Yan Xia
VIBEVOICE-ASR Technical Report
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:This report presents VibeVoice-ASR, a general-purpose speech understanding framework built upon VibeVoice, designed to address the persistent challenges of context fragmentation and multi-speaker complexity in long-form audio (e.g., meetings, podcasts) that remain despite recent advancements in short-form speech recognition. Unlike traditional pipelined approaches that rely on audio chunking, VibeVoice-ASRsupports single-pass processing for up to 60 minutes of audio. It unifies Automatic Speech Recognition, Speaker Diarization, and Timestamping into a single end-to-end generation task. In addition, VibeVoice-ASR supports over 50 languages, requires no explicit language setting, and natively handles code-switching within and across utterances. Furthermore, we introduce a prompt-based context injection mechanism that allows users to supply customized conetxt, significantly improving accuracy on domain-specific terminology and polyphonic character disambiguation.
GANeXt: A Fully ConvNeXt-Enhanced Generative Adversarial Network for MRI- and CBCT-to-CT Synthesis
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:The synthesis of computed tomography (CT) from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and cone-beam CT (CBCT) plays a critical role in clinical treatment planning by enabling accurate anatomical representation in adaptive radiotherapy. In this work, we propose GANeXt, a 3D patch-based, fully ConvNeXt-powered generative adversarial network for unified CT synthesis across different modalities and anatomical regions. Specifically, GANeXt employs an efficient U-shaped generator constructed from stacked 3D ConvNeXt blocks with compact convolution kernels, while the discriminator adopts a conditional PatchGAN. To improve synthesis quality, we incorporate a combination of loss functions, including mean absolute error (MAE), perceptual loss, segmentation-based masked MAE, and adversarial loss and a combination of Dice loss and cross-entropy for multi-head segmentation discriminator. For both tasks, training is performed with a batch size of 8 using two separate AdamW optimizers for the generator and discriminator, each equipped with a warmup and cosine decay scheduler, with learning rates of $5\times10^{-4}$ and $1\times10^{-3}$, respectively. Data preprocessing includes deformable registration, foreground cropping, percentile normalization for the input modality, and linear normalization of the CT to the range $[-1024, 1000]$. Data augmentation involves random zooming within $(0.8, 1.3)$ (for MRI-to-CT only), fixed-size cropping to $32\times160\times192$ for MRI-to-CT and $32\times128\times128$ for CBCT-to-CT, and random flipping. During inference, we apply a sliding-window approach with $0.8$ overlap and average folding to reconstruct the full-size sCT, followed by inversion of the CT normalization. After joint training on all regions without any fine-tuning, the final models are selected at the end of 3000 epochs for MRI-to-CT and 1000 epochs for CBCT-to-CT using the full training dataset.
Text2Loc++: Generalizing 3D Point Cloud Localization from Natural Language
Nov 19, 2025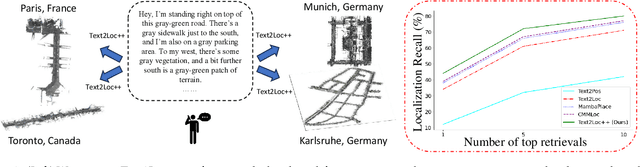
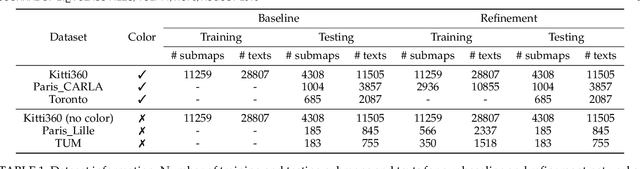
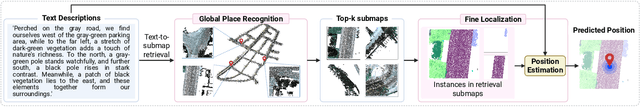
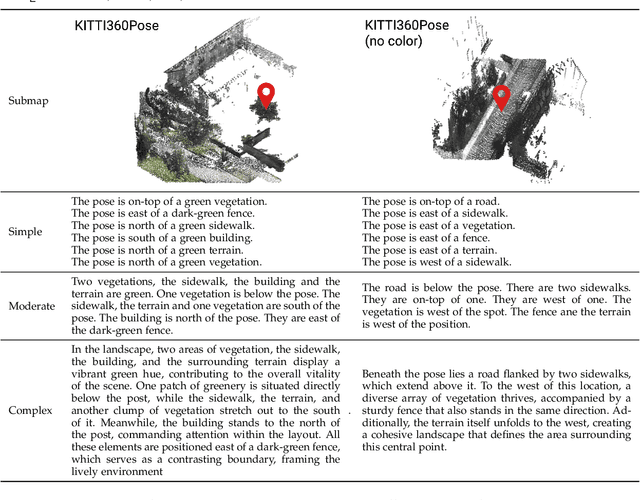
Abstract:We tackle the problem of localizing 3D point cloud submaps using complex and diverse natural language descriptions, and present Text2Loc++, a novel neural network designed for effective cross-modal alignment between language and point clouds in a coarse-to-fine localization pipeline. To support benchmarking, we introduce a new city-scale dataset covering both color and non-color point clouds from diverse urban scenes, and organize location descriptions into three levels of linguistic complexity. In the global place recognition stage, Text2Loc++ combines a pretrained language model with a Hierarchical Transformer with Max pooling (HTM) for sentence-level semantics, and employs an attention-based point cloud encoder for spatial understanding. We further propose Masked Instance Training (MIT) to filter out non-aligned objects and improve multimodal robustness. To enhance the embedding space, we introduce Modality-aware Hierarchical Contrastive Learning (MHCL), incorporating cross-modal, submap-, text-, and instance-level losses. In the fine localization stage, we completely remove explicit text-instance matching and design a lightweight yet powerful framework based on Prototype-based Map Cloning (PMC) and a Cascaded Cross-Attention Transformer (CCAT). Extensive experiments on the KITTI360Pose dataset show that Text2Loc++ outperforms existing methods by up to 15%. In addition, the proposed model exhibits robust generalization when evaluated on the new dataset, effectively handling complex linguistic expressions and a wide variety of urban environments. The code and dataset will be made publicly available.
AUVIC: Adversarial Unlearning of Visual Concepts for Multi-modal Large Language Models
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) achieve impressive performance once optimized on massive datasets. Such datasets often contain sensitive or copyrighted content, raising significant data privacy concerns. Regulatory frameworks mandating the 'right to be forgotten' drive the need for machine unlearning. This technique allows for the removal of target data without resource-consuming retraining. However, while well-studied for text, visual concept unlearning in MLLMs remains underexplored. A primary challenge is precisely removing a target visual concept without disrupting model performance on related entities. To address this, we introduce AUVIC, a novel visual concept unlearning framework for MLLMs. AUVIC applies adversarial perturbations to enable precise forgetting. This approach effectively isolates the target concept while avoiding unintended effects on similar entities. To evaluate our method, we construct VCUBench. It is the first benchmark designed to assess visual concept unlearning in group contexts. Experimental results demonstrate that AUVIC achieves state-of-the-art target forgetting rates while incurs minimal performance degradation on non-target concepts.
DSI-Bench: A Benchmark for Dynamic Spatial Intelligence
Oct 21, 2025Abstract:Reasoning about dynamic spatial relationships is essential, as both observers and objects often move simultaneously. Although vision-language models (VLMs) and visual expertise models excel in 2D tasks and static scenarios, their ability to fully understand dynamic 3D scenarios remains limited. We introduce Dynamic Spatial Intelligence and propose DSI-Bench, a benchmark with nearly 1,000 dynamic videos and over 1,700 manually annotated questions covering nine decoupled motion patterns of observers and objects. Spatially and temporally symmetric designs reduce biases and enable systematic evaluation of models' reasoning about self-motion and object motion. Our evaluation of 14 VLMs and expert models reveals key limitations: models often conflate observer and object motion, exhibit semantic biases, and fail to accurately infer relative relationships in dynamic scenarios. Our DSI-Bench provides valuable findings and insights about the future development of general and expertise models with dynamic spatial intelligence.
11Plus-Bench: Demystifying Multimodal LLM Spatial Reasoning with Cognitive-Inspired Analysis
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:For human cognitive process, spatial reasoning and perception are closely entangled, yet the nature of this interplay remains underexplored in the evaluation of multimodal large language models (MLLMs). While recent MLLM advancements show impressive performance on reasoning, their capacity for human-like spatial cognition remains an open question. In this work, we introduce a systematic evaluation framework to assess the spatial reasoning abilities of state-of-the-art MLLMs relative to human performance. Central to our work is 11Plus-Bench, a high-quality benchmark derived from realistic standardized spatial aptitude tests. 11Plus-Bench also features fine-grained expert annotations of both perceptual complexity and reasoning process, enabling detailed instance-level analysis of model behavior. Through extensive experiments across 14 MLLMs and human evaluation, we find that current MLLMs exhibit early signs of spatial cognition. Despite a large performance gap compared to humans, MLLMs' cognitive profiles resemble those of humans in that cognitive effort correlates strongly with reasoning-related complexity. However, instance-level performance in MLLMs remains largely random, whereas human correctness is highly predictable and shaped by abstract pattern complexity. These findings highlight both emerging capabilities and limitations in current MLLMs' spatial reasoning capabilities and provide actionable insights for advancing model design.
VibeVoice Technical Report
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:This report presents VibeVoice, a novel model designed to synthesize long-form speech with multiple speakers by employing next-token diffusion, which is a unified method for modeling continuous data by autoregressively generating latent vectors via diffusion. To enable this, we introduce a novel continuous speech tokenizer that, when compared to the popular Encodec model, improves data compression by 80 times while maintaining comparable performance. The tokenizer effectively preserves audio fidelity while significantly boosting computational efficiency for processing long sequences. Thus, VibeVoice can synthesize long-form speech for up to 90 minutes (in a 64K context window length) with a maximum of 4 speakers, capturing the authentic conversational ``vibe'' and surpassing open-source and proprietary dialogue models.
Vela: Scalable Embeddings with Voice Large Language Models for Multimodal Retrieval
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have seen substantial progress in recent years. However, their ability to represent multimodal information in the acoustic domain remains underexplored. In this work, we introduce Vela, a novel framework designed to adapt MLLMs for the generation of universal multimodal embeddings. By leveraging MLLMs with specially crafted prompts and selected in-context learning examples, Vela effectively bridges the modality gap across various modalities. We then propose a single-modality training approach, where the model is trained exclusively on text pairs. Our experiments show that Vela outperforms traditional CLAP models in standard text-audio retrieval tasks. Furthermore, we introduce new benchmarks that expose CLAP models' limitations in handling long texts and complex retrieval tasks. In contrast, Vela, by harnessing the capabilities of MLLMs, demonstrates robust performance in these scenarios. Our code will soon be available.
Fast and Accurate Power Load Data Completion via Regularization-optimized Low-Rank Factorization
May 25, 2025Abstract:Low-rank representation learning has emerged as a powerful tool for recovering missing values in power load data due to its ability to exploit the inherent low-dimensional structures of spatiotemporal measurements. Among various techniques, low-rank factorization models are favoured for their efficiency and interpretability. However, their performance is highly sensitive to the choice of regularization parameters, which are typically fixed or manually tuned, resulting in limited generalization capability or slow convergence in practical scenarios. In this paper, we propose a Regularization-optimized Low-Rank Factorization, which introduces a Proportional-Integral-Derivative controller to adaptively adjust the regularization coefficient. Furthermore, we provide a detailed algorithmic complexity analysis, showing that our method preserves the computational efficiency of stochastic gradient descent while improving adaptivity. Experimental results on real-world power load datasets validate the superiority of our method in both imputation accuracy and training efficiency compared to existing baselines.
A PID-Controlled Tensor Wheel Decomposition Model for Dynamic Link Prediction
May 20, 2025Abstract:Link prediction in dynamic networks remains a fundamental challenge in network science, requiring the inference of potential interactions and their evolving strengths through spatiotemporal pattern analysis. Traditional static network methods have inherent limitations in capturing temporal dependencies and weight dynamics, while tensor-based methods offer a promising paradigm by encoding dynamic networks into high-order tensors to explicitly model multidimensional interactions across nodes and time. Among them, tensor wheel decomposition (TWD) stands out for its innovative topological structure, which decomposes high-order tensors into cyclic factors and core tensors to maintain structural integrity. To improve the prediction accuracy, this study introduces a PID-controlled tensor wheel decomposition (PTWD) model, which mainly adopts the following two ideas: 1) exploiting the representation power of TWD to capture the latent features of dynamic network topology and weight evolution, and 2) integrating the proportional-integral-derivative (PID) control principle into the optimization process to obtain a stable model parameter learning scheme. The performance on four real datasets verifies that the proposed PTWD model has more accurate link prediction capabilities compared to other models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge