Yizhen Shao
NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Short-form UGC Video Quality Assessment and Enhancement: KwaiSR Dataset and Study
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:In this work, we build the first benchmark dataset for short-form UGC Image Super-resolution in the wild, termed KwaiSR, intending to advance the research on developing image super-resolution algorithms for short-form UGC platforms. This dataset is collected from the Kwai Platform, which is composed of two parts, i.e., synthetic and wild parts. Among them, the synthetic dataset, including 1,900 image pairs, is produced by simulating the degradation following the distribution of real-world low-quality short-form UGC images, aiming to provide the ground truth for training and objective comparison in the validation/testing. The wild dataset contains low-quality images collected directly from the Kwai Platform, which are filtered using the quality assessment method KVQ from the Kwai Platform. As a result, the KwaiSR dataset contains 1800 synthetic image pairs and 1900 wild images, which are divided into training, validation, and testing parts with a ratio of 8:1:1. Based on the KwaiSR dataset, we organize the NTIRE 2025 challenge on a second short-form UGC Video quality assessment and enhancement, which attracts lots of researchers to develop the algorithm for it. The results of this competition have revealed that our KwaiSR dataset is pretty challenging for existing Image SR methods, which is expected to lead to a new direction in the image super-resolution field. The dataset can be found from https://lixinustc.github.io/NTIRE2025-KVQE-KwaSR-KVQ.github.io/.
Disentangled Graph Social Recommendation
Mar 14, 2023Abstract:Social recommender systems have drawn a lot of attention in many online web services, because of the incorporation of social information between users in improving recommendation results. Despite the significant progress made by existing solutions, we argue that current methods fall short in two limitations: (1) Existing social-aware recommendation models only consider collaborative similarity between items, how to incorporate item-wise semantic relatedness is less explored in current recommendation paradigms. (2) Current social recommender systems neglect the entanglement of the latent factors over heterogeneous relations (e.g., social connections, user-item interactions). Learning the disentangled representations with relation heterogeneity poses great challenge for social recommendation. In this work, we design a Disentangled Graph Neural Network (DGNN) with the integration of latent memory units, which empowers DGNN to maintain factorized representations for heterogeneous types of user and item connections. Additionally, we devise new memory-augmented message propagation and aggregation schemes under the graph neural architecture, allowing us to recursively distill semantic relatedness into the representations of users and items in a fully automatic manner. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets verify the effectiveness of our model by achieving great improvement over state-of-the-art recommendation techniques. The source code is publicly available at: https://github.com/HKUDS/DGNN.
Entity Candidate Network for Whole-Aware Named Entity Recognition
Apr 29, 2020
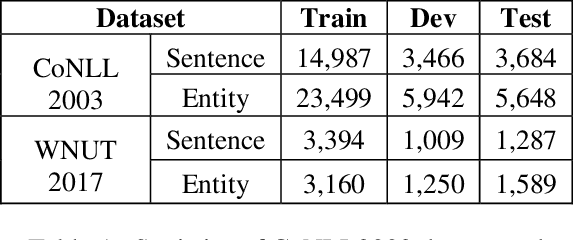
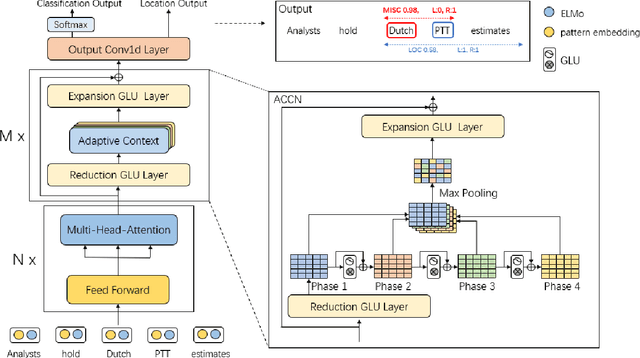
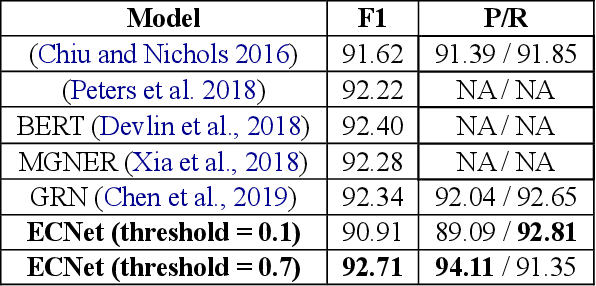
Abstract:Named Entity Recognition (NER) is a crucial upstream task in Natural Language Processing (NLP). Traditional tag scheme approaches offer a single recognition that does not meet the needs of many downstream tasks such as coreference resolution. Meanwhile, Tag scheme approaches ignore the continuity of entities. Inspired by one-stage object detection models in computer vision (CV), this paper proposes a new no-tag scheme, the Whole-Aware Detection, which makes NER an object detection task. Meanwhile, this paper presents a novel model, Entity Candidate Network (ECNet), and a specific convolution network, Adaptive Context Convolution Network (ACCN), to fuse multi-scale contexts and encode entity information at each position. ECNet identifies the full span of a named entity and its type at each position based on Entity Loss. Furthermore, ECNet is regulable between the highest precision and the highest recall, while the tag scheme approaches are not. Experimental results on the CoNLL 2003 English dataset and the WNUT 2017 dataset show that ECNet outperforms other previous state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge