Zhensong Zhang
ICo3D: An Interactive Conversational 3D Virtual Human
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:This work presents Interactive Conversational 3D Virtual Human (ICo3D), a method for generating an interactive, conversational, and photorealistic 3D human avatar. Based on multi-view captures of a subject, we create an animatable 3D face model and a dynamic 3D body model, both rendered by splatting Gaussian primitives. Once merged together, they represent a lifelike virtual human avatar suitable for real-time user interactions. We equip our avatar with an LLM for conversational ability. During conversation, the audio speech of the avatar is used as a driving signal to animate the face model, enabling precise synchronization. We describe improvements to our dynamic Gaussian models that enhance photorealism: SWinGS++ for body reconstruction and HeadGaS++ for face reconstruction, and provide as well a solution to merge the separate face and body models without artifacts. We also present a demo of the complete system, showcasing several use cases of real-time conversation with the 3D avatar. Our approach offers a fully integrated virtual avatar experience, supporting both oral and written form interactions in immersive environments. ICo3D is applicable to a wide range of fields, including gaming, virtual assistance, and personalized education, among others. Project page: https://ico3d.github.io/
Map2Thought: Explicit 3D Spatial Reasoning via Metric Cognitive Maps
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:We propose Map2Thought, a framework that enables explicit and interpretable spatial reasoning for 3D VLMs. The framework is grounded in two key components: Metric Cognitive Map (Metric-CogMap) and Cognitive Chain-of-Thought (Cog-CoT). Metric-CogMap provides a unified spatial representation by integrating a discrete grid for relational reasoning with a continuous, metric-scale representation for precise geometric understanding. Building upon the Metric-CogMap, Cog-CoT performs explicit geometric reasoning through deterministic operations, including vector operations, bounding-box distances, and occlusion-aware appearance order cues, producing interpretable inference traces grounded in 3D structure. Experimental results show that Map2Thought enables explainable 3D understanding, achieving 59.9% accuracy using only half the supervision, closely matching the 60.9% baseline trained with the full dataset. It consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods by 5.3%, 4.8%, and 4.0% under 10%, 25%, and 50% training subsets, respectively, on the VSI-Bench.
Optimizing Multimodal LLMs for Egocentric Video Understanding: A Solution for the HD-EPIC VQA Challenge
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) struggle with complex video QA benchmarks like HD-EPIC VQA due to ambiguous queries/options, poor long-range temporal reasoning, and non-standardized outputs. We propose a framework integrating query/choice pre-processing, domain-specific Qwen2.5-VL fine-tuning, a novel Temporal Chain-of-Thought (T-CoT) prompting for multi-step reasoning, and robust post-processing. This system achieves 41.6% accuracy on HD-EPIC VQA, highlighting the need for holistic pipeline optimization in demanding video understanding. Our code, fine-tuned models are available at https://github.com/YoungSeng/Egocentric-Co-Pilot.
Off The Grid: Detection of Primitives for Feed-Forward 3D Gaussian Splatting
Dec 17, 2025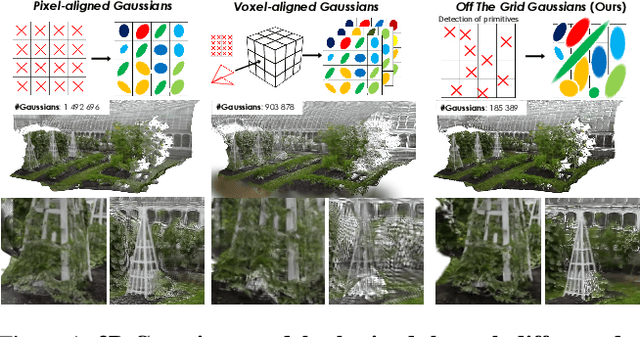
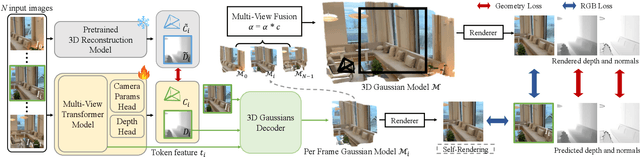

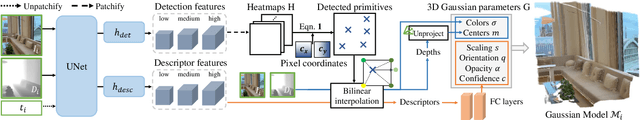
Abstract:Feed-forward 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) models enable real-time scene generation but are hindered by suboptimal pixel-aligned primitive placement, which relies on a dense, rigid grid and limits both quality and efficiency. We introduce a new feed-forward architecture that detects 3D Gaussian primitives at a sub-pixel level, replacing the pixel grid with an adaptive, "Off The Grid" distribution. Inspired by keypoint detection, our multi-resolution decoder learns to distribute primitives across image patches. This module is trained end-to-end with a 3D reconstruction backbone using self-supervised learning. Our resulting pose-free model generates photorealistic scenes in seconds, achieving state-of-the-art novel view synthesis for feed-forward models. It outperforms competitors while using far fewer primitives, demonstrating a more accurate and efficient allocation that captures fine details and reduces artifacts. Moreover, we observe that by learning to render 3D Gaussians, our 3D reconstruction backbone improves camera pose estimation, suggesting opportunities to train these foundational models without labels.
Charge: A Comprehensive Novel View Synthesis Benchmark and Dataset to Bind Them All
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a new dataset for Novel View Synthesis, generated from a high-quality, animated film with stunning realism and intricate detail. Our dataset captures a variety of dynamic scenes, complete with detailed textures, lighting, and motion, making it ideal for training and evaluating cutting-edge 4D scene reconstruction and novel view generation models. In addition to high-fidelity RGB images, we provide multiple complementary modalities, including depth, surface normals, object segmentation and optical flow, enabling a deeper understanding of scene geometry and motion. The dataset is organised into three distinct benchmarking scenarios: a dense multi-view camera setup, a sparse camera arrangement, and monocular video sequences, enabling a wide range of experimentation and comparison across varying levels of data sparsity. With its combination of visual richness, high-quality annotations, and diverse experimental setups, this dataset offers a unique resource for pushing the boundaries of view synthesis and 3D vision.
Plug-and-Play Clarifier: A Zero-Shot Multimodal Framework for Egocentric Intent Disambiguation
Nov 12, 2025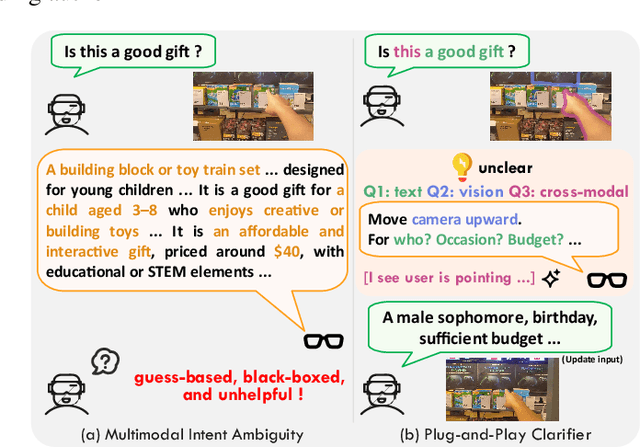
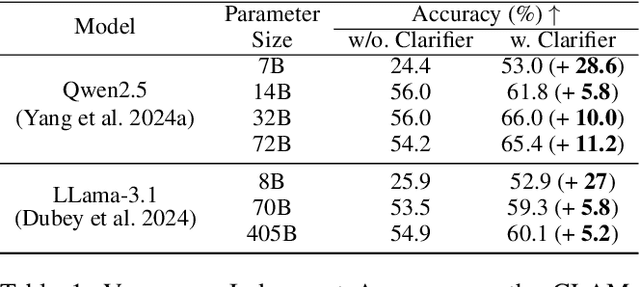
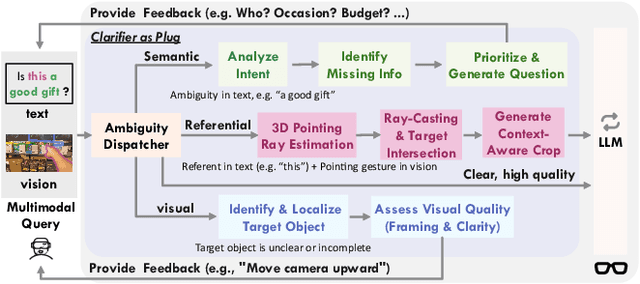
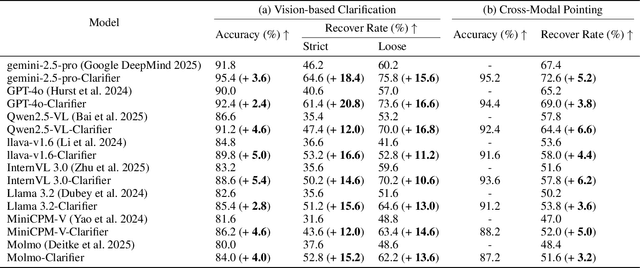
Abstract:The performance of egocentric AI agents is fundamentally limited by multimodal intent ambiguity. This challenge arises from a combination of underspecified language, imperfect visual data, and deictic gestures, which frequently leads to task failure. Existing monolithic Vision-Language Models (VLMs) struggle to resolve these multimodal ambiguous inputs, often failing silently or hallucinating responses. To address these ambiguities, we introduce the Plug-and-Play Clarifier, a zero-shot and modular framework that decomposes the problem into discrete, solvable sub-tasks. Specifically, our framework consists of three synergistic modules: (1) a text clarifier that uses dialogue-driven reasoning to interactively disambiguate linguistic intent, (2) a vision clarifier that delivers real-time guidance feedback, instructing users to adjust their positioning for improved capture quality, and (3) a cross-modal clarifier with grounding mechanism that robustly interprets 3D pointing gestures and identifies the specific objects users are pointing to. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework improves the intent clarification performance of small language models (4--8B) by approximately 30%, making them competitive with significantly larger counterparts. We also observe consistent gains when applying our framework to these larger models. Furthermore, our vision clarifier increases corrective guidance accuracy by over 20%, and our cross-modal clarifier improves semantic answer accuracy for referential grounding by 5%. Overall, our method provides a plug-and-play framework that effectively resolves multimodal ambiguity and significantly enhances user experience in egocentric interaction.
Human Motion Video Generation: A Survey
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Human motion video generation has garnered significant research interest due to its broad applications, enabling innovations such as photorealistic singing heads or dynamic avatars that seamlessly dance to music. However, existing surveys in this field focus on individual methods, lacking a comprehensive overview of the entire generative process. This paper addresses this gap by providing an in-depth survey of human motion video generation, encompassing over ten sub-tasks, and detailing the five key phases of the generation process: input, motion planning, motion video generation, refinement, and output. Notably, this is the first survey that discusses the potential of large language models in enhancing human motion video generation. Our survey reviews the latest developments and technological trends in human motion video generation across three primary modalities: vision, text, and audio. By covering over two hundred papers, we offer a thorough overview of the field and highlight milestone works that have driven significant technological breakthroughs. Our goal for this survey is to unveil the prospects of human motion video generation and serve as a valuable resource for advancing the comprehensive applications of digital humans. A complete list of the models examined in this survey is available in Our Repository https://github.com/Winn1y/Awesome-Human-Motion-Video-Generation.
* Accepted by TPAMI. Github Repo: https://github.com/Winn1y/Awesome-Human-Motion-Video-Generation IEEE Access: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/11106267
ViDAR: Video Diffusion-Aware 4D Reconstruction From Monocular Inputs
Jun 23, 2025Abstract:Dynamic Novel View Synthesis aims to generate photorealistic views of moving subjects from arbitrary viewpoints. This task is particularly challenging when relying on monocular video, where disentangling structure from motion is ill-posed and supervision is scarce. We introduce Video Diffusion-Aware Reconstruction (ViDAR), a novel 4D reconstruction framework that leverages personalised diffusion models to synthesise a pseudo multi-view supervision signal for training a Gaussian splatting representation. By conditioning on scene-specific features, ViDAR recovers fine-grained appearance details while mitigating artefacts introduced by monocular ambiguity. To address the spatio-temporal inconsistency of diffusion-based supervision, we propose a diffusion-aware loss function and a camera pose optimisation strategy that aligns synthetic views with the underlying scene geometry. Experiments on DyCheck, a challenging benchmark with extreme viewpoint variation, show that ViDAR outperforms all state-of-the-art baselines in visual quality and geometric consistency. We further highlight ViDAR's strong improvement over baselines on dynamic regions and provide a new benchmark to compare performance in reconstructing motion-rich parts of the scene. Project page: https://vidar-4d.github.io
Better Together: Unified Motion Capture and 3D Avatar Reconstruction
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:We present Better Together, a method that simultaneously solves the human pose estimation problem while reconstructing a photorealistic 3D human avatar from multi-view videos. While prior art usually solves these problems separately, we argue that joint optimization of skeletal motion with a 3D renderable body model brings synergistic effects, i.e. yields more precise motion capture and improved visual quality of real-time rendering of avatars. To achieve this, we introduce a novel animatable avatar with 3D Gaussians rigged on a personalized mesh and propose to optimize the motion sequence with time-dependent MLPs that provide accurate and temporally consistent pose estimates. We first evaluate our method on highly challenging yoga poses and demonstrate state-of-the-art accuracy on multi-view human pose estimation, reducing error by 35% on body joints and 45% on hand joints compared to keypoint-based methods. At the same time, our method significantly boosts the visual quality of animatable avatars (+2dB PSNR on novel view synthesis) on diverse challenging subjects.
GASPACHO: Gaussian Splatting for Controllable Humans and Objects
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:We present GASPACHO: a method for generating photorealistic controllable renderings of human-object interactions. Given a set of multi-view RGB images of human-object interactions, our method reconstructs animatable templates of the human and object as separate sets of Gaussians simultaneously. Different from existing work, which focuses on human reconstruction and ignores objects as background, our method explicitly reconstructs both humans and objects, thereby allowing for controllable renderings of novel human object interactions in different poses from novel-camera viewpoints. During reconstruction, we constrain the Gaussians that generate rendered images to be a linear function of a set of canonical Gaussians. By simply changing the parameters of the linear deformation functions after training, our method can generate renderings of novel human-object interaction in novel poses from novel camera viewpoints. We learn the 3D Gaussian properties of the canonical Gaussians on the underlying 2D manifold of the canonical human and object templates. This in turns requires a canonical object template with a fixed UV unwrapping. To define such an object template, we use a feature based representation to track the object across the multi-view sequence. We further propose an occlusion aware photometric loss that allows for reconstructions under significant occlusions. Several experiments on two human-object datasets - BEHAVE and DNA-Rendering - demonstrate that our method allows for high-quality reconstruction of human and object templates under significant occlusion and the synthesis of controllable renderings of novel human-object interactions in novel human poses from novel camera views.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge