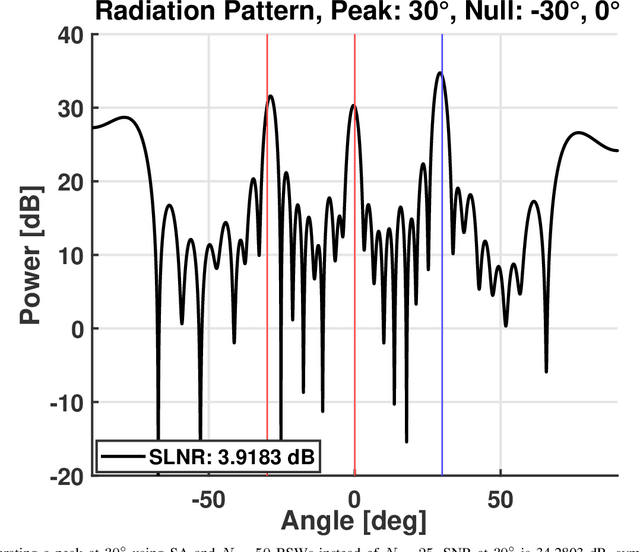
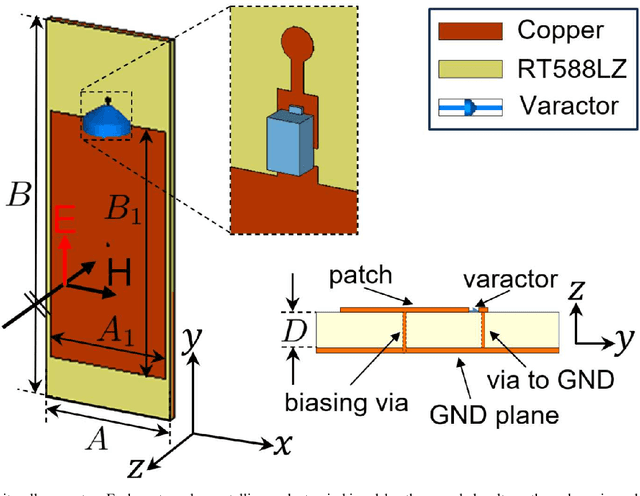
Abstract:A promising type of Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) employs tunable control of its varactors using biasing transmission lines below the RIS reflecting elements. Biasing standing waves (BSWs) are excited by a time-periodic signal and sampled at each RIS element to create a desired biasing voltage and control the reflection coefficients of the elements. A simple rectifier can be used to sample the voltages and capture the peaks of the BSWs over time. Like other types of RIS, attempting to model and accurately configure a wave-controlled RIS is extremely challenging due to factors such as device non-linearities, frequency dependence, element coupling, etc., and thus significant differences will arise between the actual and assumed performance. An alternative approach to solving this problem is data-driven: Using training data obtained by sampling the reflected radiation pattern of the RIS for a set of BSWs, a neural network (NN) is designed to create an input-output map between the BSW amplitudes and the resulting sampled radiation pattern. This is the approach discussed in this paper. In the proposed approach, the NN is optimized using a genetic algorithm (GA) to minimize the error between the predicted and measured radiation patterns. The BSW amplitudes are then designed via Simulated Annealing (SA) to optimize a signal-to-leakage-plus-noise ratio measure by iteratively forward-propagating the BSW amplitudes through the NN and using its output as feedback to determine convergence. The resulting optimal solutions are stored in a lookup table to be used both as settings to instantly configure the RIS and as a basis for determining more complex radiation patterns.
A Tutorial on MIMO-OFDM ISAC: From Far-Field to Near-Field
Apr 27, 2025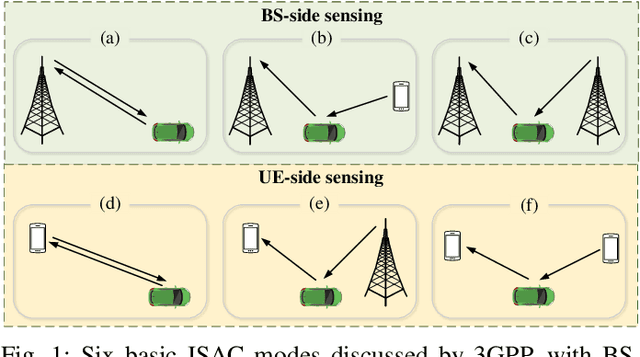
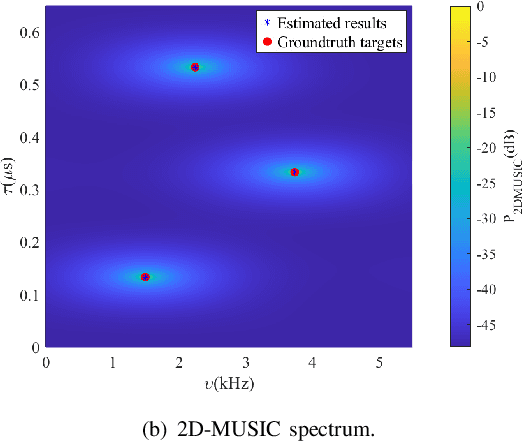
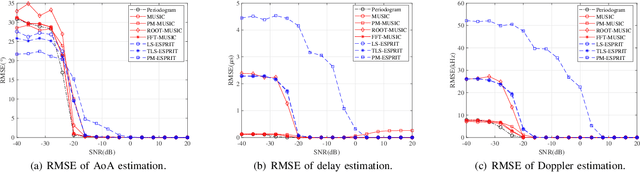
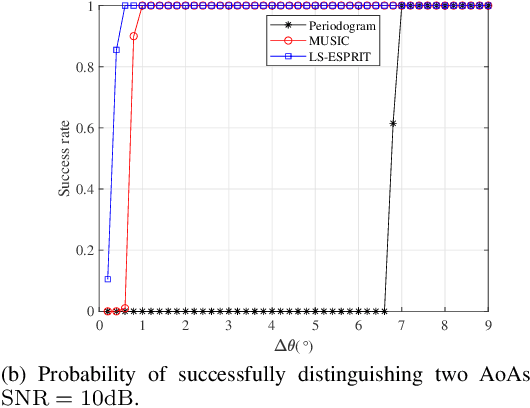
Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) is one of the key usage scenarios for future sixth-generation (6G) mobile communication networks, where communication and sensing (C&S) services are simultaneously provided through shared wireless spectrum, signal processing modules, hardware, and network infrastructure. Such an integration is strengthened by the technology trends in 6G, such as denser network nodes, larger antenna arrays, wider bandwidths, higher frequency bands, and more efficient utilization of spectrum and hardware resources, which incentivize and empower enhanced sensing capabilities. As the dominant waveform used in contemporary communication systems, orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) is still expected to be a very competitive technology for 6G, rendering it necessary to thoroughly investigate the potential and challenges of OFDM ISAC. Thus, this paper aims to provide a comprehensive tutorial overview of ISAC systems enabled by large-scale multi-input multi-output (MIMO) and OFDM technologies and to discuss their fundamental principles, advantages, and enabling signal processing methods. To this end, a unified MIMO-OFDM ISAC system model is first introduced, followed by four frameworks for estimating parameters across the spatial, delay, and Doppler domains, including parallel one-domain, sequential one-domain, joint two-domain, and joint three-domain parameter estimation. Next, sensing algorithms and performance analyses are presented in detail for far-field scenarios where uniform plane wave (UPW) propagation is valid, followed by their extensions to near-field scenarios where uniform spherical wave (USW) characteristics need to be considered. Finally, this paper points out open challenges and outlines promising avenues for future research on MIMO-OFDM ISAC.
Exploiting Symmetric Non-Convexity for Multi-Objective Symbol-Level DFRC Signal Design
Apr 19, 2025Abstract:Symbol-level precoding (SLP) is a promising solution for addressing the inherent interference problem in dual-functional radar-communication (DFRC) signal designs. This paper considers an SLP-DFRC signal design problem which optimizes the radar performance under communication performance constraints. We show that a common phase modulation applied to the transmit signals from an antenna array does not affect the performance of different radar sensing metrics, including beampattern similarity, signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR), and Cram\'er-Rao lower bound (CRLB). We refer to this as symmetric-rotation invariance, upon which we develop low-complexity yet efficient DFRC signal design algorithms. More specifically, we propose a symmetric non-convexity (SNC)-based DFRC algorithm that relies on the non-convexity of the radar sensing metrics to identify a set of radar-only solutions. Based on these solutions, we further exploit the symmetry property of the radar sensing metrics to efficiently design the DFRC signal. We show that the proposed SNC-based algorithm is versatile in the sense that it can be applied to the DFRC signal optimization of all three sensing metrics mentioned above (beampattern, SINR, and CRLB). In addition, since the radar sensing metrics are independent of the communication channel and data symbols, the set of radar-only solutions can be constructed offline, thereby reducing the computational complexity. We also develop an accelerated SNC-based algorithm that further reduces the complexity. Finally, we numerically demonstrate the superiority of the proposed algorithms compared to existing methods in terms of sensing and communication performance as well as computational requirements.
Sensing-Oriented Adaptive Resource Allocation Designs for OFDM-ISAC Systems
Apr 09, 2025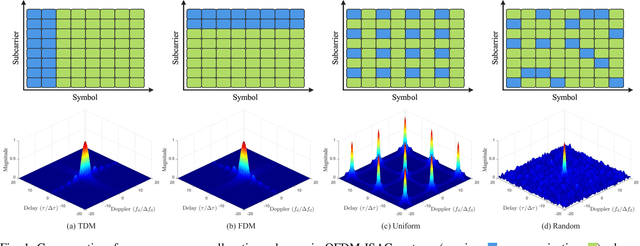
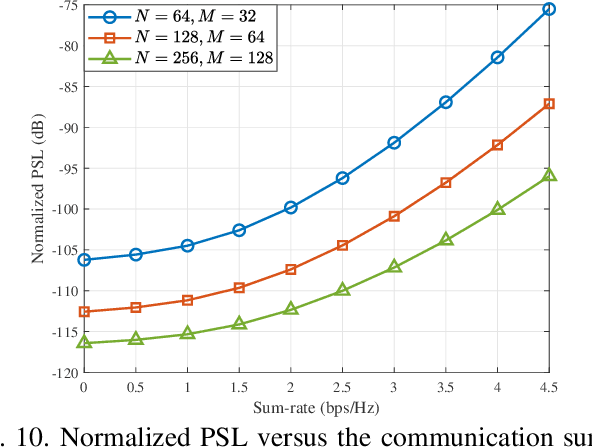
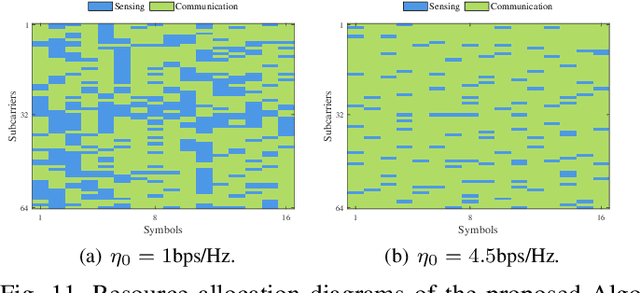
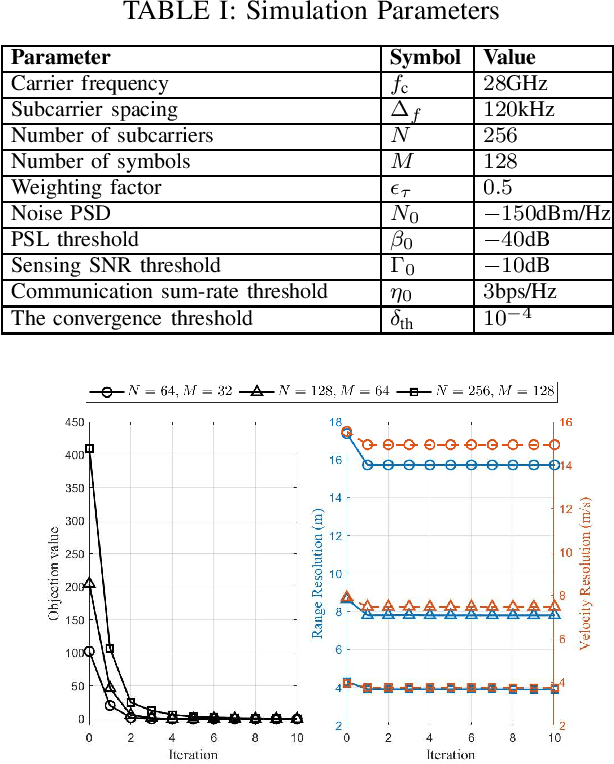
Abstract:Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing - integrated sensing and communication (OFDM-ISAC) has emerged as a key enabler for future wireless networks, leveraging the widely adopted OFDM waveform to seamlessly integrate wireless communication and radar sensing within a unified framework. In this paper, we propose adaptive resource allocation strategies for OFDM-ISAC systems to achieve optimal trade-offs between diverse sensing requirements and communication quality-of-service (QoS). We first develop a comprehensive resource allocation framework for OFDM-ISAC systems, deriving closed-form expressions for key sensing performance metrics, including delay resolution, Doppler resolution, delay-Doppler peak sidelobe level (PSL), and received signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Building on this theoretical foundation, we introduce two novel resource allocation algorithms tailored to distinct sensing objectives. The resolution-oriented algorithm aims to maximize the weighted delay-Doppler resolution while satisfying constraints on PSL, sensing SNR, communication sum-rate, and transmit power. The sidelobe-oriented algorithm focuses on minimizing delay-Doppler PSL while satisfying resolution, SNR, and communication constraints. To efficiently solve the resulting non-convex optimization problems, we develop two adaptive resource allocation algorithms based on Dinkelbach's transform and majorization-minimization (MM). Extensive simulations validate the effectiveness of the proposed sensing-oriented adaptive resource allocation strategies in enhancing resolution and sidelobe suppression. Remarkably, these strategies achieve sensing performance nearly identical to that of a radar-only scheme, which dedicates all resources to sensing. These results highlight the superior performance of the proposed methods in optimizing the trade-off between sensing and communication objectives within OFDM-ISAC systems.
Joint Array Partitioning and Beamforming Designs in ISAC Systems: A Bayesian CRB Perspective
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) has emerged as a promising paradigm for next-generation (6G) wireless networks, unifying radar sensing and communication on a shared hardware platform. This paper proposes a dynamic array partitioning framework for monostatic ISAC systems to fully exploit available spatial degrees of freedom (DoFs) and reconfigurable antenna topologies, enhancing sensing performance in complex scenarios. We first establish a theoretical foundation for our work by deriving Bayesian Cram\'{e}r-Rao bounds (BCRBs) under prior distribution constraints for heterogeneous target models, encompassing both point-like and extended targets. Building on this, we formulate a joint optimization framework for transmit beamforming and dynamic array partitioning to minimize the derived BCRBs for direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation. The optimization problem incorporates practical constraints, including multi-user communication signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) requirements, transmit power budgets, and array partitioning feasibility conditions. To address the non-convexity of the problem, we develop an efficient alternating optimization algorithm combining the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) with semi-definite relaxation (SDR). We also design novel maximum a posteriori (MAP) DOA estimation algorithms specifically adapted to the statistical characteristics of each target model. Extensive simulations illustrate the superiority of the proposed dynamic partitioning strategy over conventional fixed-array architectures across diverse system configurations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge