Rong Xiong
Direction Matters: Learning Force Direction Enables Sim-to-Real Contact-Rich Manipulation
Feb 15, 2026Abstract:Sim-to-real transfer for contact-rich manipulation remains challenging due to the inherent discrepancy in contact dynamics. While existing methods often rely on costly real-world data or utilize blind compliance through fixed controllers, we propose a framework that leverages expert-designed controller logic for transfer. Inspired by the success of privileged supervision in kinematic tasks, we employ a human-designed finite state machine based position/force controller in simulation to provide privileged guidance. The resulting policy is trained to predict the end-effector pose, contact state, and crucially the desired contact force direction. Unlike force magnitudes, which are highly sensitive to simulation inaccuracies, force directions encode high-level task geometry and remain robust across the sim-to-real gap. At deployment, these predictions configure a force-aware admittance controller. By combining the policy's directional intent with a constant, low-cost manually tuned force magnitude, the system generates adaptive, task-aligned compliance. This tuning is lightweight, typically requiring only a single scalar per contact state. We provide theoretical analysis for stability and robustness to disturbances. Experiments on four real-world tasks, i.e., microwave opening, peg-in-hole, whiteboard wiping, and door opening, demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms strong baselines in both success rate and robustness. Videos are available at: https://yifei-y.github.io/project-pages/DirectionMatters/.
ETP-R1: Evolving Topological Planning with Reinforcement Fine-tuning for Vision-Language Navigation in Continuous Environments
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Navigation in Continuous Environments (VLN-CE) requires an embodied agent to navigate towards target in continuous environments, following natural language instructions. While current graph-based methods offer an efficient, structured approach by abstracting the environment into a topological map and simplifying the action space to waypoint selection, they lag behind methods based on Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) in leveraging large-scale data and advanced training paradigms. In this paper, we try to bridge this gap by introducing ETP-R1, a framework that applies the paradigm of scaling up data and Reinforcement Fine-Tuning (RFT) to a graph-based VLN-CE model. To build a strong foundation, we first construct a high-quality, large-scale pretraining dataset using the Gemini API. This dataset consists of diverse, low-hallucination instructions for topological trajectories, providing rich supervision for our graph-based policy to map language to topological paths. This foundation is further strengthened by unifying data from both R2R and RxR tasks for joint pretraining. Building on this, we introduce a three-stage training paradigm, which culminates in the first application of closed-loop, online RFT to a graph-based VLN-CE model, powered by the Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) algorithm. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach is highly effective, establishing new state-of-the-art performance across all major metrics on both the R2R-CE and RxR-CE benchmarks. Our code is available at https://github.com/Cepillar/ETP-R1.
Seeing to Act, Prompting to Specify: A Bayesian Factorization of Vision Language Action Policy
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:The pursuit of out-of-distribution generalization in Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models is often hindered by catastrophic forgetting of the Vision-Language Model (VLM) backbone during fine-tuning. While co-training with external reasoning data helps, it requires experienced tuning and data-related overhead. Beyond such external dependencies, we identify an intrinsic cause within VLA datasets: modality imbalance, where language diversity is much lower than visual and action diversity. This imbalance biases the model toward visual shortcuts and language forgetting. To address this, we introduce BayesVLA, a Bayesian factorization that decomposes the policy into a visual-action prior, supporting seeing-to-act, and a language-conditioned likelihood, enabling prompt-to-specify. This inherently preserves generalization and promotes instruction following. We further incorporate pre- and post-contact phases to better leverage pre-trained foundation models. Information-theoretic analysis formally validates our effectiveness in mitigating shortcut learning. Extensive experiments show superior generalization to unseen instructions, objects, and environments compared to existing methods. Project page is available at: https://xukechun.github.io/papers/BayesVLA.
Neural Ranging Inertial Odometry
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Ultra-wideband (UWB) has shown promising potential in GPS-denied localization thanks to its lightweight and drift-free characteristics, while the accuracy is limited in real scenarios due to its sensitivity to sensor arrangement and non-Gaussian pattern induced by multi-path or multi-signal interference, which commonly occurs in many typical applications like long tunnels. We introduce a novel neural fusion framework for ranging inertial odometry which involves a graph attention UWB network and a recurrent neural inertial network. Our graph net learns scene-relevant ranging patterns and adapts to any number of anchors or tags, realizing accurate positioning without calibration. Additionally, the integration of least squares and the incorporation of nominal frame enhance overall performance and scalability. The effectiveness and robustness of our methods are validated through extensive experiments on both public and self-collected datasets, spanning indoor, outdoor, and tunnel environments. The results demonstrate the superiority of our proposed IR-ULSG in handling challenging conditions, including scenarios outside the convex envelope and cases where only a single anchor is available.
Mr. Virgil: Learning Multi-robot Visual-range Relative Localization
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Ultra-wideband (UWB)-vision fusion localization has achieved extensive applications in the domain of multi-agent relative localization. The challenging matching problem between robots and visual detection renders existing methods highly dependent on identity-encoded hardware or delicate tuning algorithms. Overconfident yet erroneous matches may bring about irreversible damage to the localization system. To address this issue, we introduce Mr. Virgil, an end-to-end learning multi-robot visual-range relative localization framework, consisting of a graph neural network for data association between UWB rangings and visual detections, and a differentiable pose graph optimization (PGO) back-end. The graph-based front-end supplies robust matching results, accurate initial position predictions, and credible uncertainty estimates, which are subsequently integrated into the PGO back-end to elevate the accuracy of the final pose estimation. Additionally, a decentralized system is implemented for real-world applications. Experiments spanning varying robot numbers, simulation and real-world, occlusion and non-occlusion conditions showcase the stability and exactitude under various scenes compared to conventional methods. Our code is available at: https://github.com/HiOnes/Mr-Virgil.
Toward Embodiment Equivariant Vision-Language-Action Policy
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Vision-language-action policies learn manipulation skills across tasks, environments and embodiments through large-scale pre-training. However, their ability to generalize to novel robot configurations remains limited. Most approaches emphasize model size, dataset scale and diversity while paying less attention to the design of action spaces. This leads to the configuration generalization problem, which requires costly adaptation. We address this challenge by formulating cross-embodiment pre-training as designing policies equivariant to embodiment configuration transformations. Building on this principle, we propose a framework that (i) establishes a embodiment equivariance theory for action space and policy design, (ii) introduces an action decoder that enforces configuration equivariance, and (iii) incorporates a geometry-aware network architecture to enhance embodiment-agnostic spatial reasoning. Extensive experiments in both simulation and real-world settings demonstrate that our approach improves pre-training effectiveness and enables efficient fine-tuning on novel robot embodiments. Our code is available at https://github.com/hhcaz/e2vla
BEV-ODOM2: Enhanced BEV-based Monocular Visual Odometry with PV-BEV Fusion and Dense Flow Supervision for Ground Robots
Sep 18, 2025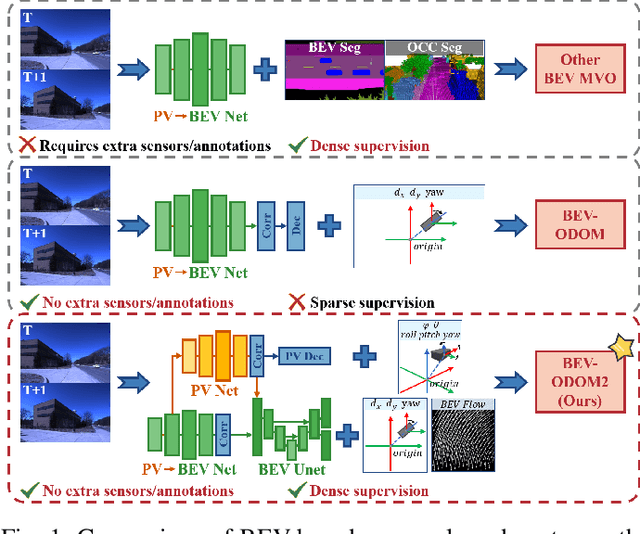
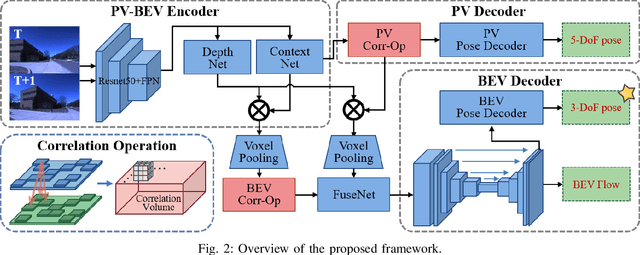
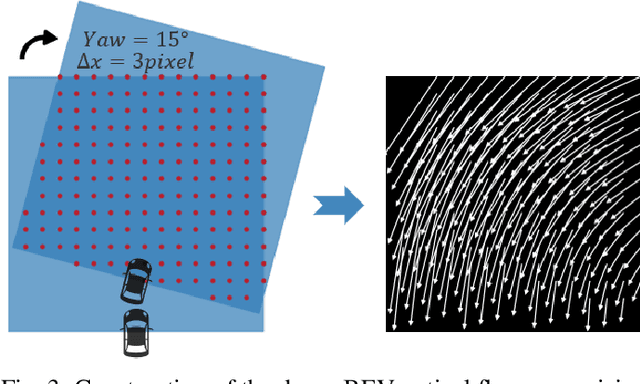
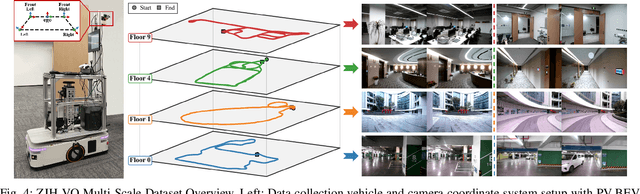
Abstract:Bird's-Eye-View (BEV) representation offers a metric-scaled planar workspace, facilitating the simplification of 6-DoF ego-motion to a more robust 3-DoF model for monocular visual odometry (MVO) in intelligent transportation systems. However, existing BEV methods suffer from sparse supervision signals and information loss during perspective-to-BEV projection. We present BEV-ODOM2, an enhanced framework addressing both limitations without additional annotations. Our approach introduces: (1) dense BEV optical flow supervision constructed from 3-DoF pose ground truth for pixel-level guidance; (2) PV-BEV fusion that computes correlation volumes before projection to preserve 6-DoF motion cues while maintaining scale consistency. The framework employs three supervision levels derived solely from pose data: dense BEV flow, 5-DoF for the PV branch, and final 3-DoF output. Enhanced rotation sampling further balances diverse motion patterns in training. Extensive evaluation on KITTI, NCLT, Oxford, and our newly collected ZJH-VO multi-scale dataset demonstrates state-of-the-art performance, achieving 40 improvement in RTE compared to previous BEV methods. The ZJH-VO dataset, covering diverse ground vehicle scenarios from underground parking to outdoor plazas, is publicly available to facilitate future research.
TOP: Time Optimization Policy for Stable and Accurate Standing Manipulation with Humanoid Robots
Aug 01, 2025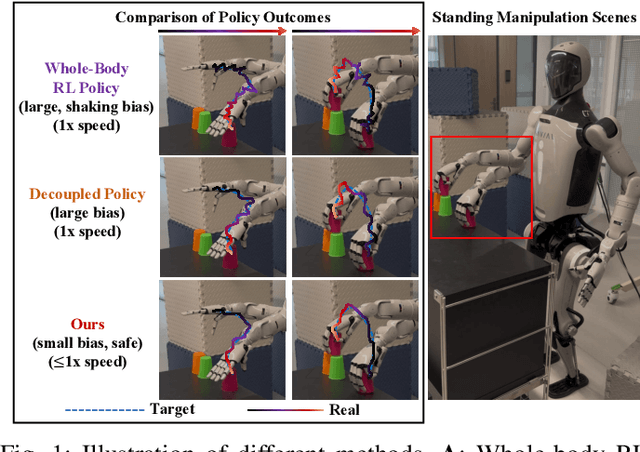
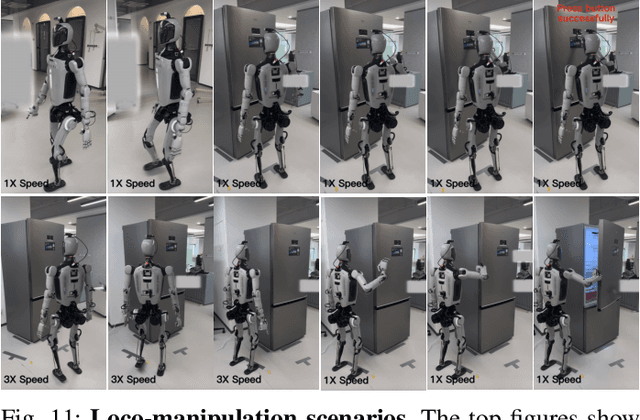
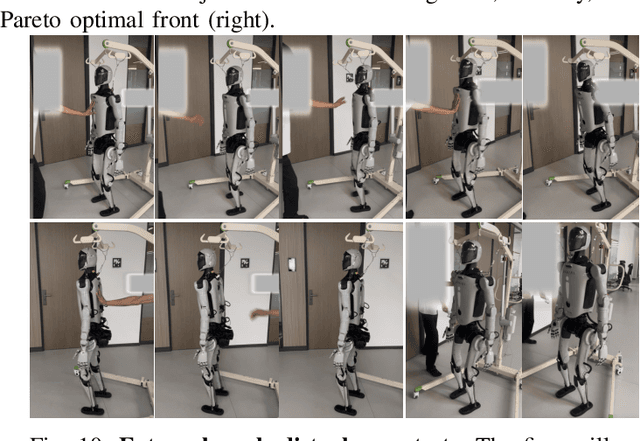

Abstract:Humanoid robots have the potential capability to perform a diverse range of manipulation tasks, but this is based on a robust and precise standing controller. Existing methods are either ill-suited to precisely control high-dimensional upper-body joints, or difficult to ensure both robustness and accuracy, especially when upper-body motions are fast. This paper proposes a novel time optimization policy (TOP), to train a standing manipulation control model that ensures balance, precision, and time efficiency simultaneously, with the idea of adjusting the time trajectory of upper-body motions but not only strengthening the disturbance resistance of the lower-body. Our approach consists of three parts. Firstly, we utilize motion prior to represent upper-body motions to enhance the coordination ability between the upper and lower-body by training a variational autoencoder (VAE). Then we decouple the whole-body control into an upper-body PD controller for precision and a lower-body RL controller to enhance robust stability. Finally, we train TOP method in conjunction with the decoupled controller and VAE to reduce the balance burden resulting from fast upper-body motions that would destabilize the robot and exceed the capabilities of the lower-body RL policy. The effectiveness of the proposed approach is evaluated via both simulation and real world experiments, which demonstrate the superiority on standing manipulation tasks stably and accurately. The project page can be found at https://anonymous.4open.science/w/top-258F/.
Grounding 3D Object Affordance with Language Instructions, Visual Observations and Interactions
Apr 07, 2025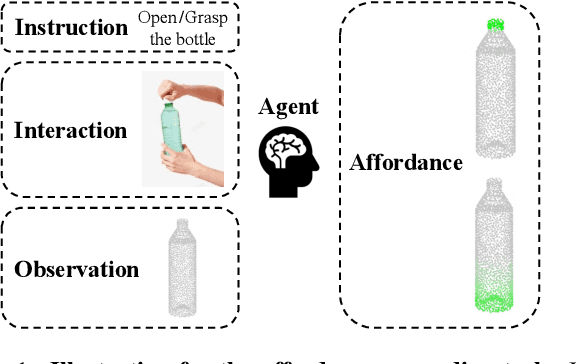
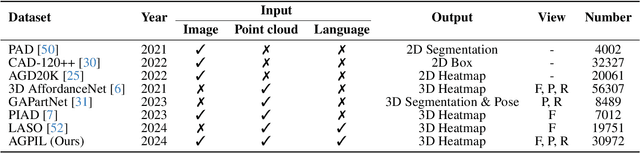
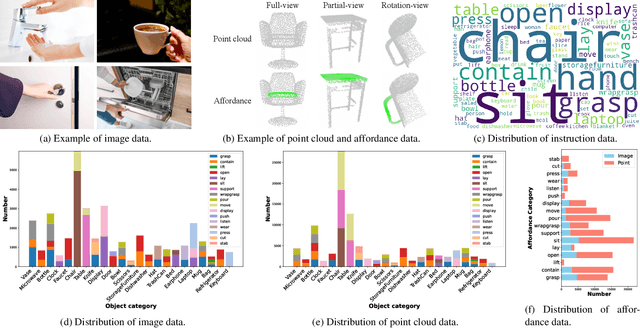

Abstract:Grounding 3D object affordance is a task that locates objects in 3D space where they can be manipulated, which links perception and action for embodied intelligence. For example, for an intelligent robot, it is necessary to accurately ground the affordance of an object and grasp it according to human instructions. In this paper, we introduce a novel task that grounds 3D object affordance based on language instructions, visual observations and interactions, which is inspired by cognitive science. We collect an Affordance Grounding dataset with Points, Images and Language instructions (AGPIL) to support the proposed task. In the 3D physical world, due to observation orientation, object rotation, or spatial occlusion, we can only get a partial observation of the object. So this dataset includes affordance estimations of objects from full-view, partial-view, and rotation-view perspectives. To accomplish this task, we propose LMAffordance3D, the first multi-modal, language-guided 3D affordance grounding network, which applies a vision-language model to fuse 2D and 3D spatial features with semantic features. Comprehensive experiments on AGPIL demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our method on this task, even in unseen experimental settings. Our project is available at https://sites.google.com/view/lmaffordance3d.
UnIRe: Unsupervised Instance Decomposition for Dynamic Urban Scene Reconstruction
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Reconstructing and decomposing dynamic urban scenes is crucial for autonomous driving, urban planning, and scene editing. However, existing methods fail to perform instance-aware decomposition without manual annotations, which is crucial for instance-level scene editing.We propose UnIRe, a 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) based approach that decomposes a scene into a static background and individual dynamic instances using only RGB images and LiDAR point clouds. At its core, we introduce 4D superpoints, a novel representation that clusters multi-frame LiDAR points in 4D space, enabling unsupervised instance separation based on spatiotemporal correlations. These 4D superpoints serve as the foundation for our decomposed 4D initialization, i.e., providing spatial and temporal initialization to train a dynamic 3DGS for arbitrary dynamic classes without requiring bounding boxes or object templates.Furthermore, we introduce a smoothness regularization strategy in both 2D and 3D space, further improving the temporal stability.Experiments on benchmark datasets show that our method outperforms existing methods in decomposed dynamic scene reconstruction while enabling accurate and flexible instance-level editing, making it a practical solution for real-world applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge