Eduardo Pérez-Pellitero
Off The Grid: Detection of Primitives for Feed-Forward 3D Gaussian Splatting
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Feed-forward 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) models enable real-time scene generation but are hindered by suboptimal pixel-aligned primitive placement, which relies on a dense, rigid grid and limits both quality and efficiency. We introduce a new feed-forward architecture that detects 3D Gaussian primitives at a sub-pixel level, replacing the pixel grid with an adaptive, "Off The Grid" distribution. Inspired by keypoint detection, our multi-resolution decoder learns to distribute primitives across image patches. This module is trained end-to-end with a 3D reconstruction backbone using self-supervised learning. Our resulting pose-free model generates photorealistic scenes in seconds, achieving state-of-the-art novel view synthesis for feed-forward models. It outperforms competitors while using far fewer primitives, demonstrating a more accurate and efficient allocation that captures fine details and reduces artifacts. Moreover, we observe that by learning to render 3D Gaussians, our 3D reconstruction backbone improves camera pose estimation, suggesting opportunities to train these foundational models without labels.
Charge: A Comprehensive Novel View Synthesis Benchmark and Dataset to Bind Them All
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a new dataset for Novel View Synthesis, generated from a high-quality, animated film with stunning realism and intricate detail. Our dataset captures a variety of dynamic scenes, complete with detailed textures, lighting, and motion, making it ideal for training and evaluating cutting-edge 4D scene reconstruction and novel view generation models. In addition to high-fidelity RGB images, we provide multiple complementary modalities, including depth, surface normals, object segmentation and optical flow, enabling a deeper understanding of scene geometry and motion. The dataset is organised into three distinct benchmarking scenarios: a dense multi-view camera setup, a sparse camera arrangement, and monocular video sequences, enabling a wide range of experimentation and comparison across varying levels of data sparsity. With its combination of visual richness, high-quality annotations, and diverse experimental setups, this dataset offers a unique resource for pushing the boundaries of view synthesis and 3D vision.
ViDAR: Video Diffusion-Aware 4D Reconstruction From Monocular Inputs
Jun 23, 2025Abstract:Dynamic Novel View Synthesis aims to generate photorealistic views of moving subjects from arbitrary viewpoints. This task is particularly challenging when relying on monocular video, where disentangling structure from motion is ill-posed and supervision is scarce. We introduce Video Diffusion-Aware Reconstruction (ViDAR), a novel 4D reconstruction framework that leverages personalised diffusion models to synthesise a pseudo multi-view supervision signal for training a Gaussian splatting representation. By conditioning on scene-specific features, ViDAR recovers fine-grained appearance details while mitigating artefacts introduced by monocular ambiguity. To address the spatio-temporal inconsistency of diffusion-based supervision, we propose a diffusion-aware loss function and a camera pose optimisation strategy that aligns synthetic views with the underlying scene geometry. Experiments on DyCheck, a challenging benchmark with extreme viewpoint variation, show that ViDAR outperforms all state-of-the-art baselines in visual quality and geometric consistency. We further highlight ViDAR's strong improvement over baselines on dynamic regions and provide a new benchmark to compare performance in reconstructing motion-rich parts of the scene. Project page: https://vidar-4d.github.io
CoMapGS: Covisibility Map-based Gaussian Splatting for Sparse Novel View Synthesis
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:We propose Covisibility Map-based Gaussian Splatting (CoMapGS), designed to recover underrepresented sparse regions in sparse novel view synthesis. CoMapGS addresses both high- and low-uncertainty regions by constructing covisibility maps, enhancing initial point clouds, and applying uncertainty-aware weighted supervision using a proximity classifier. Our contributions are threefold: (1) CoMapGS reframes novel view synthesis by leveraging covisibility maps as a core component to address region-specific uncertainty; (2) Enhanced initial point clouds for both low- and high-uncertainty regions compensate for sparse COLMAP-derived point clouds, improving reconstruction quality and benefiting few-shot 3DGS methods; (3) Adaptive supervision with covisibility-score-based weighting and proximity classification achieves consistent performance gains across scenes with varying sparsity scores derived from covisibility maps. Experimental results demonstrate that CoMapGS outperforms state-of-the-art methods on datasets including Mip-NeRF 360 and LLFF.
GASPACHO: Gaussian Splatting for Controllable Humans and Objects
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:We present GASPACHO: a method for generating photorealistic controllable renderings of human-object interactions. Given a set of multi-view RGB images of human-object interactions, our method reconstructs animatable templates of the human and object as separate sets of Gaussians simultaneously. Different from existing work, which focuses on human reconstruction and ignores objects as background, our method explicitly reconstructs both humans and objects, thereby allowing for controllable renderings of novel human object interactions in different poses from novel-camera viewpoints. During reconstruction, we constrain the Gaussians that generate rendered images to be a linear function of a set of canonical Gaussians. By simply changing the parameters of the linear deformation functions after training, our method can generate renderings of novel human-object interaction in novel poses from novel camera viewpoints. We learn the 3D Gaussian properties of the canonical Gaussians on the underlying 2D manifold of the canonical human and object templates. This in turns requires a canonical object template with a fixed UV unwrapping. To define such an object template, we use a feature based representation to track the object across the multi-view sequence. We further propose an occlusion aware photometric loss that allows for reconstructions under significant occlusions. Several experiments on two human-object datasets - BEHAVE and DNA-Rendering - demonstrate that our method allows for high-quality reconstruction of human and object templates under significant occlusion and the synthesis of controllable renderings of novel human-object interactions in novel human poses from novel camera views.
Better Together: Unified Motion Capture and 3D Avatar Reconstruction
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:We present Better Together, a method that simultaneously solves the human pose estimation problem while reconstructing a photorealistic 3D human avatar from multi-view videos. While prior art usually solves these problems separately, we argue that joint optimization of skeletal motion with a 3D renderable body model brings synergistic effects, i.e. yields more precise motion capture and improved visual quality of real-time rendering of avatars. To achieve this, we introduce a novel animatable avatar with 3D Gaussians rigged on a personalized mesh and propose to optimize the motion sequence with time-dependent MLPs that provide accurate and temporally consistent pose estimates. We first evaluate our method on highly challenging yoga poses and demonstrate state-of-the-art accuracy on multi-view human pose estimation, reducing error by 35% on body joints and 45% on hand joints compared to keypoint-based methods. At the same time, our method significantly boosts the visual quality of animatable avatars (+2dB PSNR on novel view synthesis) on diverse challenging subjects.
SCRREAM : SCan, Register, REnder And Map:A Framework for Annotating Accurate and Dense 3D Indoor Scenes with a Benchmark
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:Traditionally, 3d indoor datasets have generally prioritized scale over ground-truth accuracy in order to obtain improved generalization. However, using these datasets to evaluate dense geometry tasks, such as depth rendering, can be problematic as the meshes of the dataset are often incomplete and may produce wrong ground truth to evaluate the details. In this paper, we propose SCRREAM, a dataset annotation framework that allows annotation of fully dense meshes of objects in the scene and registers camera poses on the real image sequence, which can produce accurate ground truth for both sparse 3D as well as dense 3D tasks. We show the details of the dataset annotation pipeline and showcase four possible variants of datasets that can be obtained from our framework with example scenes, such as indoor reconstruction and SLAM, scene editing & object removal, human reconstruction and 6d pose estimation. Recent pipelines for indoor reconstruction and SLAM serve as new benchmarks. In contrast to previous indoor dataset, our design allows to evaluate dense geometry tasks on eleven sample scenes against accurately rendered ground truth depth maps.
FORCE: Dataset and Method for Intuitive Physics Guided Human-object Interaction
Mar 17, 2024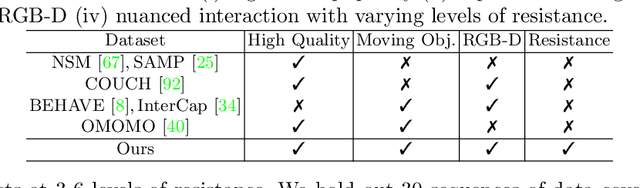
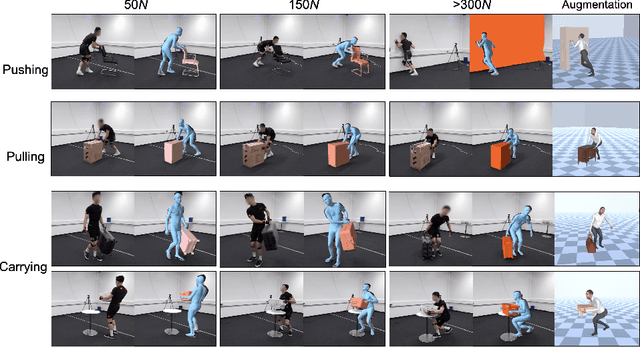
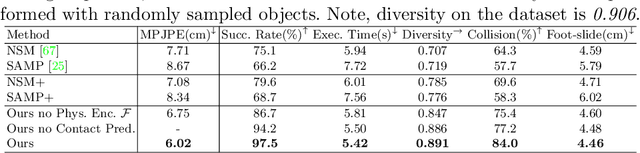
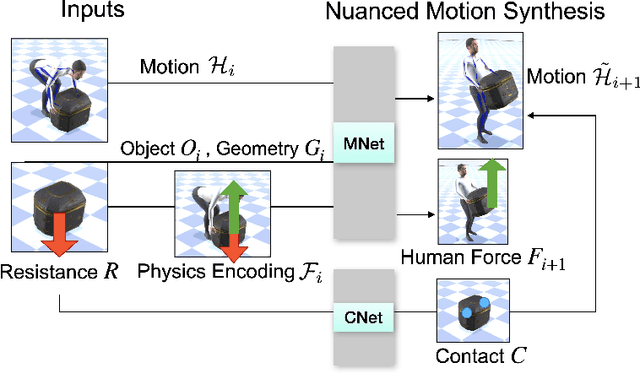
Abstract:Interactions between human and objects are influenced not only by the object's pose and shape, but also by physical attributes such as object mass and surface friction. They introduce important motion nuances that are essential for diversity and realism. Despite advancements in recent kinematics-based methods, this aspect has been overlooked. Generating nuanced human motion presents two challenges. First, it is non-trivial to learn from multi-modal human and object information derived from both the physical and non-physical attributes. Second, there exists no dataset capturing nuanced human interactions with objects of varying physical properties, hampering model development. This work addresses the gap by introducing the FORCE model, a kinematic approach for synthesizing diverse, nuanced human-object interactions by modeling physical attributes. Our key insight is that human motion is dictated by the interrelation between the force exerted by the human and the perceived resistance. Guided by a novel intuitive physics encoding, the model captures the interplay between human force and resistance. Experiments also demonstrate incorporating human force facilitates learning multi-class motion. Accompanying our model, we contribute the FORCE dataset. It features diverse, different-styled motion through interactions with varying resistances.
NCRF: Neural Contact Radiance Fields for Free-Viewpoint Rendering of Hand-Object Interaction
Feb 09, 2024Abstract:Modeling hand-object interactions is a fundamentally challenging task in 3D computer vision. Despite remarkable progress that has been achieved in this field, existing methods still fail to synthesize the hand-object interaction photo-realistically, suffering from degraded rendering quality caused by the heavy mutual occlusions between the hand and the object, and inaccurate hand-object pose estimation. To tackle these challenges, we present a novel free-viewpoint rendering framework, Neural Contact Radiance Field (NCRF), to reconstruct hand-object interactions from a sparse set of videos. In particular, the proposed NCRF framework consists of two key components: (a) A contact optimization field that predicts an accurate contact field from 3D query points for achieving desirable contact between the hand and the object. (b) A hand-object neural radiance field to learn an implicit hand-object representation in a static canonical space, in concert with the specifically designed hand-object motion field to produce observation-to-canonical correspondences. We jointly learn these key components where they mutually help and regularize each other with visual and geometric constraints, producing a high-quality hand-object reconstruction that achieves photo-realistic novel view synthesis. Extensive experiments on HO3D and DexYCB datasets show that our approach outperforms the current state-of-the-art in terms of both rendering quality and pose estimation accuracy.
HeadGaS: Real-Time Animatable Head Avatars via 3D Gaussian Splatting
Dec 05, 2023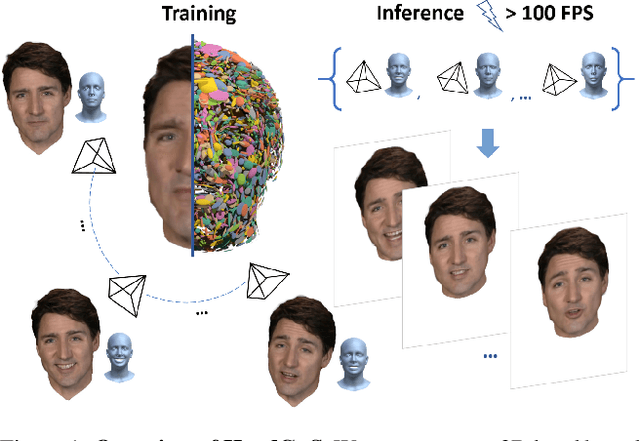
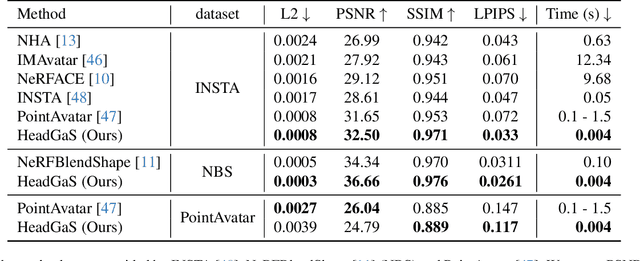
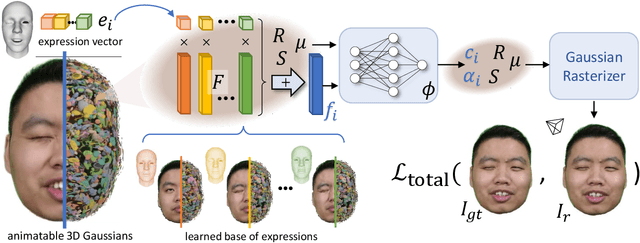
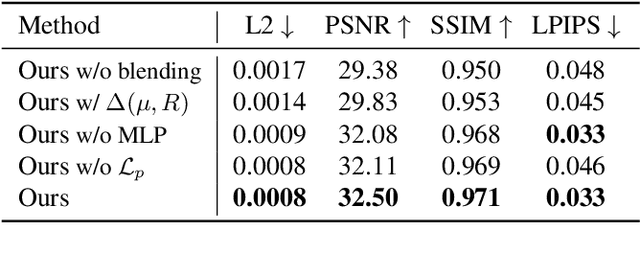
Abstract:3D head animation has seen major quality and runtime improvements over the last few years, particularly empowered by the advances in differentiable rendering and neural radiance fields. Real-time rendering is a highly desirable goal for real-world applications. We propose HeadGaS, the first model to use 3D Gaussian Splats (3DGS) for 3D head reconstruction and animation. In this paper we introduce a hybrid model that extends the explicit representation from 3DGS with a base of learnable latent features, which can be linearly blended with low-dimensional parameters from parametric head models to obtain expression-dependent final color and opacity values. We demonstrate that HeadGaS delivers state-of-the-art results in real-time inference frame rates, which surpasses baselines by up to ~2dB, while accelerating rendering speed by over x10.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge