Jifei Song
Optimizing Multimodal LLMs for Egocentric Video Understanding: A Solution for the HD-EPIC VQA Challenge
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) struggle with complex video QA benchmarks like HD-EPIC VQA due to ambiguous queries/options, poor long-range temporal reasoning, and non-standardized outputs. We propose a framework integrating query/choice pre-processing, domain-specific Qwen2.5-VL fine-tuning, a novel Temporal Chain-of-Thought (T-CoT) prompting for multi-step reasoning, and robust post-processing. This system achieves 41.6% accuracy on HD-EPIC VQA, highlighting the need for holistic pipeline optimization in demanding video understanding. Our code, fine-tuned models are available at https://github.com/YoungSeng/Egocentric-Co-Pilot.
Plug-and-Play Clarifier: A Zero-Shot Multimodal Framework for Egocentric Intent Disambiguation
Nov 12, 2025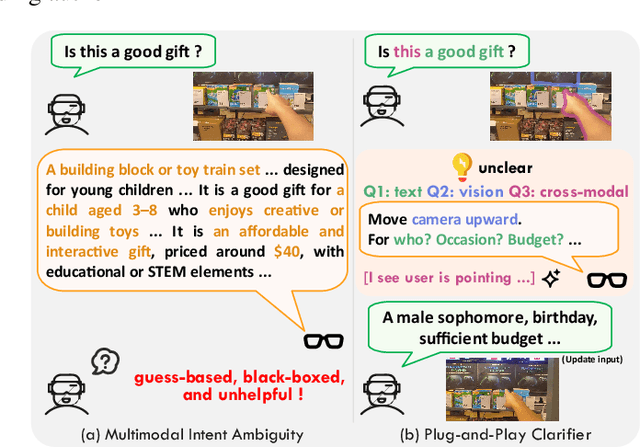
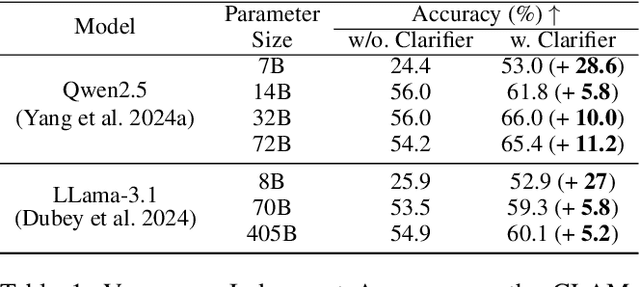
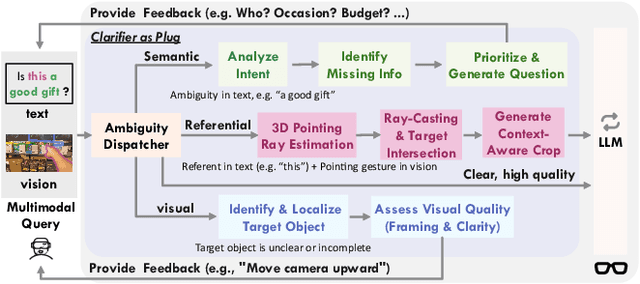
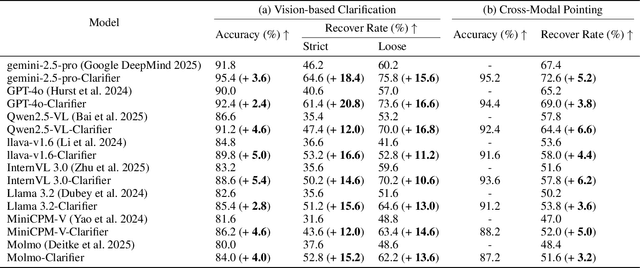
Abstract:The performance of egocentric AI agents is fundamentally limited by multimodal intent ambiguity. This challenge arises from a combination of underspecified language, imperfect visual data, and deictic gestures, which frequently leads to task failure. Existing monolithic Vision-Language Models (VLMs) struggle to resolve these multimodal ambiguous inputs, often failing silently or hallucinating responses. To address these ambiguities, we introduce the Plug-and-Play Clarifier, a zero-shot and modular framework that decomposes the problem into discrete, solvable sub-tasks. Specifically, our framework consists of three synergistic modules: (1) a text clarifier that uses dialogue-driven reasoning to interactively disambiguate linguistic intent, (2) a vision clarifier that delivers real-time guidance feedback, instructing users to adjust their positioning for improved capture quality, and (3) a cross-modal clarifier with grounding mechanism that robustly interprets 3D pointing gestures and identifies the specific objects users are pointing to. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework improves the intent clarification performance of small language models (4--8B) by approximately 30%, making them competitive with significantly larger counterparts. We also observe consistent gains when applying our framework to these larger models. Furthermore, our vision clarifier increases corrective guidance accuracy by over 20%, and our cross-modal clarifier improves semantic answer accuracy for referential grounding by 5%. Overall, our method provides a plug-and-play framework that effectively resolves multimodal ambiguity and significantly enhances user experience in egocentric interaction.
Unlocking the Potential of Diffusion Priors in Blind Face Restoration
Aug 12, 2025
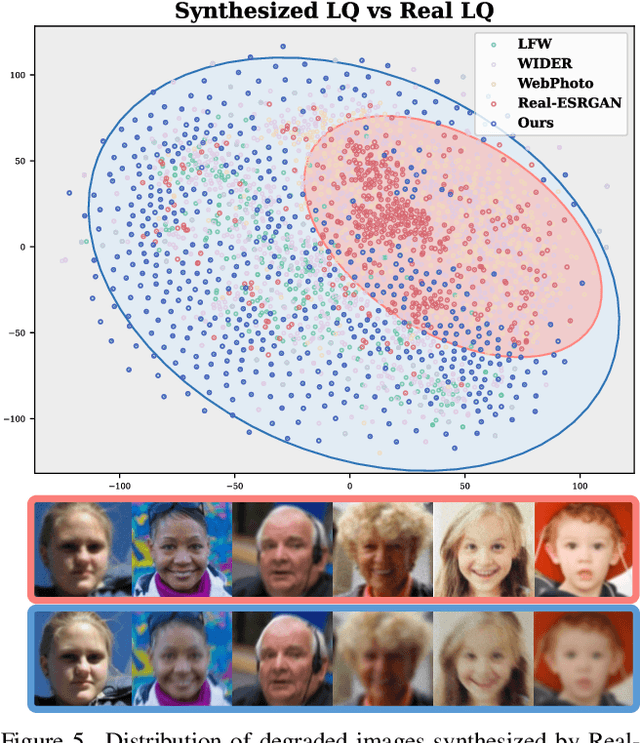
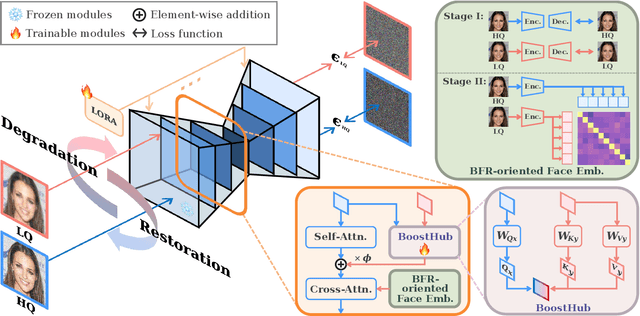
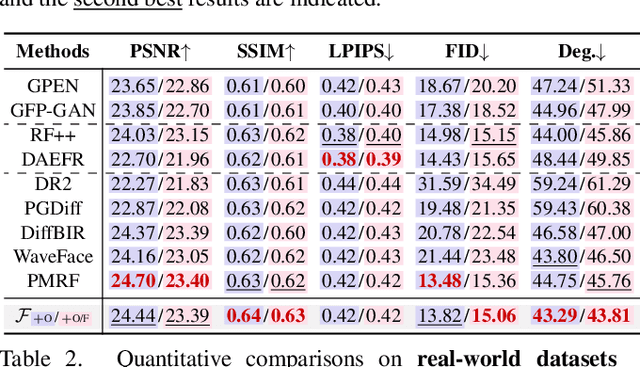
Abstract:Although diffusion prior is rising as a powerful solution for blind face restoration (BFR), the inherent gap between the vanilla diffusion model and BFR settings hinders its seamless adaptation. The gap mainly stems from the discrepancy between 1) high-quality (HQ) and low-quality (LQ) images and 2) synthesized and real-world images. The vanilla diffusion model is trained on images with no or less degradations, whereas BFR handles moderately to severely degraded images. Additionally, LQ images used for training are synthesized by a naive degradation model with limited degradation patterns, which fails to simulate complex and unknown degradations in real-world scenarios. In this work, we use a unified network FLIPNET that switches between two modes to resolve specific gaps. In Restoration mode, the model gradually integrates BFR-oriented features and face embeddings from LQ images to achieve authentic and faithful face restoration. In Degradation mode, the model synthesizes real-world like degraded images based on the knowledge learned from real-world degradation datasets. Extensive evaluations on benchmark datasets show that our model 1) outperforms previous diffusion prior based BFR methods in terms of authenticity and fidelity, and 2) outperforms the naive degradation model in modeling the real-world degradations.
ViMo: A Generative Visual GUI World Model for App Agent
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:App agents, which autonomously operate mobile Apps through Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs), have gained significant interest in real-world applications. Yet, they often struggle with long-horizon planning, failing to find the optimal actions for complex tasks with longer steps. To address this, world models are used to predict the next GUI observation based on user actions, enabling more effective agent planning. However, existing world models primarily focus on generating only textual descriptions, lacking essential visual details. To fill this gap, we propose ViMo, the first visual world model designed to generate future App observations as images. For the challenge of generating text in image patches, where even minor pixel errors can distort readability, we decompose GUI generation into graphic and text content generation. We propose a novel data representation, the Symbolic Text Representation~(STR) to overlay text content with symbolic placeholders while preserving graphics. With this design, ViMo employs a STR Predictor to predict future GUIs' graphics and a GUI-text Predictor for generating the corresponding text. Moreover, we deploy ViMo to enhance agent-focused tasks by predicting the outcome of different action options. Experiments show ViMo's ability to generate visually plausible and functionally effective GUIs that enable App agents to make more informed decisions.
UniGS: Unified Language-Image-3D Pretraining with Gaussian Splatting
Feb 25, 2025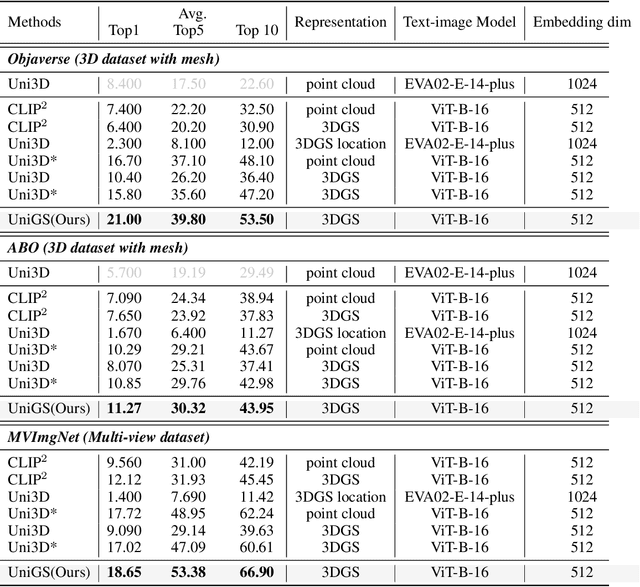

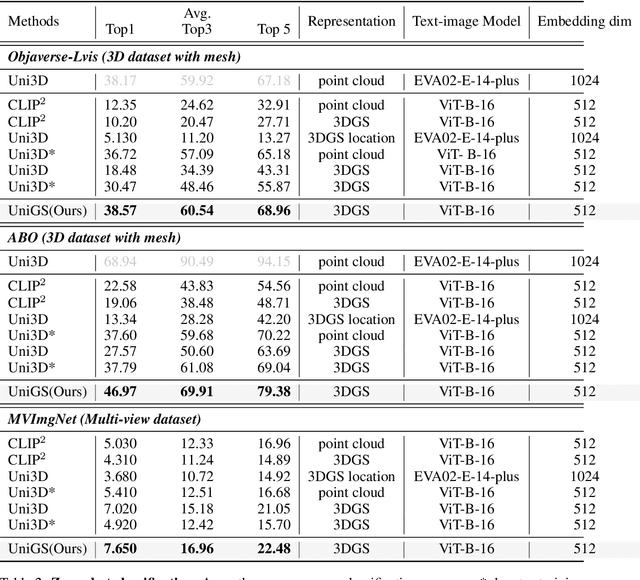

Abstract:Recent advancements in multi-modal 3D pre-training methods have shown promising efficacy in learning joint representations of text, images, and point clouds. However, adopting point clouds as 3D representation fails to fully capture the intricacies of the 3D world and exhibits a noticeable gap between the discrete points and the dense 2D pixels of images. To tackle this issue, we propose UniGS, integrating 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) into multi-modal pre-training to enhance the 3D representation. We first rely on the 3DGS representation to model the 3D world as a collection of 3D Gaussians with color and opacity, incorporating all the information of the 3D scene while establishing a strong connection with 2D images. Then, to achieve Language-Image-3D pertaining, UniGS starts with a pre-trained vision-language model to establish a shared visual and textual space through extensive real-world image-text pairs. Subsequently, UniGS employs a 3D encoder to align the optimized 3DGS with the Language-Image representations to learn unified multi-modal representations. To facilitate the extraction of global explicit 3D features by the 3D encoder and achieve better cross-modal alignment, we additionally introduce a novel Gaussian-Aware Guidance module that guides the learning of fine-grained representations of the 3D domain. Through extensive experiments across the Objaverse, ABO, MVImgNet and SUN RGBD datasets with zero-shot classification, text-driven retrieval and open-world understanding tasks, we demonstrate the effectiveness of UniGS in learning a more general and stronger aligned multi-modal representation. Specifically, UniGS achieves leading results across different 3D tasks with remarkable improvements over previous SOTA, Uni3D, including on zero-shot classification (+9.36%), text-driven retrieval (+4.3%) and open-world understanding (+7.92%).
ZeroGS: Training 3D Gaussian Splatting from Unposed Images
Nov 24, 2024

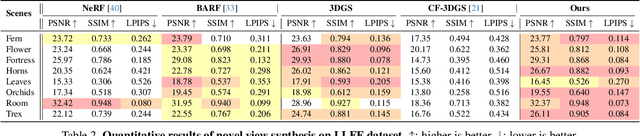

Abstract:Neural radiance fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) are popular techniques to reconstruct and render photo-realistic images. However, the pre-requisite of running Structure-from-Motion (SfM) to get camera poses limits their completeness. While previous methods can reconstruct from a few unposed images, they are not applicable when images are unordered or densely captured. In this work, we propose ZeroGS to train 3DGS from hundreds of unposed and unordered images. Our method leverages a pretrained foundation model as the neural scene representation. Since the accuracy of the predicted pointmaps does not suffice for accurate image registration and high-fidelity image rendering, we propose to mitigate the issue by initializing and finetuning the pretrained model from a seed image. Images are then progressively registered and added to the training buffer, which is further used to train the model. We also propose to refine the camera poses and pointmaps by minimizing a point-to-camera ray consistency loss across multiple views. Experiments on the LLFF dataset, the MipNeRF360 dataset, and the Tanks-and-Temples dataset show that our method recovers more accurate camera poses than state-of-the-art pose-free NeRF/3DGS methods, and even renders higher quality images than 3DGS with COLMAP poses. Our project page is available at https://aibluefisher.github.io/ZeroGS.
SCRREAM : SCan, Register, REnder And Map:A Framework for Annotating Accurate and Dense 3D Indoor Scenes with a Benchmark
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:Traditionally, 3d indoor datasets have generally prioritized scale over ground-truth accuracy in order to obtain improved generalization. However, using these datasets to evaluate dense geometry tasks, such as depth rendering, can be problematic as the meshes of the dataset are often incomplete and may produce wrong ground truth to evaluate the details. In this paper, we propose SCRREAM, a dataset annotation framework that allows annotation of fully dense meshes of objects in the scene and registers camera poses on the real image sequence, which can produce accurate ground truth for both sparse 3D as well as dense 3D tasks. We show the details of the dataset annotation pipeline and showcase four possible variants of datasets that can be obtained from our framework with example scenes, such as indoor reconstruction and SLAM, scene editing & object removal, human reconstruction and 6d pose estimation. Recent pipelines for indoor reconstruction and SLAM serve as new benchmarks. In contrast to previous indoor dataset, our design allows to evaluate dense geometry tasks on eleven sample scenes against accurately rendered ground truth depth maps.
Learning Precise Affordances from Egocentric Videos for Robotic Manipulation
Aug 19, 2024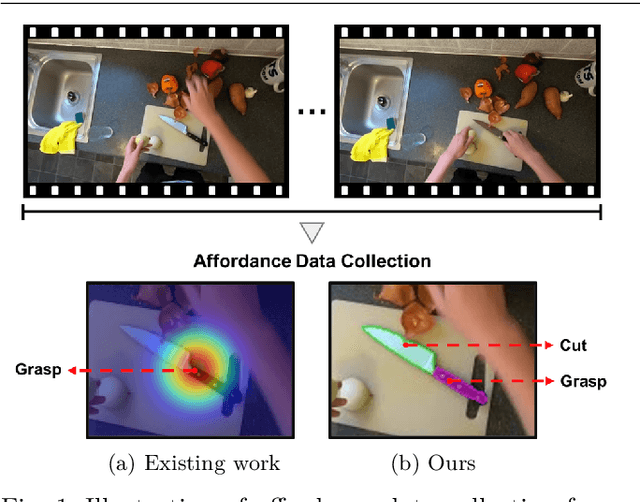

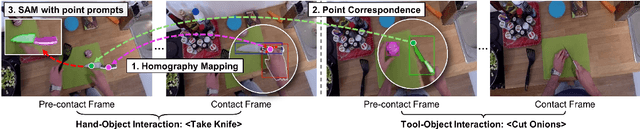
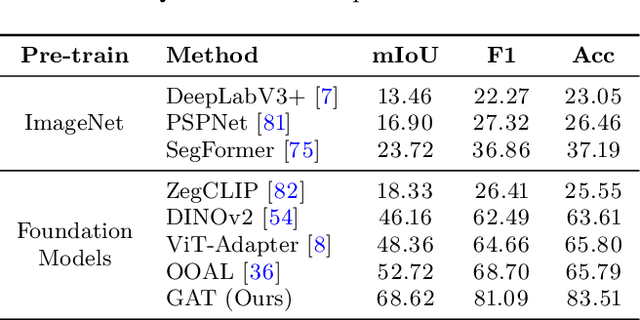
Abstract:Affordance, defined as the potential actions that an object offers, is crucial for robotic manipulation tasks. A deep understanding of affordance can lead to more intelligent AI systems. For example, such knowledge directs an agent to grasp a knife by the handle for cutting and by the blade when passing it to someone. In this paper, we present a streamlined affordance learning system that encompasses data collection, effective model training, and robot deployment. First, we collect training data from egocentric videos in an automatic manner. Different from previous methods that focus only on the object graspable affordance and represent it as coarse heatmaps, we cover both graspable (e.g., object handles) and functional affordances (e.g., knife blades, hammer heads) and extract data with precise segmentation masks. We then propose an effective model, termed Geometry-guided Affordance Transformer (GKT), to train on the collected data. GKT integrates an innovative Depth Feature Injector (DFI) to incorporate 3D shape and geometric priors, enhancing the model's understanding of affordances. To enable affordance-oriented manipulation, we further introduce Aff-Grasp, a framework that combines GKT with a grasp generation model. For comprehensive evaluation, we create an affordance evaluation dataset with pixel-wise annotations, and design real-world tasks for robot experiments. The results show that GKT surpasses the state-of-the-art by 15.9% in mIoU, and Aff-Grasp achieves high success rates of 95.5% in affordance prediction and 77.1% in successful grasping among 179 trials, including evaluations with seen, unseen objects, and cluttered scenes.
SAGS: Structure-Aware 3D Gaussian Splatting
Apr 29, 2024



Abstract:Following the advent of NeRFs, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) has paved the way to real-time neural rendering overcoming the computational burden of volumetric methods. Following the pioneering work of 3D-GS, several methods have attempted to achieve compressible and high-fidelity performance alternatives. However, by employing a geometry-agnostic optimization scheme, these methods neglect the inherent 3D structure of the scene, thereby restricting the expressivity and the quality of the representation, resulting in various floating points and artifacts. In this work, we propose a structure-aware Gaussian Splatting method (SAGS) that implicitly encodes the geometry of the scene, which reflects to state-of-the-art rendering performance and reduced storage requirements on benchmark novel-view synthesis datasets. SAGS is founded on a local-global graph representation that facilitates the learning of complex scenes and enforces meaningful point displacements that preserve the scene's geometry. Additionally, we introduce a lightweight version of SAGS, using a simple yet effective mid-point interpolation scheme, which showcases a compact representation of the scene with up to 24$\times$ size reduction without the reliance on any compression strategies. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of SAGS compared to state-of-the-art 3D-GS methods under both rendering quality and model size. Besides, we demonstrate that our structure-aware method can effectively mitigate floating artifacts and irregular distortions of previous methods while obtaining precise depth maps. Project page https://eververas.github.io/SAGS/.
NCRF: Neural Contact Radiance Fields for Free-Viewpoint Rendering of Hand-Object Interaction
Feb 09, 2024Abstract:Modeling hand-object interactions is a fundamentally challenging task in 3D computer vision. Despite remarkable progress that has been achieved in this field, existing methods still fail to synthesize the hand-object interaction photo-realistically, suffering from degraded rendering quality caused by the heavy mutual occlusions between the hand and the object, and inaccurate hand-object pose estimation. To tackle these challenges, we present a novel free-viewpoint rendering framework, Neural Contact Radiance Field (NCRF), to reconstruct hand-object interactions from a sparse set of videos. In particular, the proposed NCRF framework consists of two key components: (a) A contact optimization field that predicts an accurate contact field from 3D query points for achieving desirable contact between the hand and the object. (b) A hand-object neural radiance field to learn an implicit hand-object representation in a static canonical space, in concert with the specifically designed hand-object motion field to produce observation-to-canonical correspondences. We jointly learn these key components where they mutually help and regularize each other with visual and geometric constraints, producing a high-quality hand-object reconstruction that achieves photo-realistic novel view synthesis. Extensive experiments on HO3D and DexYCB datasets show that our approach outperforms the current state-of-the-art in terms of both rendering quality and pose estimation accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge