Huaijin Pi
CoDA: Coordinated Diffusion Noise Optimization for Whole-Body Manipulation of Articulated Objects
May 27, 2025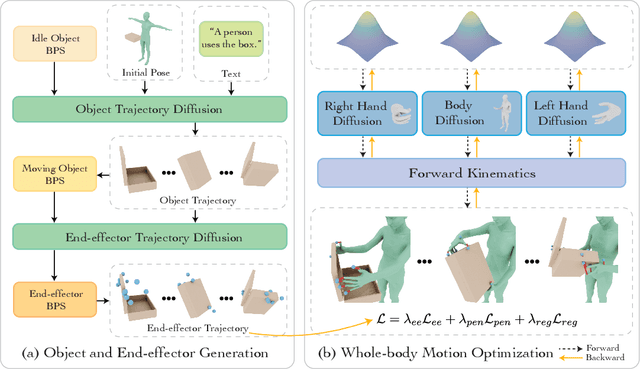
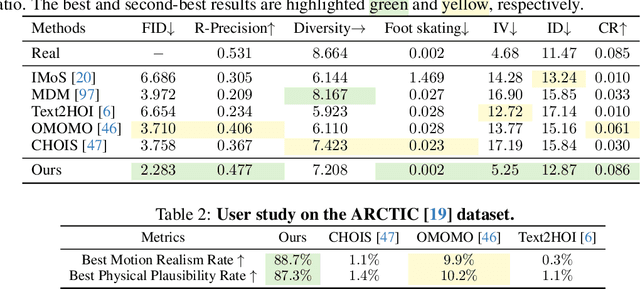
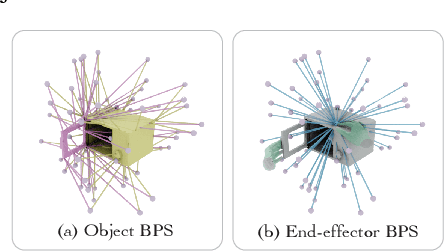
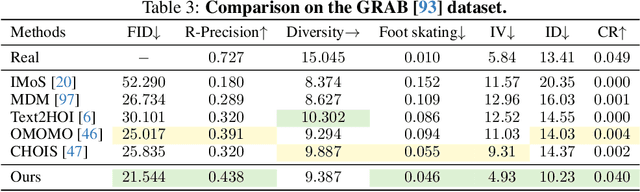
Abstract:Synthesizing whole-body manipulation of articulated objects, including body motion, hand motion, and object motion, is a critical yet challenging task with broad applications in virtual humans and robotics. The core challenges are twofold. First, achieving realistic whole-body motion requires tight coordination between the hands and the rest of the body, as their movements are interdependent during manipulation. Second, articulated object manipulation typically involves high degrees of freedom and demands higher precision, often requiring the fingers to be placed at specific regions to actuate movable parts. To address these challenges, we propose a novel coordinated diffusion noise optimization framework. Specifically, we perform noise-space optimization over three specialized diffusion models for the body, left hand, and right hand, each trained on its own motion dataset to improve generalization. Coordination naturally emerges through gradient flow along the human kinematic chain, allowing the global body posture to adapt in response to hand motion objectives with high fidelity. To further enhance precision in hand-object interaction, we adopt a unified representation based on basis point sets (BPS), where end-effector positions are encoded as distances to the same BPS used for object geometry. This unified representation captures fine-grained spatial relationships between the hand and articulated object parts, and the resulting trajectories serve as targets to guide the optimization of diffusion noise, producing highly accurate interaction motion. We conduct extensive experiments demonstrating that our method outperforms existing approaches in motion quality and physical plausibility, and enables various capabilities such as object pose control, simultaneous walking and manipulation, and whole-body generation from hand-only data.
MotionStreamer: Streaming Motion Generation via Diffusion-based Autoregressive Model in Causal Latent Space
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses the challenge of text-conditioned streaming motion generation, which requires us to predict the next-step human pose based on variable-length historical motions and incoming texts. Existing methods struggle to achieve streaming motion generation, e.g., diffusion models are constrained by pre-defined motion lengths, while GPT-based methods suffer from delayed response and error accumulation problem due to discretized non-causal tokenization. To solve these problems, we propose MotionStreamer, a novel framework that incorporates a continuous causal latent space into a probabilistic autoregressive model. The continuous latents mitigate information loss caused by discretization and effectively reduce error accumulation during long-term autoregressive generation. In addition, by establishing temporal causal dependencies between current and historical motion latents, our model fully utilizes the available information to achieve accurate online motion decoding. Experiments show that our method outperforms existing approaches while offering more applications, including multi-round generation, long-term generation, and dynamic motion composition. Project Page: https://zju3dv.github.io/MotionStreamer/
Mocap-2-to-3: Lifting 2D Diffusion-Based Pretrained Models for 3D Motion Capture
Mar 05, 2025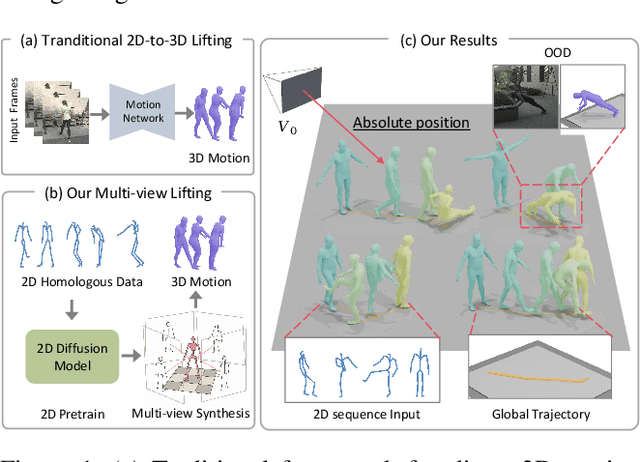
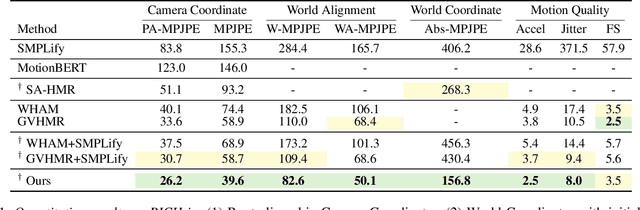
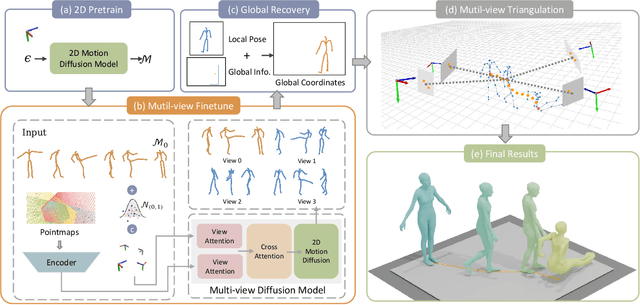
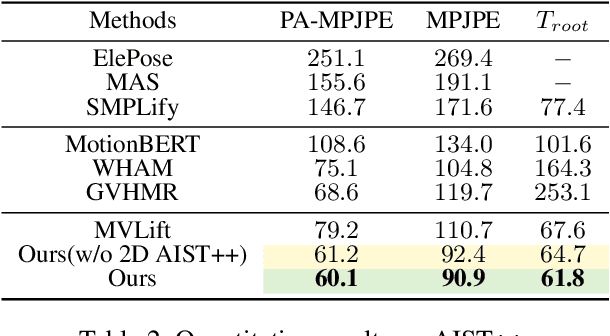
Abstract:Recovering absolute poses in the world coordinate system from monocular views presents significant challenges. Two primary issues arise in this context. Firstly, existing methods rely on 3D motion data for training, which requires collection in limited environments. Acquiring such 3D labels for new actions in a timely manner is impractical, severely restricting the model's generalization capabilities. In contrast, 2D poses are far more accessible and easier to obtain. Secondly, estimating a person's absolute position in metric space from a single viewpoint is inherently more complex. To address these challenges, we introduce Mocap-2-to-3, a novel framework that decomposes intricate 3D motions into 2D poses, leveraging 2D data to enhance 3D motion reconstruction in diverse scenarios and accurately predict absolute positions in the world coordinate system. We initially pretrain a single-view diffusion model with extensive 2D data, followed by fine-tuning a multi-view diffusion model for view consistency using publicly available 3D data. This strategy facilitates the effective use of large-scale 2D data. Additionally, we propose an innovative human motion representation that decouples local actions from global movements and encodes geometric priors of the ground, ensuring the generative model learns accurate motion priors from 2D data. During inference, this allows for the gradual recovery of global movements, resulting in more plausible positioning. We evaluate our model's performance on real-world datasets, demonstrating superior accuracy in motion and absolute human positioning compared to state-of-the-art methods, along with enhanced generalization and scalability. Our code will be made publicly available.
Ready-to-React: Online Reaction Policy for Two-Character Interaction Generation
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses the task of generating two-character online interactions. Previously, two main settings existed for two-character interaction generation: (1) generating one's motions based on the counterpart's complete motion sequence, and (2) jointly generating two-character motions based on specific conditions. We argue that these settings fail to model the process of real-life two-character interactions, where humans will react to their counterparts in real time and act as independent individuals. In contrast, we propose an online reaction policy, called Ready-to-React, to generate the next character pose based on past observed motions. Each character has its own reaction policy as its "brain", enabling them to interact like real humans in a streaming manner. Our policy is implemented by incorporating a diffusion head into an auto-regressive model, which can dynamically respond to the counterpart's motions while effectively mitigating the error accumulation throughout the generation process. We conduct comprehensive experiments using the challenging boxing task. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms existing baselines and can generate extended motion sequences. Additionally, we show that our approach can be controlled by sparse signals, making it well-suited for VR and other online interactive environments.
Motion-2-to-3: Leveraging 2D Motion Data to Boost 3D Motion Generation
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:Text-driven human motion synthesis is capturing significant attention for its ability to effortlessly generate intricate movements from abstract text cues, showcasing its potential for revolutionizing motion design not only in film narratives but also in virtual reality experiences and computer game development. Existing methods often rely on 3D motion capture data, which require special setups resulting in higher costs for data acquisition, ultimately limiting the diversity and scope of human motion. In contrast, 2D human videos offer a vast and accessible source of motion data, covering a wider range of styles and activities. In this paper, we explore leveraging 2D human motion extracted from videos as an alternative data source to improve text-driven 3D motion generation. Our approach introduces a novel framework that disentangles local joint motion from global movements, enabling efficient learning of local motion priors from 2D data. We first train a single-view 2D local motion generator on a large dataset of text-motion pairs. To enhance this model to synthesize 3D motion, we fine-tune the generator with 3D data, transforming it into a multi-view generator that predicts view-consistent local joint motion and root dynamics. Experiments on the HumanML3D dataset and novel text prompts demonstrate that our method efficiently utilizes 2D data, supporting realistic 3D human motion generation and broadening the range of motion types it supports. Our code will be made publicly available at https://zju3dv.github.io/Motion-2-to-3/.
World-Grounded Human Motion Recovery via Gravity-View Coordinates
Sep 10, 2024



Abstract:We present a novel method for recovering world-grounded human motion from monocular video. The main challenge lies in the ambiguity of defining the world coordinate system, which varies between sequences. Previous approaches attempt to alleviate this issue by predicting relative motion in an autoregressive manner, but are prone to accumulating errors. Instead, we propose estimating human poses in a novel Gravity-View (GV) coordinate system, which is defined by the world gravity and the camera view direction. The proposed GV system is naturally gravity-aligned and uniquely defined for each video frame, largely reducing the ambiguity of learning image-pose mapping. The estimated poses can be transformed back to the world coordinate system using camera rotations, forming a global motion sequence. Additionally, the per-frame estimation avoids error accumulation in the autoregressive methods. Experiments on in-the-wild benchmarks demonstrate that our method recovers more realistic motion in both the camera space and world-grounded settings, outperforming state-of-the-art methods in both accuracy and speed. The code is available at https://zju3dv.github.io/gvhmr/.
Generating Human Motion in 3D Scenes from Text Descriptions
May 13, 2024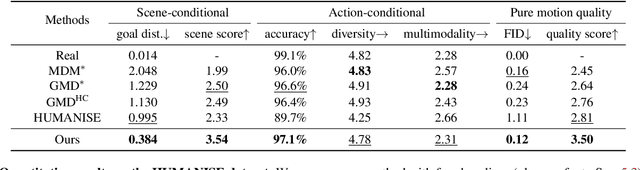
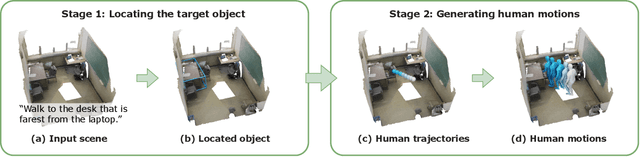
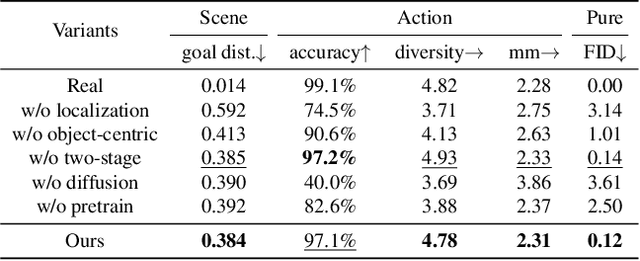
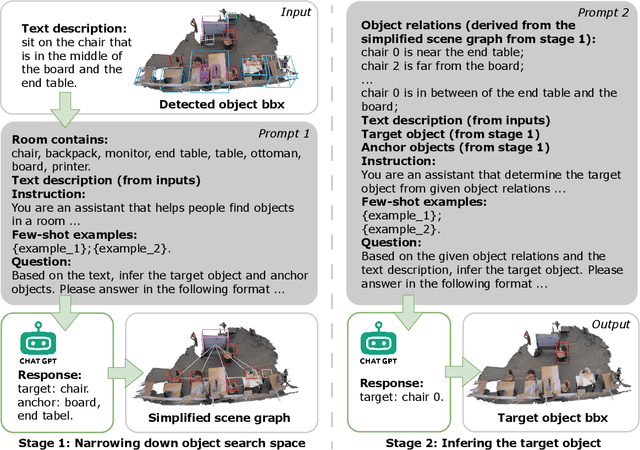
Abstract:Generating human motions from textual descriptions has gained growing research interest due to its wide range of applications. However, only a few works consider human-scene interactions together with text conditions, which is crucial for visual and physical realism. This paper focuses on the task of generating human motions in 3D indoor scenes given text descriptions of the human-scene interactions. This task presents challenges due to the multi-modality nature of text, scene, and motion, as well as the need for spatial reasoning. To address these challenges, we propose a new approach that decomposes the complex problem into two more manageable sub-problems: (1) language grounding of the target object and (2) object-centric motion generation. For language grounding of the target object, we leverage the power of large language models. For motion generation, we design an object-centric scene representation for the generative model to focus on the target object, thereby reducing the scene complexity and facilitating the modeling of the relationship between human motions and the object. Experiments demonstrate the better motion quality of our approach compared to baselines and validate our design choices.
Hierarchical Generation of Human-Object Interactions with Diffusion Probabilistic Models
Oct 03, 2023



Abstract:This paper presents a novel approach to generating the 3D motion of a human interacting with a target object, with a focus on solving the challenge of synthesizing long-range and diverse motions, which could not be fulfilled by existing auto-regressive models or path planning-based methods. We propose a hierarchical generation framework to solve this challenge. Specifically, our framework first generates a set of milestones and then synthesizes the motion along them. Therefore, the long-range motion generation could be reduced to synthesizing several short motion sequences guided by milestones. The experiments on the NSM, COUCH, and SAMP datasets show that our approach outperforms previous methods by a large margin in both quality and diversity. The source code is available on our project page https://zju3dv.github.io/hghoi.
A Joint Modeling of Vision-Language-Action for Target-oriented Grasping in Clutter
Feb 24, 2023



Abstract:We focus on the task of language-conditioned grasping in clutter, in which a robot is supposed to grasp the target object based on a language instruction. Previous works separately conduct visual grounding to localize the target object, and generate a grasp for that object. However, these works require object labels or visual attributes for grounding, which calls for handcrafted rules in planner and restricts the range of language instructions. In this paper, we propose to jointly model vision, language and action with object-centric representation. Our method is applicable under more flexible language instructions, and not limited by visual grounding error. Besides, by utilizing the powerful priors from the pre-trained multi-modal model and grasp model, sample efficiency is effectively improved and the sim2real problem is relived without additional data for transfer. A series of experiments carried out in simulation and real world indicate that our method can achieve better task success rate by less times of motion under more flexible language instructions. Moreover, our method is capable of generalizing better to scenarios with unseen objects and language instructions.
E-NeRV: Expedite Neural Video Representation with Disentangled Spatial-Temporal Context
Jul 17, 2022



Abstract:Recently, the image-wise implicit neural representation of videos, NeRV, has gained popularity for its promising results and swift speed compared to regular pixel-wise implicit representations. However, the redundant parameters within the network structure can cause a large model size when scaling up for desirable performance. The key reason of this phenomenon is the coupled formulation of NeRV, which outputs the spatial and temporal information of video frames directly from the frame index input. In this paper, we propose E-NeRV, which dramatically expedites NeRV by decomposing the image-wise implicit neural representation into separate spatial and temporal context. Under the guidance of this new formulation, our model greatly reduces the redundant model parameters, while retaining the representation ability. We experimentally find that our method can improve the performance to a large extent with fewer parameters, resulting in a more than $8\times$ faster speed on convergence. Code is available at https://github.com/kyleleey/E-NeRV.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge