Zhongxiang Zhou
Toward Embodiment Equivariant Vision-Language-Action Policy
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Vision-language-action policies learn manipulation skills across tasks, environments and embodiments through large-scale pre-training. However, their ability to generalize to novel robot configurations remains limited. Most approaches emphasize model size, dataset scale and diversity while paying less attention to the design of action spaces. This leads to the configuration generalization problem, which requires costly adaptation. We address this challenge by formulating cross-embodiment pre-training as designing policies equivariant to embodiment configuration transformations. Building on this principle, we propose a framework that (i) establishes a embodiment equivariance theory for action space and policy design, (ii) introduces an action decoder that enforces configuration equivariance, and (iii) incorporates a geometry-aware network architecture to enhance embodiment-agnostic spatial reasoning. Extensive experiments in both simulation and real-world settings demonstrate that our approach improves pre-training effectiveness and enables efficient fine-tuning on novel robot embodiments. Our code is available at https://github.com/hhcaz/e2vla
TOP: Time Optimization Policy for Stable and Accurate Standing Manipulation with Humanoid Robots
Aug 01, 2025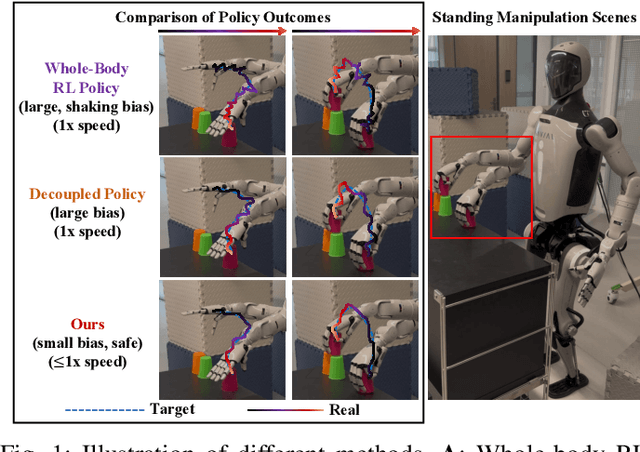
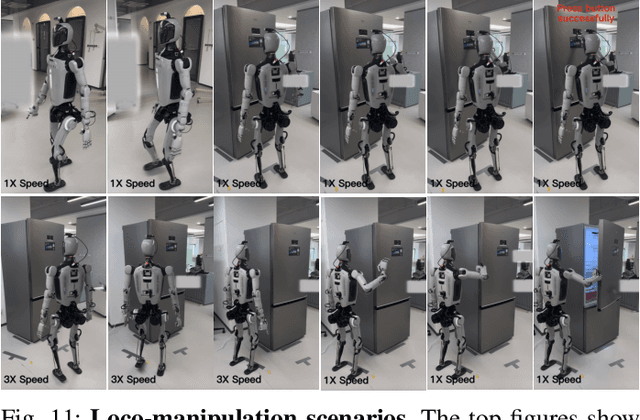
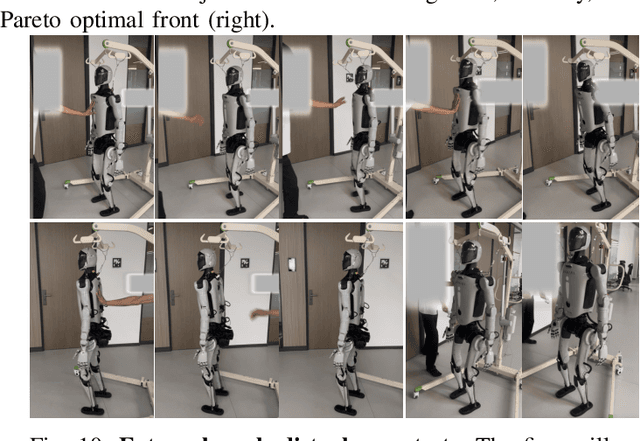

Abstract:Humanoid robots have the potential capability to perform a diverse range of manipulation tasks, but this is based on a robust and precise standing controller. Existing methods are either ill-suited to precisely control high-dimensional upper-body joints, or difficult to ensure both robustness and accuracy, especially when upper-body motions are fast. This paper proposes a novel time optimization policy (TOP), to train a standing manipulation control model that ensures balance, precision, and time efficiency simultaneously, with the idea of adjusting the time trajectory of upper-body motions but not only strengthening the disturbance resistance of the lower-body. Our approach consists of three parts. Firstly, we utilize motion prior to represent upper-body motions to enhance the coordination ability between the upper and lower-body by training a variational autoencoder (VAE). Then we decouple the whole-body control into an upper-body PD controller for precision and a lower-body RL controller to enhance robust stability. Finally, we train TOP method in conjunction with the decoupled controller and VAE to reduce the balance burden resulting from fast upper-body motions that would destabilize the robot and exceed the capabilities of the lower-body RL policy. The effectiveness of the proposed approach is evaluated via both simulation and real world experiments, which demonstrate the superiority on standing manipulation tasks stably and accurately. The project page can be found at https://anonymous.4open.science/w/top-258F/.
Disambiguate Gripper State in Grasp-Based Tasks: Pseudo-Tactile as Feedback Enables Pure Simulation Learning
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Grasp-based manipulation tasks are fundamental to robots interacting with their environments, yet gripper state ambiguity significantly reduces the robustness of imitation learning policies for these tasks. Data-driven solutions face the challenge of high real-world data costs, while simulation data, despite its low costs, is limited by the sim-to-real gap. We identify the root cause of gripper state ambiguity as the lack of tactile feedback. To address this, we propose a novel approach employing pseudo-tactile as feedback, inspired by the idea of using a force-controlled gripper as a tactile sensor. This method enhances policy robustness without additional data collection and hardware involvement, while providing a noise-free binary gripper state observation for the policy and thus facilitating pure simulation learning to unleash the power of simulation. Experimental results across three real-world grasp-based tasks demonstrate the necessity, effectiveness, and efficiency of our approach.
Grasp, See and Place: Efficient Unknown Object Rearrangement with Policy Structure Prior
Feb 23, 2024



Abstract:We focus on the task of unknown object rearrangement, where a robot is supposed to re-configure the objects into a desired goal configuration specified by an RGB-D image. Recent works explore unknown object rearrangement systems by incorporating learning-based perception modules. However, they are sensitive to perception error, and pay less attention to task-level performance. In this paper, we aim to develop an effective system for unknown object rearrangement amidst perception noise. We theoretically reveal the noisy perception impacts grasp and place in a decoupled way, and show such a decoupled structure is non-trivial to improve task optimality. We propose GSP, a dual-loop system with the decoupled structure as prior. For the inner loop, we learn an active seeing policy for self-confident object matching to improve the perception of place. For the outer loop, we learn a grasp policy aware of object matching and grasp capability guided by task-level rewards. We leverage the foundation model CLIP for object matching, policy learning and self-termination. A series of experiments indicate that GSP can conduct unknown object rearrangement with higher completion rate and less steps.
Learning adaptive manipulation of objects with revolute joint: A case study on varied cabinet doors opening
Apr 28, 2023



Abstract:This paper introduces a learning-based framework for robot adaptive manipulating the object with a revolute joint in unstructured environments. We concentrate our discussion on various cabinet door opening tasks. To improve the performance of Deep Reinforcement Learning in this scene, we analytically provide an efficient sampling manner utilizing the constraints of the objects. To open various kinds of doors, we add encoded environment parameters that define the various environments to the input of out policy. To transfer the policy into the real world, we train an adaptation module in simulation and fine-tune the adaptation module to cut down the impact of the policy-unaware environment parameters. We design a series of experiments to validate the efficacy of our framework. Additionally, we testify to the model's performance in the real world compared to the traditional door opening method.
A Hyper-network Based End-to-end Visual Servoing with Arbitrary Desired Poses
Apr 18, 2023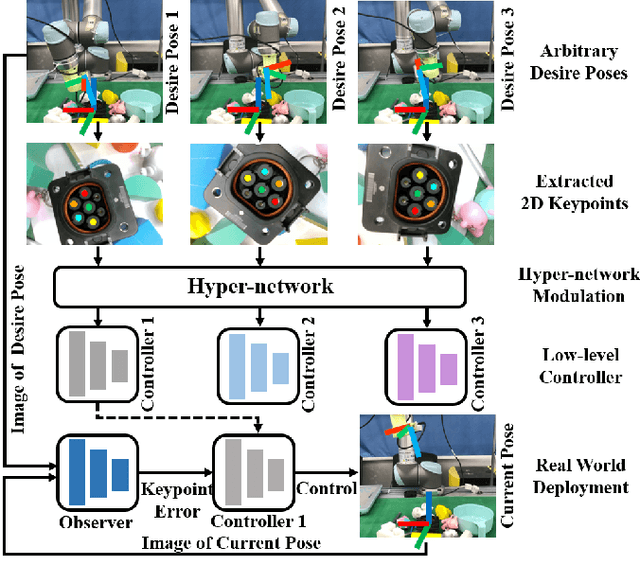
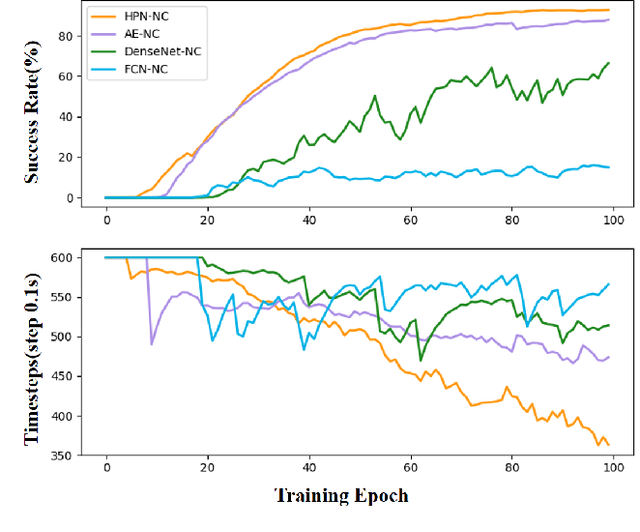
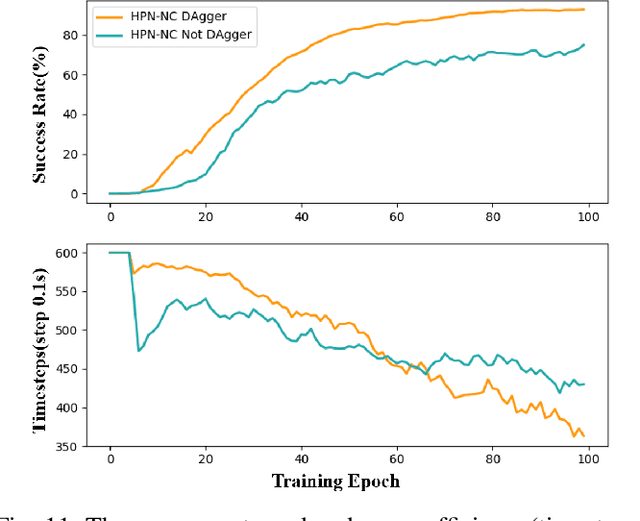
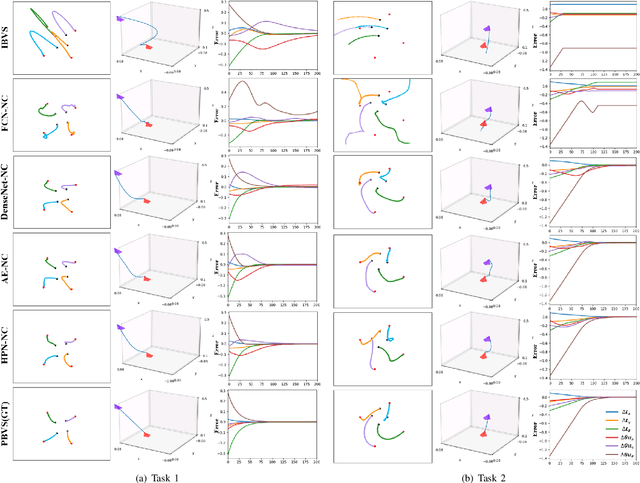
Abstract:Recently, several works achieve end-to-end visual servoing (VS) for robotic manipulation by replacing traditional controller with differentiable neural networks, but lose the ability to servo arbitrary desired poses. This letter proposes a differentiable architecture for arbitrary pose servoing: a hyper-network based neural controller (HPN-NC). To achieve this, HPN-NC consists of a hyper net and a low-level controller, where the hyper net learns to generate the parameters of the low-level controller and the controller uses the 2D keypoints error for control like traditional image-based visual servoing (IBVS). HPN-NC can complete 6 degree of freedom visual servoing with large initial offset. Taking advantage of the fully differentiable nature of HPN-NC, we provide a three-stage training procedure to servo real world objects. With self-supervised end-to-end training, the performance of the integrated model can be further improved in unseen scenes and the amount of manual annotations can be significantly reduced.
A Joint Modeling of Vision-Language-Action for Target-oriented Grasping in Clutter
Feb 24, 2023



Abstract:We focus on the task of language-conditioned grasping in clutter, in which a robot is supposed to grasp the target object based on a language instruction. Previous works separately conduct visual grounding to localize the target object, and generate a grasp for that object. However, these works require object labels or visual attributes for grounding, which calls for handcrafted rules in planner and restricts the range of language instructions. In this paper, we propose to jointly model vision, language and action with object-centric representation. Our method is applicable under more flexible language instructions, and not limited by visual grounding error. Besides, by utilizing the powerful priors from the pre-trained multi-modal model and grasp model, sample efficiency is effectively improved and the sim2real problem is relived without additional data for transfer. A series of experiments carried out in simulation and real world indicate that our method can achieve better task success rate by less times of motion under more flexible language instructions. Moreover, our method is capable of generalizing better to scenarios with unseen objects and language instructions.
Open-Set Object Detection Using Classification-free Object Proposal and Instance-level Contrastive Learning with Appendix
Nov 21, 2022Abstract:Detecting both known and unknown objects is a fundamental skill for robot manipulation in unstructured environments. Open-set object detection (OSOD) is a promising direction to handle the problem consisting of two subtasks: objects and background separation, and open-set object classification. In this paper, we present Openset RCNN to address the challenging OSOD. To disambiguate unknown objects and background in the first subtask, we propose to use classification-free region proposal network (CF-RPN) which estimates the objectness score of each region purely using cues from object's location and shape preventing overfitting to the training categories. To identify unknown objects in the second subtask, we propose to represent them using the complementary region of known categories in a latent space which is accomplished by a prototype learning network (PLN). PLN performs instance-level contrastive learning to encode proposals to a latent space and builds a compact region centering with a prototype for each known category. Further, we note that the detection performance of unknown objects can not be unbiasedly evaluated on the situation that commonly used object detection datasets are not fully annotated. Thus, a new benchmark is introduced by reorganizing GraspNet-1billion, a robotic grasp pose detection dataset with complete annotation. Extensive experiments demonstrate the merits of our method. We finally show that our Openset RCNN can endow the robot with an open-set perception ability to support robotic rearrangement tasks in cluttered environments. More details can be found in https://sites.google.com/view/openest-rcnn/
Learning to Fill the Seam by Vision: Sub-millimeter Peg-in-hole on Unseen Shapes in Real World
Apr 20, 2022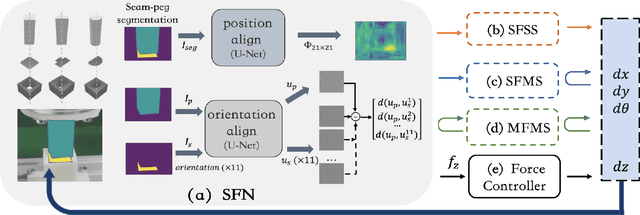
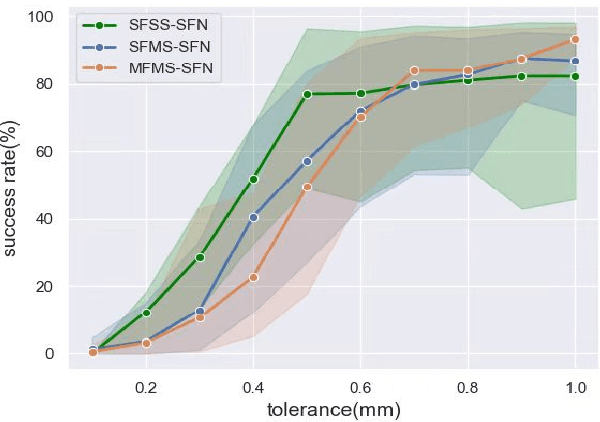
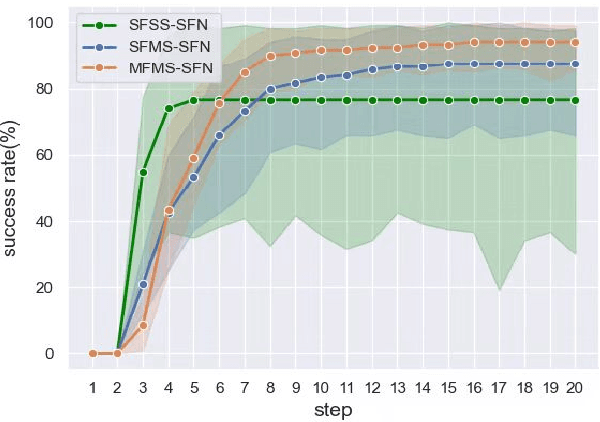

Abstract:In the peg insertion task, human pays attention to the seam between the peg and the hole and tries to fill it continuously with visual feedback. By imitating the human behavior, we design architectures with position and orientation estimators based on the seam representation for pose alignment, which proves to be general to the unseen peg geometries. By putting the estimators into the closed-loop control with reinforcement learning, we further achieve a higher or comparable success rate, efficiency, and robustness compared with the baseline methods. The policy is trained totally in simulation without any manual intervention. To achieve sim-to-real, a learnable segmentation module with automatic data collecting and labeling can be easily trained to decouple the perception and the policy, which helps the model trained in simulation quickly adapt to the real world with negligible effort. Results are presented in simulation and on a physical robot. Code, videos, and supplemental material are available at https://github.com/xieliang555/SFN.git
REDE: End-to-end Object 6D Pose Robust Estimation Using Differentiable Outliers Elimination
Oct 24, 2020



Abstract:Object 6D pose estimation is a fundamental task in many applications. Conventional methods solve the task by detecting and matching the keypoints, then estimating the pose. Recent efforts bringing deep learning into the problem mainly overcome the vulnerability of conventional methods to environmental variation due to the hand-crafted feature design. However, these methods cannot achieve end-to-end learning and good interpretability at the same time. In this paper, we propose REDE, a novel end-to-end object pose estimator using RGB-D data, which utilizes network for keypoint regression, and a differentiable geometric pose estimator for pose error back-propagation. Besides, to achieve better robustness when outlier keypoint prediction occurs, we further propose a differentiable outliers elimination method that regresses the candidate result and the confidence simultaneously. Via confidence weighted aggregation of multiple candidates, we can reduce the effect from the outliers in the final estimation. Finally, following the conventional method, we apply a learnable refinement process to further improve the estimation. The experimental results on three benchmark datasets show that REDE slightly outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches and is more robust to object occlusion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge