Shaohan Huang
Sparse-BitNet: 1.58-bit LLMs are Naturally Friendly to Semi-Structured Sparsity
Mar 05, 2026Abstract:Semi-structured N:M sparsity and low-bit quantization (e.g., 1.58-bit BitNet) are two promising approaches for improving the efficiency of large language models (LLMs), yet they have largely been studied in isolation. In this work, we investigate their interaction and show that 1.58-bit BitNet is naturally more compatible with N:M sparsity than full-precision models. To study this effect, we propose Sparse-BitNet, a unified framework that jointly applies 1.58-bit quantization and dynamic N:M sparsification while ensuring stable training for the first time. Across multiple model scales and training regimes (sparse pretraining and dense-to-sparse schedules), 1.58-bit BitNet consistently exhibits smaller performance degradation than full-precision baselines at the same sparsity levels and can tolerate higher structured sparsity before accuracy collapse. Moreover, using our custom sparse tensor core, Sparse-BitNet achieves substantial speedups in both training and inference, reaching up to 1.30X. These results highlight that combining extremely low-bit quantization with semi-structured N:M sparsity is a promising direction for efficient LLMs. Code available at https://github.com/AAzdi/Sparse-BitNet
SlideSparse: Fast and Flexible (2N-2):2N Structured Sparsity
Mar 05, 2026Abstract:NVIDIA's 2:4 Sparse Tensor Cores deliver 2x throughput but demand strict 50% pruning -- a ratio that collapses LLM reasoning accuracy (Qwen3: 54% to 15%). Milder $(2N-2):2N$ patterns (e.g., 6:8, 25% pruning) preserve accuracy yet receive no hardware support, falling back to dense execution without any benefit from sparsity. We present SlideSparse, the first system to unlock Sparse Tensor Core acceleration for the $(2N-2):2N$ model family on commodity GPUs. Our Sliding Window Decomposition reconstructs any $(2N-2):2N$ weight block into $N-1$ overlapping 2:4-compliant windows without any accuracy loss; Activation Lifting fuses the corresponding activation rearrangement into per-token quantization at near-zero cost. Integrated into vLLM, SlideSparse is evaluated across various GPUs (A100, H100, B200, RTX 4090, RTX 5080, DGX-spark), precisions (FP4, INT8, FP8, BF16, FP16), and model families (Llama, Qwen, BitNet). On compute-bound workloads, the measured speedup ratio (1.33x) approaches the theoretical upper-bound $N/(N-1)=4/3$ at 6:8 weight sparsity in Qwen2.5-7B, establishing $(2N-2):2N$ as a practical path to accuracy-preserving LLM acceleration. Code available at https://github.com/bcacdwk/vllmbench.
On-Policy Context Distillation for Language Models
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Context distillation enables language models to internalize in-context knowledge into their parameters. In our work, we propose On-Policy Context Distillation (OPCD), a framework that bridges on-policy distillation with context distillation by training a student model on its own generated trajectories while minimizing reverse Kullback-Leibler divergence against a context-conditioned teacher. We demonstrate the effectiveness of OPCD on two important applications: experiential knowledge distillation, where models extract and consolidate transferable knowledge from their historical solution traces, and system prompt distillation, where models internalize beneficial behaviors encoded in optimized prompts. Across mathematical reasoning, text-based games, and domain-specific tasks, OPCD consistently outperforms baseline methods, achieving higher task accuracy while better preserving out-of-distribution capabilities. We further show that OPCD enables effective cross-size distillation, where smaller student models can internalize experiential knowledge from larger teachers.
VIBEVOICE-ASR Technical Report
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:This report presents VibeVoice-ASR, a general-purpose speech understanding framework built upon VibeVoice, designed to address the persistent challenges of context fragmentation and multi-speaker complexity in long-form audio (e.g., meetings, podcasts) that remain despite recent advancements in short-form speech recognition. Unlike traditional pipelined approaches that rely on audio chunking, VibeVoice-ASRsupports single-pass processing for up to 60 minutes of audio. It unifies Automatic Speech Recognition, Speaker Diarization, and Timestamping into a single end-to-end generation task. In addition, VibeVoice-ASR supports over 50 languages, requires no explicit language setting, and natively handles code-switching within and across utterances. Furthermore, we introduce a prompt-based context injection mechanism that allows users to supply customized conetxt, significantly improving accuracy on domain-specific terminology and polyphonic character disambiguation.
LLM-in-Sandbox Elicits General Agentic Intelligence
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:We introduce LLM-in-Sandbox, enabling LLMs to explore within a code sandbox (i.e., a virtual computer), to elicit general intelligence in non-code domains. We first demonstrate that strong LLMs, without additional training, exhibit generalization capabilities to leverage the code sandbox for non-code tasks. For example, LLMs spontaneously access external resources to acquire new knowledge, leverage the file system to handle long contexts, and execute scripts to satisfy formatting requirements. We further show that these agentic capabilities can be enhanced through LLM-in-Sandbox Reinforcement Learning (LLM-in-Sandbox-RL), which uses only non-agentic data to train models for sandbox exploration. Experiments demonstrate that LLM-in-Sandbox, in both training-free and post-trained settings, achieves robust generalization spanning mathematics, physics, chemistry, biomedicine, long-context understanding, and instruction following. Finally, we analyze LLM-in-Sandbox's efficiency from computational and system perspectives, and open-source it as a Python package to facilitate real-world deployment.
Black-Box On-Policy Distillation of Large Language Models
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Black-box distillation creates student large language models (LLMs) by learning from a proprietary teacher model's text outputs alone, without access to its internal logits or parameters. In this work, we introduce Generative Adversarial Distillation (GAD), which enables on-policy and black-box distillation. GAD frames the student LLM as a generator and trains a discriminator to distinguish its responses from the teacher LLM's, creating a minimax game. The discriminator acts as an on-policy reward model that co-evolves with the student, providing stable, adaptive feedback. Experimental results show that GAD consistently surpasses the commonly used sequence-level knowledge distillation. In particular, Qwen2.5-14B-Instruct (student) trained with GAD becomes comparable to its teacher, GPT-5-Chat, on the LMSYS-Chat automatic evaluation. The results establish GAD as a promising and effective paradigm for black-box LLM distillation.
The Era of Agentic Organization: Learning to Organize with Language Models
Oct 30, 2025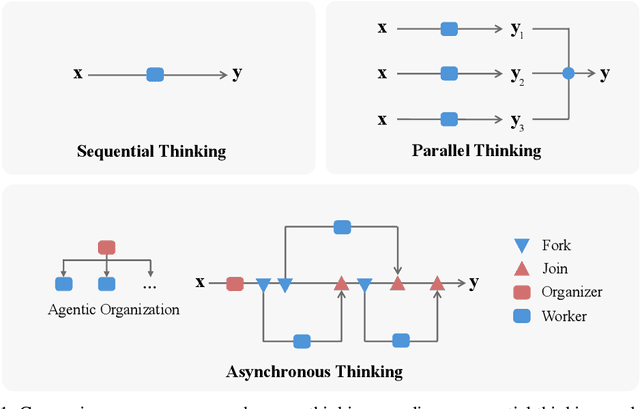
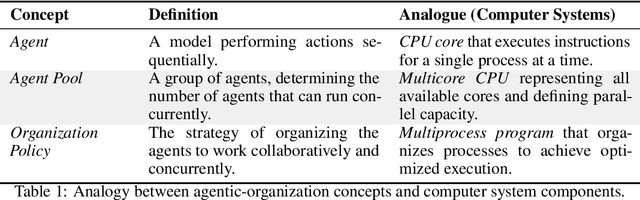
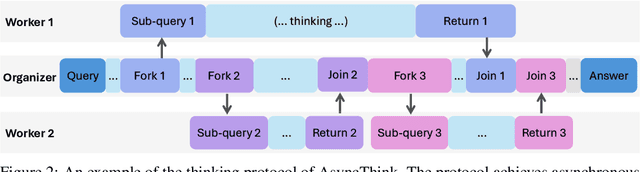
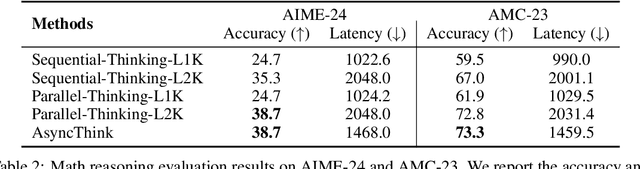
Abstract:We envision a new era of AI, termed agentic organization, where agents solve complex problems by working collaboratively and concurrently, enabling outcomes beyond individual intelligence. To realize this vision, we introduce asynchronous thinking (AsyncThink) as a new paradigm of reasoning with large language models, which organizes the internal thinking process into concurrently executable structures. Specifically, we propose a thinking protocol where an organizer dynamically assigns sub-queries to workers, merges intermediate knowledge, and produces coherent solutions. More importantly, the thinking structure in this protocol can be further optimized through reinforcement learning. Experiments demonstrate that AsyncThink achieves 28% lower inference latency compared to parallel thinking while improving accuracy on mathematical reasoning. Moreover, AsyncThink generalizes its learned asynchronous thinking capabilities, effectively tackling unseen tasks without additional training.
Towards Stable and Effective Reinforcement Learning for Mixture-of-Experts
Oct 27, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in reinforcement learning (RL) have substantially improved the training of large-scale language models, leading to significant gains in generation quality and reasoning ability. However, most existing research focuses on dense models, while RL training for Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures remains underexplored. To address the instability commonly observed in MoE training, we propose a novel router-aware approach to optimize importance sampling (IS) weights in off-policy RL. Specifically, we design a rescaling strategy guided by router logits, which effectively reduces gradient variance and mitigates training divergence. Experimental results demonstrate that our method significantly improves both the convergence stability and the final performance of MoE models, highlighting the potential of RL algorithmic innovations tailored to MoE architectures and providing a promising direction for efficient training of large-scale expert models.
VibeVoice Technical Report
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:This report presents VibeVoice, a novel model designed to synthesize long-form speech with multiple speakers by employing next-token diffusion, which is a unified method for modeling continuous data by autoregressively generating latent vectors via diffusion. To enable this, we introduce a novel continuous speech tokenizer that, when compared to the popular Encodec model, improves data compression by 80 times while maintaining comparable performance. The tokenizer effectively preserves audio fidelity while significantly boosting computational efficiency for processing long sequences. Thus, VibeVoice can synthesize long-form speech for up to 90 minutes (in a 64K context window length) with a maximum of 4 speakers, capturing the authentic conversational ``vibe'' and surpassing open-source and proprietary dialogue models.
VisCodex: Unified Multimodal Code Generation via Merging Vision and Coding Models
Aug 13, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have significantly advanced the integration of visual and textual understanding. However, their ability to generate code from multimodal inputs remains limited. In this work, we introduce VisCodex, a unified framework that seamlessly merges vision and coding language models to empower MLLMs with strong multimodal code generation abilities. Leveraging a task vector-based model merging technique, we integrate a state-of-the-art coding LLM into a strong vision-language backbone, while preserving both visual comprehension and advanced coding skills. To support training and evaluation, we introduce the Multimodal Coding Dataset (MCD), a large-scale and diverse collection of 598k samples, including high-quality HTML code, chart image-code pairs, image-augmented StackOverflow QA, and algorithmic problems. Furthermore, we propose InfiBench-V, a novel and challenging benchmark specifically designed to assess models on visually-rich, real-world programming questions that demand a nuanced understanding of both textual and visual contexts. Extensive experiments show that VisCodex achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source MLLMs and approaches proprietary models like GPT-4o, highlighting the effectiveness of our model merging strategy and new datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge