Chao Zhou
Jack
Low-complexity Design for Beam Coverage in Near-field and Far-field: A Fourier Transform Approach
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:In this paper, we study efficient beam coverage design for multi-antenna systems in both far-field and near-field cases. To reduce the computational complexity of existing sampling-based optimization methods, we propose a new low-complexity yet efficient beam coverage design. To this end, we first formulate a general beam coverage optimization problem to maximize the worst-case beamforming gain over a target region. For the far-field case, we show that the beam coverage design can be viewed as a spatial-frequency filtering problem, where angular coverage can be achieved by weight-shaping in the antenna domain via an inverse FT, yielding an infinite-length weighting sequence. Under the constraint of a finite number of antennas, a surrogate scheme is proposed by directly truncating this sequence, which inevitably introduces a roll-off effect at the angular boundaries, yielding degraded worst-case beamforming gain. To address this issue, we characterize the finite-antenna-induced roll-off effect, based on which a roll-off-aware design with a protective zoom is developed to ensure a flat beamforming-gain profile within the target angular region. Next, we extend the proposed method to the near-field case. Specifically, by applying a first-order Taylor approximation to the near-field channel steering vector (CSV), the two-dimensional (2D) beam coverage design (in both angle and inverse-range) can be transformed into a 2D inverse FT, leading to a low-complexity beamforming design. Furthermore, an inherent near-field range defocusing effect is observed, indicating that sufficiently wide angular coverage results in range-insensitive beam steering. Finally, numerical results demonstrate that the proposed FT-based approach achieves a comparable worst-case beamforming performance with that of conventional sampling-based optimization methods while significantly reducing the computational complexity.
Near-field Physical Layer Security: Robust Beamforming under Location Uncertainty
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:In this paper, we study robust beamforming design for near-field physical-layer-security (PLS) systems, where a base station (BS) equipped with an extremely large-scale array (XL-array) serves multiple near-field legitimate users (Bobs) in the presence of multiple near-field eavesdroppers (Eves). Unlike existing works that mostly assume perfect channel state information (CSI) or location information of Eves, we consider a more practical and challenging scenario, where the locations of Bobs are perfectly known, while only imperfect location information of Eves is available at the BS. We first formulate a robust optimization problem to maximize the sum-rate of Bobs while guaranteeing a worst-case limit on the eavesdropping rate under location uncertainty. By transforming Cartesian position errors into the polar domain, we reveal an important near-field angular-error amplification effect: for the same location error, the closer the Eve, the larger the angle error, severely degrading the performance of conventional robust beamforming methods based on imperfect channel state information. To address this issue, we first establish the conditions for which the first-order Taylor approximation of the near-field channel steering vector under location uncertainty is largely accurate. Then, we propose a two-stage robust beamforming method, which first partitions the uncertainty region into multiple fan-shaped sub-regions, followed by the second stage to formulate and solve a refined linear-matrix-inequality (LMI)-based robust beamforming optimization problem. In addition, the proposed method is further extended to scenarios with multiple Bobs and multiple Eves. Finally, numerical results validate that the proposed method achieves a superior trade-off between rate performance and secrecy robustness, hence significantly outperforming existing benchmarks under Eve location uncertainty.
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
Codebook Design for Limited Feedback in Near-Field XL-MIMO Systems
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:In this paper, we study efficient codebook design for limited feedback in extremely large-scale multiple-input-multiple-output (XL-MIMO) frequency division duplexing (FDD) systems. It is worth noting that existing codebook designs for XL-MIMO, such as polar-domain codebook, have not well taken into account user (location) distribution in practice, thereby incurring excessive feedback overhead. To address this issue, we propose in this paper a novel and efficient feedback codebook tailored to user distribution. To this end, we first consider a typical scenario where users are uniformly distributed within a specific polar-region, based on which a sum-rate maximization problem is formulated to jointly optimize angle-range samples and bit allocation among angle/range feedback. This problem is challenging to solve due to the lack of a closed-form expression for the received power in terms of angle and range samples. By leveraging a Voronoi partitioning approach, we show that uniform angle sampling is optimal for received power maximization. For more challenging range sampling design, we obtain a tight lower-bound on the received power and show that geometric sampling, where the ratio between adjacent samples is constant, can maximize the lower bound and thus serves as a high-quality suboptimal solution. We then extend the proposed framework to accommodate more general non-uniform user distribution via an alternating sampling method. Furthermore, theoretical analysis reveals that as the array size increases, the optimal allocation of feedback bits increasingly favors range samples at the expense of angle samples. Finally, numerical results validate the superior rate performance and robustness of the proposed codebook design under various system setups, achieving significant gains over benchmark schemes, including the widely used polar-domain codebook.
Near-field Target Localization: Effect of Hardware Impairments
Dec 25, 2025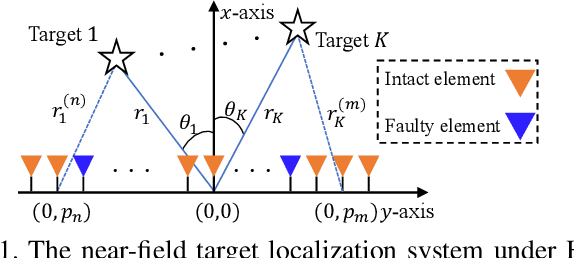
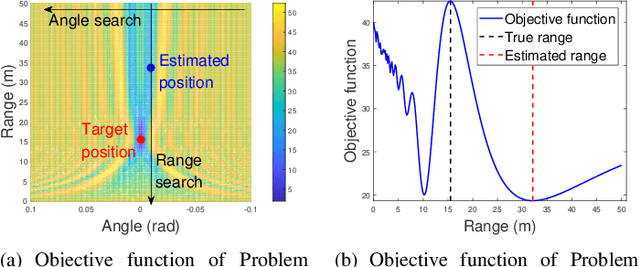
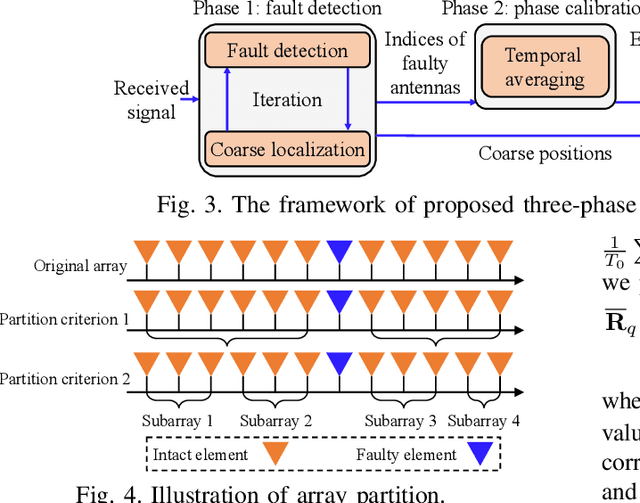
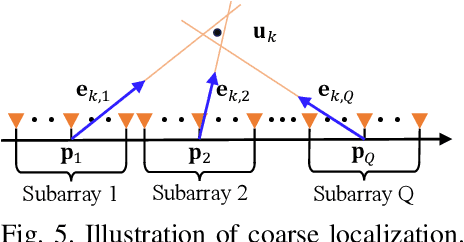
Abstract:The prior works on near-field target localization have mostly assumed ideal hardware models and thus suffer from two limitations in practice. First, extremely large-scale arrays (XL-arrays) usually face a variety of hardware impairments (HIs) that may introduce unknown phase and/or amplitude errors. Second, the existing block coordinate descent (BCD)-based methods for joint estimation of the HI indicator, channel gain, angle, and range may induce considerable target localization error when the target is very close to the XL-array. To address these issues, we propose in this paper a new three-phase HI-aware near-field localization method, by efficiently detecting faulty antennas and estimating the positions of targets. Specifically, we first determine faulty antennas by using compressed sensing (CS) methods and improve detection accuracy based on coarse target localization. Then, a dedicated phase calibration method is designed to correct phase errors induced by detected faulty antennas. Subsequently, an efficient near-field localization method is devised to accurately estimate the positions of targets based on the full XL-array with phase calibration. Additionally, we resort to the misspecified Cramer-Rao bound (MCRB) to quantify the performance loss caused by HIs. Last, numerical results demonstrate that our proposed method significantly reduces the localization errors as compared to various benchmark schemes, especially for the case with a short target range and/or a high fault probability.
Position Optimization for Two-layer Movable Antenna Systems
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Movable antenna (MA) is a promising technology for improving the performance of wireless communication systems by providing new degrees-of-freedom (DoFs) in antenna position optimization. However, existing works on MA systems have mostly considered element-wise single-layer MA (SL-MA) arrays, where all the MAs move within the given movable region, hence inevitably incurring high control complexity and hardware cost in practice. To address this issue, we propose in this letter a new two-layer MA array (TL-MA), where the positions of MAs are jointly determined by the large-scale movement of multiple subarrays and the small-scale fine-tuning of per-subarray MAs. In particular, an optimization problem is formulated to maximize the sum-rate of the TL-MA-aided communication system by jointly optimizing the subarray-positions, per-subarray (relative) MA positions, and receive beamforming. To solve this non-convex problem, we propose an alternating optimization (AO)-based particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm, which alternately optimizes the positions of subarrays and per-subarray MAs, given the optimal receive beamforming. Numerical results verify that the proposed TL-MA significantly reduces the sum-displacement of MA motors (i.e., the total moving distances of all motors) of element-wise SL-MA, while achieving comparable rate performance.
Neural B-frame Video Compression with Bi-directional Reference Harmonization
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Neural video compression (NVC) has made significant progress in recent years, while neural B-frame video compression (NBVC) remains underexplored compared to P-frame compression. NBVC can adopt bi-directional reference frames for better compression performance. However, NBVC's hierarchical coding may complicate continuous temporal prediction, especially at some hierarchical levels with a large frame span, which could cause the contribution of the two reference frames to be unbalanced. To optimize reference information utilization, we propose a novel NBVC method, termed Bi-directional Reference Harmonization Video Compression (BRHVC), with the proposed Bi-directional Motion Converge (BMC) and Bi-directional Contextual Fusion (BCF). BMC converges multiple optical flows in motion compression, leading to more accurate motion compensation on a larger scale. Then BCF explicitly models the weights of reference contexts under the guidance of motion compensation accuracy. With more efficient motions and contexts, BRHVC can effectively harmonize bi-directional references. Experimental results indicate that our BRHVC outperforms previous state-of-the-art NVC methods, even surpassing the traditional coding, VTM-RA (under random access configuration), on the HEVC datasets. The source code is released at https://github.com/kwai/NVC.
MA-enhanced Mixed Near-field and Far-field Covert Communications
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose to employ a modular-based movable extremely large-scale array (XL-array) at Alice for enhancing covert communication performance. Compared with existing work that mostly considered either far-field or near-field covert communications, we consider in this paper a more general and practical mixed-field scenario, where multiple Bobs are located in either the near-field or far-field of Alice, in the presence of multiple near-field Willies. Specifically, we first consider a two-Bob-one-Willie system and show that conventional fixed-position XL-arrays suffer degraded sum-rate performance due to the energy-spread effect in mixed-field systems, which, however, can be greatly improved by subarray movement. On the other hand, for transmission covertness, it is revealed that sufficient angle difference between far-field Bob and Willie as well as adequate range difference between near-field Bob and Willie are necessary for ensuring covertness in fixed-position XL-array systems, while this requirement can be relaxed in movable XL-array systems thanks to flexible channel correlation control between Bobs and Willie. Next, for general system setups, we formulate an optimization problem to maximize the achievable sum-rate under covertness constraint. To solve this non-convex optimization problem, we first decompose it into two subproblems, corresponding to an inner problem for beamforming optimization given positions of subarrays and an outer problem for subarray movement optimization. Although these two subproblems are still non-convex, we obtain their high-quality solutions by using the successive convex approximation technique and devising a customized differential evolution algorithm, respectively. Last, numerical results demonstrate the effectiveness of proposed movable XL-array in balancing sum-rate and covert communication requirements.
LLM-based Multi-Agent Copilot for Quantum Sensor
Aug 07, 2025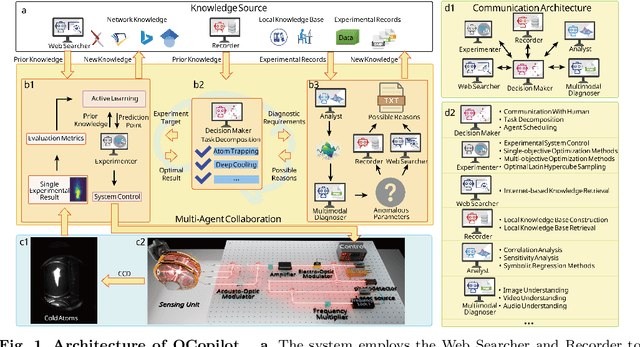
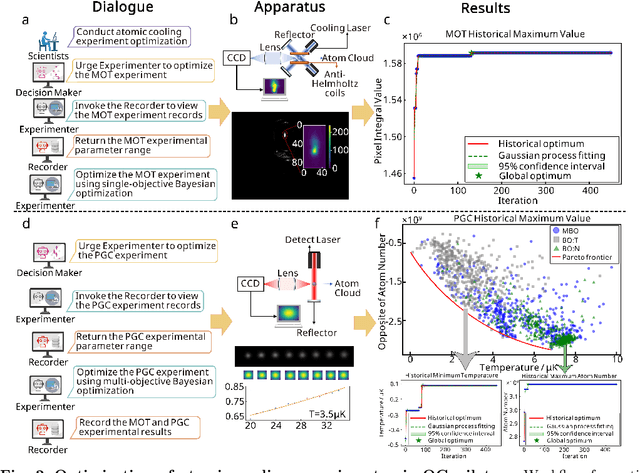
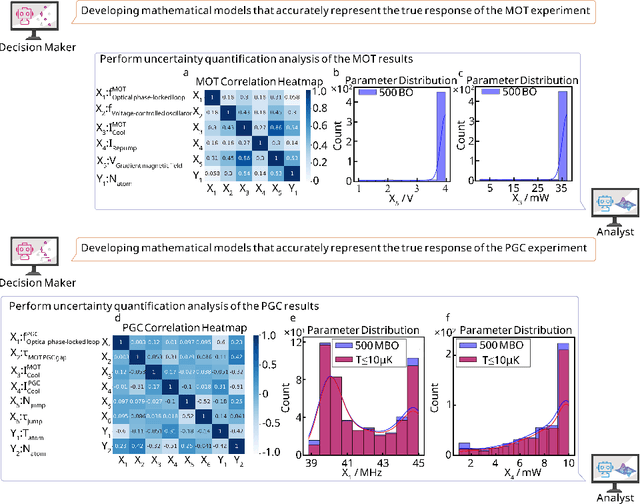
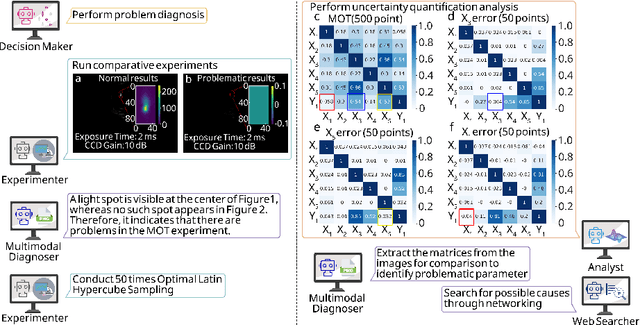
Abstract:Large language models (LLM) exhibit broad utility but face limitations in quantum sensor development, stemming from interdisciplinary knowledge barriers and involving complex optimization processes. Here we present QCopilot, an LLM-based multi-agent framework integrating external knowledge access, active learning, and uncertainty quantification for quantum sensor design and diagnosis. Comprising commercial LLMs with few-shot prompt engineering and vector knowledge base, QCopilot employs specialized agents to adaptively select optimization methods, automate modeling analysis, and independently perform problem diagnosis. Applying QCopilot to atom cooling experiments, we generated 10${}^{\rm{8}}$ sub-$\rm{\mu}$K atoms without any human intervention within a few hours, representing $\sim$100$\times$ speedup over manual experimentation. Notably, by continuously accumulating prior knowledge and enabling dynamic modeling, QCopilot can autonomously identify anomalous parameters in multi-parameter experimental settings. Our work reduces barriers to large-scale quantum sensor deployment and readily extends to other quantum information systems.
Pay Attention to Small Weights
Jun 26, 2025Abstract:Finetuning large pretrained neural networks is known to be resource-intensive, both in terms of memory and computational cost. To mitigate this, a common approach is to restrict training to a subset of the model parameters. By analyzing the relationship between gradients and weights during finetuning, we observe a notable pattern: large gradients are often associated with small-magnitude weights. This correlation is more pronounced in finetuning settings than in training from scratch. Motivated by this observation, we propose NANOADAM, which dynamically updates only the small-magnitude weights during finetuning and offers several practical advantages: first, this criterion is gradient-free -- the parameter subset can be determined without gradient computation; second, it preserves large-magnitude weights, which are likely to encode critical features learned during pretraining, thereby reducing the risk of catastrophic forgetting; thirdly, it permits the use of larger learning rates and consistently leads to better generalization performance in experiments. We demonstrate this for both NLP and vision tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge