Gerard Pons-Moll
MPI for Informatics
FrankenMotion: Part-level Human Motion Generation and Composition
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Human motion generation from text prompts has made remarkable progress in recent years. However, existing methods primarily rely on either sequence-level or action-level descriptions due to the absence of fine-grained, part-level motion annotations. This limits their controllability over individual body parts. In this work, we construct a high-quality motion dataset with atomic, temporally-aware part-level text annotations, leveraging the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). Unlike prior datasets that either provide synchronized part captions with fixed time segments or rely solely on global sequence labels, our dataset captures asynchronous and semantically distinct part movements at fine temporal resolution. Based on this dataset, we introduce a diffusion-based part-aware motion generation framework, namely FrankenMotion, where each body part is guided by its own temporally-structured textual prompt. This is, to our knowledge, the first work to provide atomic, temporally-aware part-level motion annotations and have a model that allows motion generation with both spatial (body part) and temporal (atomic action) control. Experiments demonstrate that FrankenMotion outperforms all previous baseline models adapted and retrained for our setting, and our model can compose motions unseen during training. Our code and dataset will be publicly available upon publication.
ELITE: Efficient Gaussian Head Avatar from a Monocular Video via Learned Initialization and TEst-time Generative Adaptation
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:We introduce ELITE, an Efficient Gaussian head avatar synthesis from a monocular video via Learned Initialization and TEst-time generative adaptation. Prior works rely either on a 3D data prior or a 2D generative prior to compensate for missing visual cues in monocular videos. However, 3D data prior methods often struggle to generalize in-the-wild, while 2D generative prior methods are computationally heavy and prone to identity hallucination. We identify a complementary synergy between these two priors and design an efficient system that achieves high-fidelity animatable avatar synthesis with strong in-the-wild generalization. Specifically, we introduce a feed-forward Mesh2Gaussian Prior Model (MGPM) that enables fast initialization of a Gaussian avatar. To further bridge the domain gap at test time, we design a test-time generative adaptation stage, leveraging both real and synthetic images as supervision. Unlike previous full diffusion denoising strategies that are slow and hallucination-prone, we propose a rendering-guided single-step diffusion enhancer that restores missing visual details, grounded on Gaussian avatar renderings. Our experiments demonstrate that ELITE produces visually superior avatars to prior works, even for challenging expressions, while achieving 60x faster synthesis than the 2D generative prior method.
Animated 3DGS Avatars in Diverse Scenes with Consistent Lighting and Shadows
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:We present a method for consistent lighting and shadows when animated 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) avatars interact with 3DGS scenes or with dynamic objects inserted into otherwise static scenes. Our key contribution is Deep Gaussian Shadow Maps (DGSM), a modern analogue of the classical shadow mapping algorithm tailored to the volumetric 3DGS representation. Building on the classic deep shadow mapping idea, we show that 3DGS admits closed form light accumulation along light rays, enabling volumetric shadow computation without meshing. For each estimated light, we tabulate transmittance over concentric radial shells and store them in octahedral atlases, which modern GPUs can sample in real time per query to attenuate affected scene Gaussians and thus cast and receive shadows consistently. To relight moving avatars, we approximate the local environment illumination with HDRI probes represented in a spherical harmonic (SH) basis and apply a fast per Gaussian radiance transfer, avoiding explicit BRDF estimation or offline optimization. We demonstrate environment consistent lighting for avatars from AvatarX and ActorsHQ, composited into ScanNet++, DL3DV, and SuperSplat scenes, and show interactions with inserted objects. Across single and multi avatar settings, DGSM and SH relighting operate fully in the volumetric 3DGS representation, yielding coherent shadows and relighting while avoiding meshing.
MoLingo: Motion-Language Alignment for Text-to-Motion Generation
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:We introduce MoLingo, a text-to-motion (T2M) model that generates realistic, lifelike human motion by denoising in a continuous latent space. Recent works perform latent space diffusion, either on the whole latent at once or auto-regressively over multiple latents. In this paper, we study how to make diffusion on continuous motion latents work best. We focus on two questions: (1) how to build a semantically aligned latent space so diffusion becomes more effective, and (2) how to best inject text conditioning so the motion follows the description closely. We propose a semantic-aligned motion encoder trained with frame-level text labels so that latents with similar text meaning stay close, which makes the latent space more diffusion-friendly. We also compare single-token conditioning with a multi-token cross-attention scheme and find that cross-attention gives better motion realism and text-motion alignment. With semantically aligned latents, auto-regressive generation, and cross-attention text conditioning, our model sets a new state of the art in human motion generation on standard metrics and in a user study. We will release our code and models for further research and downstream usage.
CARI4D: Category Agnostic 4D Reconstruction of Human-Object Interaction
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Accurate capture of human-object interaction from ubiquitous sensors like RGB cameras is important for applications in human understanding, gaming, and robot learning. However, inferring 4D interactions from a single RGB view is highly challenging due to the unknown object and human information, depth ambiguity, occlusion, and complex motion, which hinder consistent 3D and temporal reconstruction. Previous methods simplify the setup by assuming ground truth object template or constraining to a limited set of object categories. We present CARI4D, the first category-agnostic method that reconstructs spatially and temporarily consistent 4D human-object interaction at metric scale from monocular RGB videos. To this end, we propose a pose hypothesis selection algorithm that robustly integrates the individual predictions from foundation models, jointly refine them through a learned render-and-compare paradigm to ensure spatial, temporal and pixel alignment, and finally reasoning about intricate contacts for further refinement satisfying physical constraints. Experiments show that our method outperforms prior art by 38% on in-distribution dataset and 36% on unseen dataset in terms of reconstruction error. Our model generalizes beyond the training categories and thus can be applied zero-shot to in-the-wild internet videos. Our code and pretrained models will be publicly released.
AHA! Animating Human Avatars in Diverse Scenes with Gaussian Splatting
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:We present a novel framework for animating humans in 3D scenes using 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), a neural scene representation that has recently achieved state-of-the-art photorealistic results for novel-view synthesis but remains under-explored for human-scene animation and interaction. Unlike existing animation pipelines that use meshes or point clouds as the underlying 3D representation, our approach introduces the use of 3DGS as the 3D representation to the problem of animating humans in scenes. By representing humans and scenes as Gaussians, our approach allows for geometry-consistent free-viewpoint rendering of humans interacting with 3D scenes. Our key insight is that the rendering can be decoupled from the motion synthesis and each sub-problem can be addressed independently, without the need for paired human-scene data. Central to our method is a Gaussian-aligned motion module that synthesizes motion without explicit scene geometry, using opacity-based cues and projected Gaussian structures to guide human placement and pose alignment. To ensure natural interactions, we further propose a human-scene Gaussian refinement optimization that enforces realistic contact and navigation. We evaluate our approach on scenes from Scannet++ and the SuperSplat library, and on avatars reconstructed from sparse and dense multi-view human capture. Finally, we demonstrate that our framework allows for novel applications such as geometry-consistent free-viewpoint rendering of edited monocular RGB videos with new animated humans, showcasing the unique advantage of 3DGS for monocular video-based human animation.
ECHO: Ego-Centric modeling of Human-Object interactions
Aug 29, 2025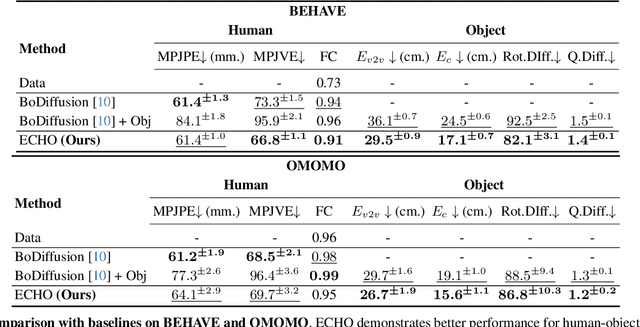
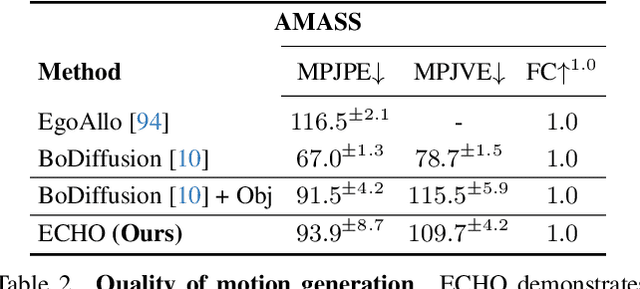
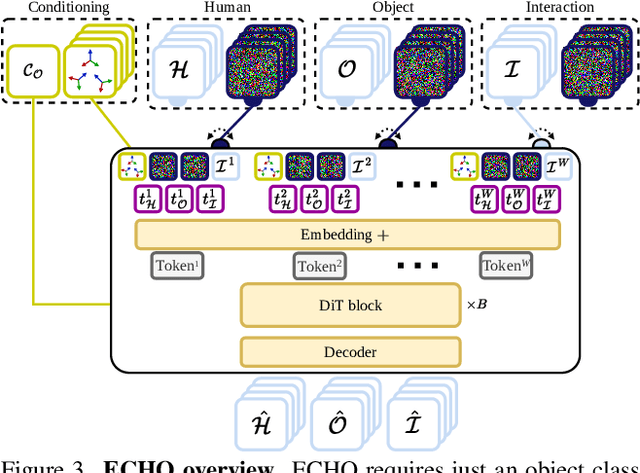
Abstract:Modeling human-object interactions (HOI) from an egocentric perspective is a largely unexplored yet important problem due to the increasing adoption of wearable devices, such as smart glasses and watches. We investigate how much information about interaction can be recovered from only head and wrists tracking. Our answer is ECHO (Ego-Centric modeling of Human-Object interactions), which, for the first time, proposes a unified framework to recover three modalities: human pose, object motion, and contact from such minimal observation. ECHO employs a Diffusion Transformer architecture and a unique three-variate diffusion process, which jointly models human motion, object trajectory, and contact sequence, allowing for flexible input configurations. Our method operates in a head-centric canonical space, enhancing robustness to global orientation. We propose a conveyor-based inference, which progressively increases the diffusion timestamp with the frame position, allowing us to process sequences of any length. Through extensive evaluation, we demonstrate that ECHO outperforms existing methods that do not offer the same flexibility, setting a state-of-the-art in egocentric HOI reconstruction.
SCENIC: Scene-aware Semantic Navigation with Instruction-guided Control
Dec 20, 2024



Abstract:Synthesizing natural human motion that adapts to complex environments while allowing creative control remains a fundamental challenge in motion synthesis. Existing models often fall short, either by assuming flat terrain or lacking the ability to control motion semantics through text. To address these limitations, we introduce SCENIC, a diffusion model designed to generate human motion that adapts to dynamic terrains within virtual scenes while enabling semantic control through natural language. The key technical challenge lies in simultaneously reasoning about complex scene geometry while maintaining text control. This requires understanding both high-level navigation goals and fine-grained environmental constraints. The model must ensure physical plausibility and precise navigation across varied terrain, while also preserving user-specified text control, such as ``carefully stepping over obstacles" or ``walking upstairs like a zombie." Our solution introduces a hierarchical scene reasoning approach. At its core is a novel scene-dependent, goal-centric canonicalization that handles high-level goal constraint, and is complemented by an ego-centric distance field that captures local geometric details. This dual representation enables our model to generate physically plausible motion across diverse 3D scenes. By implementing frame-wise text alignment, our system achieves seamless transitions between different motion styles while maintaining scene constraints. Experiments demonstrate our novel diffusion model generates arbitrarily long human motions that both adapt to complex scenes with varying terrain surfaces and respond to textual prompts. Additionally, we show SCENIC can generalize to four real-scene datasets. Our code, dataset, and models will be released at \url{https://virtualhumans.mpi-inf.mpg.de/scenic/}.
Feat2GS: Probing Visual Foundation Models with Gaussian Splatting
Dec 12, 2024Abstract:Given that visual foundation models (VFMs) are trained on extensive datasets but often limited to 2D images, a natural question arises: how well do they understand the 3D world? With the differences in architecture and training protocols (i.e., objectives, proxy tasks), a unified framework to fairly and comprehensively probe their 3D awareness is urgently needed. Existing works on 3D probing suggest single-view 2.5D estimation (e.g., depth and normal) or two-view sparse 2D correspondence (e.g., matching and tracking). Unfortunately, these tasks ignore texture awareness, and require 3D data as ground-truth, which limits the scale and diversity of their evaluation set. To address these issues, we introduce Feat2GS, which readout 3D Gaussians attributes from VFM features extracted from unposed images. This allows us to probe 3D awareness for geometry and texture via novel view synthesis, without requiring 3D data. Additionally, the disentanglement of 3DGS parameters - geometry ($\boldsymbol{x}, \alpha, \Sigma$) and texture ($\boldsymbol{c}$) - enables separate analysis of texture and geometry awareness. Under Feat2GS, we conduct extensive experiments to probe the 3D awareness of several VFMs, and investigate the ingredients that lead to a 3D aware VFM. Building on these findings, we develop several variants that achieve state-of-the-art across diverse datasets. This makes Feat2GS useful for probing VFMs, and as a simple-yet-effective baseline for novel-view synthesis. Code and data will be made available at https://fanegg.github.io/Feat2GS/.
Gen-3Diffusion: Realistic Image-to-3D Generation via 2D & 3D Diffusion Synergy
Dec 09, 2024Abstract:Creating realistic 3D objects and clothed avatars from a single RGB image is an attractive yet challenging problem. Due to its ill-posed nature, recent works leverage powerful prior from 2D diffusion models pretrained on large datasets. Although 2D diffusion models demonstrate strong generalization capability, they cannot guarantee the generated multi-view images are 3D consistent. In this paper, we propose Gen-3Diffusion: Realistic Image-to-3D Generation via 2D & 3D Diffusion Synergy. We leverage a pre-trained 2D diffusion model and a 3D diffusion model via our elegantly designed process that synchronizes two diffusion models at both training and sampling time. The synergy between the 2D and 3D diffusion models brings two major advantages: 1) 2D helps 3D in generalization: the pretrained 2D model has strong generalization ability to unseen images, providing strong shape priors for the 3D diffusion model; 2) 3D helps 2D in multi-view consistency: the 3D diffusion model enhances the 3D consistency of 2D multi-view sampling process, resulting in more accurate multi-view generation. We validate our idea through extensive experiments in image-based objects and clothed avatar generation tasks. Results show that our method generates realistic 3D objects and avatars with high-fidelity geometry and texture. Extensive ablations also validate our design choices and demonstrate the strong generalization ability to diverse clothing and compositional shapes. Our code and pretrained models will be publicly released on https://yuxuan-xue.com/gen-3diffusion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge