Cen Liu
Near-Field Secure Beamfocusing With Receiver-Centered Protected Zone
May 26, 2025Abstract:This work studies near-field secure communications through transmit beamfocusing. We examine the benefit of having a protected eavesdropper-free zone around the legitimate receiver, and we determine the worst-case secrecy performance against a potential eavesdropper located anywhere outside the protected zone. A max-min optimization problem is formulated for the beamfocusing design with and without artificial noise transmission. Despite the NP-hardness of the problem, we develop a synchronous gradient descent-ascent framework that approximates the global maximin solution. A low-complexity solution is also derived that delivers excellent performance over a wide range of operating conditions. We further extend this study to a scenario where it is not possible to physically enforce a protected zone. To this end, we consider secure communications through the creation of a virtual protected zone using a full-duplex legitimate receiver. Numerical results demonstrate that exploiting either the physical or virtual receiver-centered protected zone with appropriately designed beamfocusing is an effective strategy for achieving secure near-field communications.
Successive Pose Estimation and Beam Tracking for mmWave Vehicular Communication Systems
Aug 05, 2023Abstract:The millimeter wave (mmWave) radar sensing-aided communications in vehicular mobile communication systems is investigated. To alleviate the beam training overhead under high mobility scenarios, a successive pose estimation and beam tracking (SPEBT) scheme is proposed to facilitate mmWave communications with the assistance of mmWave radar sensing. The proposed SPEBT scheme first resorts to a Fast Conservative Filtering for Efficient and Accurate Radar odometry (Fast-CFEAR) approach to estimate the vehicle pose consisting of 2-dimensional position and yaw from radar point clouds collected by mmWave radar sensor. Then, the pose estimation information is fed into an extend Kalman filter to perform beam tracking for the line-of-sight channel. Owing to the intrinsic robustness of mmWave radar sensing, the proposed SPEBT scheme is capable of operating reliably under extreme weather/illumination conditions and large-scale global navigation satellite systems (GNSS)-denied environments. The practical deployment of the SPEBT scheme is verified through rigorous testing on a real-world sensing dataset. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed SPEBT scheme is capable of providing precise pose estimation information and accurate beam tracking output, while reducing the proportion of beam training overhead to less than 5% averagely.
NTIRE 2022 Challenge on High Dynamic Range Imaging: Methods and Results
May 25, 2022
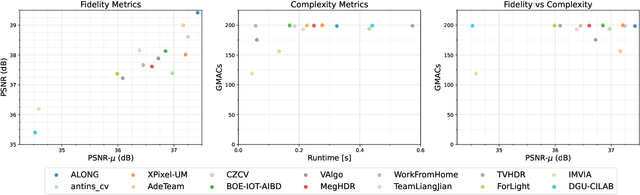
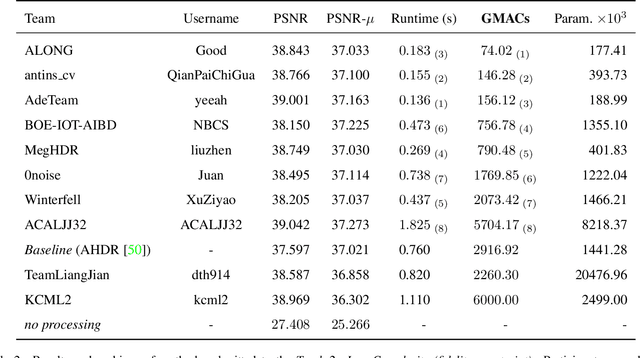
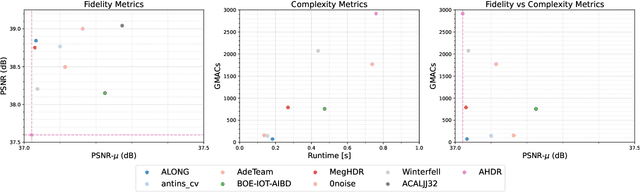
Abstract:This paper reviews the challenge on constrained high dynamic range (HDR) imaging that was part of the New Trends in Image Restoration and Enhancement (NTIRE) workshop, held in conjunction with CVPR 2022. This manuscript focuses on the competition set-up, datasets, the proposed methods and their results. The challenge aims at estimating an HDR image from multiple respective low dynamic range (LDR) observations, which might suffer from under- or over-exposed regions and different sources of noise. The challenge is composed of two tracks with an emphasis on fidelity and complexity constraints: In Track 1, participants are asked to optimize objective fidelity scores while imposing a low-complexity constraint (i.e. solutions can not exceed a given number of operations). In Track 2, participants are asked to minimize the complexity of their solutions while imposing a constraint on fidelity scores (i.e. solutions are required to obtain a higher fidelity score than the prescribed baseline). Both tracks use the same data and metrics: Fidelity is measured by means of PSNR with respect to a ground-truth HDR image (computed both directly and with a canonical tonemapping operation), while complexity metrics include the number of Multiply-Accumulate (MAC) operations and runtime (in seconds).
* CVPR Workshops 2022. 15 pages, 21 figures, 2 tables
A Technical Report for ICCV 2021 VIPriors Re-identification Challenge
Sep 30, 2021



Abstract:Person re-identification has always been a hot and challenging task. This paper introduces our solution for the re-identification track in VIPriors Challenge 2021. In this challenge, the difficulty is how to train the model from scratch without any pretrained weight. In our method, we show use state-of-the-art data processing strategies, model designs, and post-processing ensemble methods, it is possible to overcome the difficulty of data shortage and obtain competitive results. (1) Both image augmentation strategy and novel pre-processing method for occluded images can help the model learn more discriminative features. (2) Several strong backbones and multiple loss functions are used to learn more representative features. (3) Post-processing techniques including re-ranking, automatic query expansion, ensemble learning, etc., significantly improve the final performance. The final score of our team (ALONG) is 96.5154% mAP, ranking first in the leaderboard.
AIM 2020 Challenge on Real Image Super-Resolution: Methods and Results
Sep 25, 2020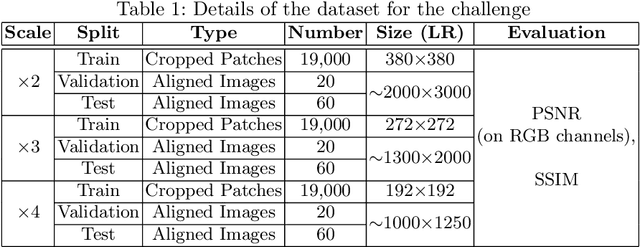
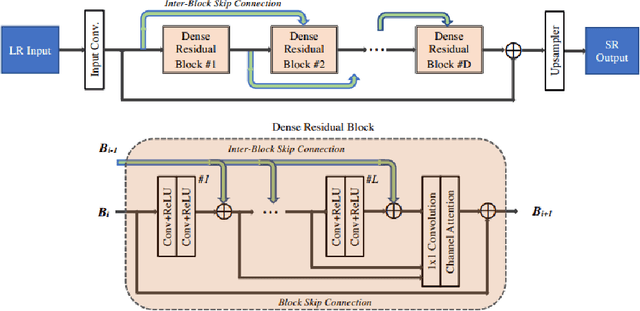
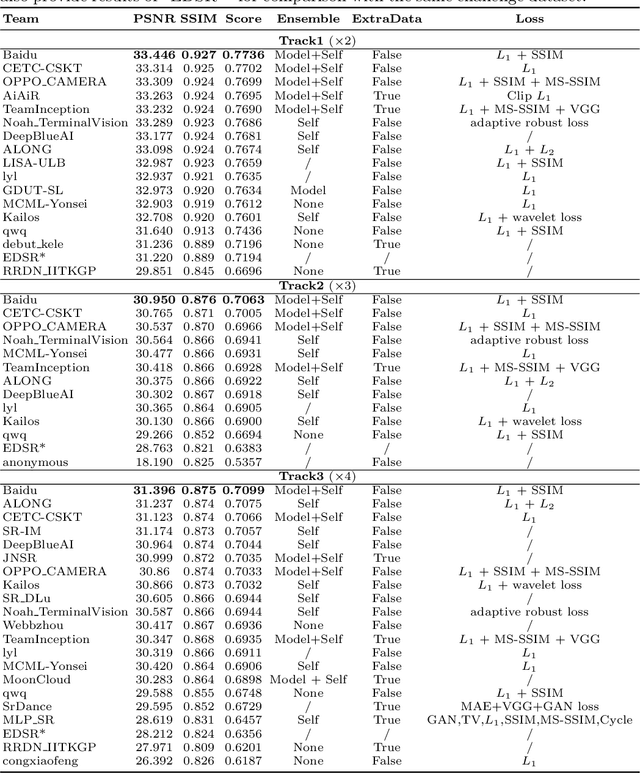
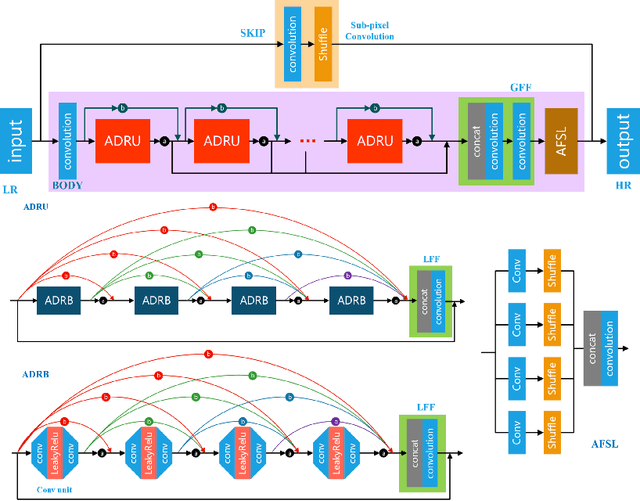
Abstract:This paper introduces the real image Super-Resolution (SR) challenge that was part of the Advances in Image Manipulation (AIM) workshop, held in conjunction with ECCV 2020. This challenge involves three tracks to super-resolve an input image for $\times$2, $\times$3 and $\times$4 scaling factors, respectively. The goal is to attract more attention to realistic image degradation for the SR task, which is much more complicated and challenging, and contributes to real-world image super-resolution applications. 452 participants were registered for three tracks in total, and 24 teams submitted their results. They gauge the state-of-the-art approaches for real image SR in terms of PSNR and SSIM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge