Hyung Jin Chang
VL4Gaze: Unleashing Vision-Language Models for Gaze Following
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Human gaze provides essential cues for interpreting attention, intention, and social interaction in visual scenes, yet gaze understanding remains largely unexplored in current vision-language models (VLMs). While recent VLMs achieve strong scene-level reasoning across a range of visual tasks, there exists no benchmark that systematically evaluates or trains them for gaze interpretation, leaving open the question of whether gaze understanding can emerge from general-purpose vision-language pre-training. To address this gap, we introduce VL4Gaze, the first large-scale benchmark designed to investigate, evaluate, and unlock the potential of VLMs for gaze understanding. VL4Gaze contains 489K automatically generated question-answer pairs across 124K images and formulates gaze understanding as a unified VQA problem through four complementary tasks: (1) gaze object description, (2) gaze direction description, (3) gaze point location, and (4) ambiguous question recognition. We comprehensively evaluate both commercial and open-source VLMs under in-context learning and fine-tuning settings. The results show that even large-scale VLMs struggle to reliably infer gaze semantics and spatial localization without task-specific supervision. In contrast, training on VL4Gaze brings substantial and consistent improvements across all tasks, highlighting the importance of targeted multi-task supervision for developing gaze understanding capabilities in VLMs. We will release the dataset and code to support further research and development in this direction.
RTGaze: Real-Time 3D-Aware Gaze Redirection from a Single Image
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Gaze redirection methods aim to generate realistic human face images with controllable eye movement. However, recent methods often struggle with 3D consistency, efficiency, or quality, limiting their practical applications. In this work, we propose RTGaze, a real-time and high-quality gaze redirection method. Our approach learns a gaze-controllable facial representation from face images and gaze prompts, then decodes this representation via neural rendering for gaze redirection. Additionally, we distill face geometric priors from a pretrained 3D portrait generator to enhance generation quality. We evaluate RTGaze both qualitatively and quantitatively, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance in efficiency, redirection accuracy, and image quality across multiple datasets. Our system achieves real-time, 3D-aware gaze redirection with a feedforward network (~0.06 sec/image), making it 800x faster than the previous state-of-the-art 3D-aware methods.
Roll Your Eyes: Gaze Redirection via Explicit 3D Eyeball Rotation
Aug 08, 2025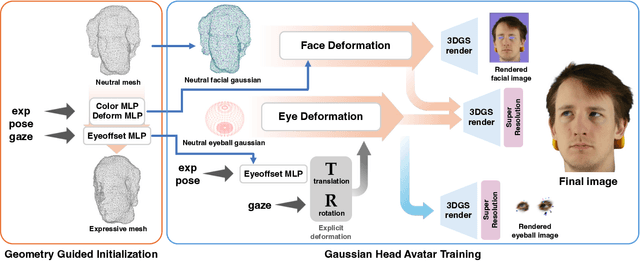
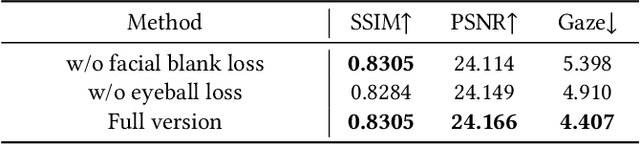
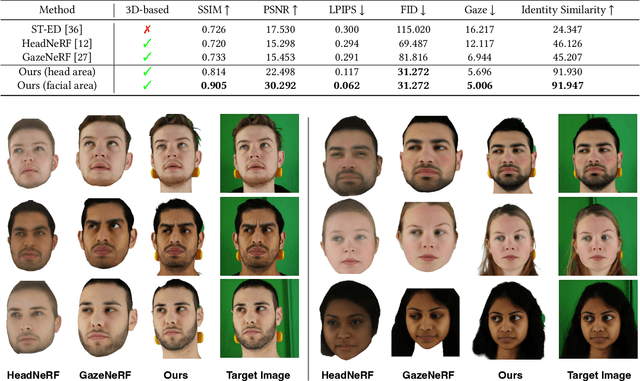
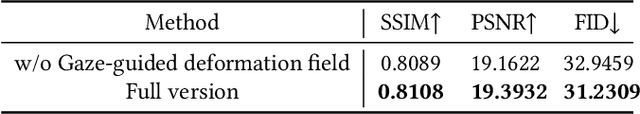
Abstract:We propose a novel 3D gaze redirection framework that leverages an explicit 3D eyeball structure. Existing gaze redirection methods are typically based on neural radiance fields, which employ implicit neural representations via volume rendering. Unlike these NeRF-based approaches, where the rotation and translation of 3D representations are not explicitly modeled, we introduce a dedicated 3D eyeball structure to represent the eyeballs with 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). Our method generates photorealistic images that faithfully reproduce the desired gaze direction by explicitly rotating and translating the 3D eyeball structure. In addition, we propose an adaptive deformation module that enables the replication of subtle muscle movements around the eyes. Through experiments conducted on the ETH-XGaze dataset, we demonstrate that our framework is capable of generating diverse novel gaze images, achieving superior image quality and gaze estimation accuracy compared to previous state-of-the-art methods.
Instruction-Grounded Visual Projectors for Continual Learning of Generative Vision-Language Models
Aug 01, 2025Abstract:Continual learning enables pre-trained generative vision-language models (VLMs) to incorporate knowledge from new tasks without retraining data from previous ones. Recent methods update a visual projector to translate visual information for new tasks, connecting pre-trained vision encoders with large language models. However, such adjustments may cause the models to prioritize visual inputs over language instructions, particularly learning tasks with repetitive types of textual instructions. To address the neglect of language instructions, we propose a novel framework that grounds the translation of visual information on instructions for language models. We introduce a mixture of visual projectors, each serving as a specialized visual-to-language translation expert based on the given instruction context to adapt to new tasks. To avoid using experts for irrelevant instruction contexts, we propose an expert recommendation strategy that reuses experts for tasks similar to those previously learned. Additionally, we introduce expert pruning to alleviate interference from the use of experts that cumulatively activated in previous tasks. Extensive experiments on diverse vision-language tasks demonstrate that our method outperforms existing continual learning approaches by generating instruction-following responses.
PoseBH: Prototypical Multi-Dataset Training Beyond Human Pose Estimation
May 23, 2025Abstract:We study multi-dataset training (MDT) for pose estimation, where skeletal heterogeneity presents a unique challenge that existing methods have yet to address. In traditional domains, \eg regression and classification, MDT typically relies on dataset merging or multi-head supervision. However, the diversity of skeleton types and limited cross-dataset supervision complicate integration in pose estimation. To address these challenges, we introduce PoseBH, a new MDT framework that tackles keypoint heterogeneity and limited supervision through two key techniques. First, we propose nonparametric keypoint prototypes that learn within a unified embedding space, enabling seamless integration across skeleton types. Second, we develop a cross-type self-supervision mechanism that aligns keypoint predictions with keypoint embedding prototypes, providing supervision without relying on teacher-student models or additional augmentations. PoseBH substantially improves generalization across whole-body and animal pose datasets, including COCO-WholeBody, AP-10K, and APT-36K, while preserving performance on standard human pose benchmarks (COCO, MPII, and AIC). Furthermore, our learned keypoint embeddings transfer effectively to hand shape estimation (InterHand2.6M) and human body shape estimation (3DPW). The code for PoseBH is available at: https://github.com/uyoung-jeong/PoseBH.
Foundation Model-Driven Framework for Human-Object Interaction Prediction with Segmentation Mask Integration
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:In this work, we introduce Segmentation to Human-Object Interaction (\textit{\textbf{Seg2HOI}}) approach, a novel framework that integrates segmentation-based vision foundation models with the human-object interaction task, distinguished from traditional detection-based Human-Object Interaction (HOI) methods. Our approach enhances HOI detection by not only predicting the standard triplets but also introducing quadruplets, which extend HOI triplets by including segmentation masks for human-object pairs. More specifically, Seg2HOI inherits the properties of the vision foundation model (e.g., promptable and interactive mechanisms) and incorporates a decoder that applies these attributes to HOI task. Despite training only for HOI, without additional training mechanisms for these properties, the framework demonstrates that such features still operate efficiently. Extensive experiments on two public benchmark datasets demonstrate that Seg2HOI achieves performance comparable to state-of-the-art methods, even in zero-shot scenarios. Lastly, we propose that Seg2HOI can generate HOI quadruplets and interactive HOI segmentation from novel text and visual prompts that were not used during training, making it versatile for a wide range of applications by leveraging this flexibility.
PersonaBooth: Personalized Text-to-Motion Generation
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces Motion Personalization, a new task that generates personalized motions aligned with text descriptions using several basic motions containing Persona. To support this novel task, we introduce a new large-scale motion dataset called PerMo (PersonaMotion), which captures the unique personas of multiple actors. We also propose a multi-modal finetuning method of a pretrained motion diffusion model called PersonaBooth. PersonaBooth addresses two main challenges: i) A significant distribution gap between the persona-focused PerMo dataset and the pretraining datasets, which lack persona-specific data, and ii) the difficulty of capturing a consistent persona from the motions vary in content (action type). To tackle the dataset distribution gap, we introduce a persona token to accept new persona features and perform multi-modal adaptation for both text and visuals during finetuning. To capture a consistent persona, we incorporate a contrastive learning technique to enhance intra-cohesion among samples with the same persona. Furthermore, we introduce a context-aware fusion mechanism to maximize the integration of persona cues from multiple input motions. PersonaBooth outperforms state-of-the-art motion style transfer methods, establishing a new benchmark for motion personalization.
3D Prior is All You Need: Cross-Task Few-shot 2D Gaze Estimation
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:3D and 2D gaze estimation share the fundamental objective of capturing eye movements but are traditionally treated as two distinct research domains. In this paper, we introduce a novel cross-task few-shot 2D gaze estimation approach, aiming to adapt a pre-trained 3D gaze estimation network for 2D gaze prediction on unseen devices using only a few training images. This task is highly challenging due to the domain gap between 3D and 2D gaze, unknown screen poses, and limited training data. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework that bridges the gap between 3D and 2D gaze. Our framework contains a physics-based differentiable projection module with learnable parameters to model screen poses and project 3D gaze into 2D gaze. The framework is fully differentiable and can integrate into existing 3D gaze networks without modifying their original architecture. Additionally, we introduce a dynamic pseudo-labelling strategy for flipped images, which is particularly challenging for 2D labels due to unknown screen poses. To overcome this, we reverse the projection process by converting 2D labels to 3D space, where flipping is performed. Notably, this 3D space is not aligned with the camera coordinate system, so we learn a dynamic transformation matrix to compensate for this misalignment. We evaluate our method on MPIIGaze, EVE, and GazeCapture datasets, collected respectively on laptops, desktop computers, and mobile devices. The superior performance highlights the effectiveness of our approach, and demonstrates its strong potential for real-world applications.
Collaborative Learning for 3D Hand-Object Reconstruction and Compositional Action Recognition from Egocentric RGB Videos Using Superquadrics
Jan 13, 2025

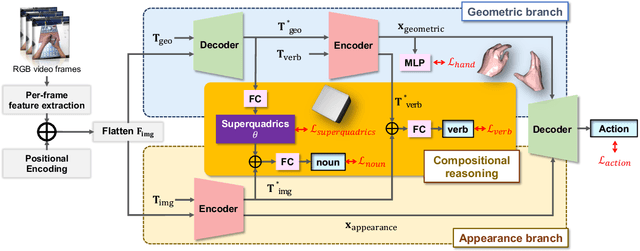

Abstract:With the availability of egocentric 3D hand-object interaction datasets, there is increasing interest in developing unified models for hand-object pose estimation and action recognition. However, existing methods still struggle to recognise seen actions on unseen objects due to the limitations in representing object shape and movement using 3D bounding boxes. Additionally, the reliance on object templates at test time limits their generalisability to unseen objects. To address these challenges, we propose to leverage superquadrics as an alternative 3D object representation to bounding boxes and demonstrate their effectiveness on both template-free object reconstruction and action recognition tasks. Moreover, as we find that pure appearance-based methods can outperform the unified methods, the potential benefits from 3D geometric information remain unclear. Therefore, we study the compositionality of actions by considering a more challenging task where the training combinations of verbs and nouns do not overlap with the testing split. We extend H2O and FPHA datasets with compositional splits and design a novel collaborative learning framework that can explicitly reason about the geometric relations between hands and the manipulated object. Through extensive quantitative and qualitative evaluations, we demonstrate significant improvements over the state-of-the-arts in (compositional) action recognition.
Few Exemplar-Based General Medical Image Segmentation via Domain-Aware Selective Adaptation
Oct 11, 2024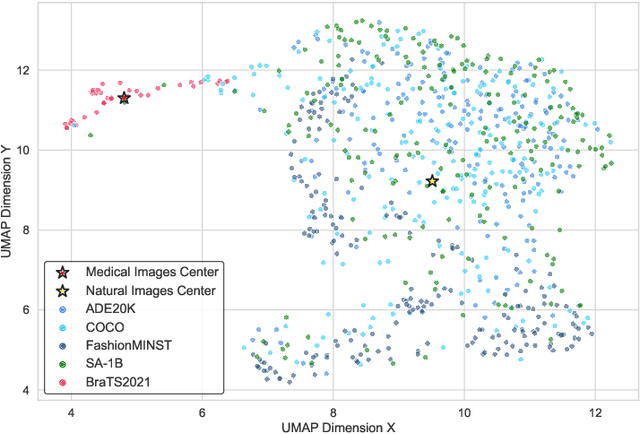
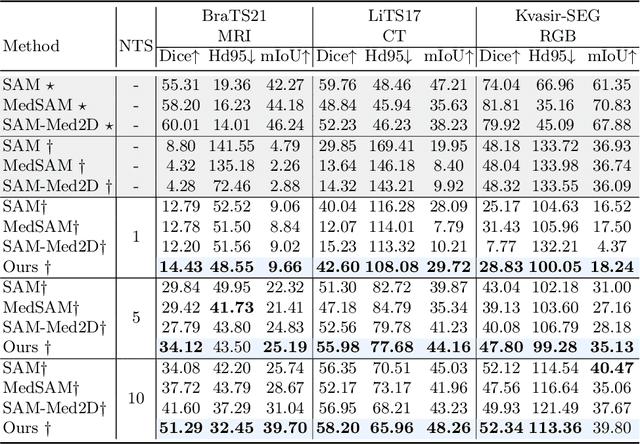
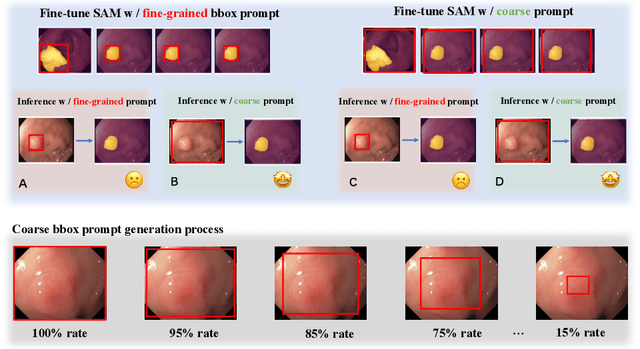
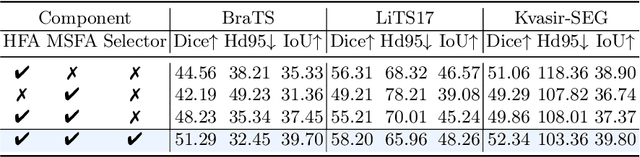
Abstract:Medical image segmentation poses challenges due to domain gaps, data modality variations, and dependency on domain knowledge or experts, especially for low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). Whereas for humans, given a few exemplars (with corresponding labels), we are able to segment different medical images even without exten-sive domain-specific clinical training. In addition, current SAM-based medical segmentation models use fine-grained visual prompts, such as the bounding rectangle generated from manually annotated target segmentation mask, as the bounding box (bbox) prompt during the testing phase. However, in actual clinical scenarios, no such precise prior knowledge is available. Our experimental results also reveal that previous models nearly fail to predict when given coarser bbox prompts. Considering these issues, in this paper, we introduce a domain-aware selective adaptation approach to adapt the general knowledge learned from a large model trained with natural images to the corresponding medical domains/modalities, with access to only a few (e.g. less than 5) exemplars. Our method mitigates the aforementioned limitations, providing an efficient and LMICs-friendly solution. Extensive experimental analysis showcases the effectiveness of our approach, offering potential advancements in healthcare diagnostics and clinical applications in LMICs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge